In two minds: Why we need to embrace the good and bad in everything
Opinion + AnalysisRelationships
BY Dr Tim Dean 9 AUG 2023
If we are to engage with the ethical complexity of the world, we need to learn how to hold two contradictory judgements in our mind at the same time.
Do I contradict myself?
Very well then I contradict myself,
(I am large, I contain multitudes.)
– Walt Whitman, Song of Myself
A fraction of a second after the first atomic bomb was detonated in New Mexico in 1945, a dense blob of superheated gas with a temperature of over 20,000 degrees expanded to a diameter of 250 metres, casting a light brighter than the sun and illuminating the surrounding valley as if it were daytime. We know what the atomic blast looked like at this nascent moment because there is a black and white photograph of it, taken using a specialised high-speed camera developed just for this test.
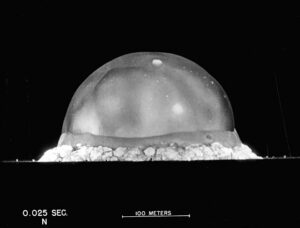
I vividly remember seeing this photo for the first time in a school library book. I spent long stretches contemplating the otherworldly beauty of the glowing sphere, marvelling at the fundamental physical forces on display, awed and diminished by their power. Yet I was also deeply troubled by what the image represented: a weapon designed for indiscriminate killing and the precursor to the device dropped on Nagasaki, taking over 200,000 lives – most civilians.
I’m not the only one to have mixed feelings about the atomic test. The “father” of the atomic bomb, J. Robert Oppenheimer – the subject of the new Christopher Nolan film – expressed pride at the accomplishment of his team in developing a weapon that could end a devastating war, but he also experienced tremendous guilt at starting an arms race that could end humanity itself. He reportedly told the U.S. President Harry S. Truman that his involvement in developing the atomic bomb left him feeling like he had blood on his hands.
In expressing this, Oppenheimer was displaying ethical ambivalence, where he held two opposing views at the same time. Today, we might regard Oppenheimer and his legacy with similar ambivalence.
This is not necessarily an easy thing to do; our minds often race to collapse ambivalence into certainty, into clean black and white. But it’s also an important ethical skill to develop if we’re to engage with the complexities of a world rendered in shades of grey.
In all things good, in all things bad
It’s rare that we come across someone or something that is entirely good or entirely bad. Fossil fuels have lit the darkness and fended off the cold of winter, but they also contribute to destabilising the world’s climate. Natural disasters can cause untold damage and suffering, but they can also awaken the charity and compassion within a community. And many of those who have offered the greatest contributions to art, culture or science have also harboured hidden vices, such as maintaining abusive relationships in private.
When confronted by these conflicted cases, we often enter a state of cognitive dissonance. Contemplating the virtues and vices of fossil fuels at the same time, or appreciating the art of Pablo Picasso while being aware of his relationship towards women, is akin to looking at the word “red” written in blue ink. Our minds recoil from the contradiction and race to collapse it into a singular judgement: good or bad.
But in our rush to escape the discomfort of dissonance, we can cut ourselves off from the full ethical picture. If we settle only on the bad then we risk missing out on much that is good, beautiful or enriching. The paintings of Picasso still retain their artistic virtues despite our opinion of its creator. Yet if we settle only on the good, then we risk excusing much that is bad. Just because we appreciate Picasso’s portraits doesn’t mean we should endorse his treatment of women, even if his relationships with those women informed his art.
Ambivalence doesn’t mean withholding judgement; we can still decide that the balance falls clearly on one side or the other. But even if we do judge something as being overall bad, we can still appreciate the good in it.
The key is to learn how to appreciate without endorsement. Indeed, how to appreciate and condemn simultaneously.
This might change the way we represent some historical figures. If we want to acknowledge both the accomplishments and the colonial consequences of figures like James Cook, that might mean doing so in a museum rather than erecting statues, which by their nature are unambiguous artifacts intended to elevate an individual in the public eye.
Despite our minds yearning to collapse the discomfort of ambivalence into certainty, if we are to engage with the full ethical complexity of world and other people, then we need to be willing to embrace good and bad simultaneously and with nuance, even if that means holding contradictory attitudes at the same time.
So, while I remain committed to the view that nuclear weapons represent an unacceptable threat to the future of humanity, I still appreciate the beauty of that photo of the first atomic test. It does feel contradictory to hold these two views simultaneously. Very well, I contradict myself. I, like every facet of reality, contain multitudes.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Agree to disagree: 7 lessons on the ethics of disagreement
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinkers: Laozi and Zhuangzi
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Who are you? Why identity matters to ethics
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Science + Technology




