Israel or Palestine: Do you have to pick a side?
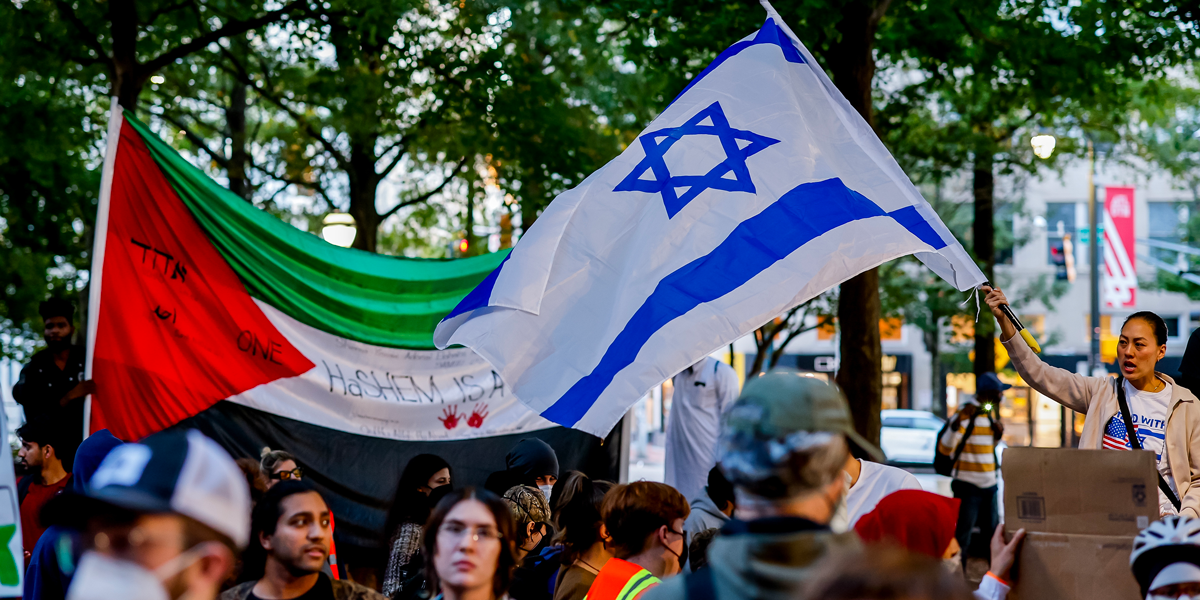

Israel or Palestine: Do you have to pick a side?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY The Ethics Centre 27 OCT 2023
We are inclined to pick a side in complex conflicts, but doing so can diminish our ethical point of view.
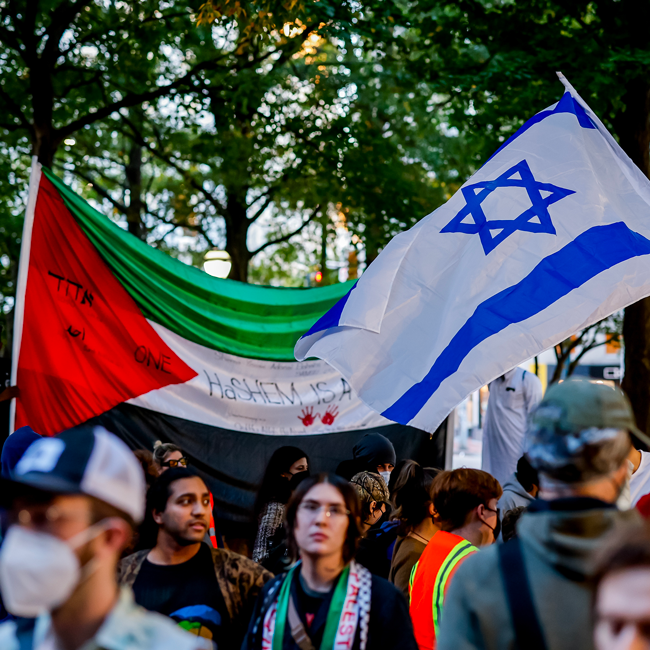
In the early hours of 7 October 2023, Hamas launched a barrage of rockets from Gaza into Israel while armed terrorists crossed the border and began a rampage of death and destruction targeting civilians, including children. In the days that followed, Israeli forces retaliated by blockading Gaza, cutting off food, electricity and water supplies, and began bombarding the densely populated city, killing thousands of Palestinian civilians, including children.
When our news screens are filled with footage of such horrors, our moral minds cry out for justice. But justice for whom?
One of the quirks of our moral minds is that we tend to see the world in terms of black and white or good and evil. If we hear about a heinous or unjust act, our sympathies go out to the victims while outrage inspires us to want the perpetrators to be punished. This sorts the world into two categories: the wronged, who deserve sympathy and protection, and the wrongdoers, who are morally diminished or even dehumanised.
Another quirk of our moral minds is that we struggle with ambivalence, which is the ability to see something as being both good and bad at the same time. Once someone – or a group – are painted as the wronged, it’s difficult to also perceive them simultaneously as being wrongdoers in some other capacity. Attempting to do so creates an uncomfortable state of dissonance, and the easiest way to resolve it is to dismiss the troubling thought and collapse things back into black and white.
On top of this we have our personal connections and affiliations, or a sense of shared identity that can cause us to feel solidarity with one side rather than the other. This in-group solidarity is then reinforced through shared expressions of grief and outrage. It is also policed, with any signs of sympathy for the “other side” drawing stiff rebuke.
This is all natural. It’s how our moral minds are wired. So, it’s no surprise that in the case of the Israel-Palestine conflict, many people have already picked a side. But just because it’s a natural inclination doesn’t mean it’s always a healthy one.
Picking a side can shrink our view, making us see the world through that side’s ethical lens and dismissing other possibly valid perspectives.
This is particularly apparent when we’re faced with gaps in the information we receive – as we often are during times of conflict. We tend to fill ambiguity with our own biases, and we seek out information to reinforce our view while discounting evidence to the contrary.
Picking sides can also prevent us from seeing the bigger ethical picture. And in the case of the conflict between Israel and Palestine, the bigger picture is a long history laced with ethical complexities.
However, there is another way. It requires us to acknowledge, but not necessarily follow, our moral intuitions, and instead step back to take a more universal ethical point of view. This is not the same as a neutrality that is indifferent to the claims of either side or to questions of right and wrong. It is taking the side of principle, which is a basis by which we can judge all parties.
Justice for all
Most ethical frameworks offered by philosophers are universalist, in the sense that they apply equally to all morally worthwhile individuals in similar situations. So, if you believe that it’s wrong to kill a particular individual because they’re an innocent civilian, then you should also believe that it’s wrong to kill any individual who is an innocent civilian.
You might justify that in consequentialist terms, such as by arguing that killing innocent civilians causes undue and irrevocable harm, and that the world is a better place when civilians are protected from such harm. You could equally justify it using a rights-based ethics, such as by arguing that all people have a fundamental right to life and safety.
While philosophers have a variety of views on which specific ethical framework or universal principles we ought to adopt, there are some principles that are widely accepted, with many being coded into the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. These include things like a right to life, liberty and security of person, a right to freedom of movement within the borders of one’s state, and that people shall not be arbitrarily deprived of property, as well as a right to the free expression of one’s religion.
The virtue of taking such a principled approach is that is gives us a bedrock upon which we can base our judgements of any action, agent or government. It promotes a sympathetic stance towards all suffering, and aims us towards justice for all, without shying away from condemning that which is harmful or unjust.
It might challenge our partisan feelings that favour the interests of one side over the other, but it urges us to condemn wrongdoing on any side, such attacks targeting civilians or waging war without ethical constraint.
A principled perspective also enables us to navigate complex ethical issues, such as saying that the Israeli occupation of Palestinian land might be unjust, but that it shouldn’t justify Hamas attacking civilians. Or that Hamas’s attacking civilians is clearly morally repugnant, but that shouldn’t justify the collective punishment of Gazans by Israel. And it can allow us to assert that Israel might have a right to defend its territory and citizens from attack, but it – indeed, all parties – must adhere to just war principles, such as proportionality and distinguishing between enemy combatants and civilians. And it ought to reinforce our commitment to seeing a lasting peace in the region, which will inevitably require some compromises on both sides.
Of course, even if everyone agreed on the same set of principles, there will still be substantial differences in interpretation or points of view. A principled stance must also acknowledge that there are fundamental incompatibilities between the interests and demands of both sides that no single ethical framework will be able to resolve without some kind of compromise. For example, when both sides claim certain sites as sacred, and demand exclusivity, there is no way to resolve that without compromise that will be deemed unacceptable to at least one side. However, such uncertainties and complexities don’t undermine the fact that the same universal principles ought to apply to all people involved.
Choosing to side with ethical principle rather than one side or the other is not without its challenges. It forces us to push back on some of our deep moral intuitions and sit with ambivalence and ambiguity. We might be admonished by both sides in the conflict for not backing all their claims, or called a traitor for criticising them. However, the strength is that we can respond to each of these challenges by resorting to the universal principles, compassion and desire for justice that underpins our views on both sides of the conflict.
While the internet and media landscape seem to urge us to take sides in any conflict, it is entirely possible – and often wise – to step back and apply a broader set of principles rather than fall in with a particular partisan perspective. Adopting such a principled stance doesn’t require that you have all the solutions to the conflict, it is sufficient that you have good reason to wish for a just and peaceful solution for all involved.
Image: AAP Photo / Erik S. Lesser
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights
Big Thinker: Malcolm X
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
When our possibilities seem to collapse
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Should corporate Australia have a voice?
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Big Thinker: Slavoj Žižek
You’re the Voice: It’s our responsibility to vote wisely

You’re the Voice: It’s our responsibility to vote wisely
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY The Ethics Centre 13 SEP 2023
The Voice referendum is a high stakes decision that could affect many thousands of lives, and that means we have an ethical responsibility to choose how we vote carefully.
Not all decisions are created equal. Some are trivial in their consequences, like whether you choose the chocolate or strawberry ice cream for dessert. Some have higher stakes, like whether you decide to prioritise your career over travelling the world. Yet, these decisions still only affect how you live and are unlikely to impact anyone else.
You can make these decisions in a considered or a flippant way. Or you can choose to not make them at all (although doing so is still making a choice, of sorts). With low stakes personal decisions, you don’t even need to have a good reason for choosing what you do. The only person to whom you owe a justification is yourself – and you can always choose to free yourself of that burden.
But there are other kinds of decisions, ones that impact not just us but other people too. Decisions like these demand more from us and we cannot be so flippant with them. In these cases, we have a greater ethical responsibility to come to a more considered position, to weigh up the options more carefully, and be ready to justify our decision with good reasons.
This is the type of decision are we making when it comes to the Voice to Parliament referendum.
The stakes
In the case of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Voice, the stakes are whether Indigenous peoples are afforded constitutional protection for a consultatory body that will advise government on legislation affecting their communities – a body that cannot be legislated away with a change of government.
Leading Indigenous figures representing peoples from across Australia and the Torres Strait have asked the Australian people to make the constitutional change because they believe such a consultatory body will have a significant impact on the wellbeing of their peoples and will help correct over two centuries of political disempowerment and discrimination.
Be a good citizen
So, you have a decision to make, one that will likely have a significant impact on a vulnerable population. That places an ethical responsibility on each registered voter to take the decision seriously. This means not treating it flippantly and having a principled reason for voting, regardless of which way you vote. This is what it means to be a “good citizen”.
It’s easy to think of citizenship as simply affording us rights, such a right to have a say in how we’re governed or a right to be treated fairly under the law. However, citizenship also bestows upon us responsibilities, like voting in elections and serving on a jury if called.
But these are just the minimal responsibilities involved in citizenship. We need to do more to be a “good citizen”, including keeping ourselves engaged in issues of public significance and maintaining a basic level of political literacy. A good citizen also doesn’t just grumble about the state of society, they act to make it better. Finally, a good citizen sees themselves as members of an interconnected society, and is willing to make sacrifices or compromise for the common good. So, a good citizen will see the Voice referendum as an opportunity to exercise their responsibilities and engage with the issue actively to make an informed decision.
Be informed
The good news is that there is an abundance of information readily available for each of us to come to a principled decision. However, there is also a wealth of misinformation and disinformation floating around as well. Some of this is shared due to genuine confusion and some is spread by bad faith actors who have their own motivations for attempting to sway votes.
Explore what you really think
This is why it’s important to look at who is speaking and understand their motivations, which might not always be reflected in their arguments. Many people are motivated to vote one way or the other simply because that’s how their perceived political allies are voting, or they might be swayed by unconscious biases and use plausible sounding arguments as post-hoc rationalisations for how they feel deep down.
You can tell that someone is pushing post-hoc rationalisations when you successfully challenge their argument, such as by showing they have been duped by misinformation, but they still don’t change their mind. In this case, simply throwing more facts at them is unlikely to sway them.
A more successful approach is to be sceptical that the first reasons they give are the true motivations for their views. Instead, ask more questions about why they believe what they do and what they’re concerned will happen if the vote doesn’t go their way. Ask questions about how they can be confident their facts are true or what it would take to change their mind.
Rather than positioning yourself as an opponent, try taking the stance as a fellow traveller trying to get to the bottom of the matter. If you’re able to show respect, build trust and lower defensiveness, you’ll have a better chance of opening their mind to alternative perspectives – although it’s also crucial to remain open to alternate perspectives yourself.
There is no right answer
This is because there is no one “right answer” to the referendum question. Reasonable people can disagree on whether a Voice to Parliament is the best mechanism to promote the welfare and representation of Indigenous peoples, or whether a Voice ought to be enshrined in the constitution. When discussing the issue with others, it’s easy to assume that people who disagree with us must harbour some problematic views or that they are simply misguided. Resist that urge and ask questions that aim to tease out good reasons for or against the Voice.
The stakes involved in the Voice referendum mean that we should all take our responsibility to vote in a considered way seriously, and we should be mindful of how we make our decision. Even though there are many pressing issues facing the Australian public, from the cost of living through to climate change, that doesn’t mean we can’t also engage with the longstanding issue of Indigenous disadvantage, especially because there’s often not much we can do about many big issues but we’ve been explicitly invited to have a say on the Voice.
For everything you need to know about the Voice to Parliament visit here.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A new era of reckoning: Teela Reid on The Voice to Parliament
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Climate + Environment
What we owe each other: Intergenerational and intertemporal justice
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Ask an ethicist: Why should I vote when everyone sucks?
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Free markets must beware creeping breakdown in legitimacy
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
If politicians can’t call out corruption, the virus has infected the entire body politic

If politicians can’t call out corruption, the virus has infected the entire body politic
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY Simon Longstaff 3 JUL 2023
Nothing can or should diminish the good done by Gladys Berejiklian. And nothing can or should diminish the bad. One does not cancel the other. Both are true. Both should be acknowledged for what they are.
Yet, in the wake of Independent Commission Against Corruption’s finding that the former premier engaged in serious corrupt conduct, her political opponent, Premier Chris Minns, has refused to condemn the conduct that gave rise to this finding. Other politicians have gone further, putting personal and political allegiance ahead of sound principle to promote a narrative of denial and deflection.
Political corruption is like a highly contagious virus that infects the cells of the brain. It tends to target people who believe their superior virtue makes them immune to its effects. It protects itself from detection by convincing its hosts that they are in perfect ethical health, that the good they do outweighs the harm corruption causes, that noble intentions excuse dishonesty and that corruption only “counts” when it amounts to criminal conduct.
By any measure, Berejiklian was a good premier. Her achievements deserve to be celebrated. I am also certain that she is, at heart, a decent person who sincerely believes she always acted in the best interests of the people of NSW. By such means, corruption remains hidden – perhaps even from the infected person and those who surround them.
In painstaking legal and factual detail, those parts of the ICAC report dealing with Berejiklian reveal a person who sabotaged her own brilliant career, not least by refusing to avail herself of the protective measures built into the NSW Ministerial Code of Conduct. The code deals explicitly with conflicts of interest. In the case of a premier, it requires that a conflict be disclosed to other cabinet ministers so they can determine how best to manage the situation.
The code is designed to protect the public interest. However, it also offers protection to a conflicted minister. Yet, in violation of her duty and contrary to the public interest, Berejiklian chose not to declare her obvious conflict.
At the height of the COVID pandemic, did we excuse a person who, knowing themselves to be infected by the virus, continued to spread the disease because they were “a good person” doing ‘a good job’? Did we turn a blind eye to their disregard for public health standards just because they thought they knew better than anyone else? Did it matter that wilfully exposing others to risk was not a criminal offence? Of course not. They were denounced – not least by the leading politicians of the day.
But in the case of Berejiklian, what we hear in reply is the voice of corruption itself – the desire to excuse, to diminish, to deflect. Those who speak in its name may not even realise they do so. That is how insidious its influence tends to be. Its aim is to normalise deviance, to condition all whom it touches to think the indefensible is a mere trifle.
This is especially dangerous in a democracy. When our political leaders downplay conflicts of interest in the allocation of public resources, they reinforce the public perception that politicians cannot be trusted to use public power and resources solely in the public interest.
Our whole society, our economy, our future rest on the quality of our ethical infrastructure. It is this that builds and sustains trust. It is trust that allows society to be bold enough to take risks in the hope of a better future. We invest billions building physical and technical infrastructure. We invest relatively little in our ethical infrastructure. And so trust is allowed to decay. Nothing good can come of this.
When our ethical foundations are treated as an optional extra to be neglected and left to rot, then we are all the poorer for it.
What Gladys Berejiklian did is now in the past. What worries me is the uneven nature of the present response. Good people can make mistakes. Even the best of us can become the authors of bad deeds. But understanding the reality of human frailty justifies neither equivocation nor denial when the virus of corruption has infected the body politic.
This article was originally published in The Sydney Morning Herald.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A critical thinker’s guide to voting
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Sportswashing: How money and politics are corrupting sport
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Israel or Palestine: Do you have to pick a side?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Why fairness is integral to tax policy
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
How far should you go for what you believe in?

How far should you go for what you believe in?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY Cameryn Cass 28 MAR 2023
Do we all have a right to protest? And does it count if it doesn’t result in radical change? Grappling with its many faces and forms, philosopher Dr Tim Dean, and human rights lawyer and chair of Amnesty International UK, Dr Senthorun (Sen) Raj unpack what it means to ethically protest in our modern society.
In the wake of 2023 World Pride and Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras, Raj and Dean reflect on a fundamental question present in all protest: What is it you’re protesting?
The first challenge is in agreeing on what the problem is: Is it freedom we’re fighting for? Equal rights? Sustainability? From there, you’ve got to expose the fault to enough people who are motivated to join in on the resistance.
“We can hope for a better future, but is it enough to just hope?” – Sen Raj
Even if a protest is small in numbers, it can be lasting in impact; just consider Sydney’s first Mardi Gras. It was a relatively modest event that’s now grown to nearly 12,500 marchers and 300,000 spectators. But it began with a fraction of those numbers. Late in the evening on 24 June 1978, a group marched toward Hyde Park with a small stereo system and banners decorating the back of a single flat-bed truck, like a scaled-down parade float. The march intentionally coincided with anniversary of the 1969 Stonewall riots, which remains a symbol of resistance and solidarity among the gay and lesbian community. As the night progressed, police confiscated the truck and sound system. Eventually, 53 people were charged – despite having a permit to march – after they fought back in response to the police violence. To this, Ken Davis, who helped lead the march, said, “The police attack made us more determined to run Mardi Gras the next year.”

“Protest” has multiple meanings
A meaningful protest doesn’t have to be major like Mardi Gras. Sometimes, protests by brave individuals alone have extraordinary impacts.
Thích Quảng Đức, a Mahayana Buddhist monk, famously burned himself to death at a busy intersection in Vietnam on 11 June 1963. In the height of the Buddhist crisis in South Vietnam, Quảng Đức performed this self-immolation to protest Buddhist persecution. The harrowing photo of him calmly seated while burning alive touched all corners of the globe and inspired similar acts of sacrifice in the name of religious freedom.
Protests need not be so drastic, though, to have an impact. On 16 December 1965, a group of American students protested the Vietnam War by wearing black armbands with peace signs on them to school. When administrators told the students to remove the bands and they refused, they were sent home. Backed by their families, the Iowa school’s barring of student protest reached the Supreme Court. The famed Tinker v. Des Moines decision held that students don’t “shed their constitutional rights to freedom of speech or expression at the schoolhouse gate.”
The Tinker case is proof that protests, no matter how minor, can give rise to reformation. But we shouldn’t enter all protests with an expectation of radical change. Dean and Raj agree the assumption that transformation is the mark of a successful protest ought to be re-examined, as a clear outcome isn’t the only metric of success. As Raj said, “There is a tendency at times to assume that a protest will have a very clear message – a defined endpoint or outcome.”

Though progress might prove slow, it’s progress, nonetheless. We should act with the intention of spreading a message and entering a larger conversation that may or may not modify the status quo. Does a protest count for nothing if it doesn’t result in sweeping change? Is it not enough to ignite the spirit of defiance in just one soul? Or to simply express your authentic self even if it has no impact?
“For me, being queer, being trans, being part of a community that is marginalised and stigmatised for who you are or what you do, in itself, is a form of protest.” – Sen Raj
For members of the LGBTQIA+ community, Raj highlights how, “by virtue of existing, these individuals are being policed.” He says, “For me, being queer, being trans, being part of a community that is marginalised and stigmatised for who you are or what you do, in itself, is a form of protest.” So by refusing to conform and loving who they want, not holding themselves to gender or sexual norms, LGBTQIA+ people protest every day. It’s not a large mass gathering, but it’s a kind of protest, nonetheless. Authentic expression begets liberation; we ought not trivialise the importance of any protest, big or small, as it takes real courage to take part in something larger than yourself.
Does violence have a place in protests?
Just as protests can manifest in many forms, they can also be carried out differently.
Because tragedy and injustice are what usually catalyse protests, they’re often charged with strong – and sometimes overwhelmingly negative – emotions. It’s no surprise, then, that some protests turn violent.
But is violence ever permissible in a protest? And if police instigate it, do protesters have a right to protect themselves?

During the racial tensions in 1960s America, many protests ended in violence, especially by police. Images capture the savage behaviour in Birmingham, Alabama, where police unleashed high-powered hoses and dogs on Black protesters. In spite of such violence, they had no space to defend themselves; fighting back meant certain arrest. As Dean and Raj detailed in the discussion, sometimes authorities use this tendency towards self-defence to provoke violence and thus justify further oppression. Race riots persist in America as the fight against systematic racism and police brutality continues. The Black Lives Matter movement (BLM), founded in 2013 and popularised after a policeman wrongfully killed George Floyd in 2020, continues the fight for Black rights.
The fragility of protesting
The right to protest isn’t guaranteed and must be protected. In the absence of protest, the government and other institutions could operate unchallenged.
In Hong Kong, China enacted a new national security law in 2020 that’s a major barrier to protesting. Already, hundreds of protesters have been arrested. On paper, the law protects against terrorism and subversion, but in practice, it criminalises dissent. In the absence of protest, the powerful can ignore and silence the concerns of the masses. If a system is broken, binding together and protesting is an essential step in fixing it. Without protests, a broken system will remain broken.
“That’s what gives rise to protests, is that refusal. That refusal to allow for social or political worlds that oppress you to continue unchecked, and to say ‘Enough’.” – Sen Raj
Anti-protest laws aren’t a uniquely Hong Kong phenomenon. In April 2022, the New South Wales government passed more stringent legislation that punishes both protests and protesters that illegally dissent on public land. By blocking protests that prevent economic activity, critics say it’s an extremely undemocratic measure and threatens protests at large. Plus, it creates a hierarchy among protests, where some are viewed as valid while others aren’t. This raises the larger question of whether it’s the government’s place to determine which protests should be allowed. Does asking permission to protest do an injustice to the demonstration?
A way forward
It’s important to note that there’s no one way to protest. The textbook protest of a group of angry, fed-up citizens waving signs and shouting in the streets doesn’t always hold true. And so we’ve got to remember that protest need not look a certain way or foster radical change to be successful. It need not be a grandiose display of floats and intricate costumes parading down Oxford Street, like today’s Mardi Gras; sometimes it’s enough for one person to speak their mind.
Raj reminds us that protest ought to be messy, joyous and painful but should include care, respect and solidarity. He encourages us to abandon the stereotypical depiction of protest and embrace the possibility of many protests. It’s limiting to try and definitively define what it means. “Protest” is encapsulating of so many movements, minor and mammoth. Instead of trying to box it into one definition, let’s find beauty in its vastness.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights
Big Thinker: Judith Jarvis Thomson
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Social philosophy
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
Pleasure without justice: Why we need to reimagine the good life
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
An angry electorate
BY Cameryn Cass
Cameryn Cass is a curious writer and an editor-in-training who studied at Michigan State University. Her primary focus is environmental storytelling, as she deeply loves the natural world and intends to use her voice to defend it. Outside of work, she loves to hike, rock climb and practice yoga.
Who’s afraid of the strongman?

Who’s afraid of the strongman?
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Georgia Fagan 23 NOV 2022
Donald Trump has announced his second run for presidency in 2024. With a reputation for both passive and active violence, and a disregard for democratic integrity, the prospect of another Trump presidency is feared by many. But for others, his re-election would mark the promising return of a strong, capable leader. How do we begin to make sense of these contemporary communities which seem to either fear or revere their elected leaders? And are there ways such polarised receptions can ever be avoided?
Historian Ruth Ben-Ghiat knows just how Trump, operates. He’s following the strongman’s playbook, one that has four guiding features. Strongmen put their personalities at the front of their politics, they embrace machismo norms, relish in corruption, and do not shy away from the power of violence. We can use these insights to sniff out the strongmen lurking in systems of governance. Ben-Ghiat emphasises that we should be strongly motivated to do just this, as there is ‘too much at risk not to try’.
Cultish personalities are formed around these political leaders as they work to present themselves as ‘a man of the people’. They emphasise their standout character while simultaneously asserting themselves to be no different than the common citizen.
Their embracing of machismo, Ben-Ghiat explains, is reflected in hypermasculine behaviours, showcasing these examples with shirtless photos of both Trump and Putin. Women, they say, are ‘the enemy of the strongman’.
Corruption in the case of the strongman is of both the ‘moral and professional’ variety. We are told that the strongman commonly grants pardons which ‘free up criminals for service’, channelling those who some may take to be immoral offenders into positions of political power.
To convey their relationship to violence, Ben-Ghiat directs us to the presence of weapons in recent Republican political campaigns in the United States, telling us that these men ‘think they look strong, but it is really a sign of insecurity’. The strongman is making up for something.
Ben-Ghiat tell us that a contemporary commonality of these men is that they are often democratically elected, and that they pose considerable threats to the democratic systems in which they embed themselves.
Trump’s rallying tactics and his subsequent role in and commentary on the 2021 Capitol riot may be taken as emblematic of these strongman features. His mass appeal has been argued as being largely derived from ‘performative’ techniques that obfuscate his political goals or capacities more broadly. Trump continues to claim the democratic integrity of the United States to be under threat, asserting the actions of the Capitol rioters as warranted given the presence of electoral fraud in the country.
In these ways and others Trump seems to aptly align with Ben-Ghiat’s constructed, strongman persona. Impeachment, ongoing congressional hearings and public scrutiny evidently do little to undermine Trump’s confidence and his desire to reobtain the political power he once held.
There are mounting concerns that this phenomenon is not isolated to the United States. And that politicians globally can be seen as working to strengthen centralised systems of political power in ways which align with authoritarian leadership regimes. Could there be a risk that even the most historically democratic governments could begin to shift in comparable ways? If so, what could be done to manage that risk?
–
Pursuing political instigators of harm is a coherent goal and a strong incentive to Ben-Ghiat’s work. State leaders, even when democratically elected, are fashioned with powers that endow them the capacity to do both a world of good, and a world of harm. Many people were directly harmed by policies of the Trump administration; even more were harmed from the uncertainty his particular presence in office brought into their daily lives.
Ben-Ghiat recognises these sorts of harms and aims to call out the various features which they take as both forging and propagating them, egotistical, corruptive, and violent figureheads. When bundled together, these form the strongman, and for Ben-Ghiat the strongman should be our target.
If the goals of this work are the management of uncertainty and the desire to retain confidence in our capacity to uphold democratic structures and installed systems of justice, and we are sympathetic to these goals, we need ask what Ben-Ghiat’s approach to achieving them misses, or more poignantly, what it risks.
Bertrand Russel, not unlike Ben-Ghiat, was similarly sceptical of politicians. He remarks, “since politicians are divided into rival groups, they aim at similarly dividing the nation…”. Importantly distinct from Ben-Ghiat however, Russel’s scepticism is namely directed at the two-party political system as it stood in early 20th century Britain, and the impact this system has on the wider populations who comprise it.
Features of Ben-Ghiat’s strongman criteria are not in opposition to Russel’s characterisation of political figures more broadly. Yet Russel’s evaluations of these harm attend more heavily to the relationships that citizens, or voters, have to these politicians.
“The power of the politician, in a democracy” Russel writes, “depends upon his adopting the opinions which seem right to the average man”. For Russel, both the best and the worst of our politicians are reflections of and responsive to the ideas and sentiments of the populations they operate within.
The risk of Ben-Ghiat’s approach is that attending so heavily to the strongman, determining what he is and is not, may unhelpfully be turning our gaze away from our communities who, as Ben-Ghiat remarks, oftentimes democratically elect the very figureheads they and others wish to repudiate.
Sources of harm do not always come to us wrapped up in neat and tidy (shirtless) packages. Tirelessly seeking to group together ‘bad men’ can diminish our capacity to see other less precise but perhaps more pervasive sources of harm.
Comprehensively managing any risk a strongman may pose to our society will only be minimally addressed by stringing together various features that are said to necessarily render that man strong.
There is certainly time and space for the sort of work Ben-Ghiat dedicates themselves to.
Though if we are committed to protecting systems of democracy, and to ensuring that basic rights are genuinely upheld, we may be best served by turning our attention away from contemporary figureheads and towards those who cast their votes in favour of them, and to those systems of governance that forge and foster polarisation.
Naming and shaming the strongman, however accurately, will do little in the face of many who take his central features to be admirable strengths. Let us ensure that our pursuits of certainty and stability do not come at the cost of neglecting to engage with those around us who evidently have different assessments about just how risky a strongman really is.
Tune into Ruth Ben-Ghiat’s full FODI 2022 discussion, Return of the Strongman
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Political aggression worsens during hung parliaments
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Power without restraint: juvenile justice in the Northern Territory
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Society + Culture
The Ethics Centre: A look back on the highlights of 2018
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Is constitutional change what Australia’s First People need?
BY Georgia Fagan
Georgia has an academic and professional background in applied ethics, feminism and humanitarian aid. They are currently completing a Masters of Philosophy at the University of Sydney on the topic of gender equality and pragmatic feminist ethics. Georgia also holds a degree in Psychology and undertakes research on cross-cultural feminist initiatives in Bangladeshi refugee camps.
We are on the cusp of a brilliant future, only if we choose to embrace it

We are on the cusp of a brilliant future, only if we choose to embrace it
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Simon Longstaff 22 JUN 2022
Speaking a couple of days after the 2022 Federal Election, renowned Australian journalist, Stan Grant, noted that although the election of the Albanese government had been a moment of national ‘catharsis’, it was more difficult to discern in the result a commitment to a clear, positive direction for the nation. In that sense, the future shape of Australia remained an ‘open question’.
This was not to deny that the Australian electorate seemed to express, through their vote, a few clear preferences: an end to the debilitating ‘climate wars’, higher standards of integrity in federal politics and more generally, a preference for a more diverse and inclusive form of representation in our national parliament and government.
There is every reason to believe that these expectations will be met. Indeed, one might be encouraged to hope for something more. For example, it was remarkable that the first utterance of Prime Minister Albanese, on claiming victory, was to promise a referendum to enshrine in the Constitution an Indigenous ‘Voice to Parliament’ as called for in the Uluru Statement From The Heart. The surprise in this was that this issue had barely been mentioned during the election campaign – yet had clearly loomed large in the mind of the new PM.
So, what else might we aim to achieve as a democratic nation endowed with the most fortuitous circumstances of any nation on earth? Yes, despite the current ‘doom and gloom’, we are on the cusp of a truly brilliant future – if only we choose to embrace it.
We have everything any society could need: vast natural resources, abundant clean energy and an unrivalled repository of wisdom held in trust by the world’s oldest continuous culture supplemented by a richly diverse people drawn from every corner of the planet. However, whether this future can be grasped depends not on our natural resources, our financial capital, or our technical nous. The ultimate determinant lies in our character.
Three forces can shatter our path to prosperity. First, enemies from without who seek to exploit our grievances and divide our nation into warring factions. Second, a collective fear of the unknown and a lack of trust in those who would lead us there. Third, a lingering, persistent doubt about the legitimacy of a society that violently dispossessed the first peoples of our continent.
Each of these threats can be neutralised – if only we have the collective will and the courage to do so. With this in mind, I have outlined below a set of core, national objectives that I think would secure the endorsement of a vast majority of Australians. It is the realisation of these objectives that will unlock the brilliant future that is available to all Australians.
In five years, we can fashion a society that is at ease with itself and its place in the world. We can have sown the seeds out of which will grow a universal sense of belonging – a gift bestowed by First Nations people who have only ever asked for respect, truth and justice. That sense of unfettered connection, informed by an Indigenous understanding of country that has grown over time immemorial, will be the glue that binds us into one people of many parts. Once established and reinforced, nothing will dissolve that bond.
In five years, we can grow the confidence to embrace radical change – confident that no individual or group will be asked to bear a disproportionate burden while others take an unfair share of the gains. Our commitment to a broadly egalitarian society will move from myth to reality. While we may not all rise to equal heights, no one will be left to fall into the depths of neglect or obscurity. This will allow us to be brave, to take risks and to harvest the rewards of doing so.
In five years, we can be better led. Confidence can be restored in our governments – that they will truly honour their democratic obligation to act solely in the public interest – whether in their use of public resources or in the policies and practices they adopt.
In five years, the aged, the sick and infirm should be cared for by a workforce who are properly valued and rewarded for their support of the most vulnerable.
In five years, all Australians should have a genuine opportunity to make a home for themselves in affordable, secure accommodation.
In five years, everyone should feel more safe and secure in their homes, their workplaces, their cities and towns.
In five years, a confident Australia can build and reinforce enduring alliances with nations who share our desire to live in a just and orderly world free from the heavy yoke of authoritarian governments.
All of this is possible. For the most part our physical and technical infrastructure is world class. Our ethical infrastructure could be better. We need to invest in this area – confident that in doing so we will unlock both social and economic benefits of staggering proportions. As Deloitte Access Economics has estimated, a mere 10% increase in the level of ethics in Australia would lead to an increase in GDP of $45B (yes, billion) every year – not through some kind of ‘magical effect’ but as a direct consequence of the increased trust that better ethics would create.
Do this and we can embrace the brilliant future that beckons us.
With your support, The Ethics Centre can continue to be the leading, independent advocate for bringing ethics to the centre of life in Australia. Click here to make a tax deductible donation today.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
In the court of public opinion, consistency matters most
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
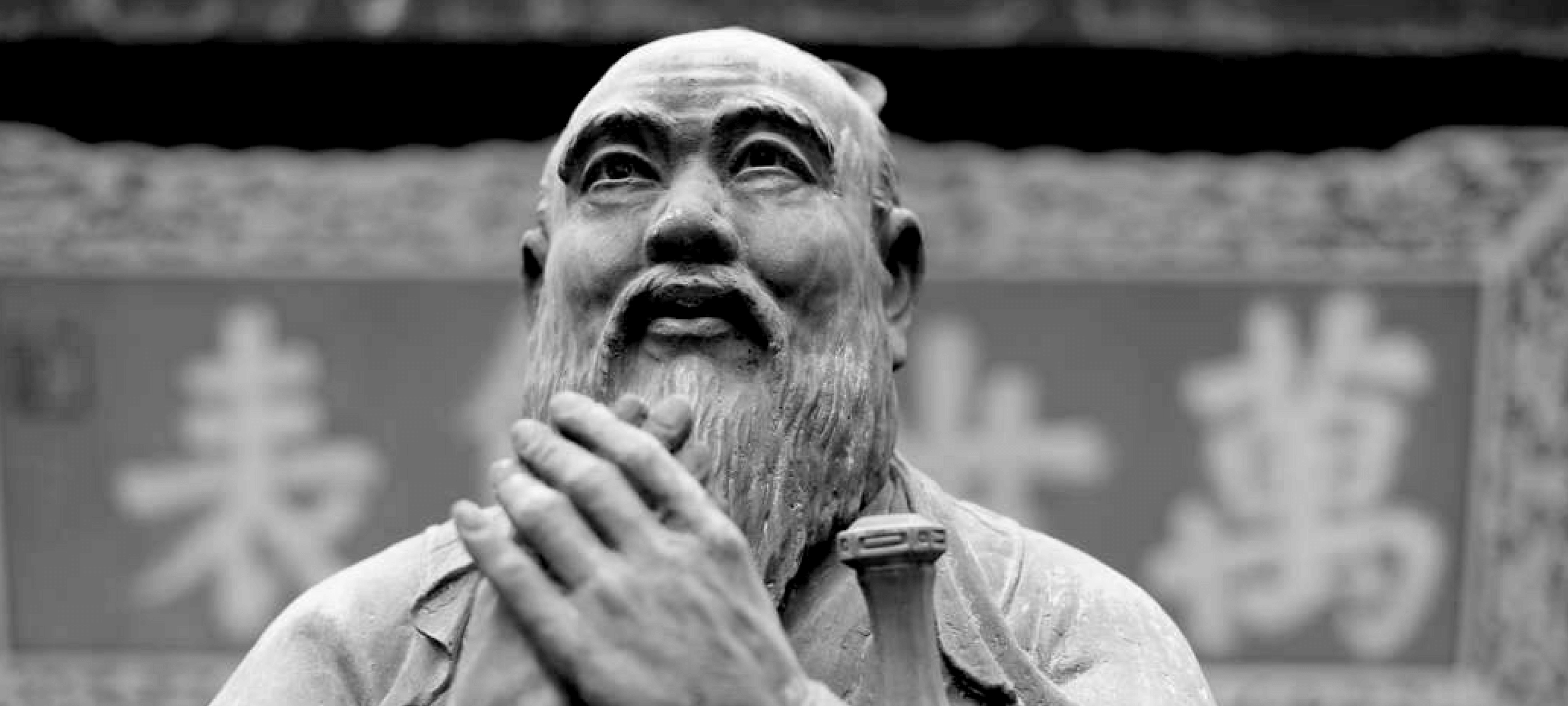
Big Thinker: Confucius
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Australia’s ethical obligations in Afghanistan
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Holly Kramer on diversity in hiring
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
We're being too hard on hypocrites and it’s causing us to lose out

We’re being too hard on hypocrites and it’s causing us to lose out
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Dr Cressida Gaukroger 19 MAY 2022
Everyone hates a hypocrite. And apparently they are everywhere.
In the last week alone British Labour leader Keir Starmer has been accused of hypocrisy for having a beer and curry with colleagues in violation of lockdown rules; feminist social commentator and writer (and election candidate) Jane Caro has been labelled a hypocrite for advocating action on climate change, but also flying a lot; teal independents have been called hypocrites for their sources of funding after criticising Australia’s donation rules; the president of the Solomon Islands has accused Australia of hypocrisy for criticising their security pact with China while pursuing its own AUKUS agreement…
Hypocrisy is a sin regularly and loudly identified in politics and the media. And not without cause. However, this discourse regularly goes too far, to no good end.
We should be less critical of hypocrisy. Our obsession with hypocrisy prevents us from engaging in reasoned debate, it robs us of the tools to identify and express what others are doing wrong, and it risks leading us and others to becoming worse people.
What is the problem with hypocrites?
Though the term ‘hypocrite’ is often used as a catch-all term of moral condemnation, vaguely pointing to people whose actions appear to be inconsistent with their words, it is worth distinguishing between different types of hypocrites.
First there are insincere hypocrites – people who lie to gain advantage. Their actions, however, reveal that they genuinely do not hold the convictions they espouse. They are intentionally mis-leading and using others. Which is particularly egregious when they hold significant power over others as is in the case of politicians. But note that, here, the lying and manipulation are typically far more serious offences than the inconsistency and hypocrisy.
There are also exceptionalist hypocrites – those who make or police rules which they have no qualms about violating themselves. At the heart of it, this feels really unfair. However, it is not a universal wrong. Think of parents who make rules for their children that they do not follow – “you are not allowed to drink”, they say, while nursing a glass of wine; “it is always wrong to lie”, they say, while putting out mince pies for Father Christmas.
Such exceptionalist hypocrisy can sometimes reveal a greater wrong, or potential for wrong. For example, Boris Johnson made laws that kept large parts of his country in lockdown, but was breaking social distancing rules and attending parties. His actions demonstrated a lack of respect for others and, importantly, for those people whose interests he is meant to represent. The hypocrite hater could also point out that Johnson’s actions likely contributed to less adherence to the rules as people looked at his actions and felt “if he gets to do that, why shouldn’t I?”. However, modelling bad behaviour can encourage bad behaviour in others whether or not it is exhibited by a hypocrite. In this respect, the hypocrisy does not worsen the situation.
And then there is the weak-willed or inadvertent hypocrite. This person fails to live up to their espoused rules or ethical principles, not due to malice or deep insincerity, or because they think the rules don’t apply to them, but because it can be hard to be really good all the time. Think of the Christian who believes in the sanctity of marriage but finds themself desperate to leave a loveless marriage. The animal rights advocate who cares passionately about protecting native wildlife, but can’t bring themself to give up their beloved cat that steadfastly resists being kept indoors.
Inadvertent hypocrites may do better to reflect on their own experiences of struggle before harshly criticising others for not living up to their principles. But if they are unempathetic or overly aggressive in their attacks on others who violate their ethical rules, isn’t that the greater crime than not fully living up to those rules themselves? Wouldn’t that be problematic whether or not they lived according to those rules? And is it unempathetic of us to demonise the inadvertent hypocrite for an understandable weakness of will?
We shouldn’t just dismiss hypocrites
As soon as someone is called a hypocrite we feel licence to ignore them. But just because someone is bad, that doesn’t mean what they are saying is incorrect. Rather than shutting hypocrites down it is rational to ask if their hypocrisy is relevant to their argument.
Consider the smoker suffering from lung cancer who tells young people not to smoke because it can ruin their lives. Is their testimony any less reliable because they did not listen to their own advice? Or an environmental activist who flies to climate action conferences. Does this mean that they are any less right when they say we need to take action on climate change?
Our focus on hypocrisy can distract attention from the real issues or moral problems with a person (or institution) or their actions, such as: Are they lying to or manipulating people? Are they showing that they don’t respect the people they are meant to represent? Are they being aggressive or unsympathetic to others? Are they espousing something false or acting in a way that is morally wrong – whether or not their actions and words match up?
This should not dissuade people from rationally engaging in discussions with others about whether their moral principles are consistent. Highlighting ethical inconsistencies is the bread and butter of contemporary moral philosophy. If holding one principle should entail another but your friend holds the first while rejecting the second, talking through this can shed light on their values: help them realise the connection between the two. But throwing around the term ‘hypocrisy’ when you do it can turn a potentially neutral observation that they should reflect more on whether their ethical principles are consistent (shouldn’t we all?) to simply telling them that they are bad.
Being inconsistent is better than being consistently bad
A hypocrite says one thing and does another: so at least they are getting something right. Would we prefer someone who is all bad?
An obsession with hypocrisy can lead us to expect moral perfection in everyone. But inconsistency is part of moral life. There is nothing wrong with having high moral standards while recognising that we won’t always meet them.
Our desire for consistency can lead to unachievably high expectations that, when unmet, lead us to rejecting an entire principle or endeavour rather than living with our moral imperfections and trying to gradually improve our actions next time. Like the dieter who fasts for a week and then immediately gives up because of one slip with a slice of cake, or the long-time vegetarians or vegans who returned to eating meat after an extended stint in a country where vegetarian options were extremely limited. It is not surprising that they broke with their vegetarian principles while in those countries. It may well have been inconsistent with the view that all else being equal it is wrong to eat meat, but that makes it no less understandable an action to take. Rather, it is surprising that they continued to eat meat once they returned to a country where vegetarians were once again well catered for. Their actions changed first and their values followed. They ended up being more consistent perhaps, but (at least for those who believe that it is wrong to eat meat) things went the wrong way.
We are all hypocrites sometimes. The desperate desire to avoid hypocrisy can lead us to strive to be all good and, when that fails, to be all bad, rather than trying to be ‘good enough’ – being guided by moral principles we will likely never fully live up to.
My recommendation is to take it easy on hypocrisy. If you are in a debate, attack arguments not people. Where people are bad the wrongness of their actions or words should speak for themselves, and you should focus on pointing out the actual problem with them, rather than using a catch-all term. When it comes to yourself it may also help to start by aiming for the good, not the perfect. Improving incrementally is still improvement, even if it sometimes means you will be inconstant.
And if all of that doesn’t convince you, then you better hope that you have never exhibited inconsistency in your own principles and your actions. Because if you have, judging others for being hypocritical would be, well, very hypocritical of you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Drawing a line on corruption: Operation eclipse submission
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Conscience
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
What’s the use in trying?
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Mutuality of care in a pandemic
BY Dr Cressida Gaukroger
Dr Cressida Gaukroger is a former lecturer in Ethics at Oxford University now a Senior Policy Advisor focusing on wellbeing-led approaches to government.
Housing affordability crisis: The elephant in the room stomping young Australians

Housing affordability crisis: The elephant in the room stomping young Australians
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Intifar Chowdhury 16 MAY 2022
Affordably housing its peoples is a hallmark of a developed society. Yet, Australia’s housing system has been failing young people, argues Intifar Chowdhury.
Squeezed by rising rents and aggressive increase in property prices, young Australians are increasingly being locked out of the housing market, and thus are being denied the stability and financial security that was taken for granted by previous generations.
The housing affordability crisis deepens as inflation, cost of living and housing prices rise at a faster rate than wages. Similarly, Australia’s rental crisis worsens with natural disasters such as flooding and increased competition as the country reopens to international students.
The backdrop to the COVID-19 pandemic will also exacerbate this growing economic inequality across generations. In fact, those in their late 20s and early 30s have now known two crises: the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) of 2008-2009 and the COVID-19 crisis of 2020-2021. This puts them at unique risk and financial disadvantage compared to other members of society.
The reality on the ground is that, compared to their parents and grandparents, today’s young people are not only poor homeowners but also poor renters. The reality is an intergenerational theft.
While some have argued that housing should be at the front and centre of the upcoming federal election, housing affordability has not taken on a sufficient degree of importance in the policy narratives of the two major parties.
In fact, I’d agree that young Australians have been betrayed by both parties. Although the youth need a proper national plan for housing affordability and supply, their situation is sometimes met with rather condescending comments from the political leadership.
Prime Minister Scott Morrison’s comment – that “if you can’t afford rent, buy a house” is both comical and disturbing at first reading. As the PM flaunted in the first 2022 leader’s debate, first home buyer loan schemes allowed 160, 000 Australians to gain access to the property ladder last year. And his recent proposal to allow young people to tap into their superannuation has a similar ambition.
But what he neglects is how housing affordability concerns 67 per cent of Australians, many of whom are young people with low wealth and heavily taxed incomes. And government subsidies for a relative minority put upward pressure on prices for the many, presenting a trade-off of where it is more difficult to save a deposit for a home. Therefore, such comments are disturbing reflections of how far removed Australian political leaders are from the reality on the ground.
Housing affordability: a sticky problem?
Housing unaffordability has been identified as a pressing problem for more than decade now, so why then does it remain unresolved? The simple answer to this is that the politics around the problem prevents a permanent solution.
The housing affordability crisis persists because of two political reasons. First, more voters have an incentive to maintain the status quo compared to those who could benefit from a more equitable housing system. Although the growth in property prices entrenches economic inequality, it is a positive for incumbent homeowners who want to capitalise on their investment.
Further, impenetrable, cumbersome and ambiguous policies spook those with property. They fall into the status quo bias. For example, Labor’s 2019 election slogan to tone down investment incentives and introduce the housing tax upset property and construction industries and offended a large constituency of property owners. These radical proposals cost Labor the election.
Existing housing policies also fail to address the root cause of the problem. Most efforts to deal with unaffordability aim to cool housing demand rather than increasing supply. Pete Wargent, co-founder of BuyersBuyers, believes this approach would “make a marginal difference to affordability over time”.
Although investment incentives like CGT discounts and negative gearing are touted as the key drivers, recent review of six economic papers revealed that the combination of both contributed only a small 1 per cent to 4 per cent increase in dwelling prices. Whereas zoning restrictions, which limit the supply of land on which to build homes, contribute to almost half the rise of average detached house prices in major metropolitans, like Sydney and Melbourne. Centre for Independent Studies’ chief economist and a former RBA official, Peter Tulip, suggests increasing supply and lifting zoning restrictions can have huge benefits.
Yet, these are difficult to attain. The politics of improving housing affordability is determined by whether there are more voters who are property owners than not.
That is, whether there are more beneficiaries of unaffordability who will vote in their self-interest and support policies and parties that will keep prices high and rising, even if that compromises the future security of young people.
According to the Australian Electoral Commission, in 2022, there are 4.2 million voters aged over 65 compared to 3.1 million voters under 29. That is a difference of 1.1 million between lightly taxed, asset-rich older Australians, and younger wage earners. This intergenerational inequality is therefore a function of the classic headlock between the older haves and the younger have-nots.
Simple fix: increase supply?
Housing unaffordability is a complex structural issue that can’t be viewed through a simplistic lens.
Despite a plethora of issues influencing the housing market, the imbalance in supply and demand is at the crux of the matter. Rather unsurprisingly, the Property Council of Australia, recommends major parties to address supply shortages to improve affordability.
But adequate supply of housing doesn’t just mean constructing a certain number of dwellings on greenfield sites. It needs to be well-located and well-serviced with job, social and community infrastructures.
At both federal and state level, more commitment is requited to increase urgent need for more social housing. With a historically low level of social housing, (i.e. a non market rental housing sector), this would be more affordable and secure for low-income earners. Both major parties, however, fall short on public housing investment this election.
Supply of affordable housing can be increased by institutional investments, but investors show relatively little interest in affordable housing largely due to perceptions of risk and comparatively low returns. This is where government incentives and the introduction of some form of financial instrument (similar to the discontinued National Rental Affordability Scheme) could work.
However, evidence from Europe and Britain, suggest that government intervention may decline as affordability worsens. There is a major challenge to rolling out reforms: homeowners want to protect their properties from being undermined by growing housing supply, resulting in less support for government intervention. This feeds into inequality.
Another option is rent control. But opponents suggest that more limitations in the rental property make owning far less appealing. This again points to the headlocks between homeowners and renters; as the classic adage from former PM John Howard goes: no one is complaining in the streets about their house value going up.
Under the current structure, young people are common losers of the housing system. A change in government won’t be a silver bullet for housing affordability in Australia. What is needed is a structural change which is hard to attain given competing interests, imbalanced power and wealth dynamics among stakeholders.
Explore the role that ownership plays in our lives. Join Executive Director of The Ethics Centre Dr Simon Longstaff AO for The Ethics of Ownership on the 17th of August 6:30pm AEST. Tickets on sale now.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
If politicians can’t call out corruption, the virus has infected the entire body politic
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights
Big Thinker: Judith Jarvis Thomson
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Accountability the missing piece in Business Roundtable statement
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Trump and the failure of the Grand Bargain
BY Intifar Chowdhury
Intifar is an Associate Lecturer at the ANU School of Politics and International Relations. Her doctoral research tackles the important question of whether young people are turning away from democracy. Her political commentary on the engagement of young people in politics and issues affecting youth voters has been published in The Conversation, ABC, The Guardian, The Canberra Times and ANU's Policy Forum.
Antisocial media: Should we be judging the private lives of politicians?

Antisocial media: Should we be judging the private lives of politicians?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY Isabella Vacaflores 13 MAY 2022
The footage was grainy, but the man stepping out of the gay sex club was easily recognisable.
David Campbell, then transport minister of the New South Wales Government, was outed in the evening news, prompting his resignation the following day. His sexuality was the subject of intense media coverage, not least because of the impact it would have on his wife and children.
As headline grabbing and salacious as such personal scandals might be, one might question whether we should have the right to know about the private lives of politicians in the first place. After all, the fact of being queer alone bears little relevance to one’s ability to speak for their constituents, therefore arguably falling outside the realm of the public interest.
Yet, the journalist who broke the story felt differently, noting that the politician in question had “purported to be a family man”. As such, some might see this as an act of exposing hypocrisy, speaking to a deeper issue of character that is highly problematic for representative democracy.
So when it comes to dealing with information about the private lives of public officials, how morally justified are we in caring about what is done outside of parliament?
When rights collide
Although privacy is beneficial for human well-being and flourishing, it is not unequivocally good because such a claim can equally be used to hide information. This poses a significant threat when we consider how the personal lives of those wielding political power might influence their decision-making abilities, negatively impacting those that they claim to represent.
This tension between the claims to privacy of public officials and the rights of the public and the media to freedom of information is an undeniably hard one to resolve.
On the one hand, the revelation of Gladys Berejiklian’s relationship with Daryl Maguire and her subsequent resignation over accusations of corruption vindicate the idea that we should hold the private lives of politicians under constant scrutiny.
Yet, on the other, the case of David Campbell highlights the murky waters in which public interest claims lurk, with a person being pressured to end their political career over a seemingly inconsequential fact about their personal lives.
Are we morally justified in paying attention to and seeking out private information about public officials? After all, prima facie, all individuals have morally and legally robust claims to privacy.
Nevertheless, we generally consider it reasonable for interviewers to enquire about a potential employee’s prior working history to ensure that they are a good fit, or for a detective to ask someone questions about their private life to solve a crime. This is because privacy can and sometimes should be forfeited (with our knowing consent) for other rights or purposes, such as safety and transparency.
On a similar note, many citizens would see certain information about the private lives of politicians as relevant to their decision of who to vote for. This interest is warranted because public officials attain their legitimacy and authority from being entrusted to represent their constituents.
Ultimately, serving in government is ethically demanding – to avoid the corruption of power, we must elect individuals who have a track record of not abusing such privileges. According to the perpetually relevant ‘unity of virtues’ theory of the ancient Greeks, individual morality exists across both public and private spheres of decision-making.
As such, an absence or excess of good behaviour in one’s personal life may be illuminating with regard to professional conduct.
For instance, the media has recently reported that Boris Johnson, in his previous job as a motoring correspondent, accrued over £4000 in parking tickets. This fact, whilst seemingly trite, implies a historical pattern of rule flouting behaviour by the British Prime Minister, suggesting that we ought not be surprised by his involvement in the Partygate scandal.
Such cases highlight the often-blurry public/private divide and justify why we might look to politicians’ personal lives for clues as to how they might fulfil their moral duty to represent their constituents and their interests – even if this conflicts with their own.
Social media and the personalisation of politics
Furthermore, many politicians willingly open themselves up to public scrutiny by using their personal virtues and achievements to appeal to voters. We need not look further than Scott Morrison’s Twitter and Facebook feeds, which regularly feature pictures of the politician cooking up a curry in Kirribilli House and donning blue in support of the Cronulla-Sutherland Sharks, to see how political figures selectively reveal aspects of their private life to project a likeable image.
For as long as public officials advertise themselves and attack others on the basis of irrelevant personal characteristics and decisions (see criticisms recently directed at Anthony Albanese for everything from his weight loss efforts to having a “quiet week” of campaigning despite being in isolation for Covid) they cannot also claim to be innocent victims of the press, particularly when journalists are merely reporting on these assertions.
Nevertheless, politicians often resort to the refrain that ‘the media goes too far’ to divert attention away from their more questionable acts. When it was revealed that self-proclaimed family man and current Deputy Prime Minister Barnaby Joyce was having an extramarital affair with a staffer, a formal complaint about news coverage of the incident was made despite the couple accepting $150,000 to do a tell-all interview about it on live television.
The omnipresent pressure for news outlets to turn a profit leads them to sensationalist reporting and a rather liberal stance as to what information falls into the purview of the public interest.
However, political journalism acts as an irreplaceable check on power, and we ought to be wary of solutions that involve stifling it more than it already is under Australia’s extremely rigid defamation laws.
Towards a better discourse
Instead, content relating to the private lives of politicians needs to be understood in terms of its relevance to their ability to execute their role. We should actively dismiss and avoid searching for details that tell us nothing about the honesty, accountability, competence, integrity, judgement, and self-discipline of a public official, no matter how salacious. However, we can feel justified in pursuing information that reveals their historic performance in such areas.
Admittedly, this is a long laundry list that leaves few areas off-limits. It is important to note here that judgements about protected characteristics alone – such as race, sexuality, religion and gender – are not morally acceptable ways in which to judge the competence of an individual, as established under anti-discrimination laws.
That said, we cannot shy away from investigating how public officials have acted when they thought nobody was looking, particularly when such actions reveal how they use (and abuse) power or contradict their espoused values.
Because the relevance of this information can only be ascertained once it has been made publicly available, there will always be some politicians that have their privacy unjustly violated. This is a trade-off that can be easily defended when we consider the immense number of people that benefit from having a government composed of honest and accountable representatives.
Additionally, anyone entering a public-facing role knowingly places their privacy in a position of vulnerability. If they have something to hide, politics is probably not the place for them, practically and principally speaking.
Furthermore, we can limit the collateral damage of this proposal by encouraging journalists to prioritise reporting on facts that expose political corruption and speak truth to power. By choosing not to indulge in amusing but inconsequential gossip about the private lives of politicians, we can help change the incentive structure of the media system whilst simultaneously promoting enlightened attitudes towards sex and other areas of intense, but often illegitimate, public interest.
The democratic function of the press falters when trivial details about the lives of politicians consume all the resources of our finite attention economy. As such, it is a moral imperative for news outlets to maintain strong ethical standards when it comes to their reporting on the private lives of politicians, focusing their coverage on that which is relevant to their ability to bear office.
Finally, as public ethicist Patrick Dobel writes, “we should judge as mortals judging other mortals”. Public officials are not perfect people, but if they can recover from a fall from grace by regaining trust and legitimacy in the eyes of the people then we should leave them (and their sex scandals) be.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Society + Culture
The sticky ethics of protests in a pandemic
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
Pleasure without justice: Why we need to reimagine the good life
Big thinker
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Judith Butler
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
We are on the cusp of a brilliant future, only if we choose to embrace it
BY Isabella Vacaflores
Isabella is currently working as a research assistant at the Global Institute for Women’s Leadership. She has previously held research positions at Grattan Institute, Department of Prime Minister & Cabinet and the School of Politics and International Relations at the Australian National University. She has won multiple awards and scholarships, including recently being named the 2023 Australia New Zealand Boston Consulting Group Women’s Scholar, for her efforts to improve gender, racial and socio-economic equality in politics and education.
How to have a conversation about politics without losing friends

How to have a conversation about politics without losing friends
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Dr Tim Dean 21 APR 2022
There’s a reason our parents told us to steer clear of discussing politics (along with sex and religion) in polite company. Because as soon as politics is raised, there’s a very real chance that the company will become significantly less polite.
One reason political disagreements can be so divisive is that, unlike other contentious topics, like whether pineapple belongs on pizza, politics taps into our deeply held moral values and emotions: taxation policy isn’t just about the budget’s bottom line, it’s fundamentally about fairness; climate policy isn’t just about decarbonisation, it’s about the harm that our society is inflicting on future generations.
The moral dimension of politics can make us less tolerant of disagreement and more likely to see other views as not just different but mistaken, and perhaps dangerously so. It’s easier to shrug off someone’s opinion about the latest episode of The Bachelor than it is to let their views on asylum seekers pass without rebuttal.
The good news is that there are ways to have fruitful conversations about political differences if you approach them with care.
Before you start
Disagreements don’t have to be corrosive to our relationships or wellbeing. In fact, genuine disagreements give us an opportunity to learn, grow and share our perspectives with others. But they take time and effort to set up.
So before you utter a contrary opinion to a friend or family member about a political issue, first reflect on the strength of your own views and how open you are to new perspectives and evidence.
In today’s heated political environment there can be a great deal of pressure on us to form an opinion and take a side before we’ve had a chance to digest all the relevant information. There’s also a strong tribal element to politics that makes us more likely to adopt the views of ‘our side’ and oppose anything said by the ‘other side’. Many of us might even admit we hold opinions that we would struggle to justify if pressed.
Ideally, the strength of our convictions should be proportional to the strength of the reasons and evidence we can muster in their support. It’s still OK to form an opinion without doing a Masters degree on it first, but it does mean we should remain open to new information and perspectives that could change our mind. As a rule of thumb, if there are no reasons or evidence that could even hypothetically change your mind, then you’re being dogmatic and will likely receive no joy arguing about your views with others.
Before deciding to engage in a political disagreement, it’s also worth pausing to consider whether it’s worth arguing at all. It’s natural to feel compelled to correct a view you believe is harmful or wrong. But if it is likely that a disagreement could get heated or emotional, or it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to influence the other person at all, then getting into a debate might end up being entirely fruitless. All you might achieve is damaging the relationship, even if you’re in the right.
Sometimes relationships matter more than being right. If you’re arguing with someone close to you, someone you care for or depend on, it may not be worth eroding that relationship for the sake of a political argument, especially if it’s almost certain to go nowhere.
And if you do want to actually change someone’s mind, you need to establish a base of trust and respect first. Foregoing one heated conversation in order to strengthen a relationship means you can build enough trust and respect so that you can have a constructive disagreement sometime in the future. Once you’re sure they’re willing to listen to you, you might even have a shot at changing their mind.
Where to start
If you do decide to wade in, the very first thing to do is keep your mouth shut! At least at the start of the conversation.
When we hear someone say something we disagree with, our first impulse is often to express our own contrary opinion. The problem is that this immediately frames the conversation as a ‘war of ideas,’ which can trigger all the baggage this metaphor implies. We see our conversation partner as our ‘opponent,’ we become focused on ‘winning,’ on ‘undermining’ and ‘outflanking’ their position. And absurdly, if we do learn something and change our mind, that’s considered ‘losing’.
It’s better to frame the conversation in terms of fellow travellers exploring an issue together. You might have different perspectives, but you have the same ultimate goal: improving your understanding of the world.
In order to avoid slipping into the argument-as-war frame, instead of expressing your opinion up front, start by asking questions. Ask why your conversation partner believes what they do. Get them to elaborate on what they mean by various terms. Then listen carefully, paying special attention to both the content of what they say as well as their emotional state when saying it.
Once they’ve had a chance to express themselves uninterrupted, summarise their view back to them and validate how they feel. You can do this without necessarily validating the content of their beliefs, even if you disagree with them. You might say something like “I see you’re really concerned about the economic impact of climate policy”, which acknowledges how they feel but doesn’t commit you to agreeing or disagreeing with them.
This kind of reflective listening achieves two crucial things. First, it gives you a fighting chance of actually understanding their view in detail rather than assuming you know what it is. This is important because people often mean different things when they use terms like ‘freedom’ in a political context, which can lead to confusion and crossed wires unless you probe them on what they mean.
Secondly, reflective listening helps people feel heard, which signals respect and can lower the temperature of a conversation. In fact, a lot of defensiveness can simply be a result of people wanting to be heard and feeling like no-one is listening.
Common ground
If you want to progress the conversation, the next stage is to seek out common ground, especially around values or goals that you both agree upon. For example, you might both care about taxes not being wasted, or you both care about the wellbeing of the next generation. At this point you can start to frame your difference in perspective as being different strategies to achieve common goals. This can take a lot of the edge out of arguments, making them feel less like you’re fundamentally at odds and show that you’re only disagreeing about the means to achieving shared ends.
Crucially, if you ever feel the conversation getting heated to the point where it’s difficult for either of you to engage constructively, then it can be wise to back out and change the subject before it’s too late. You can always revisit the topic once things have cooled down.
It’s also important to not let the conversation drag out. It’s unlikely that you’ll be able to fully grasp someone’s views or change their mind in a single conversation. But even a short conversation can help you better understand their views and allow you to offer up a different perspective. And if it’s done with patience and respect, it can open the door to future constructive conversations. After a few such chats, you might even find you change their mind – or find that your own view has changed. That’s not a bad thing.
The highly charged moral dimension to politics is why conversations about it are so fraught. But if we engage thoughtfully and respectfully we can have a rich conversation about politics, and still have a fighting chance of making it to dessert with friendships and family relationships intact.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
How to respectfully disagree
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Education is more than an employment outcome
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
It takes a village to raise resilience
Big thinker
Relationships, Society + Culture