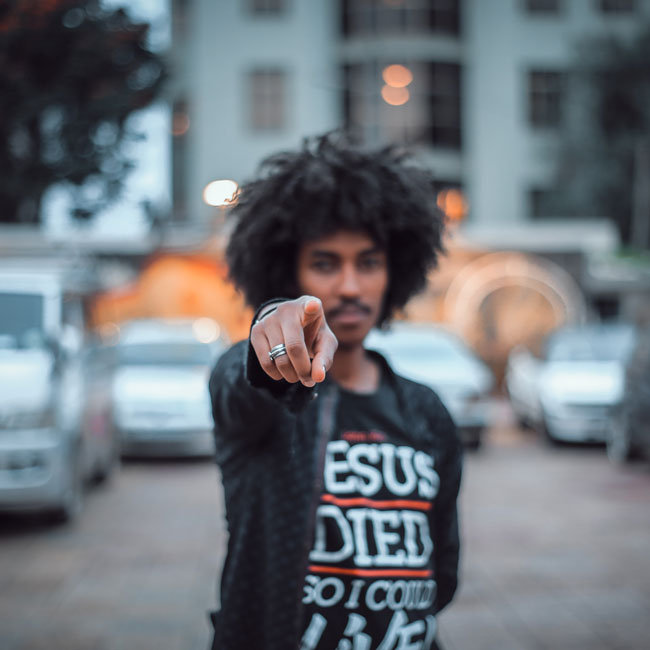
You won't be able to tell whether Depp or Heard are lying by watching their faces

You won’t be able to tell whether Depp or Heard are lying by watching their faces
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Joseph Earp 2 JUN 2022
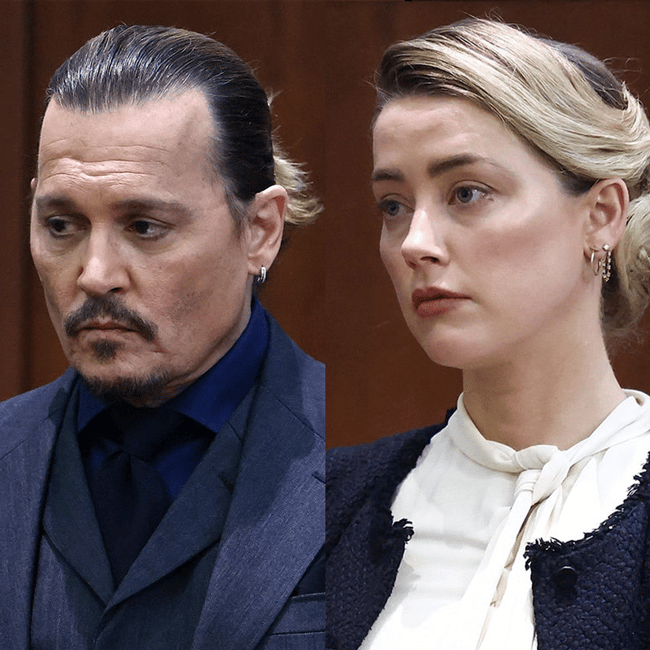
The Johnny Depp and Amber Heard defamation trial is now over.
Heard has been found guilty of defaming the actor with an op-ed she wrote – that did not name him explicitly – about being a survivor of domestic violence. Depp’s legal team too has been found guilty of defamation, but the amount that Heard has to now pay Depp is a much higher figure than he has to pay her.
The proceedings are done. But the media reaction to the trial – both from traditional outlets, and the deluge of posts about it crowding every single social platform like ants across an old plate of food – will linger.
This is because, in many circles, the all-too public spectacle has been treated like an unprecedented event. Pored over ad nauseum, it has been subject to endless thinkpieces, YouTube breakdowns, and Twitch streams. Twitter is awash with “fan edits”, compilations of carefully selected moments cut to the jaunty music usually associated with dance trends, or videos of dogs playing with each other in suburban backyards. There’s no use blocking keywords associated with it on social media. Videos still find a way to slip through, because the trial is everywhere.
This isn’t so surprising. The trial is on one level, a glimpse into the personal lives of the usually alien upper class. On another, it is shocking and disturbing enough – whichever side one takes – that it provides the vicious thrills that a culture which has become obsessed with true crime obsessively seeks out. This is all information, content. But how much of it do we need to make an informed decision about the outcome of the trial? And more than that, is this a useful kind of information? Where does it lead us? What does it give us?
The trial is foreign, it’s taboo, it’s ugly, and it’s glossy. What it isn’t, however, is quite as novel as it first seems.
Old Stories; New Faces
Much like the O.J. Simpson trial, or the proceedings against Lindy Chamberlain-Creighton, the Australian woman who claimed a dingo ate her baby, the Depp/Heard case is an example of a media-captivated society channeling abstract arguments through the lens of a high stakes legal proceeding, populated by faces that viewers have already developed complex parasocial relationships with. And, importantly, in each case, there has been an intense public scrutiny on how the figures in these cases should act – a fixation on their body language, their expressions, and the way they sound out words.
During the Simpson trial, the abstract arguments at play concerned race relations. Now, the tensions underlying the Depp/Heard trial are to do with what is sometimes referred to as our “post-metoo world”, a culture that has seen abusers reckoned with, and vast systems of deception that protect those abusers brought to light.
All of these court cases represented, and now represent, an opportunity for the public at large to discuss topics they might not normally have considered polite to bring up at the dinner table, or around the water cooler. “Is O.J. guilty?” was a way of saying, “tell me what you think about race and class in this country.” “Is Amber Heard a liar?” is now a way of saying, “what do you think abuse looks like? And what do we do about it?”
But there is at least one way that the Depp/Heard trial is involved with a trend that is breaking new ground. Unlike the Simpson trial, or the case against Chamberlain-Creighton, most viewers are watching the case through the internet. In turn, that means viewers have a unique ability to craft their own content about the proceedings, filtering key moments pulled from hours of footage through whatever pre-existing narrative they have constructed about the hero and the villain of this painful, and very sad story.
These content creators, who are often cutting together their videos in their spare time for no gain except rallying their audience around them, can watch over the trial’s footage as frequently as they like. They can scrutinize the same few seconds over and over; slow stretches of it down; freeze them in place.
In turn, that has turned a growing number of these amateur video essayists into amateur psychologists. A large subset of Depp/Heard content creators have come to believe that they can work out which of the players are lying by closely watching their expressions, unpacking their body language, and picking over the slightest tic, or absent gaze. For these sleuths, the case’s conclusion is as clear as Heard’s grimace, or the smile unfurling in the corner of Depp’s lips.
The Face Of A Liar
Those who seek to excavate the “truth” hiding beneath the trial by studying the body language and facial expressions of Depp and Heard start from a justifiable philosophical position. It was the philosopher Baruch Spinoza, a famous monist, who believed that every bodily state is underwritten by a mental state. For Spinoza, all things are of the one matter – variously called “nature”, or “God” by his intellectual interpreters. On this view, there is no distinction between any two substances, let alone a distinction between the way we hold ourselves, and what we think. The mind is the body, and the body is the mind.
From this starting point, it makes some sense to believe that the flesh might hold some insight into the secret thoughts and desires of two people who are very famous and very rich – and thus largely inaccessible, because nothing buys privacy like money and influence. Or, if not insight, then evidence gathered as post-hoc justification. Decisions as to guilt change based on a variety of factors – but they’re sometimes made early, and data can be gathered after those decisions have already been made, propping up pre-existing positions.
The mistake, however, is to generalise what these embodied states look like, and thus to generalise the emotional and mental states they are tied to.
There is, quite simply, no one way that all of us look when we lie, or are distressed, or happy. We are distinct in the way that we consider the world around us, and thus distinct in the way that we physically appear when we do.
Many of the “tell-tale signs” that get neurotically returned to, over and over again, on social media – Heard’s tone of voice, Depp’s drawl – could have any number of associated affective states, from anxiety, to pain, to yes, perhaps, the desire to lie. “It can be tough to accurately interpret someone through their body language since someone may feel tense or look uneasy for so many reasons,” said the therapist and author Dr. Jenny Taitz.
If we follow Spinoza, we will believe that our bodies and our thoughts are intertwined – but that’s not the same as saying the former will reveal the latter. These are slabs of affect, expressed both physically and mentally, but they are not as easily comprehensible as that makes them sound.
Indeed, psychological studies have proved for decades that none of us are skilled when it comes to weeding out those spinning “falsehoods”, and those not. A 2004 study of lying found that “agents of the FBI, the CIA and the National Security Agency – as well as judges, local police, federal polygraph operators, psychiatrists and laymen – performed no better at detecting lies than if they had guessed randomly.”
There is, after all, an immense social advantage to picking liars. If we could do it, and do it reliably, then that would be an invaluable skill, one we would expect to spread and be adopted across communities quickly. The fact that there is no dominant method of analysing the way our bodies twist and pose when speaking in itself speaks to the impossibility of using faces to get at what we mean when we talk about “the truth.”
Moreover, even most “body language experts” – an increasingly popular and media-saturated sub-set of pop psychologists, who have almost no science to back up their claims – admit that we need to get a baseline of our subject’s physical reactions before we can even attempt the fraught and mostly doomed work of trying to understand if they’re lying.
Which is to say, we need to at least know what people look like when they’re telling the truth before we can tell if they’re not. And we don’t know Johnny Depp, or Amber Heard, despite the illusion of closeness granted by social media. We don’t have enough data about how they move through the world, or what they look like when they do. How could we possibly guess at the motives and thoughts of utter strangers?
The Actors
Heard’s critics in particular have developed the line that she is a “performer”, going through the mere motions of grief and trauma – and not particularly well. They highlight a moment in which Heard appeared to pause while waiting for a cameraperson to snap a picture of her pained face, and another in which she seemed to flicker, composing herself for her next line as an actress on set would.
Of course, Heard is performing, on some level. But she is not performing in a way different to Depp. Though his defenders do not often note it, he too is signaling to the cameras, and to the jury – his smiles, and asides to his legal team, make that clear.
Nor, even, are these two distinct from the rest of us. We are all performing. We are social creatures, who have the ability to tell when we are being watched by others. Theory of mind, the term used to describe our understanding that other human beings see and think like we do, means that we can throw ourselves into the perspective of our observers. We do this constantly. It is part of what it means to have a body, and to be a person.
As philosopher Jean-Paul Sartre pointed out, we don’t even have to be actively watched to know that we could be watched. We carry with us the sense that we are what Sartre called a “thing in the world” – an entity that, at any time, could be stumbled across, and studied. As a result, we are always aware of ourselves, and how we might appear. Even when we are totally alone, we are never really alone. We are always with others – whether they’re flesh and blood observers, or ones we’ve made up in our head.
Where The Truth Lies
None of this has been an attempt to argue that Depp is telling the truth over Heard, or vice versa. It is not even a question of “truth”, as that word has been contemporaneously used.
The binary between the “real” and the “fake”, aggressively emphasised in media reactions to the trial, is itself overly simplistic, an outdated harbinger dangerously trickled down into the culture by analytic philosophy.
That is not to diminish the hurt, or the trauma, that clearly sits at the centre of the trial. That pain is real. That pain can be understood, but only when we look at the evidence in totality – the actual evidence, not the faces on the stand – and then causally tie it to certain parties.
We should, however, remember there is no objective state of affairs – no perfect place from which, like God, we can dispel the lies and embrace the world as it really is. The judge overseeing the Depp/Heard trial is not neutral. None of us are. At best, in this case as in so many others, we should, like the great pragmatist Richard Rorty, argue for ethnocentric justification for our claims, rather than tying them to a standpoint that sits outside of history, and belief, and bias. In doing so, we can embrace the changeability of our own positions – not on guilt and innocence, exactly, but the societal pressures that are so at play here – and examine them, seeing them as the flexible systems of thought that they are.
Throughout, however, we should remember that whatever we’re looking for when we hope to untangle a messy and painful relationship between two strangers who we will almost certainly never meet, it will not be found in their faces.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
Ethics on your bookshelf
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
How to pick a good friend
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
On truth, controversy and the profession of journalism
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Should parents tell kids the truth about Santa?
BY Joseph Earp
Joseph Earp is a poet, journalist and philosophy student. He is currently undertaking his PhD at the University of Sydney, studying the work of David Hume.
Big Thinker: Sally Haslanger

Sally Haslanger (1955-present) is one of the most influential feminist philosophers in contemporary philosophy. She is one of the pioneers of social philosophy and works to make the field of philosophy more inclusive.
She has some interesting life experiences, to say the least. Haslanger was born in 1955 in Connecticut, but moved to Los Angeles in 1963, where Jim Crow laws legalising racial segregation were still in effect. Moving from an unsegregated to a segregated part of the US as a child had an impact on her philosophical interests.
Her mother and grandmother were Christian Scientists, a small sect of Christianity that doesn’t believe in modern medicine, and she grew up attending their church. Later, her family moved to Texas where she attended an Episcopal boarding school, and started college before she had finished high school.
In a Q&A with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology ( MIT), Haslanger says that her interest in feminist philosophy was catalysed when she was sexually assaulted as an undergraduate student at Reed University. Afterwards, she became involved in feminist activism, especially during her time as a graduate student at University of California, Berkeley. Later in life, she and her husband adopted and raised two African-American children. Haslanger says that these life experiences have played an important role in directing her philosophical interests.
What is race? What is gender?
While these seem like straightforward questions, Haslanger has spent a large part of her academic career trying to answer them. Race and gender are categories that allow us to group people in particular ways, predominantly based on physical characteristics. However, she doesn’t believe that the categories of race and gender refer to just physical characteristics, they also refer to social positions. Social positions refer to where someone fits into their society: – they could be in a privileged position or a more marginalised one.
“On my view,” she said, “both race and gender are social positions that individuals occupy by virtue of their body being interpreted a certain way.”
In 2000, Haslanger published what is now one of her most well-known and controversial papers: Gender and Race: (What) are they? (What) do we want them to be? In her paper, one of the things she tried to do is find a characteristic that all women have or experience. The characteristic she finds and defends in her paper is systematic subordination. On Haslanger’s view, to be a woman is to occupy a lower position in society because of the way that her body is interpreted by others.
Her definition sparked controversy amongst transgender rights activists. Some people identify as women, but are not necessarily perceived by society as women. Haslanger’s definition of a woman excludes these people, – namely, trans women who have not yet transitioned.
Since the paper was published, Haslanger has taken on a lot of the criticism and worked to make her definition more inclusive. However, she still holds that gender and race refer to more than physical characteristics; they also refer to positions within society.
Advocacy and inclusivity
Haslanger feels strongly about promoting feminist causes outside of the field of philosophy. During the 2016 US presidential election, she wrote about some of the ways Hillary Clinton’s campaign was being undermined by sexism.
“As long as ‘being presidential’ and ‘looking presidential’ are about being and looking masculine, we will be unable to address what is ripping [the US] apart as a country.”
Within the field of philosophy, she is a strong advocate for inclusivity and making the field a more inviting space for women and people of colour. Now, as a philosophy professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Haslanger predominantly teaches courses in social and political philosophy, feminist philosophy, philosophy of race, and history of philosophy.
To boost participation from traditionally underrepresented groups in philosophy, Haslanger worked to create a summer program alongside a few other philosophers in 2014. Philosophy in an Inclusive Key Summer Institute (PIKSI) creates a space for underrepresented undergraduate students to work in more formal areas of philosophy (such as logic and metaphysics) or in areas that may be seen as less important and rigorous (such as the philosophy of gender and race).
Haslanger is also the founder of the Women in Philosophy Task Force (WPHTF), which is a group of women who work to coordinate initiatives and intensify the efforts to advance women in philosophy.
“Philosophers spend a lot of time worrying about the mind: what is it? How does the mind relate to the body? They can hardly get a handle on the mind, so the social is completely out of reach. I’m a little impatient. I’m not going to wait until the mind is figured out to figure out the social world.” – MIT Q&A
Sally Haslanger has had a considerable impact on inclusivity in philosophy. Her work has encouraged philosophers and activists to investigate and question what we thought we could take to be truths about race and gender. Her work today continues to facilitate important discussions on how society functions and what we might be able to do to make it more equitable.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
From capitalism to communism, explained
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Immanuel Kant
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Who are you? Why identity matters to ethics
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Akrasia
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
We're being too hard on hypocrites and it’s causing us to lose out

We’re being too hard on hypocrites and it’s causing us to lose out
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Dr Cressida Gaukroger 19 MAY 2022
Everyone hates a hypocrite. And apparently they are everywhere.
In the last week alone British Labour leader Keir Starmer has been accused of hypocrisy for having a beer and curry with colleagues in violation of lockdown rules; feminist social commentator and writer (and election candidate) Jane Caro has been labelled a hypocrite for advocating action on climate change, but also flying a lot; teal independents have been called hypocrites for their sources of funding after criticising Australia’s donation rules; the president of the Solomon Islands has accused Australia of hypocrisy for criticising their security pact with China while pursuing its own AUKUS agreement…
Hypocrisy is a sin regularly and loudly identified in politics and the media. And not without cause. However, this discourse regularly goes too far, to no good end.
We should be less critical of hypocrisy. Our obsession with hypocrisy prevents us from engaging in reasoned debate, it robs us of the tools to identify and express what others are doing wrong, and it risks leading us and others to becoming worse people.
What is the problem with hypocrites?
Though the term ‘hypocrite’ is often used as a catch-all term of moral condemnation, vaguely pointing to people whose actions appear to be inconsistent with their words, it is worth distinguishing between different types of hypocrites.
First there are insincere hypocrites – people who lie to gain advantage. Their actions, however, reveal that they genuinely do not hold the convictions they espouse. They are intentionally mis-leading and using others. Which is particularly egregious when they hold significant power over others as is in the case of politicians. But note that, here, the lying and manipulation are typically far more serious offences than the inconsistency and hypocrisy.
There are also exceptionalist hypocrites – those who make or police rules which they have no qualms about violating themselves. At the heart of it, this feels really unfair. However, it is not a universal wrong. Think of parents who make rules for their children that they do not follow – “you are not allowed to drink”, they say, while nursing a glass of wine; “it is always wrong to lie”, they say, while putting out mince pies for Father Christmas.
Such exceptionalist hypocrisy can sometimes reveal a greater wrong, or potential for wrong. For example, Boris Johnson made laws that kept large parts of his country in lockdown, but was breaking social distancing rules and attending parties. His actions demonstrated a lack of respect for others and, importantly, for those people whose interests he is meant to represent. The hypocrite hater could also point out that Johnson’s actions likely contributed to less adherence to the rules as people looked at his actions and felt “if he gets to do that, why shouldn’t I?”. However, modelling bad behaviour can encourage bad behaviour in others whether or not it is exhibited by a hypocrite. In this respect, the hypocrisy does not worsen the situation.
And then there is the weak-willed or inadvertent hypocrite. This person fails to live up to their espoused rules or ethical principles, not due to malice or deep insincerity, or because they think the rules don’t apply to them, but because it can be hard to be really good all the time. Think of the Christian who believes in the sanctity of marriage but finds themself desperate to leave a loveless marriage. The animal rights advocate who cares passionately about protecting native wildlife, but can’t bring themself to give up their beloved cat that steadfastly resists being kept indoors.
Inadvertent hypocrites may do better to reflect on their own experiences of struggle before harshly criticising others for not living up to their principles. But if they are unempathetic or overly aggressive in their attacks on others who violate their ethical rules, isn’t that the greater crime than not fully living up to those rules themselves? Wouldn’t that be problematic whether or not they lived according to those rules? And is it unempathetic of us to demonise the inadvertent hypocrite for an understandable weakness of will?
We shouldn’t just dismiss hypocrites
As soon as someone is called a hypocrite we feel licence to ignore them. But just because someone is bad, that doesn’t mean what they are saying is incorrect. Rather than shutting hypocrites down it is rational to ask if their hypocrisy is relevant to their argument.
Consider the smoker suffering from lung cancer who tells young people not to smoke because it can ruin their lives. Is their testimony any less reliable because they did not listen to their own advice? Or an environmental activist who flies to climate action conferences. Does this mean that they are any less right when they say we need to take action on climate change?
Our focus on hypocrisy can distract attention from the real issues or moral problems with a person (or institution) or their actions, such as: Are they lying to or manipulating people? Are they showing that they don’t respect the people they are meant to represent? Are they being aggressive or unsympathetic to others? Are they espousing something false or acting in a way that is morally wrong – whether or not their actions and words match up?
This should not dissuade people from rationally engaging in discussions with others about whether their moral principles are consistent. Highlighting ethical inconsistencies is the bread and butter of contemporary moral philosophy. If holding one principle should entail another but your friend holds the first while rejecting the second, talking through this can shed light on their values: help them realise the connection between the two. But throwing around the term ‘hypocrisy’ when you do it can turn a potentially neutral observation that they should reflect more on whether their ethical principles are consistent (shouldn’t we all?) to simply telling them that they are bad.
Being inconsistent is better than being consistently bad
A hypocrite says one thing and does another: so at least they are getting something right. Would we prefer someone who is all bad?
An obsession with hypocrisy can lead us to expect moral perfection in everyone. But inconsistency is part of moral life. There is nothing wrong with having high moral standards while recognising that we won’t always meet them.
Our desire for consistency can lead to unachievably high expectations that, when unmet, lead us to rejecting an entire principle or endeavour rather than living with our moral imperfections and trying to gradually improve our actions next time. Like the dieter who fasts for a week and then immediately gives up because of one slip with a slice of cake, or the long-time vegetarians or vegans who returned to eating meat after an extended stint in a country where vegetarian options were extremely limited. It is not surprising that they broke with their vegetarian principles while in those countries. It may well have been inconsistent with the view that all else being equal it is wrong to eat meat, but that makes it no less understandable an action to take. Rather, it is surprising that they continued to eat meat once they returned to a country where vegetarians were once again well catered for. Their actions changed first and their values followed. They ended up being more consistent perhaps, but (at least for those who believe that it is wrong to eat meat) things went the wrong way.
We are all hypocrites sometimes. The desperate desire to avoid hypocrisy can lead us to strive to be all good and, when that fails, to be all bad, rather than trying to be ‘good enough’ – being guided by moral principles we will likely never fully live up to.
My recommendation is to take it easy on hypocrisy. If you are in a debate, attack arguments not people. Where people are bad the wrongness of their actions or words should speak for themselves, and you should focus on pointing out the actual problem with them, rather than using a catch-all term. When it comes to yourself it may also help to start by aiming for the good, not the perfect. Improving incrementally is still improvement, even if it sometimes means you will be inconstant.
And if all of that doesn’t convince you, then you better hope that you have never exhibited inconsistency in your own principles and your actions. Because if you have, judging others for being hypocritical would be, well, very hypocritical of you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Living well or comfortably waiting to die?
Big thinker
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Judith Butler
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Australia’s fiscal debt will cost Gen Z’s future
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Blame
BY Dr Cressida Gaukroger
Dr Cressida Gaukroger is a former lecturer in Ethics at Oxford University now a Senior Policy Advisor focusing on wellbeing-led approaches to government.
Yellowjackets and the way we hunger

Yellowjackets and the way we hunger
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Joseph Earp 10 MAY 2022
Yellowjackets, with its widely acclaimed first season, has a more disturbing element than its surface of considerable violence and horror.
Sure, the Showtime series, which follows a group of young athletes as they crash-land following a disastrous plane trip in the middle of the wilderness and turn, with visceral, enjoyable brevity, to cannibalism and taboo-shattering behaviour, contains a lot in the way of gore. There are broken limbs; bodies eating up bodies; physically construed nightmares which the protagonists cannot escape.
But underneath that immediate level of violence is a claim, considerably more unsettling than fractured calcium, that our ethical systems are far from stable and robust. We’re not bent towards virtue. We seem to be shaped in the opposite way. Yellowjackets knows that. And more than that, the show loves it.
Corruption Seeps In, Naturally
Yellowjacket’s “heroes” – a word which only means to indicate those characters who are applied with a particular, and frequently intense, narrative scrutiny – are the stereotypes of “ordinary” people. The show, which flips back and forth between the present and the deep, traumatic past, makes a great deal of effort to depict that. There are extended shots of the central characters, moving their way through the world, not even thinking about the trauma they inflicted on others, deep in their pasts.
Indeed, the flashback structure of proceedings, one that allows the central mystery to unfurl slowly – who ate who, following that terrible plane crash? – mines much from the main characters’ attempts to live their lives freely in the aftermath of their great collectively-constructed horror.
In the show’s temporal present, these plane crash survivors are all people who wake up every day, and apply themselves to their jobs, and are loved and love in turn. You’d meet them, and catch their eyes in a shopping centre, and smile, astonishingly oblivious of their histories. It’s only when we get painful stabs of their past, unfolded in flashback, that we come to understand that there is something hiding here; a history streaked by vicious behaviour.
That “something” can’t be pinned down to the specifics of our heroes’ lives, either. We can’t shirk the implication that we’d fail to avoid the same behaviour – it is nothing less than the human capacity for violence. We are all confronted, more frequently than we would like to admit, with the idea that we have a potential for evil.
Remember that time you stood on the train platform, and considered, all of a sudden, pushing a stranger onto the tracks? Not for any reason – just because you could. Because, despite what we hope ethics might teach us, there’s something actively joyful about vicious behaviour.
Yellowjackets doesn’t make anything extraordinary out of its central characters. These are just human beings, ones who happen to have been freed – predictably, almost boringly – from the social code of morality, and plunged into horror. We all could be there. All that Yellowjackets tells us is that, most worrying of all, we would enjoy it.

So Why?
The philosopher David Hume constructed his ethical system out of twin poles: pleasure and pain. Hume believed that we all have a natural repulsion to pain, and an attraction to pleasure. That, for him, was the foundation of all ethical behaviour, the starting point that explains empathy, charity, and goodness.
Yellowjackets tells us that’s not true. The show’s spark of originality is not to prove that we all have a propensity for inflicting suffering. That’s already been explored through multiple works of art – consider, for example, the Netflix smash hit Squid Game, which should be considered the contemporary final word on what happens when you guide desperate people towards viciousness.
No. What makes Yellowjackets special is that its central characters have spent the rest of their lives following the plane crash pursuing the highs of gnawing on another human being. They’re not tortured – they’re hungry.
We Do What We Want – Thank God
If that sounds horrifically bleak, it’s because, despite its considerable vein of humour, Yellowjackets is horrifically bleak. We are inundated with art that aims to provide us with a moral compass, designating bad and good behaviour, and telling us how to navigate both. The thematic work, quite often, in these pieces of popular culture, is to condition us emotionally – to train us to be repulsed by horror, and drawn to goodness.
Yellowjackets does not do this. It makes the horrendous appear attractive: “look at these regular people, who ate one another, and defied the social norm, and found themselves in the process.” And it makes the virtuous seem weak: “look at those fools who let their sense of goodness stop them from doing what they want to do.”
If there’s any hope here, then, it’s our capacity to understand pleasure and pain in a more complicated way than Hume did, and that much contemporary art concerned with morality encourages us to do so. Rather than monoliths of feeling – this is pleasurable, and thus morally good; this is not pleasurable, and thus morally bad – Yellowjackets encourages us to mine the depth of our affect, and see it as being filled with nuance.
As Yellowjackets teaches us, we can’t hope that we will have an intrinsic and affective pull away from vicious behaviour, and a pull towards virtuous behaviour. What we can hope, instead, is that we understand our emotional states of pleasure and pain as containing more complexity than mere repulsion and attraction. We should become the experts in our own emotional states – not merely how they feel, but how they tell us to act.
After all, as plane crash victims who begin gnawing on each other’s bones tell us – not to mention addicts, or those who hurt the people they love – we can sink, pleasurably, into horror, and feel good about things that we don’t like, or no longer want to do.
We will never extinguish the joy of doing something we know we shouldn’t do. That’s the kid peeking at the Christmas presents before he should; of turning to our friend, maimed in a plane crash, and eyeing up their naked leg, considering our teeth in it. But what we can do is explore those feelings, and truly feel their complexity, and understand that no affect leads us more closely to one conclusion than any other. It’s up to us. That’s scary. But it’s also beautiful.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
The five biggest myths of ethical fashion
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Ad Hominem Fallacy
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Ethical concerns in sport: How to solve the crisis
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
It’s time to take citizenship seriously again
BY Joseph Earp
Joseph Earp is a poet, journalist and philosophy student. He is currently undertaking his PhD at the University of Sydney, studying the work of David Hume.
How to have a conversation about politics without losing friends

How to have a conversation about politics without losing friends
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Dr Tim Dean 21 APR 2022
There’s a reason our parents told us to steer clear of discussing politics (along with sex and religion) in polite company. Because as soon as politics is raised, there’s a very real chance that the company will become significantly less polite.
One reason political disagreements can be so divisive is that, unlike other contentious topics, like whether pineapple belongs on pizza, politics taps into our deeply held moral values and emotions: taxation policy isn’t just about the budget’s bottom line, it’s fundamentally about fairness; climate policy isn’t just about decarbonisation, it’s about the harm that our society is inflicting on future generations.
The moral dimension of politics can make us less tolerant of disagreement and more likely to see other views as not just different but mistaken, and perhaps dangerously so. It’s easier to shrug off someone’s opinion about the latest episode of The Bachelor than it is to let their views on asylum seekers pass without rebuttal.
The good news is that there are ways to have fruitful conversations about political differences if you approach them with care.
Before you start
Disagreements don’t have to be corrosive to our relationships or wellbeing. In fact, genuine disagreements give us an opportunity to learn, grow and share our perspectives with others. But they take time and effort to set up.
So before you utter a contrary opinion to a friend or family member about a political issue, first reflect on the strength of your own views and how open you are to new perspectives and evidence.
In today’s heated political environment there can be a great deal of pressure on us to form an opinion and take a side before we’ve had a chance to digest all the relevant information. There’s also a strong tribal element to politics that makes us more likely to adopt the views of ‘our side’ and oppose anything said by the ‘other side’. Many of us might even admit we hold opinions that we would struggle to justify if pressed.
Ideally, the strength of our convictions should be proportional to the strength of the reasons and evidence we can muster in their support. It’s still OK to form an opinion without doing a Masters degree on it first, but it does mean we should remain open to new information and perspectives that could change our mind. As a rule of thumb, if there are no reasons or evidence that could even hypothetically change your mind, then you’re being dogmatic and will likely receive no joy arguing about your views with others.
Before deciding to engage in a political disagreement, it’s also worth pausing to consider whether it’s worth arguing at all. It’s natural to feel compelled to correct a view you believe is harmful or wrong. But if it is likely that a disagreement could get heated or emotional, or it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to influence the other person at all, then getting into a debate might end up being entirely fruitless. All you might achieve is damaging the relationship, even if you’re in the right.
Sometimes relationships matter more than being right. If you’re arguing with someone close to you, someone you care for or depend on, it may not be worth eroding that relationship for the sake of a political argument, especially if it’s almost certain to go nowhere.
And if you do want to actually change someone’s mind, you need to establish a base of trust and respect first. Foregoing one heated conversation in order to strengthen a relationship means you can build enough trust and respect so that you can have a constructive disagreement sometime in the future. Once you’re sure they’re willing to listen to you, you might even have a shot at changing their mind.
Where to start
If you do decide to wade in, the very first thing to do is keep your mouth shut! At least at the start of the conversation.
When we hear someone say something we disagree with, our first impulse is often to express our own contrary opinion. The problem is that this immediately frames the conversation as a ‘war of ideas,’ which can trigger all the baggage this metaphor implies. We see our conversation partner as our ‘opponent,’ we become focused on ‘winning,’ on ‘undermining’ and ‘outflanking’ their position. And absurdly, if we do learn something and change our mind, that’s considered ‘losing’.
It’s better to frame the conversation in terms of fellow travellers exploring an issue together. You might have different perspectives, but you have the same ultimate goal: improving your understanding of the world.
In order to avoid slipping into the argument-as-war frame, instead of expressing your opinion up front, start by asking questions. Ask why your conversation partner believes what they do. Get them to elaborate on what they mean by various terms. Then listen carefully, paying special attention to both the content of what they say as well as their emotional state when saying it.
Once they’ve had a chance to express themselves uninterrupted, summarise their view back to them and validate how they feel. You can do this without necessarily validating the content of their beliefs, even if you disagree with them. You might say something like “I see you’re really concerned about the economic impact of climate policy”, which acknowledges how they feel but doesn’t commit you to agreeing or disagreeing with them.
This kind of reflective listening achieves two crucial things. First, it gives you a fighting chance of actually understanding their view in detail rather than assuming you know what it is. This is important because people often mean different things when they use terms like ‘freedom’ in a political context, which can lead to confusion and crossed wires unless you probe them on what they mean.
Secondly, reflective listening helps people feel heard, which signals respect and can lower the temperature of a conversation. In fact, a lot of defensiveness can simply be a result of people wanting to be heard and feeling like no-one is listening.
Common ground
If you want to progress the conversation, the next stage is to seek out common ground, especially around values or goals that you both agree upon. For example, you might both care about taxes not being wasted, or you both care about the wellbeing of the next generation. At this point you can start to frame your difference in perspective as being different strategies to achieve common goals. This can take a lot of the edge out of arguments, making them feel less like you’re fundamentally at odds and show that you’re only disagreeing about the means to achieving shared ends.
Crucially, if you ever feel the conversation getting heated to the point where it’s difficult for either of you to engage constructively, then it can be wise to back out and change the subject before it’s too late. You can always revisit the topic once things have cooled down.
It’s also important to not let the conversation drag out. It’s unlikely that you’ll be able to fully grasp someone’s views or change their mind in a single conversation. But even a short conversation can help you better understand their views and allow you to offer up a different perspective. And if it’s done with patience and respect, it can open the door to future constructive conversations. After a few such chats, you might even find you change their mind – or find that your own view has changed. That’s not a bad thing.
The highly charged moral dimension to politics is why conversations about it are so fraught. But if we engage thoughtfully and respectfully we can have a rich conversation about politics, and still have a fighting chance of making it to dessert with friendships and family relationships intact.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
But how do you know? Hijack and the ethics of risk
Big thinker
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Judith Butler
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
Corporate whistleblowing: Balancing moral courage with moral responsibility
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Immanuel Kant
BY Dr Tim Dean
Dr Tim Dean is Philosopher in Residence at The Ethics Centre and author of How We Became Human: And Why We Need to Change.
Big Thinker: Tyson Yunkaporta

Tyson Yunkaporta is a researcher, arts critic, poet, and traditional wood carver. He works as a senior lecturer in Indigenous Knowledges and is the founder of the Indigenous Knowledge Systems Lab at Deakin University.
A scholar of free-ranging ideas
Yunkaporta is not your typical academic. In a recent interview, he said:
“I try to avoid naming anything. And I try to avoid making too much sense, and I try to say things a bit differently every time and to mix it up. And I’ll make points that you can’t put together. I do that quite deliberately because I don’t want the things I’m thinking or working on to become an ideology or a brand, or something that people can use as a name… you’ve got to avoid that packaging and repackaging of ideas and let these things be free-range.”
Yunkaporta tries to keep his writing and discussions “free-range” because he doesn’t want to give complex ideas or concepts an “artificial simplicity.”
According to Yunkaporta, when we simplify complex ideas, they can become easily distorted or manipulated and the original intention behind them can become lost. But more problematically, when we simplify complex ideas, we fail to see how they connect to the larger patterns of creation at work.
“There is a pattern to the universe and everything in it.”
Nothing is really created or destroyed, it merely moves and changes. When we start to pay attention to the way that things move and change, and take note of the patterns that they make, we gain a better understanding of the world around us.
This is important, Yunkaporta states, because “future survival of all life on this planet will be dependent on humans being able to perceive and be the custodians of the patterns of creation again.”
Indigenous thinking can save the world
Yunkaporta’s recent book Sand Talk: How Indigenous Thinking Can Save the World, is all about identifying and learning from the patterns of creation.
Sand Talk has sometimes been described as an exercise in “reverse-anthropology”, because rather than looking at Indigenous knowledge systems and practices from a Western perspective, Yunkaporta examines Western knowledge systems and practices from an Indigenous perspective.
He is careful about what knowledge he shares in the process, explaining that symbolic knowledge is often restricted (for example, by age or birth order) or is only appropriate for a specific places or groups (for example, members of particular clans).
However, he shares enough to help his readers start to recognise patterns in the world around them and to “come into Aboriginal ways of thinking and knowing, as a framework for the understandings needed in the co-creation of sustainable systems.”
Although Yunkaporta believes that sustainable systems cannot be manufactured by individuals (this is something that we must undertake collectively), he does think that each of us plays an important role as an agent of sustainability.
Agents of sustainability have four main protocols or guidelines, according to Yunkaporta: diversify, connect, interact, and adapt.
These guidelines tell us that we should diversify our interactions, so that we engage with people and systems that are dissimilar to ourselves and what we’re used to.
We should also aim to expand the networks of people that we currently engage with, so that we connect with as many new people and engage with as many new systems as we can.
Through these connections, we should also share knowledge, energy, and resources. But most importantly, we should allow ourselves to be transformed by the knowledge, energy and resources that are shared with us.
Ironically, Yunkaporta believes that frameworks are nothing more than “window dressing.” Yet, as he himself highlights, the four main protocols for sustainability agents are a kind of framework for sustainability.
This contradiction is, however, just part of Yunkaporta’s style. He describes his work as a “free-range ramble that should never be taken at face value.”
He writes to provoke thought and reflection in his audience, not to give them all the answers. After all, he muses, “perhaps the worst possible outcome of this work would be civilisation embracing these ideas.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Eleanor Roosevelt
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
To deal with this crisis, we need to talk about ethics, not economics
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Male suicide is a global health issue in need of understanding
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
What ethics should athletes live by?
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Agree to disagree: 7 lessons on the ethics of disagreement

Agree to disagree: 7 lessons on the ethics of disagreement
Opinion + AnalysisRelationships
BY Dr Luara Ferracioli Dr Sam Shpall 12 APR 2022
Senior Lecturers in Philosophy at the University of Sydney, Dr Luara Ferracioli and Dr Sam Shpall, participated in a live Ethics Centre conversation last year, discussing: how do we respectfully disagree? Ferracioli and Shpall concluded the following seven lessons, and how there can be value in disagreeing.
It often feels like we’ve lost a sense of principled disagreement – the idea that it’s OK if reasonable people think differently about something that matters.
In part, this is because we’ve changed the boundaries on what it’s OK to disagree about. Today, disagreement and debate about sensitive issues is seen by some as harmful or violent.
This can be interpreted as both attempts to de-platform bigoted ideologies, and also as those upholding the status quo having their power threatened and hiding behind a veil of civil society. It’s why subjects like Black Lives Matter and Critical Race Theory attract so much opprobrium – they speak directly to and challenge power, particularly latent and overt power dynamics.
We can all be guilty of treating disagreement as something that must have a winner and a loser. Whilst in other times disagreement has been used as a tool for everyone to learn; today, we disagree without any readiness to be persuaded.
When should we respectfully disagree? Should we always be open to having our mind changed? Can we remain friends with someone who we disagree with about things that really matter?
1. Genuine disagreement is not a bad thing.
There is value in good disagreement. Arguing well helps to flesh out all sides of an issue, bring to light underrepresented perspectives and contribute to solutions that benefit the most people; as in a true, functioning democracy and political system.
People occasionally conflate disagreement over an idea with a personal attack. This is a mistake, because disagreeing over issues and rationally debating the outcome – whether it’s who will do the dishes or how to allocate the national budget – is the best way to ensure a measured outcome that is in the best interests of the greatest majority. The more diversity of opinion there is in the discussion, the better the chance that the outcome will be balanced and representative of the greatest range of points of view.
The trouble lies in ensuring that the debate is measured, rational and charitable, and does not resort to humiliation and point scoring, as it often does in politics and personal disagreements. It’s important, also, to consider whether some disagreements of opinion are so fundamental that they license strong non-engagement moves like cancellation, de-platforming, and defriending; for example, boycotting a festival because of the presence on the bill of an act or speaker with whose ideas you disagree, or demanding their invitation to speak be withdrawn, such as in the recent case of Sydney Festival.
2. Genuine disagreement is often positively necessary for intellectual and emotional development.
Hopefully it’s already clear that cancelling and de-platforming people’s voices is not the way to stimulate a healthy culture of disagreement. Imagine I disagree with my partner about the wisdom of buying an apartment. One of us could simply acquiesce to make things more comfortable. This seems dangerous and unproductive. It makes it more likely that we will make the wrong decision, and it makes it more likely that at least one of us will feel ignored, disrespected and resentful. Notice how familiar the gendered dynamic is here in heterosexual romantic relationships: the controlling, all too often abusive man makes the decisions and expects or enforces compliance.
To make the right decision we both need to express our needs, wants and arguments clearly, and treat each other’s opinions with respect, working our way through the pros and cons to eventually reach a compromise based on mutual respect, not on one person overpowering the other.
In the case of the marriage equality debate in Australia, it came down to a national referendum, where the majority voted in favour of same sex marriage, proving pointless all the misleading ad campaigns and snarky media baiting of politicians and pundits.
3. Sometimes what people call “disagreement” is not disagreement at all.
Rather than disagreeing over philosophical ideas, sometimes people resort to the tactics of personal attack and outright hostility. If your aim is to humiliate a political opponent or win an election, you might well find that genuine disagreement and a contest of ideas is a less effective strategy than belittling them and misrepresenting their policies. (This goes partway to explaining political apathy, because it appears that many politicians are more interested in humiliating their opponent and scoring a point than having a real battle of ideas.)
Similarly, if your aim is to “win” a fight with your partner (and make yourself feel good, humiliate them, and put them in their place), you might find that genuine disagreement is a less effective strategy than personal attack. How often in a personal disagreement have you found yourself wanting to bring up a time in the past when the person has wronged you, that has no bearing on the current situation?
These analogies run quite deep, involving posturing, self-absorption, strong rhetoric, a lack of charity, no engagement with the “opponent’s” perspective, and so on. It’s not a true “disagreement” and contest of ideas, though, but a personal attack motivated by ego.
4. Sometimes what people call “offensive” and “hostile” is in fact disagreement.
In any interlocution, the first interaction always sets the tone: if it starts off hostile, that hostility will only escalate. You need to ask yourself: are you attempting a good faith engagement, or are you being defensive and stereotyping and categorising your opponent’s argument points?
Take, for example, the disagreement in the media and social media between podcaster Joe Rogan and musician Neil Young. Young removed his music from streaming service Spotify to protest its hosting of Rogan’s podcast, accusing The Joe Rogan Experience of spreading misleading information about Covid-19 vaccines.
Young followed up with a plea for Spotify employees to leave the company before it “eats up [their] souls”. Other prominent social media users then posted clips of Rogan using racial slurs. Rogan apologised for the slurs and said he will try, “in the future, to balance things out” with information on Covid. Spotify CEO Daniel Ek wrote, “based on the feedback over the last several weeks, it’s become clear to me that we have an obligation to do more to provide balance.”
5. Contemporary technologies (text messaging, emailing, social media) can make it harder to disagree well.
Communicating through the brevity of screens does not do much to help the art of good disagreement. With social media we’re getting less charitable with our opponents’ points of view and not always assuming the best version of their views. The way social media enables discussion is counter-productive – it’s so short, often anonymous, and you’re not looking at each other so you can’t see that your opponent is generally trying to have a good faith discussion.
Sarcasm and irony do not translate over text – consider how many times you’ve been misunderstood over email or text message. Abbreviating our vocabulary down into the bite size shapes of an emoji also engenders a poverty of language and ideas that benefits nobody. Consider Godwin’s law, that the longer an online discussion grows, the more the probability of a reference to the Nazis or Adolf Hitler reduces to zero.
6. Philosophical-collegial disagreement is a useful model for productive transformations of disagreement, from the personal to the political.
The philosophical model of disagreement has some valuable tools that should be exported for use in everything from intimate relationships, work environments and political culture to anonymous social interaction. One of the hallmarks of bad disagreement is a lack of charity – presenting your interlocutor in an unflattering light.
One of the things philosophers try to do at a university level is to reconstruct the best, most plausible, compelling version of the argument that one’s opponent is presenting. The principle of charity is related to a lot of other principles of agreeing well, such as the principle of intellectual humility, understanding that even one’s most cherished beliefs could be improved or better justified.
You want to win not because you put your opponent down but because you’ve made the best argument and your opponent can see why it should go your way.
7. Some disagreements are not worth having
The phrase ‘agree to disagree’ is a funny one that’s worth thinking about – it’s usually employed in the same way as phrases such as ‘it’s all subjective anyway’ or ‘everyone has their opinion’, not as a real move in a conversation but more as an ending to the conversation. Sometimes we need to end a conversation because it’s not getting anywhere, but sometimes we employ phrases like that to paper over the fact that we don’t have anything more to add to our argument.
But what about when one party to a disagreement rejects the foundational presuppositions of liberalism? For example, if someone thinks that men and women are fundamentally different and women deserve to be paid less than men, it might be very difficult to have a reasonable conversation with them when your foundational viewpoints are so radically different.
We have laws that prohibit certain forms of hate speech, of course, but these are hard to enforce and do not really help to answer many of the practical questions about how to interact with people who have these views.
We can’t give an overall theory about what to do in such cases, but we want to suggest that we steer clear of two dangers:
- failing to confront the genuinely inegalitarian, illiberal views; pretending that such views deserve the same sorts of consideration as liberal ones;
- and overstretching this response to illiberal exceptions.
Maybe you disagree with us about some of the things we’ve written, but hopefully you agree that there is value in disagreeing well.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology
If humans bully robots there will be dire consequences
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Social philosophy
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Inside The Mind Of FODI Festival Director Danielle Harvey
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Anti-natalism: The case for not existing
BY Dr Luara Ferracioli
Luara Ferracioli is Associate Professor in Political Philosophy at the University of Sydney and ARC DECRA fellow. She was awarded her PhD from the Australian National University in 2013, and has held appointments at the University of Oxford, Princeton University, and the University of Amsterdam. Her first book Liberal Self-Determination in a World of Migration was published in 2022 with Oxford University Press, and her new book Parenting and the Goods of Childhood is forthcoming (with Oxford University Press).
BY Dr Sam Shpall
Dr Sam Shpall is Senior Lecturer in the Department of Philosophy at The University of Sydney. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Southern California in 2011, and was a Postdoctoral Fellow there from 2011-2013. From 2013-2015 he was the Postdoctoral Associate in Law and Philosophy at Yale University, and a Lecturer at the Yale Law School. He also taught philosophy in four New York State Correctional Facilities from 2014-2015 as a faculty member of the Bard Prison Initiative. He works mostly in ethics, moral psychology, and the philosophy of art.
Ethics Explainer: Teleology

Often, when we try to understand something, we ask questions like “What is it for?”. Knowing something’s purpose or end-goal is commonly seen as integral to comprehending or constructing it. This is the practice or viewpoint of teleology.
Teleology comes from two Greek words: telos, meaning “end, purpose or goal”, and logos, meaning “explanation or reason”.
From this, we get teleology: an explanation of something that refers to its end, purpose or goal.
For example, take a kitchen knife. We might ask why a knife takes the form and features that it does. If we referred to the past – to the process of its making, for example – that would be a causal (etiological) explanation. But a teleological explanation would be something that refers to its end, like: “Its purpose is to cut”. Someone might then ask: “But what makes a good knife?”, and the answer would be: “A good knife is a knife that cuts well.” It’s this guiding principle – knowing and focusing on the purpose – that allows knife-makers to make confident decisions in the smithing process and know that their knife is good, even if it’s never used.
What once was an acorn…
In Western philosophy, teleology originated in the writings and ideas of Plato and then Aristotle. For the Ancient Greeks, telos was a bit more grounded in the inherent nature of things compared to the man-made example of a knife.
For example, a seed’s telos is to grow into an adult plant. An acorn’s telos is to grow into an oak tree. A chair’s telos is to be sat on. For Aristotle, a telos didn’t necessarily need to involve any deliberation, intention or intelligence.
However, this is where teleological explanations have caused issue.
Teleological explanations are sometimes used in evolutionary biology as a kind of shorthand, much to the dismay of many scientists. This is because the teleological phrasing of biological traits can falsely present the facts as supporting some kind of intelligent design.
For example, take the long neck of giraffes. A shorthand teleological explanation of this trait might be that “evolution gave giraffes long necks for the purpose of reaching less competitive food sources”. However, this explanation wrongly implies some kind of forward-looking purpose for evolved traits, or that there is some kind of intention baked into evolution.
Instead, evolutionary biology suggests that giraffes with short necks were less likely to survive, leaving the longer-necked giraffes to breed and pass on their long-neck genes, eventually increasing the average length of their necks.
Notice how the accurate explanation doesn’t refer to any purpose or goal. This kind of description is needed when talking about things like nature or people (at least, if you don’t believe in gods), though teleological explanations can still be useful elsewhere.
Ethics and decision-making
Teleology is more helpful and impactful in ethics, or decision-making in general.
Aristotle was a big proponent of human teleology, seen in the concept of eudaimonia (flourishing). He believed that human flourishing was the goal or purpose of each person, and that we could all strive towards this “life well-lived” by living in moderation, according to various virtues.
Teleology is also often compared or confused with consequentialism, but they are not the same. If you were to take a business that specialises in home security, for example, a consequentialist would tell you to look at the consequences of your service to see if it is effective and good. Sometimes, though, it will be hard to tell if the outcome (e.g., fewer break-ins or attempted break-ins) can be attributed to your business and not other factors, like changes in laws, policing, homelessness, etc., or you might not yet have any outcomes to analyse.
Instead, teleological approaches to business decision-making would have you focus on the purpose of your service i.e., to prevent home intrusion and ensure security. With that in mind, you could construct your services to meet these goals in a variety of ways, keeping this purpose in mind when making hiring decisions, planning redundancies, etc., and be confident that your service would fulfil its purpose well (even if it is never needed!).
But how do we decide what a good purpose is?
Simply using a teleological lens doesn’t make us ethical. If we’re trying to be ethical, we want to make sure that our purpose itself is good. One option to do this is to find a purpose that is intrinsically good – things like justice, security, health and happiness, rather than things that are a means to an end, like profit or personal gain.
This viewpoint needn’t only apply to business. In trying to be better, more ethical people, we can employ these same teleological views and principles to inform our own decisions and actions. Rather than thinking about the consequences of our actions, we can instead think about what purpose we’re trying to achieve, and then form our decisions based on whether they align with that purpose.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Anzac Day: militarism and masculinity don’t mix well in modern Australia
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: René Descartes
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Meet Dr Tim Dean, our new Senior Philosopher
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
What we owe to our pets
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Periods and vaccines: Teaching women to listen to their bodies

Periods and vaccines: Teaching women to listen to their bodies
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationshipsScience + Technology
BY Lucy Peach 1 APR 2022
Most people probably know more about the cycle on a washing machine than the one that got us all here. I’m talking about the menstrual cycle (again).
It’s true that we’ve made major gains in shedding some of the menstrual stigma in recent years but there is still a lack of awareness and interest in the cyclical lives of 26% of all people on Earth. There are real consequences to this.
For a start, menstrual education is still reduced to two things: the management of a period and how to control our capacity to reproduce. No one explained that the hormones of the menstrual cycle weren’t just for making babies and that my cycle hormones shape who and how I am. I didn’t know, that far from being an unpredictable rollercoaster (that I would internalise as constant feelings of being too much or not enough), that there was a pattern to the emotional landscape of my month, that there were predictable phases to the cycle that could be harnessed. That it was ok to feel differently from week to week.
At a tender age, I learnt that my body was a problem to be fixed, with pads, tampons and soon enough with the pill. I believed I was safest while my cycle was disarmed. Until I was ready for a baby, what was the point in having one at all or so I thought? The truth is, without ovulation, we have no hormones and therefore no cycle at all. I wonder, would I have been so eager to reject ovulation in favor of the pill during my teens and twenties had I known of this?
I didn’t know that there were short and long-term protective health benefits to ovulation that taking the pill would eliminate. I didn’t know it was common to feel depressed and flat while taking it. I felt crazy. Instead of cultivating care and curiosity for my young body and what it could do, I leant not to trust it.
This disregard for menstrual cycles extended to the scientific community such that until the 90’s, clinical trials for new drugs weren’t required to include women at all.
Because menstrual cycles were seen as too complicated, men were considered the biological norm.
It seems that even amid a growing movement of awareness and appreciation for menstrual cycles, this default male setting still persists.
When thousands and thousands of women and menstruators reported changes to their cycle after taking the Covid vaccine, their concerns were initially dismissed by the medical fraternity. Women were waved away and stress was cited as the probable culprit for the mostly temporary changes.
It is true that stress can wreak havoc on a cycle — and who hasn’t felt stressed in new ways since the arrival of the pandemic? But the real kicker, was that there was no proof to speak of; important early clinical trials investigating the side effects of the Covid vaccine failed to consider the impacts on women’s menstrual cycles. This glaring omission at such a critical juncture is menstrual stigma still in action. That women were dismissed before being asked about their experiences after the vaccine is an indictment into how far we haven’t come.
Women were dismissed before being asked about their experiences after the vaccine is an indictment into how far we haven’t come.
In the absence of due diligence, people worried and concerns for post vaccination fertility also proliferated, risking confidence in the vaccine unnecessarily.
Vaccines work by creating an immune response which can cause the body stress. It stands to reason that there might be side effects to our cycles when our immune system is triggered. The latest research was funded by the NIH and published in Obstetrics and Gynecology. It was confirmed that while changes were (on average) minor and temporary, it was true: there was an impact. After looking at three cycles before and after vaccination, on average, the impact on cycle length following vaccination was just under a day.
For people who had both shots within one cycle, the average cycle length extension was 2 days and of these people, there were 10% who experienced cycle delays of 8 days or more. All of these changes were reported to have been resolved within two subsequent cycles and there was no effect found on the length of the bleed itself. Obviously within all of the experiences that create averages, the range for individuals could be considerable but with variations of up to 8 days considered to be within the realm of a normal cycle, these results are generally reassuring. Furthermore, in another study with more than 2000 couples there was no difference found in fertility when comparing unvaccinated and vaccinated couples. Conversely, a Covid infection was associated with a temporary decline in male fertility. So far so good.
Research like this is a positive step after a bungled start and authors of the menstrual study have called for more investigation into how the Covid-19 vaccination could affect other aspects of menstruation such as pain and changes to the bleeding itself. Going forward, bigger sample sizes that also include menstruators with more varied experiences are important.
With access to information and the stains of stigma beginning to fade, women and menstruators are learning to listen to their bodies and to speak up about their experiences. To be wary of doctors who prescribe the pill to fix a period when it merely masks underlying issues. To demand better than the average wait time of eight years to receive an endometriosis diagnosis and subsequent treatments. Weary of being disregarded when it comes to our health, we are finally beginning to trust ourselves. As Lisa Hendrickson-Jack explains in ‘The Fifth Vital Sign’, the menstrual cycle gives us important insights and is a critical marker of our overall health, just like heart rate or body temperature. Understanding your menstrual cycle is basic body literacy that is crucial to wellness.
The changes to menstrual cycles may be no more significant than a sore arm, but that doesn’t mean we don’t deserve to know about them. Small changes can still be significant to people hoping to plan or avoid a pregnancy, for instance. We need vaccines to combat Covid but we also need to be informed.
If there are any silver linings to be had during Covid it’s that we know that the old ‘normal’ wasn’t working for many of us.
Women’s health has long been overlooked, under-researched and under reported and now perhaps the new normal is to consider women’s health from the outset.
Hopefully it will be for the future we are carrying.
Normalise asking people about their cycles whether you are a researcher, a doctor, a partner or even a friend. Normalise noticing your own cycle and how you feel throughout the month. Normalise expecting better.
Lucy Peach, day 28 and vaccinated.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Society + Culture
You won’t be able to tell whether Depp or Heard are lying by watching their faces
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Freedom and disagreement: How we move forward
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Why we should be teaching our kids to protest
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Is it ok to visit someone in need during COVID-19?
BY Lucy Peach
Lucy Peach is a long-time champion of the power of the menstrual cycle and an advocate for self-love and positive body literacy. She’s educated and empowered thousands with her theatre performances, workshops, and book, using science stories and songs to shift the period narrative in our culture from one of shame to one of pride. Lucy has spent the past two decades studying human biology, woman’s health & wellbeing, and Menstruality Leadership. She has a Bachelor of Science in human biology and biomedicine with honours in medicine, and a graduate diploma of education in human biology.
The Dark Side of Honour

The Dark Side of Honour
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Dr Tim Dean 30 MAR 2022
If someone insulted a family member, would you rush to defend their honour? If you said “yes”, then you’re not alone. In fact, American actor Will Smith did just this when he confronted comedian Chris Rock on stage at the 94th Academy Awards in March 2022.
It happened after Rock directed a joke at Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett-Smith, that appeared to make light of her alopecia, a medical condition that causes hair loss. Smith mounted the stage, strode up to Rock and slapped him across the face, before returning to his seat shouting “Keep my wife’s name out of your fucking mouth!”
Many onlookers in the room and around the world were shocked at this outburst of violence, even if they thought the joke was offensive and hurtful to Pinkett-Smith. But others interpreted things differently. They saw a chivalrous husband doing what a good husband should do.
One such defence of Smith came from American comedian and actress, Tiffany Haddish. “As a woman, who has been unprotected, for someone to say, ‘Keep my wife’s name out your mouth, leave my wife alone,’ that’s what your husband is supposed to do, right? Protect you”, she told the media during the awards.
“That meant the world to me. And maybe the world might not like how it went down, but for me, it was the most beautiful thing I’ve ever seen because it made me believe that there are still men out there that love and care about their women, their wives.”
Haddish is speaking about the importance of an old moral concept: honour. It’s one that has been a core feature of many cultures around the world and throughout history, and even where its influence has waned, it still exerts some pull on our hearts, as we can see in the case of Will Smith.
But honour also has a dark side, not least contributing to violence as well as the oppression of women. The question is whether honour ought to play a role in our ethical thinking today, or whether it should be replaced by a more liberal ethic that prioritises reducing harm and injustice.
Reputation is life
At its heart, honour is about protecting one’s reputation as a virtuous and trustworthy individual. Anything that threatens that reputation, whether scurrilous gossip or a verbal insult, can – or even must – be forcefully challenged, violently if necessary.
Honour is particularly prevalent in smaller-scale societies that lack trustworthy institutions that prevent people from lying or cheating others, like law courts or government regulation of business. In smaller societies, it’s often left to individuals to figure out who can be trusted and who should be avoided.
This is where reputation plays a key role. If you have a good reputation, others will be happy to cooperate with you. If you’re found to be an untrustworthy cheat, word will get around that you should be avoided. In a society where cooperation might be essential to your survival, a bad reputation could be tantamount to a death sentence.
This is one reason why insults trigger such an acute response to people who value honour. An insult does two things: first it besmirches the target’s good name, often accusing them of some deviant or dishonourable act; and second it paints them as being weak, which is seen as a kind of moral vice in itself, especially in honour cultures that have norms that equate masculinity with strength.
As the psychologists Richard Nisbett and Dov Cohen describe in their famous study of the honour culture in the Southern United States:
“A key aspect of the culture of honor is the importance placed on the insult and the necessity to respond to it. An insult implies that the target is weak enough to be bullied. Since a reputation for strength is of the essence in the culture of honor, the individual who insults someone must be forced to retract; if the instigator refuses, he must be punished – with violence or even death.”
Even when honour culture has waned in popularity, as it has in the Southern United States, it can continue to influence the way people behave. Nisbett and Cohen describe one experiment that showed that when university students from Southern states were insulted, they were more likely to show signs of elevated hormones related to stress and aggression than students from the Northeastern states.
The price of honour
If an insult is to be met with force rather than shrugged off, then it can easily descend into conflict even over trivial statements. It can also easily lead to violence. Nisbett and Cohen cite evidence that the homicide rate in the Southern United States is significantly higher than other regions.
But there’s another price of honour: the oppression of women. Honour cultures are usually also patriarchal, with men occupying most of the positions of power. In these societies, men often seek to control women, especially their sexuality.
One motivation is to help ensure the paternity of their children, which is difficult without modern medical technology. One way to do so is to only marry a woman who is virgin and then to control her sexuality to guarantee sexual exclusivity. This is one reason why many honour cultures are obsessed with sexual fidelity, primarily of women, and why promiscuous women can be subject to “honour killings” by their own families.
This connects with another motivation for men to control women’s sexuality: alliances. Marriage has been used as a strategic tool for millennia to create bonds between families, usually to serve the interests of the heads of those families, who were predominantly men.
Again, virginity and sexual fidelity make marriable women more attractive as mates for other men, which feeds into an honour culture that seeks to protect the reputation of women as being faithful and chaste. These same cultures often encourage men to violently respond to any perceived slight against their female family members, or to ostracise or enact violence towards women who choose to deviate from the sexually oppressive norms constraining them.
The decline of honour
None of this is to suggest that Will Smith was seeking to control women as a sexual or political resource. But the same sensitivity to honour that motivated him to stand in his wife’s defence can be used to control and disempower women. Indeed, some interpreted Smith’s slap as robbing Pinkett-Smith of her own voice when it came to defending herself.
While honour can be a vehicle to encourage people to take responsibility for their actions, to promote virtues like honesty and loyalty, it can also place a higher priority on protecting one’s reputation – and that of their family (and often the women in their family) – over de-escalating violence and solving injustices through other means.
Honour is also largely redundant in a world with institutions that protect us from miscreants. We no longer live or die by our reputation. This is why we teach children the “sticks and stones” rhyme. Yet it is all too easy in the heat of the moment to let a sensitivity to our reputation carry us away, compromising the values of care and justice that have become dominant in liberal societies.
It is precisely these values that are reflected in Will Smith’s public apology, posted the day after the Academy Awards when some of the heat had died down. “Violence in all of its forms is poisonous and destructive,” he wrote in an Instagram post. “There is no place for violence in a world of love and kindness.”
The question for each of us to answer next time someone insults us or a loved one is what do we value more: a society of reactive violence or a society where we prioritise compassion and justice through more considered responses?
Image: Ana Gremard / Flickr
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Kate Manne
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
Corporate whistleblowing: Balancing moral courage with moral responsibility
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Relationships
Care is a relationship: Exploring climate distress and what it means for place, self and community
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology