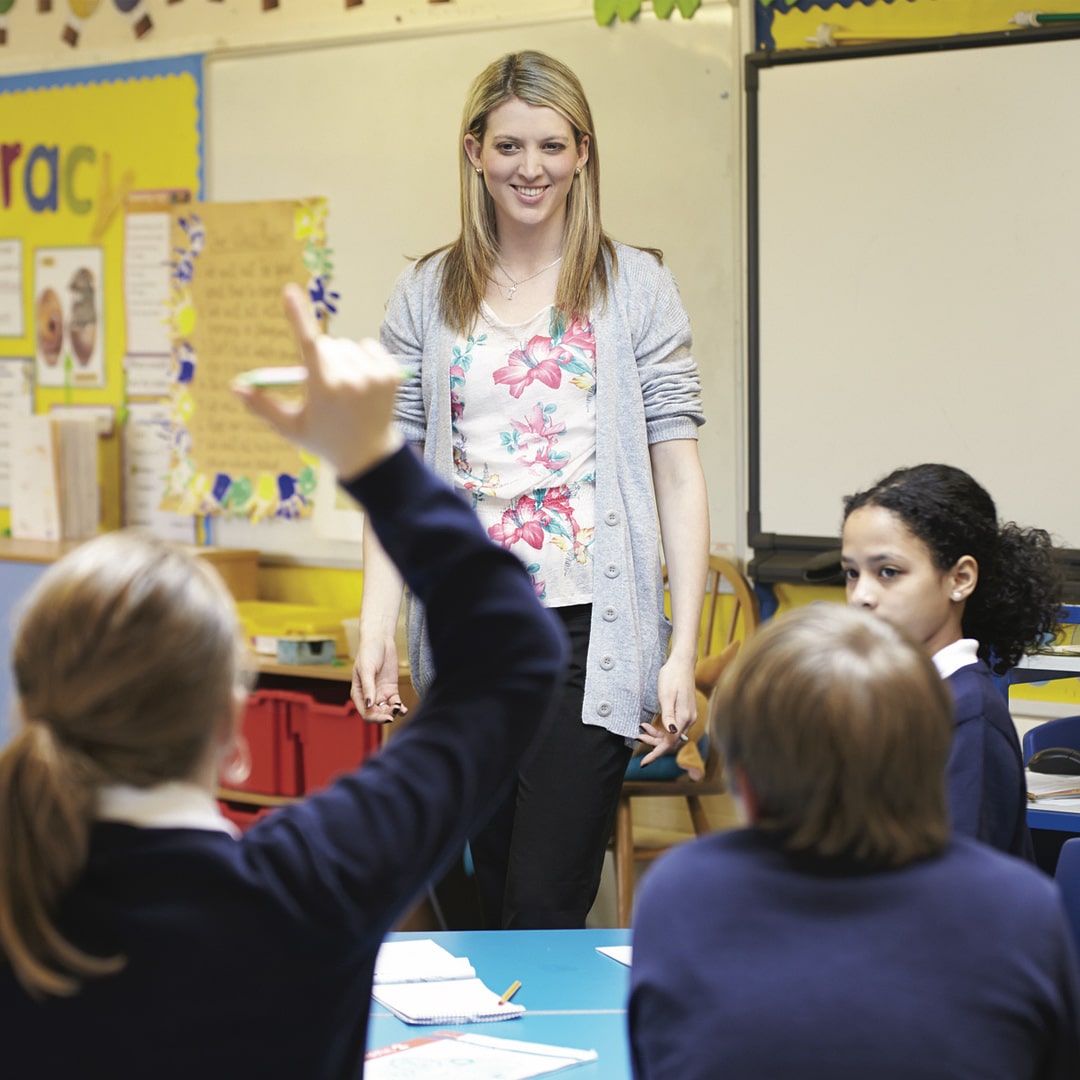
Ask an ethicist: do teachers have the right to object to returning to school?

Ask an ethicist: do teachers have the right to object to returning to school?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 4 MAY 2020
In recent weeks, there has been a particularly intense debate about whether or not students should return to the classroom.
This article was first published by Crikey, in their weekly Ask the Ethicist column featuring Dr Simon Longstaff.
Much of that debate has focused on the interests of the children and their families. However, there is a third stakeholder group – the nation’s teachers – who need to be considered. Part ‘essential worker’, part ‘political football’, they have been celebrated on one hand and condemned on the other. So, what are the ethical obligations of those who teach our children during COVID-19.
As a starting point, let’s agree that education is a significant ‘good’ and that children should not be deprived of its benefits unless there are compelling reasons for doing so. Compelling reasons would include the potential risk of infection due to school attendance.
At present, the balance of evidence is that the risk of children becoming infected is low and that they are unlikely to be transmitters of the disease to adults – especially in well-controlled environments. However, why take any risk – if viable alternatives are available?
Here, we should note that the education of children has not been suspended during the crisis. Instead, it has continued by other – ‘online’ – means. This has required a massive effort by the teaching profession to ‘recalibrate’ the learning environment to support distance learning.
We should also note that the ability to provide distance education distinguishes teachers from other essential workers who, of necessity, must provide a face-to-face service. For example, while some doctors can consult with patients using ‘telemedicine’, most health care workers need to be physically present (e.g. when administering a flu injection, or caring for a bed-ridden patient, etc.).
So, if distance learning achieves the same educational outcomes as classroom teaching, teachers would not seem to be under any moral obligation to return to the classroom. However, the Federal Government has recently cited reports suggesting that online learning produces ‘sub-optimal’ outcomes for students (unwelcome news for children living in remote communities and educated by the ‘school of the air’).
If this is true, then it would suggest two things. First that the government should be massively increasing its investment in education for children who have no option but to engage in distance education. Second, that teachers should be heading back into the classroom.
However, what of the teacher who lives with people for whom COVID-19 is a particular threat … the aged and infirm? In those cases, the choice is not just a matter of balancing a public duty as an educator against a preference for personal safety. Rather, the teacher is caught in an ethical dilemma of competing duties.
In such a case, I think it would be reasonable for a teacher to claim they have a conscientious objection to returning to the classroom – grounded in a refusal to be the potential cause of harm to a loved one – especially when the only certain protection for the loved one is that the teacher remain isolated.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Kate Manne
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Easter and the humility revolution
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Big Thinker: Audre Lorde
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Stopping domestic violence means rethinking masculinity
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
How to put a price on a life - explaining Quality-Adjusted Life Years (QALY)

How to put a price on a life – explaining Quality-Adjusted Life Years (QALY)
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationshipsScience + Technology
BY Matthew Beard The Ethics Centre 1 MAY 2020
In all the time I’ve spent teaching ethics – from trolley problems to discussions of civilian casualties at war to the ethics of firefighting – there have been a few consistent trends in what matters to people.
One of the most common is that in life-and-death situations, details matter. People want to know exactly who might die or be rescued: how old are they? Are they healthy? Do they have children? What have they done with their life?
What they’re doing, whether they know it or not, is exploring what factors could help decide which life it would be most reasonable, or most ethical to save, relative to the other lives on the table.
Moreover, it’s not only in times of war or random thought experiments that these questions arise. Every decision about where to allocate health resources is likely to have life-or-death consequences. Allocate more funding to women’s shelters to address domestic violence and you’ll save lives. However, how many lives would you save if that same money were used to fund more hospital beds, or was invested into mental health support in rural communities?
One widely-used method for ensuring health resources are allocated as efficiently as possible is to use QALY’s – quality-adjusted life years. QALY is an approach that was developed in the 1970’s to more precisely, consistently and objectively determine the effectiveness and efficiency of different health measures.
Here’s how it works: imagine a year of life enjoyed at full health. It gets assigned a score of 1. Every year of life lived at less than full health gets assigned a lower score. The worse off the person’s health, the lower the score.
For example, take someone who has to undergo chemotherapy for five years. They have full mobility, but have some difficulty with usual activities, severe pain and mild mental health challenges. They might be given a QALY score of 0.55.
Once we’ve gotten a QALY score, we then need to work out how much the healthcare costs. Then, it’s simple maths: multiply the cost by the QALY score and you get an idea of how much each QALY is costing you. Then you can compare the cost effectiveness of different health programs.
QALY’s are usually seen as a utilitarian method of allocating health resources – it’s about maximising the utility of the healthcare system as a whole. However, like most utilitarian approaches, what works best overall doesn’t work best in individual cases. And that’s where criticisms of QALY arise.
Let’s say two patients come in with the same condition – COVID-19. One of them is young, non-disabled and has no other health conditions affecting their quality of life. The other person is elderly, has a range of other health conditions and is in the early stages of dementia. Both patients have the same condition. However, according to the QALY approach, they are not necessarily entitled to the same level of care – for example, a ventilator if resources are scarce. The cost per QALY for the younger patient is far lower than for the elderly patient.
For this reason, QALY’s are sometimes seen as inherently unjust. They fail to provide all people with equal access to healthcare treatment. Moreover, as philosopher and medical doctor Bryan Mukandi argues, if two patients with the same condition are expected to have different health outcomes, there’s a chance that’s the result of historical injustices. Say, a person with type-2 diabetes receives a lower QALY score as a result, but type-2 diabetes is correlated with lower income, the scoring system might serve to entrench existing advantage and disadvantage.
Like any algorithmic approach to decision-making, QALYs present as neutral, mathematic and scientific. That’s why it’s important to remember, as Cathy O’Neil says in Weapons of Math Destruction, that algorithms are “opinions written in code.”
Embedded within QALY’s method are a range of assumption about what ‘full health’ is and what it is not. For instance, a variation on the QALY methodology call DALY – disability-adjusted life years – “explicitly presupposes that the lives of disabled people have less value than those of people without disabilities.”
An alternative to the QALY approach is to adopt what is known simply as a ‘needs-based’ approach. It’s sometimes described as a ‘first come, first served’ approach. It prioritises the ideal of healthcare justice above health efficiency – everyone deserves equal access to healthcare, so if you need treatment, you get treatment.
This means, to go back to our elderly and young patients with COVID-19, that whoever arrives at the hospital first and has a clinical need of a ventilator will get one. QALY advocates will argue that in times of scarcity, this is an inefficient approach that may border on immoral. After all, shouldn’t the younger person be given the same chance at life as the elderly person?
However, there is something radical underneath the needs-based approach. QALY’s starting point is that there are limited health resources, and therefore some people will have to miss out. A needs-based approach allows us to do something more radical: to demand that our healthcare is equipped, as much as possible, to respond to the demand. Rather than doing the best with what we have, we make sure we have what is necessary to do the best job.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
There is something very revealing about #ToiletPaperGate
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
The etiquette of gift giving
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
The dilemma of ethical consumption: how much are your ethics worth to you?
Explainer
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Values
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
The value of a human life

The value of a human life
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsScience + Technology
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 1 MAY 2020
One of the most enduring points of tension during the COVID-19 pandemic has concerned whether the national ‘lockdown’ has done more harm than good.
This issue was squarely on the agenda during a recent edition of ABC TV’s Q+A. The most significant point of contention arose out of comments made by UNSW economist, Associate Professor Gigi Foster. Much of the public response was critical of Dr. Foster’s position – in part because people mistakenly concluded she was arguing that ‘economics’ should trump ‘compassion’.
That is not what Gigi Foster was arguing. Instead, she was trying to draw attention to the fact that the ‘lockdown’ was at risk of causing as much harm to people (including being a threat to their lives) as was the disease, COVID-19, itself.
In making her case, Dr. Foster invoked the idea of Quality Adjusted Life Years (QALYs). As she pointed out, this concept has been employed by health economists for many decades – most often in trying to decide what is the most efficient and effective allocation of limited funds for healthcare. In essence, the perceived benefit of a QALY is that it allows options to be assessed on a comparable basis – as all human life is made measurable against a common scale.
In essence, the perceived benefit of a QALY is that it allows options to be assessed on a comparable basis – as all human life is made measurable against a common scale.
So, Gigi Foster was not lacking in compassion. Rather, I think she wanted to promote a debate based on the rational assessment of options based on calculation, rather than evaluation. In doing so, she drew attention to the costs (including significant mental health burdens) being borne by sections of the community who are less visible than the aged or infirm (those at highest risk of dying if infected by this coronavirus).
I would argue that there are two major problems with Gigi Foster’s argument. First, I think it is based on an understandable – but questionable – assumption that her way of thinking about such problems is either the only or the best approach. Second, I think that she has failed to spot a basic asymmetry in the two options she was wanting to weigh in the balance. I will outline both objections below.
In invoking the idea of QALYs, Foster’s argument begins with the proposition that, for the purpose of making policy decisions, human lives can be stripped of their individuality and instead, be defined in terms of standard units. In turn, this allows those units to be the objects of calculation. Although Gigi Foster did not explicitly say so, I am fairly certain that she starts from a position that ethical questions should be decided according to outcomes and that the best (most ethical) outcome is that which produces the greatest good (QALYs) for the greatest number.
Many people will agree with this approach – which is a limited example of the kind of Utilitarianism promoted by Bentham, the Mills, Peter Singer, etc. However, there will have been large sections of the Q+A audience who think this approach to be deeply unethical – on a number of levels. First, they would reject the idea that their aged or frail mother, father, etc. be treated as an expression of an undifferentiated unit of life. Second, they would have been unnerved by the idea that any human being should be reduced to a unit of calculation.
…they would have been unnerved by the idea that any human being should be reduced to a unit of calculation.
To do so, they might think, is to violate the ethical precept that every human being possesses an intrinsic dignity. Gigi Foster’s argument sits squarely in a tradition of thinking (calculative rationality) that stems from developments in philosophy in the late 16th and 17th Centuries. It is a form of thinking that is firmly attached to Enlightenment attempts to make sense of existence through the lens of reason – and which sought to end uncertainty through the understanding and control of all variables. It is this tendency that can be found echoing in terms like ‘human resources’.
Although few might express a concern about this in explicit terms, there is a growing rejection of the core idea – especially as its underlying logic is so closely linked to the development of machines (and other systems) that people fear will subordinate rather than serve humanity. This is an issue that Dr Matthew Beard and I have addressed in the broader arena of technological design in our publication, Ethical By Design: Principles for Good Technology.
The second problem with Dr. Foster’s position is that it failed to recognise a fundamental asymmetry between the risks, to life, posed by COVID-19 and the risks posed by the ‘lockdown’. In the case of the former: there is no cure, there is no vaccine, we do not even know if there is lasting immunity for those who survive infection.
We do not yet know why the disease kills more men than women, we do not know its rate of mutation – or its capacity to jump species, etc. In other words, there is only one way to preserve life and to prevent the health system from being overwhelmed by cases of infection leading to otherwise avoidable deaths – and that is to ‘lockdown’.
…there is only one way to preserve life and to prevent the health system from being overwhelmed by cases of infection leading to otherwise avoidable deaths – and that is to ‘lockdown’.
On the other hand, we have available to us a significant number of options for preventing or minimising the harms caused by the lockdown. For example, in advance of implementing the ‘lockdown’, governments could have anticipated the increased risks to mental health leading to a massive investment in its prevention and treatment.
Governments have the policy tools to ensure that there is intergenerational equity and that the burdens of the ‘lockdown’ do not fall disproportionately on the young while the benefits were enjoyed disproportionately by the elderly.
Governments could have ensured that every person in Australia received basic income support – if only in recognition of the fact that every person in Australia has had to play a role in bringing the disease under control. Is it just that all should bear the burden and only some receive relief – even when their needs are as great as others?
Whether or not governments will take up the options that address these issues is, of course, a different question. The point here is that the options are available – in a way that other options for controlling COVID-19 are not. That is the fundamental asymmetry mentioned above.
I think that Gigi Foster was correct to draw attention to the potential harm to life, etc. caused by the ‘lockdown’. However, she was mistaken not to explore the many options that could be taken up to prevent the harm she and many others foresee. Instead, she went straight to her argument about QALYs and allowed the impression to form that the old and the frail might be ‘sacrificed’ for the greater good.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Critical Race Theory
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing
Gen Z and eco-existentialism: A cigarette at the end of the world
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Autonomy
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
Corporate whistleblowing: Balancing moral courage with moral responsibility
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
FODI launches free interactive digital series

FODI launches free interactive digital series
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY The Ethics Centre 1 MAY 2020
FODI Digital, announced today, is an exciting series of free, online conversations to be live-streamed on May 9 and 10.
The line-up will feature a selection of the international and Australian speakers originally slated for the live festival that was cancelled, by government order, as the COVID-19 lockdown came into effect last month.
“The theme for 2020’s live festival was Dangerous Realities and we seem to well and truly have encountered one. Critical thinking is essential, especially as we isolate further from our communities, families and global neighbours.” said Festival Director, Danielle Harvey.
Executive Director of The Ethics Centre and Co-Founder of FODI Simon Longstaff says FODI digital is a timely invitation to think critically.
“We may submit to a lockdown of our bodies, but never our minds. If ever there was a time to test the boundaries of our thinking … it is today!”
The series of online conversations takes inspiration from the original FODI 2020 theme of ‘Dangerous Realities’, with online sessions being streamed via the festival website. The series will interrogate the reality of the current pandemic and its wider implications for our world and society.
Audiences can contribute questions live while the discussions take place.
For Festival Director Danielle Harvey, there’s never been a more important time for these critical conversations. “Decisions are being made at every level that will shape how we live our lives both now and in the future.
“While we can’t present the program in the way originally planned, these digital conversations will address topics that really need to be put under the microscope. COVID-19 will hopefully end at some point, and understanding what kind of world we will then be entering is essential.”
Sessions include:
- The Truth About China – Former Prime Minister Kevin Rudd is joined by journalists Peter Hartcher and Vicky Xiuzhong Xu, with Human Rights Watch researcher Yaqiu Wang, and strategist Jason Yat-Sen Li, in a wide-ranging discussion about China;
- The Future Is History – Russian-American journalist, high-profile LGBTQI activist and outspoken critic of Vladimir Putin and Donald Trump, Masha Gessen, shares her thoughts on Russia and the coming US elections;
- Snap Back To Reality – Philosopher Simon Longstaff leads a discussion with social researcher Rebecca Huntley, political journalist Stan Grant, and fellow philosopher Tim Soutphommasane, on the social shifts, policy and economic consequences that await us in a post-COVID-19 world;
- States of Surveillance – Futurist Mark Pesce, 3A Institute data expert Ellen Broad, and founder of Old Ways, New Angie Abdilla discuss the issue of digital surveillance for virus tracking and the potential threat posed by the ‘normalisation’ of government surveillance;
- Misinformation Is Infectious – First Draft’s Claire Wardle, tech journalist Ariel Bogle discuss COVID-19-related conspiracy theories and what they tell us about technology’s role in the spread of damaging misinformation;
- Stolen Inheritance – Australian youth leaders, Daisy Jeffrey, Audrey Mason-Hyde and Dylan Storer discuss their concerns for the world they will inherit: a world of debt, educational disadvantage, diminished job opportunities, climate catastrophe and … future pandemics;
- The Ethics of the Pandemic – Philosophers Matt Beard, Eleanor Gordon-Smith and Bryan Mukandi take a step back from the day-to-day dilemmas of the pandemic to try to understand what’s really going on, the lessons we learn and the hidden costs of the choices we make;
- Political Correct-Mess – Conservative Australian commentator Kevin Donnelly, journalist Chris Kenny, and journalist Osman Faruqi join journalist Sarah Dingle to dissect political correctness and ask, “Has it gone too far?”;
- Ageing is a Disease – Biologist David Sinclair talks about cracking and reversing the ageing process, which may help the elderly in their fight against a range of diseases and viruses.
The event will live stream straight from The Festival of Dangerous Ideas website across May 9-10. Visit www.festivalofdangerousideas.com to view the program.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
How to have a conversation about politics without losing friends
Opinion + Analysis
Science + Technology, Society + Culture
That’s not me: How deepfakes threaten our autonomy
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Kate Manne
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Academia’s wicked problem
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Moral fatigue and decision-making

Moral fatigue and decision-making
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationships
BY Cris Parker The Ethics Centre 24 APR 2020
A senior executive starts making out-of-character decisions that reflect his personal fears. Teams are frozen in indecision as the ground continually shifts beneath them. Days become punctuated with emotional meltdowns from people you have always relied upon in a crisis.
At home, you might be disagreeing with loved ones about the right response to COVID -19. Is the situation as serious as officials claim? Or are people exaggerating the risks? What is the right amount of physical distancing? Why should the whole of a society bear the costs for the sake of the few? Is this even a fair way to frame the questions?
These are some of the signs that the prolonged impact of COVID-19 is causing moral fatigue in the people around you.
Moral fatigue can occur when the “right thing to do” is unclear. Who should bear the cost of protecting a business? What if personally caring for elderly parents risks exposing them to deadly infection? It can be exhausting to make decisions in this kind of ambiguity, day after day.
Michael Baur, Associate Professor in the Philosophy Department at Fordham University and an Adjunct Professor at Fordham Law School, says moral fatigue comes from situations where attempts to do good also result in “destroying a good”.
“People have often referred to the idea of moral fatigue as compassion fatigue or moral distress,” he told me on a zoom call from the US. “What we have in the current context is a situation that makes it increasingly difficult to understand if I’m doing the right thing. It’s no longer possible to assume that the good that I’m doing is unambiguously good,” he says.
It could be dangerous to keep running a business, for instance, if it means employees are in danger. “There’s a real conflict there. And there are no rules.”
Why people panic
Usually, as people go about their normal lives many actions are performed on “autopilot”. Typing on a keyboard, for instance, is done out of habit; the decision of which keys to hit doesn’t exercise mental exertion; one’s finger ‘do the work’. Baur says a crisis such as COVID-19 “jumbles” the keys on the keyboard. It changes the rules and worse still, you don’t know what those new rules are as they can change, minute-by-minute.
“It’s really disorienting,” says Baur. “People go back to what they know is safe, and they become more infantile, more self-protective and defensive.”
This is the kind of response that decreases our capacity to make good decisions. It leads to the hoarding behaviours we have seen in supermarkets, anxiety about money and a focus on individual survival.
Slow down and be more forgiving
Thinking about ‘just getting beyond this’ assumes a future state where the problem no longer exists and everything is the same as before. It’s too simplistic to suggest we will all be ok – many of us won’t be, unless we adapt.
A common result of moral fatigue can be impatience. When we try to think through frameworks that no longer serve us well we can become increasingly impatient, the more we do so, the more mistakes we make – leading to even more frustration.
Baur likens our situation to building the raft at the same time that you are using it to survive. He says, it’s okay to make mistakes because we’re all trying to refashion this raft, even as we’re stepping on top of each other trying to stay afloat. Mistakes will be made.
“You’re not alone. Everybody feels the same way. We have to be more forgiving of others and I think individuals have to be more forgiving of themselves in the sense that it’s okay to be freaked out. Everybody is.”
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing
When you hire a philosopher as your ethicist, you are getting a unicorn
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Should I have children? Here’s what the philosophers say
Big thinker
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Big Thinker: Temple Grandin
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Ethical concerns in sport: How to solve the crisis
BY Cris Parker
Cris Parker is the former Head of The Ethics Alliance and a Director of the Banking and Finance Oath at The Ethics Centre.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Seven COVID-friendly activities to slow the stress response

Seven COVID-friendly activities to slow the stress response
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationships
BY Karina Morgan 16 APR 2020
The coronavirus pandemic has affected nearly everything we do in our everyday lives. The things that give us joy and meaning – going to the gym, the beach, meeting friends for coffee – are no longer possible.
This is having a real impact on our mental health and capacity for good decision making. Beyond Blue have reported a four-fold increase in the number of calls and enquiries related to COVID-19 since March, a level far exceeding the period during the summer fires.
Our brains are wired to seek certainty and our neural circuits register unexpected events as threats. This triggers a fear response, known commonly as ‘fight or flight’, which causes a cascading chemical reaction in our bodies. That response prevents or impairs access to the higher levels of the brain where we deal with complex decisions.
So, it’s fair to say that uncertainty and fear reduce our capacity for quality decision making. This is, in part, because the area of impeded access involves the pre-frontal cortex, the part of our brain that actively processes information, accesses creative thinking and enables good decision making.
At its very core, ethics is about making good decisions. It asks us to consider all the ways we might act and to choose for the best. To take responsibility for our beliefs and our actions, and live a life that is entirely our own.
We know that many of you are facing challenging choices in circumstances that involve an unprecedented level of change and uncertainty in our individual and collective lives.
People are moving to work from home with kids in the house, facing job losses, closing businesses and deciding how to care for vulnerable loved ones. Many people are also experiencing the impacts of hyper-connection and feeling overwhelmed by the constant stream of new information.
With the sense of control and certainty taken from us, it’s easy for our decisions to be overcome by what we fear. With that in mind, it’s important to make time to find new activities that will help to activate the feel-good chemicals in our brains.
These seven activities can be practised while experiencing physical distancing. They are proven to slow down the stress response and boost your mood.
-
Take a nature break
2,500 years ago, Hippocrates, the Ancient Greek Physician and so-called ‘father of medicine’, said “walking is man’s best medicine”. Having invented the Hippocratic oath, he certainly wouldn’t lie! The moment you step outside the concrete jungle and into nature, your body shows its gratitude by releasing serotonin, a mood-regulating neurotransmitter. We are encouraged to stay at home. But if you have a backyard or nature reserve nearby, take regular breaks from the computer for fresh air or to use these spaces for exercise. Just be mindful to ensure you’re following recommendations and maintaining safe physical distancing in the process.
-
Move your body
Physical exercise acts like a power booster, it increases endorphins, the ‘peptide good guys’ that reduce pain perception and trigger positivity. Literally, happy days. Running and walking are great ways to shift pent-up energy. If you’re in self-isolation, try skip rope, something you could make, at a stretch, with a plastic cord or clothes line. A 32 year old French man ran the entire length of a marathon on his balcony during lockdown! Give yourself a tech-tox and move your body, ideally in nature, even if it’s just for ten minutes.
-
Take a bath
Many people experience a sense of calm around water and it’s no surprise if you consider the fact that our bodies are 60% water, and our brains more than 70%. Both Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine believe that the water element is crucial to rebalancing the body. With many beaches closed, look to what you can do within your own home. Fill up the bathtub and immerse your body in water. To super charge the experience you might even soften the lighting or drop in some essential oils to stimulate your senses.
-
Have a laugh
Laughter triggers the release of dopamine into the brain’s reward centre, giving you a high that lowers stress levels and increases your receptivity to pleasure. What may come as a surprise is that research also suggests that simply anticipating a laugh can have a similarly powerful effect. The expectation of something funny turns on our parasympathetic response system. So, it seems there’s never been a better time to practise your best ‘dad jokes’ on friends or the kids. There’s plenty of funny fodder available on streaming services. Check out Vulture’s list of the 50 best comedies on Netflix.
-
Practice yoga
The benefits of this ancient practise go far beyond the physical. In a yoga class, the combination of breath awareness and asana (postures) act to still the fluctuations of the mind and deepen your mind-body connection. Studies have shown that just a single one-hour yoga class can have a positive biochemical impact on your brain. Regular practise can reduce stress, anxiety, post traumatic stress disorder and depression. With traditional classes currently cancelled, many yoga teachers and studios are live streaming offerings, by donation or free of charge, for you to practise from home.
6. Listen to some tunes
Music makes your brain sing. You know that happy rush you get when your favourite song comes on the radio? It’s a chemical romance, one that lets off steam, injects the good vibes and let’s be real, is just a whole lot of fun. When music triggers your pleasure receptors dopamine is released into the striatum, the same part of the brain that responds to sex, chocolate, and is stimulated by artificial narcotics like cocaine. Research has also found that that some music has meditative qualities and can positively impact stress reduction and overall happiness. Fun fact: neuroscientists have found that listening to this song can reduce anxiety by up to 65%.
-
Dance it out
Dancing, like any other physical activity, releases neurotransmitters and endorphins to alleviate stress. Combining the dopamine response stimulated by music with these endorphins has the potential to supercharge your positivity. Plus, it’s almost certain that you’ll laugh along the way. Right now, you really can dance around the house like no one is watching. Prefer company? Have a virtual dance party. Many companies are rolling out video call dance breaks to manage the impacts of social isolation on extroverts in the workforce. Whether you want to do it with work, or friends, it’s easy to set up a time, pick a song, and all jump on a video call to dance it out together.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
You are more than your job
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Plato
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing
Defining mental illness – what is normal anyway?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
When are secrets best kept?
BY Karina Morgan
Karina is a communications specialist, avid hiker and volunteer primary ethics teacher, with a penchant for the written word.
Moving work online

Moving work online
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipRelationships
BY Talya Wiseman The Ethics Centre 10 APR 2020
As the COVID-19 dominos continue to fall, many organisations are scrambling to rethink the way they work. These changes are happening in real time; on a scale both unprecedented and unpredicted.
The last pandemic of this nature, the Spanish Flu, occurred 100 years ago – well before anyone had dreamed up the internet, computers and video conferencing. In 2020, advances in technology, such as international flights, have allowed this virus to spread at a much faster rate. However, they have also afforded many organisations the opportunity to pivot their operations online.
Schools and universities have, for the most part, managed this at an incredibly fast pace. With barely any notice, teachers have become adept at using online delivery platforms and are coming up with new ways to engage their students online.
Students are able to continue their same classes via platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams; all the while knowing that the rest of their class is right there, learning alongside them.
Now that all but essential workers are urged to stay at home, ideas about working environments have also been forced to alter at an unusually rapid pace. For example, workplaces and teams have begun to adapt to meeting online. A popular meme doing the rounds at the moment depicts a scenario 40 years from now when a grandchild asks their grandparent with wonder “Go to work? You used to actually GO to work?”
It is incredible to see how many fundamental changes and shifts in thinking have occurred in such a short space of time. We simply had neither the time nor the opportunity to incorporate long policy discussions, carefully timed rollout plans or trial periods. Many organisations that previously assumed they needed a common workplace are now questioning the validity of this assumption.
What happens next?
The big question is this: when all of this is over and we return to normal, what will normal look like? Will organisations revert to their old ways? Or will we have seen the value in new patterns of working? Our eyes have been opened through this experience. Our assumptions about the nature of work have been challenged. Having reorientated towards online workplaces, will it be so easy to pivot back? And will we want to?
There are certainly benefits to workplaces accepting remote working as a viable option. Parents and carers, who previously struggled to convince their employers that they could effectively work from home, will likely find this argument much easier to make. If people have been able to fulfill their work duties in these most trying times, clearly it will be easier for them to continue to do so when it is an option they are choosing.
The stigma of working from home has rapidly been removed. It should no longer be seen as the ‘lesser’ option compared to attending an office. Organisations are finding innovative ways to ensure staff feel supported while working from home; while also maintaining expectations of staff – wherever they happen to be located.
The role of the physical workplace
However, there is a risk in realising just how easy it is to do things online. The role that work plays for individuals is much more than just providing an income. Work is also about fulfilment; it is about social interaction. The best initiatives can arise from bouncing ideas around with colleagues. Families can laugh together at the dinner table when sharing work stories and funny moments that occurred at the office. Colleagues can celebrate each other’s success and commiserate together when things don’t go as planned. Work is about so much more than ‘work.’
One of our principles, here at The Ethics Centre, is to “know your world and know yourself”. We believe in the importance of questioning who we are and being conscious of what we do. If the nature of work is fundamentally to change, we must recognise what we are giving up, as well as the opportunities that may arise. Just because we were rushed into this new reality doesn’t mean we can’t carefully consider the best way to move on from it.
Let’s not just fall back into old patterns. Let’s use this as an opportunity for questioning and for finding a better ‘normal’. That might well be a workplace that embraces flexible arrangements and is open to non-traditional office environments, while at the same time never losing touch with deeply human moments and interactions.
Perhaps we will realise that work, regardless of industry, is about purpose, fulfilment and human interaction.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
“I’m sorry *if* I offended you”: How to apologise better in an emotionally avoidant world
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Society + Culture
The Ethics Institute: Helping Australia realise its full potential
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Dennis Altman
Big thinker
Society + Culture, Business + Leadership
Big Thinker: Ayn Rand
BY Talya Wiseman
is an experienced educator who has worked extensively in both the formal and experiential education space. At The Ethics Centre, Talya is the Educational Program Manager creating innovative, engaging and quality ethics-focused education
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Is it ok to visit someone in need during COVID-19?

Is it ok to visit someone in need during COVID-19?
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationships
BY Matthew Beard 9 APR 2020
You’ve been hitting us up with your COVID-19 ethical questions. We’ve been sending our ethicists into the philosophy lab to cook up some answers.
This week, we’re talking about trade-offs. How do we the balance risks and potential harms from our behaviours against the value they might have?
I have family members who are at high-risk from COVID-19 but who are also at risk of mental stress from isolation, what should I prioritise – their physical safety or their psychological wellbeing?
When I was teaching medical students (about ethics, nobody wants me teaching them science), I was often relieved to find an openness to considering the holistic needs of the patient. They weren’t interested in healing the body at the expense of the mind. This was thanks in part to something called the ‘biopsychosocial model of health’, which basically suggests that we need to think of health at the intersection of the physical body, the mind and the environment we find ourselves in.
What this model reminds us of is that we don’t make trades between mental and physical health – those terms are somewhat of a misnomer. There aren’t different kinds of health; there’s just health. Someone who is suffering from a virus isn’t enjoying a healthy life; nor is someone whose depression is worsening as a result of isolation.
Think about it this way: if your family members were diabetic and needed to go to the pharmacy to fill their insulin prescription, you wouldn’t advise them not to go because they were high risk of COVID-19; because that’s not the only thing that’s going to set back their health. I’m not convinced you should think about their health any differently because the problem is mental rather than physical.
That said, it’s important to bear in mind that you should still do what you can to minimise the risk to your family members – not least because they may not be the only ones who are at increased risk of infection if you choose to visit. Again, think of the diabetes analogy. It would be unreasonable to tell them not to go to the pharmacy for fear of COVID-19, but it would be safer if someone who wasn’t high risk collected their prescription on their behalf.
By the same logic, if there are ways you can alleviate their sense of loneliness and isolation without increasing their risk, then you should do those things. You might not have to choose between minimising the risk of infection and helping a lonely family member at a time when loneliness is rife. But if you can’t, it’s helpful to remember that you’re dealing with risky options either way.
I’m struggling to decide whether I should visit my two loved ones in their aged care facilities right now. Do I leave them and trust they will get the correct care if the outbreak spreads or ‘check in’ and visit them?
Ever heard the story of the two wolves? It’s an old proverb. A Native American elder explains to a young man that there are two wolves inside us all. One represents the lesser demons of our nature, and the other the better angels. The wolves are in constant battle with one another to determine the kind of person we’ll be. ‘Which wolf wins?’, asks the young man. The elder responds, ‘the one you feed.’
In times of enormous stress and uncertainty, the two wolves duking it out inside us tend to be our attitudes toward control. One wolf screams ‘Jesus take the wheel!’ and surrenders all sense of agency – throwing in the towel and hoping for the best, taking no responsibility for the future. The other wolf cries, ‘let me drive!’ and tries to manage every possible variable to secure a half-decent outcome. And, just like the story goes, the wolf we feed – the one we reinforce through behaviour and habit – is the one that will win out.
The reason I share the story of the wolves with you is because your concern for loved ones doesn’t seem to be primarily about giving them social connection or making sure they’re not lonely. Rather, your question suggests what’s bothering you most is whether the carers will do a good job without you to check in. That kind of distrust is likely the product of one of two things: reason or anxiety.
Do you have reasons why you suspect the care for your loved ones will languish in your absence? If so, I can only imagine how heart-wrenching it must be to stay away at a time like this. However, if you’ve generally had good experiences and haven’t had any reason to distrust the staff until now, it’s worth reflecting on whether your inner micro-managerial wolf needs some time off to meditate.
I mean that sincerely – most of us need to meditate during this pandemic – to get clarity on how we manage uncertainty. Do we have trouble accepting our lack of control? Are we too lackadaisical or passive when shit hits the fan?
The truth is, I can’t answer the question of whether you should check in on your family – and in doing so expose them and everyone else at those aged care facilities – because I don’t know if you’ve got good reasons for concern. But let me plead with you on behalf of every person who has loved ones in aged care: if you’re doing this because you’re anxious and scared, please stay at home. We’re all scared for our loved ones, but hopefully you can see that resolving that fear by exposing the people you love to risk is as pointless as howling at the moon.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Akrasia
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
5 stars: The age of surveillance and scrutiny
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing
Gen Z and eco-existentialism: A cigarette at the end of the world
Explainer
Relationships, Science + Technology
Ethics Explainer: Post-Humanism
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
There’s more than lives at stake in managing this pandemic

There’s more than lives at stake in managing this pandemic
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Matthew Beard The Ethics Centre 3 APR 2020
Imagine a parallel universe somewhere, one without a pandemic. What would you be spending this week concerned with? What social and political issues would you be wrestling with? How would you be spending your day?
Ironically, my parallel life looks very similar. Locked in a room, thinking a lot about pandemics. I’m not an epidemiologist or a public health expert though – in my parallel universe, I’m preparing to run a thought experiment for The Festival of Dangerous Ideas: The Ethics of the Apocalypse.
The basic premise is to find out whether, facing a couple of end-of-the-world scenarios, the audience can save the human race without losing their humanity in the process. I won’t give away how the event works or is scored, but there are a bunch of different victory conditions – survival is a necessary condition of success, but alone, it’s not sufficient.
That point bears repeating as we live through a pandemic of our very own: survival is a necessary, but insufficient condition for success.
By focusing solely on what is going to guarantee success or best facilitate a flattening of the curve and minimise deaths, we risk permitting a political and social environment that we would, in that parallel universe, reject outright.
Over the last few weeks, as Australia’s containment measures around COVID-19 have grown increasingly strict, there’s been a widespread movement demanding an immediate lockdown. #Lockusdown and other variations have trended on Twitter, and major mastheads have called for increasingly severe policing measures to manage the pandemic. Writing for The Guardian, Grattan Institute CEO John Daley wrote:
“There is no point trying to finesse which strategies work best; instead the imperative would be to implement as many as possible at once, including closing schools, universities, colleges, public transport and non-essential retail, and confining people to their homes as much as possible.
Police should visibly enforce the lockdown, and all confirmed cases should be housed in government-controlled facilities. This might seem unimaginable, but it is exactly what has already happened in China, South Korea and Italy.”
Similar comments have been made by other public commentators in support of such measures, including the ABC’s Norman Swan. Swan has pointed to the efficiency with which China were able to control the spread through draconian measures – including in one case, welding people inside their apartment building.
Imagine in a pre-COVID world, suggesting a liberal democracy like Australia look to the authoritarian state of China for political guidance. Yet, this is what happens when we reduce all things to a single metric: the goal of keeping people at home and flattening the curve of new infections. It is easy to conceptualise. We can visualise what it involves and we can imagine the benefits it confers.
However, whilst this logic is comforting – especially in times when fear and uncertainty are rife – it places us dangerously close to the crude and morally repugnant catch cry: the ends justify the means.
In NSW, new laws and extreme penalties aim to enforce self-isolation regimes – as John Daley’s piece suggested. The maximum penalties for leaving your home without a reasonable excuse (of which sixteen are listed) are six months imprisonment or a fine of up to $11,000.
Are you cooped up in your share house, finding it impossible to work? If you choose to go to the park, you’ll face a severe penalty. Considering using the time your teenager has off school to rack up some learner driving hours by leaving the city and heading to the mountains for a bushwalk? Want to do a drive-by birthday celebration in lieu of an actual party? All of them are now subject to police enforcement. Do any of them, and you’re potentially breaking the law.
There are still those who will argue that it’s good these activities have been made illegal. After all, if you go to the park and sit at a bench, you might pick up coronavirus from someone who was just sitting there, or leave some behind for somebody else. If you go for a drive, you may need to stop for petrol, or break down and need mechanical assistance… more exposures means more risk for vulnerable Australians. The elderly, those with chronic illness, Indigenous Australians and immunocompromised people might be more at risk if you do this. However, it doesn’t follow from this that we should threaten people with prison sentences for failing to play ball.
In suspending our ordinary ways of life, we don’t also suspend the moral norms and ethical principles that give them direction and meaning. Punishments should still be reasonable and proportionate to the offenses; we should still aim to strike a reasonable balance between risk, security and freedom.
As Schwatz Media’s Osman Faruqi – who has been following the authoritarian developments around COVID-19 management – noted ,we should remember that increased law enforcement itself carries a cost. Whilst we’re all equal before the law in principle, in practice, minority communities, the poor, homeless and a range of other groups – vulnerable Australians – tend to bear the brunt of increased police activity around the world.
Police have been encouraged to use their discretion in enforcing these laws, but discretion is subject to bias and inconsistency, as is any other aspect of our decision-making. If new police powers are necessary to protect vulnerable Australians from COVID-19, who will be protecting the Australians made vulnerable by these new laws?
In the best-selling board game, Pandemic: Legacy, players have to combat a fast-evolving, unknown virus, using various measures. Options range from quarantines to military lockdowns to the literal, nuclear option. However, because the goal of the game is simply to ensure humanity’s survival and the effective control of the pandemic, these options are all seen as morally equal.
In a game, that’s fine. In reality, as we go from suspending ordinary life to suspending more basic moral and political norms and rights, we need to be able to understand and consider the costs it involves. We can’t do that if our sole metric for success is flattening the curve.
In his column, John Daley wrote that “Covid-19 is the real-life “trolley problem” in which someone is asked to choose between killing a few or killing many.” This framing only obfuscates the deeper issues which pit health and safety against other essential political values; short-term outcomes against a long-term political landscape and the competing needs of different of vulnerable communities.
That’s not a simple trolley problem, it’s a political smorgasbord. And we need a much more sophisticated scoring system to work out what success looks like.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
The rights of children
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Beyond consent: The ambiguity surrounding sex
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Power without restraint: juvenile justice in the Northern Territory
Big thinker
Relationships, Society + Culture
Big Thinker: Simone de Beauvoir
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
This isn't home schooling, it's crisis schooling

This isn’t home schooling, it’s crisis schooling
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationships
BY Talya Wiseman The Ethics Centre 1 APR 2020
The COVID-19 pandemic has shaken a way of life we previously took for granted – going to work, celebrating weddings, seeing friends and wandering aimlessly down fully-stocked supermarket aisles.
However, one of the biggest changes for many parents is that kids are being urged to stay home unless it is absolutely essential they go to school. Overnight, parents have had to become teachers, along with everything else they are attempting to squeeze into already overfilled schedules.
Where a few weeks ago home schooling was a vague and unfamiliar concept, it’s now become the norm. Parents are scrambling to find a new routine where kids are at home while continuing their education.
As a parent, former school teacher and professional educator who now runs The Ethics Centre’s education programs from my lounge room – with two young kids and a husband in the same room – I’m struggling to do the same.
The juggle of schooling at home
What’s happening here is not home schooling, it’s crisis schooling. Parents who home school have made a conscious decision to educate their child at home. Those parents have spent time organising their resources and routines, deliberating over how to ensure an optimal learning environment for their child, specific to their own needs. Home school parents often have networks of other parents who have also chosen this option, and together, they collaborate and socialise their children.
Crisis schooling is different. With very little notice or choice, suddenly kids are home. Crisis schooling has opened a range of dilemmas which parents are now facing, including:
- “How do I prioritise between helping my child learn and continuing to do my job?”
- “I’ve always tried to teach my kids health and fitness and limit screen time, but giving my child a device is now the only way I get a break.”
- “My wife and I are both working full time while the kids are at home, which one of us must sacrifice our work time to learn with the children?”
So how do we navigate these new challenges?
As we often teach in workshops at The Ethics Centre, there are no ready-made answers to ethical challenges. Instead, we have to respond to the circumstances and relationships at play – which will be different for each of us – and try to balance these with our personal ethics; our purpose, values and principles.
It may help to keep in mind some advice from Greek philosopher, Socrates, who maintained that in order for education to occur a person must accept what they do not know. Parents don’t know how to be teachers, except for those who are trained to be so. Let’s not pretend to ourselves or our kids that we’re fully equipped to do this. We’re not.
As parents, we can use the resources that teachers have readily made available. We can admit to our children that there are some things that we don’t know how to do, and that we need to figure it out together.
What we can control
What parents do know is how to love and care for their children. Parents understand their children better than anyone else in the world and can provide them with the love and support they need. During this incredibly uncertain and anxious time, that really is their most important need. Rather than being overly concerned with how much they are learning, whether or not they’re reading enough, practicing fractions or working on their fine motor skills, let’s focus on our children’s mental wellbeing.
The world is a stressful place right now and anxiety is contagious. Children need to feel supported and comforted. Home is supposed to be a safe space for children, regardless of what is happening outside in the world, and this applies today, more than ever.
So, let’s throw out the rule book on schooling. Let’s remember we are in crisis and although we have moved rapidly to this point, we do not have to adjust with the same speed to a new home-based education system. Do what feels right for your family, even if that means throwing out the schedule. Try not to compare what you are doing to others posting about their experience on social media. What works for one family, might not work for yours.
Human beings are incredibly resilient, children especially so. We’ll all adapt. One day soon, normal life will resume – with a much greater appreciation for the things we took for granted before. What our kids will remember is the extra time they got to spend with their parents; the extra cuddles, the extra stories.
Right now, let’s all take a deep breath and cherish the closeness that comes with distancing.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Social philosophy
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Living well or comfortably waiting to die?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
“I’m sorry *if* I offended you”: How to apologise better in an emotionally avoidant world
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology