Duties of care: How to find balance in the care you give
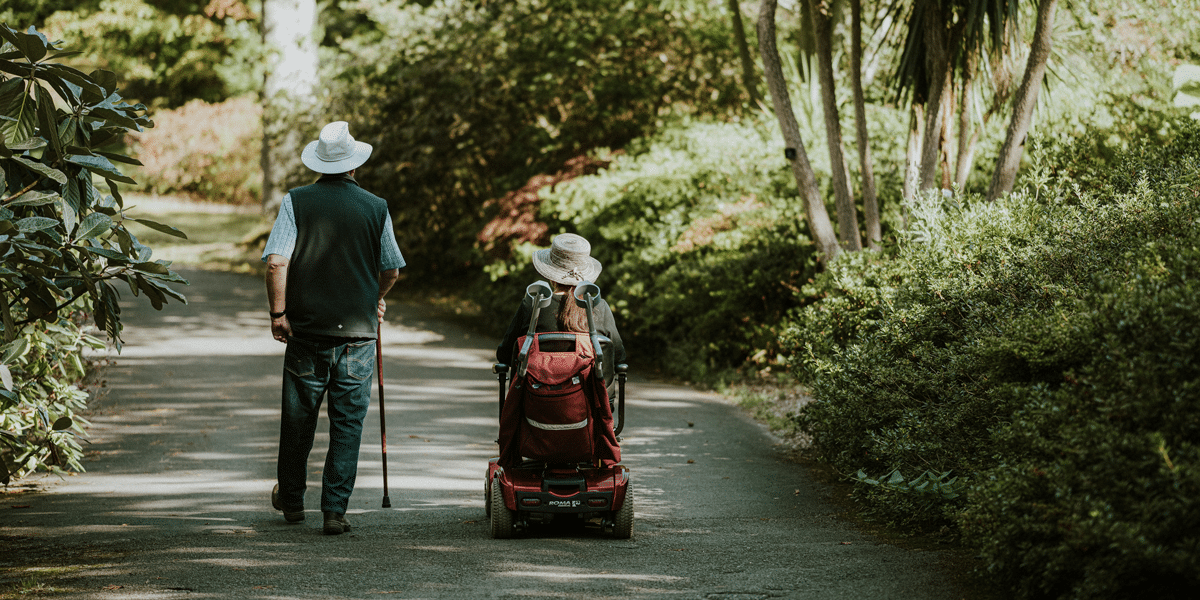

Duties of care: How to find balance in the care you give
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationships
BY Tim Dean 13 OCT 2025
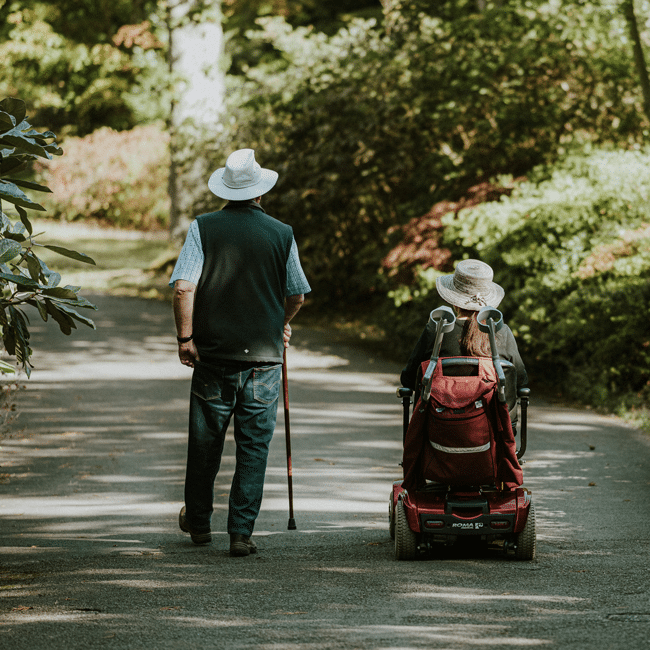
Caring for others can be a joy as well as a burden. Here’s how to balance your duty to care for others in your life with your own right to live a full life.
Sue’s* father, Jack*, isn’t like he used to be. Since his stroke, Jack has been forgetful, irritable and he gets even more frustrated when he gets confused, which happens often. He is increasingly reliant on Sue’s care these days. She prepares his meals, does his laundry and bathes him when he’s too tired to do it himself. Meanwhile, Sue’s children – both of whom have just started high school – have issues of their own that require her attention.
Sue has had to reduce her hours at work, right before she was slated for a promotion to a senior role. The reduction in income has compounded the significant cut to her free time; she now spends most days looking after Jack, even though he seems thoroughly ungrateful for her care, as well as keeping her kids on track.
There are times when Sue thinks about moving Jack into a nursing home, even though she knows he’d resist. But she longs to return to work, which was a tremendous source of meaning for her, and she hasn’t seen her friends in months. Such thoughts fill her with guilt, and she quickly puts them aside. But she’s not sure how much longer she can go on like this. It’s certainly far from the life she envisaged for herself at this age.
While the names have been changed*, this scenario is based on a true story. Actually, many true stories. One of the most popular questions posed by callers to our Ethi-call service is how to balance our responsibility to care for others with our own rights to live our life. And it’s one of the most complex questions to answer. However, there are some key considerations that can help people facing this dilemma to decide on an ethical way forward, one that respects both the duties that they have to others as well as their own right to live a good life.
Finding the right balance
Caring for others is a fundamental part of the human experience. We naturally feel empathy and concern for people close to us, especially for loved ones and those who are vulnerable or unable to fully care for themselves. But we also have rights of our own that need to be taken into consideration.
While some philosophers argue that every human’s moral worth is equal, and that we ought to weigh everyone’s needs equally, others have argued that we have special relationships with some people – such as parents with their children, or spouses with each other – and those relationships imply special obligations to those individuals.
This ‘ethic of care’ says that we ought to prioritise the interests of people we have a special relationship with over the interests of others. It also says we have a special duty to care for those people, especially when they are vulnerable or cannot care for themselves.
We can see this sense of duty in the words of Kim Paxton, who was caring for her husband, Graham, after he was diagnosed with a serious medical condition, while waiting on governmental support. “You just do it,” she told The Guardian Australia. “I don’t know. You get tired, but they’re your family, your loved ones. It breaks my heart … It’s a bit like being a mum, isn’t it, with a newborn baby. You start living with less sleep and you work harder and you just do what you do for the love of your kids.”
Some philosophers also emphasise the role of rights and duties when it comes to thinking about the care we give. Rights are a kind of entitlement that each person has in order to be treated a particular way. For example, a right to dignity means we are entitled to be treated in ways that don’t diminish our dignity. If someone has a right, others have a duty to respect that right.
We can also have duties because of the social role or relationship we have. For example, a doctor has a duty to protect their patient’s interests by virtue of their professional role, and a parent has a duty to support their children until they are old enough to support themselves. Similarly, some people have a duty to care for a family member if they are unable to care for themselves.
However, rights and duties often come into conflict. A caregiver might have a duty to care for both children and elderly parents, and it might be impossible for them to satisfy both of those obligations to everyone’s satisfaction. In that case, it’s reasonable to appeal to the adage “ought implies can” – meaning if it’s impossible to do something, then you’re free from blame if you’re unable to do it. That might mean balancing your care among multiple people and managing expectations of what you can reasonably achieve.
What about me?
But duties don’t necessarily override all other concerns. We also have a right to pursue our own interests and our vision of a good life, and this right can be balanced with the rights of others to be cared for by us. Each of us has a right to agency, meaning our ability to act on our interests and desires. One reason we might care for others is to help remove the barriers that prevent them from exercising their agency.
But it’s important for us to also have agency, and that might mean not expending all of our time and energy on care.
It’s also important that those receiving care don’t morally impose on their caregivers by expecting an unreasonable degree of sacrifice on their behalf. If there are alternatives that can reduce the burden of care they place on family members, such as external help or respite care, then it could be important to explore those options, even if it isn’t their first preference.
There is also a pragmatic argument for placing boundaries on the care you give: if you want to ensure you are delivering the best care possible, you need to have the energy to actually deliver that care. If you become burnt out, you’re not able to satisfy your obligations to care for others.
To ensure you don’t run flat, you might need to devote some resources to self-care. That might mean taking a break from time to time, perhaps taking a relaxing holiday. Even if that feels indulgent, there’s no guilt in taking the time to recharge the batteries so you can return to our caring duties reinvigorated.
It can be difficult in practice to balance conflicts of interest or duties. However, there can be good ethical reasons to place some boundaries and set expectations on the care you give to others.
Tough decisions are a part of life, but you don’t have to make them alone. Ethi-call, a free independent helpline from The Ethics Centre, can help you find a path forward. Book now.

BY Tim Dean
Dr Tim Dean is a public philosopher, speaker and writer. He is Philosopher in Residence and Manos Chair in Ethics at The Ethics Centre.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Praying for Paris doesn’t make you racist
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Relationships
“Animal rights should trump human interests” – what’s the debate?
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Society + Culture
Of what does the machine dream? The Wire and collectivism
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Immanuel Kant
Service for sale: Why privatising public services doesn’t work

Service for sale: Why privatising public services doesn’t work
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingBusiness + Leadership
BY Dr Kathryn MacKay 1 OCT 2025
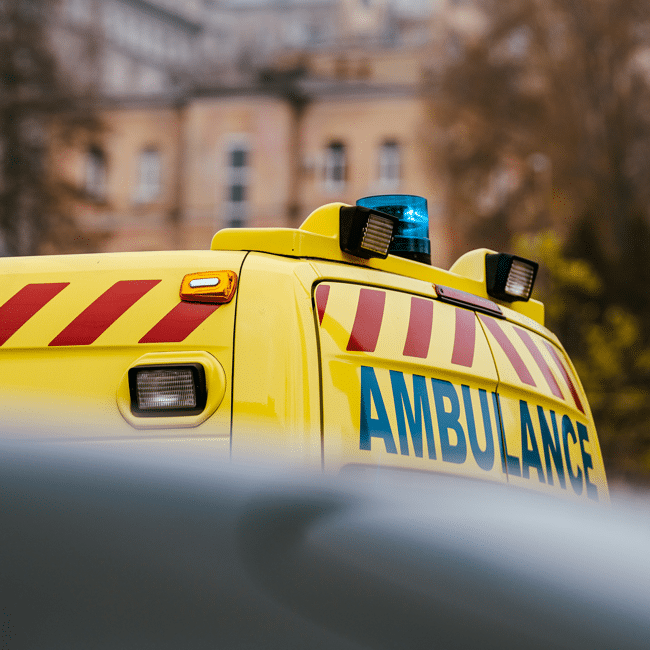
What do the recent Optus 000-incidents, childcare centre abuse allegations, and the Northern Beaches Hospital deaths have in common?
Each of these incidents plausibly resulted from the privatisation of public services, in which the government has systematically disinvested funds and withdrawn oversight.
On the 18th of September, Optus’ 000 service went down for the second time in two years. This time, the outage affected people in Western Australia, and as a result of not being able to get through to the 000 service, it appears that three people have died.
This highlights a more general issue that we see in Australia across a range of public services, including emergency, hospital, and childcare services. The government has sought to privatise important parts of the care economy that are badly suited to generating private profits, leading to moral and practical problems.
Privatisation of public services
Governments in Australia follow economic strategies that can be described as neoliberal. This means that they prefer limited government intervention and favour market solutions to match the value that people are willing to pay with the value that people want to charge for goods and services.
As a result, public goods and services like healthcare, energy, and telecommunications have been gradually sold off in Australia to private companies. This is because, firstly, it’s not considered within the government’s remit to provide them, and secondly, policy makers think the market will provide more efficient solutions for consumers than the government can.
We see then, for example, a proliferation of energy suppliers popping up, offering the most competitive rates they can for consumers against the real cost of energy production. And we see telecommunications companies, like Telstra and Optus, emerging to compete for consumers in the market of cellular and internet services.
So far, so good. In principle, these systems of competition should drive companies to provide the best possible services for the lowest competitive rates, which would mean real advantages for consumers. Indeed, many have argued that governments can’t provide similar advantages for consumers, given that they end up with no competition and no drive for technical improvements.
However, the picture in reality is not so rosy.
Public services: Some things just can’t be privatised
There’s a term in economics called ‘market failure’. This describes a situation where, for a few different possible reasons, the market fails to efficiently respond to supply and demand flows, affecting the nature of public goods and services.
A classic public good has two features: it is non-rival, and non-excludable. A non-rival good is one where one person’s use doesn’t deplete how much of that good is left for others – so we are not rivals because there is enough for everyone. A non-excludable good is one where my use of it doesn’t prevent anyone else from using it either. So, I can’t claim this good because I’m using it right now; it remains open to others to use.
Consider a jumper. This is a rival and excludable good. If I purchase a jumper out of a stock of jumpers, there are fewer jumpers for you and everyone else who wants one. The jumper is a rival good. When I buy the jumper and wear it, no one else can buy it or wear it; it is an excludable good.
Now, consider the 000 service. In theory, if you and I are both facing an emergency, we can both call 000 and get through to an operator. The 000 service is a non-rival, non-excludable good. It is not the sort of thing that anyone can deplete the stock of, nor can anyone exclude anyone else from using it.
Such goods and services present a problem for the market. Private companies have little reason to provide public goods or services, like roads, street lights, 000 services, clean air, or public health care. That’s because these sorts of goods don’t return them much of a profit. There is little or no reason that anyone would pay to use these services when they can’t be excluded from their use and their stock won’t be depleted. Of course, that has not stopped governments from trying to privatise these things anyway, as we see from toll roads, 000, and private care.
Public goods, private incentives
The primary moral problem that arises in the privatisation of public goods and services is two-fold. First, it puts the provision of important goods and services in the hands of companies whose interests directly oppose the nature of the goods to be provided. Second, people are made vulnerable to an unreliable system of private provision of public goods and services.
A private company’s main objective is to make the most possible profit for shareholders. Given that public goods will not make much of a profit, there is little incentive for a private company to give them attention. This means that essential goods and services, like the 000 service, are deprioritised in favour of those other services that will make the company more of a profit.
Further, people become vulnerable to unreliable service providers, as proper oversight and governance undercuts the profit of private companies. Any time a company has to pay for staff re-training, for revision of protocols, or firing and replacing an employee, they make their profits smaller. So, private companies have incentives to cut corners where they can, and oversight, governance, and quality control seem to be the most frequent things to go.
Most of the time, these cut corners go unnoticed. Until, that is, something goes wrong with the service and people get hurt, or worse.
So why does this system continue?
Successive governments have made the decision to privatise goods and services, making their public expenditures smaller and therefore also making it look like they are being more ‘responsible’ with tax revenues. It’s an attractive look for the neoliberal government, which emphasises how small and non-interventionist it is. But is it working for Australians?
It seems like the government’s quest for a smaller bottom line is at odds with the needs of Australian people. The stable provision of a 000 service, safe hospitals with appropriate oversight, and reliable childcare services with proper governance are all essential goods that Australians want, and which private companies consistently seem unable to provide.
It’s a moral – if not economic – imperative that Australian governments reverse course and begin to provide essential goods and services again. The 000 service, the childcare system, and hospitals provide only a few examples of where the government’s involvement in providing public services is very obviously missing. People are getting hurt, and people are dying, for the sake of private profits.

BY Dr Kathryn MacKay
Kathryn is a Senior Lecturer at Sydney Health Ethics, University of Sydney. Her background is in philosophy and bioethics, and her research involves examining issues of human flourishing at the intersection of ethics, feminist theory and political philosophy. Kathryn’s research is mainly focussed on developing a theory of virtue for public health ethics, and on the ethics of public health communication. Her book Public Health Virtue Ethics is forthcoming with Routledge.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Business + Leadership
Ethics Explainer: Consent
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Pulling the plug: an ethical decision for businesses as well as hospitals
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Hunger won’t end by donating food waste to charity
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Alpha dogs and the toughness trap: How we can redefine modern masculinity
Women’s pain in pregnancy and beyond is often minimised
Women’s pain in pregnancy and beyond is often minimised
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + Wellbeing
BY Laura Kotevska 1 OCT 2025
Some recent discussions of pain relief during pregnancy frame the issue of paracetamol use as a maternal-foetal conflict, ignoring science, eroding trust in doctors, dismissing women’s pain, and limiting women’s autonomy. ‘Toughing it out’ is not the answer.
Last week, US president Donald Trump held a press conference announcing the results of his administration’s investigations into the root causes of autism. During the event, he shared several recommendations for the use of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in pregnancy, namely that women should not use it.
Medical experts have criticised the claims as dangerous and poorly informed, and researchers have shown that the recommendations are politicised interpretations of weaker medical studies. In Australia, the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists’ recommendations for paracetamol use in pregnancy remain unchanged.
While most expert attention has been paid to debunking the administration’s claims and communicating insights from our best scientific knowledge on the topic, less attention has been given to the tenor of the president’s announcement. How can the ethics of pregnancy help us to understand the rhetorical moves of this speech and how we treat women in pregnancy and beyond?
The ethics of pregnancy care
Trump’s recommendation to avoid paracetamol use in pregnancy is predicated on the assumption that doing so is harmful to the foetus. In this instance, it is recommended that a pregnant woman avoid pain relieving medication on the basis that it may cause autism. Putting aside the fact that there is little evidence of the harmful effects of paracetamol use in pregnancy, the White House press conference framed this issue as a maternal-foetal conflict – an instance of maternal interests (in pain or fever relief) conflicting with the interests of the foetus (of not developing autism). According to the White House, the maternal-foetal conflict should be resolved in favour of the foetus with the recommendation that paracetamol use be avoided in all but the most severe cases. In medicine and maternal decision making, prioritising the foetus is very common, but is hardly a foregone conclusion.
Yet in this instance, and in many other obstetric cases, the central conflict is not between the mother and foetus, but between the mother and others who believe they know better.
Here, the adversary is the White House, and the effect of their remarks is the erosion of trust between the pregnant patient and their physician. This is because the pregnant woman must now contend with information that may contradict her doctor’s advice. Such intervention is “counter-productive relative to the goal of promoting foetal health”, researchers Baylis, Rodgers and Young inform us, since this erosion of trust prevents doctors from providing “the education which would promote the birth of healthier babies”.
Secondly, the maternal-foetal conflict framing ignores the fact that the interests of mother and foetus are inextricably linked. Currently, many health experts are at pains to communicate that paracetamol is a safe for treating fevers and providing pain relief, and that sustained fevers in pregnancy can result in miscarriage, birth malformations and, later, still birth while untreated significant pain can also result in complications. Even in cases where there are certain risks to a foetus, withholding or delaying treatment can potentially lead to increased maternal and foetal morbidity and mortality. The White House’s rhetoric simplifies the often challenging or agonising decisions women and their physicians routinely make during pregnancy.
These examples show that protecting a woman’s health is oftentimes the strongest path to guaranteeing foetal and neonatal outcomes. More than this, recommendations that are laden with unscientific bias erode trust in physicians and limit a woman’s capacity to make informed choices, infringing upon women’s autonomy and potentially risking greater foetal harm.
Toughing it out
It was the experience of giving birth that led the author Anushay Hossain to reflect on the treatment of women’s pain. In The Pain Gap, she writes “Doctors still don’t always believe women when they describe their pain, or they dismiss women’s symptoms as being psychosomatic.” For Hussain, the concept of hysteria is useful to explaining a woman’s experience of the medical system. The common characterisation of women’s pain as hysterical, she writes, shifts blame and judgment onto women. The conversation becomes ‘is your pain real? Is it that bad? Why can’t you cope with it?’
This was the text and subtext of the White House press conference last week. On many occasions in his speech and responses to media outlets, Trump told women to ‘tough it out.’ And if you can’t tough it out? “You know, it’s easy for me to say tough it out, but sometimes in life where a lot of other things, you have to tough it out also. Don’t take Tylenol.” Once again, the blame for pain falls at the feet of women.
Setting aside the aforementioned evidence that women ‘toughing it out’ leads to worse outcomes for their foetuses, telling women to tolerate their pain is not only cruel, but also an example of medical misogyny. Medical misogyny describes the gendered ways patients experience healthcare, often marked by missed diagnoses, delayed treatments, and the dismissal or minimisation of symptoms, including but is not limited to pain. It is startlingly common in Australia with 2 out of 3 women reporting experiences of discrimination in healthcare. For non-white women, the experience is worse.
How should we respond?
To address these widespread issues, governments in Australia and the United Kingdom, among others, have established inquiries into women’s pain and reproductive health. More recently, the Sydney Morning Herald has collected patient testimonies that detail women’s experiences of medical misogyny, bringing about wider awareness of the issue and adding urgency to the call for systemic change.
At a time when many individuals and institutions are working to dismantle the gendered and racial barriers to accessing quality healthcare, dismissing women’s suffering and asking them to ‘tough it out’ reinforces a long history of medical misogyny that leaves women unheard, untreated and unwell.

BY Laura Kotevska
Laura Kotevska is Senior Lecturer in the Office of the Deputy Vice-Chancellor Education and Discipline of Philosophy at the University of Sydney.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Moral fatigue and decision-making
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing
Democracy is hidden in the data
Big thinker
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights
Big Thinkers: Thomas Beauchamp & James Childress
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Male suicide is a global health issue in need of understanding
Free speech is not enough to have a good conversation

Free speech is not enough to have a good conversation
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsSociety + Culture
BY Tim Dean 23 SEP 2025
When I facilitate a Circle of Chairs conversation at The Ethics Centre, I always pause before starting and remind myself that I’m about to enter a potentially dangerous space. There are few domains that are as hotly contested and emotionally charged as ethics.
In this space, people might have their deepest values questioned, their most cherished views challenged, and they are likely to encounter people who hold radically different moral and political beliefs to their own.
Yet, after stepping into many Circles, I can’t think of a single time when I haven’t stepped out having witnessed a rich, deep and often challenging conversation that has left everyone feeling closer together as humans, even if they remain far apart in their views.
This is because we don’t just encourage any kind of speech in a Circle of Chairs. We do acknowledge the importance of free speech, not least because it’s our best means of challenging conventional wisdom, correcting errors and seeking the truth. But we also recognise that just protecting free speech sets a perilously low bar for the quality of discourse.
Now seems like a good time to talk about how we talk to each other. Especially so in the wake of conservative commentator, Charlie Kirk’s, assassination in the United States. That horrific event, coupled with two late night talk show hosts being taken off air in recent months, ostensibly due to comments made that have offended the Trump administration and its ideological allies, has sparked numerous conversations about the nature of good faith debate and the limits of free speech.
But if we just limit ourselves to removing speech that is directly harmful, hateful or incites violence, it still leaves a lot of room for speech that can be deceptive, offensive, divisive and dehumanising. Which is why at The Ethics Centre, we treat free speech as a baseline and add other norms on top that serve to promote constructive discourse.
These norms enable people to engage with views that are vastly different to their own – including arguing for their own perspectives and challenging those they believe are wrong – without things slipping into vitriol or worse.
I wonder if these norms might be useful when it comes to think about how we ought to speak to each other. And I stress: these are norms, not laws. They are expectations around how to behave. They’re not intended to be used to silence or punish those who fail to conform to them. They are offered as a guide for those who want to break out of the cycles of polarising and vilifying speech that we see all too often today.
Respect
The first norm is in some ways the simplest, but also the most important: respect. It states that we should always recognise others’ inherent humanity, no matter how obtuse or perverse their beliefs.
What this means is that we might choose not to say something if we think doing so will disrespect or injure their dignity as a person. We already do this in many domains of our lives. If someone has just lost a loved one, we might refrain from criticising the deceased, even if we have a genuine grievance. Likewise, we might choose not to say something we believe is true if it might dehumanise or objectify someone. As they say, “honesty without compassion is cruelty”.
This doesn’t mean we shouldn’t strongly challenge others’ beliefs, especially if we feel they are false or harmful. Sometimes, we should do so even if it might offend them. But there’s a pragmatic element: without mutual respect, our challenges will likely fall on deaf ears, triggering defensiveness rather than encouraging openness.
Showing respect to someone you disagree with is a powerful tool to build the kind of trust that is necessary to have them actually listen to what you have to say. And the more trust and respect you build, the less chance you have of being seen to be disrespectful, and the more frank you can afford to be when you speak.
Good faith
The second norm is to always speak in good faith. This has two elements. The first is that we speak with good intention, with the aim to understand, find the truth and make the world a better place, rather than speaking to intimidate, self-aggrandise or hide an insecurity. The second element is that we speak with intellectual honesty, acknowledging our fallibility and being open to the possibility of being wrong.
We all know it’s all too easy to slip into bad faith, especially when emotions run high or we feel threatened. We might utter a barbed comment, or defend a position we don’t really understand, or we dig in our heels so we don’t look dumb. We also know what it’s like to encounter bad faith, like when you dismantle someone’s argument only to discover they haven’t changed their mind. It’s infuriating, and it can rapidly devolve a conversation into mutual bad faith attacks. You know, like what we see on social media.
Charity
The third norm is charity, which is just the flip side of good faith. Charity means we assume good faith on behalf of the person we’re speaking to rather than assuming the worst about them and their beliefs. It means filling in the blanks with the best possible version of their argument instead of jumping to attack the weakest possible version.
Charity also means giving people an on-ramp back to good faith if we do discover they are speaking in bad faith. Rather than writing them off, we try to show respect and find some mote of common ground – a shared value or belief – and build on that until we can better understand where we diverge, and talk about that.
These norms don’t guarantee all speech will be constructive. They’re not always easy to implement – especially in the unregulated wilderness of social media. But see them as being more aspirational, a kind of soft expectation that we place on ourselves and hope to demonstrate to others through the way we speak.
When we’re mindful of them, they can change conversations. I’ve seen it happen many times. I’ve seen political opponents really listen to each other and acknowledge that the other has a point. I’ve seen a climate denier and an environmental activist hug after a long conversation. I’ve seen an anti-vaxxer thank a science journalist for disagreeing without calling them names. It won’t always go like that. But in a world where we’re thrust into proximity with those we disagree with, where the threat of political violence will always hover in the wings, ready to take the stage when speech fails, I’m convinced these three norms can make a difference.

BY Tim Dean
Dr Tim Dean is a public philosopher, speaker and writer. He is Philosopher in Residence and Manos Chair in Ethics at The Ethics Centre.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships, Society + Culture
Look at this: the power of women taking nude selfies
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
To deal with this crisis, we need to talk about ethics, not economics
LISTEN
Health + Wellbeing, Business + Leadership, Society + Culture
Life and Shares
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Yellowjackets and the way we hunger
Can beggars be choosers?

As a shockingly picky child who rejected everything from unpeeled apples to mashed potatoes, I was the victim of every method of persuasion my parents tried to expand my palate — bribes of candy, hiding foods in other foods, even heartfelt pleas about starving kids hungry enough to be grateful to eat anything.
I didn’t think that last part was true — I couldn’t imagine any hunger powerful enough to overcome my disgust at seafood. While this was the naive view of a privileged seven-year-old, I later realised I was right in a different way. Not about chicken nuggets being peak cuisine, but about the idea that emotional reactions to food — often dismissed as “wants” — cannot be ignored, even for those in need. This idea is central to one of the most significant problems we face in humanitarian aid.
While hunger does make us more receptive to different foods, there are limits to this acceptance. We see this clearly in the case study of Plumpy’Nut, an incredibly powerful Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Food (RUTF) widely used to combat malnutrition. With its calorie and nutrient-rich mixture of peanut butter, milk powder, and essential vitamins, the paste helped 95% of the Malawian children in its first six-week trial in 2001 make a full recovery, while only 25% of children treated through hospitals did. It’s still being used today, including in the Gaza famine.
However, in her book First Bite (2015), Bee Wilson reveals a different side of this otherwise miraculous invention — its reception outside of Africa. In Bangladesh, a place where 2 in 3 children live in food poverty, the sweet, sticky paste hasn’t been nearly as well-received as we might think. Out of 149 Bangladeshi caregivers, six out of ten said Plumpy’Nut was not an acceptable food, and 37% of caregivers said it made their children vomit. Many children despised the smell of the peanuts, a food foreign to Bangladeshi cuisine, while others reviled its sweetness and thick texture. This is despite 112 parents also admitting that it had helped children gain weight.
It was as if they refused to accept that this strange brown paste, so unlike food as they knew it, could satisfy a child’s hunger even despite seeing real results.
If it were true that a “really hungry” child would eat anything, then residents of Dhaka slums ought to be overjoyed to receive free packets of Plumpy’Nut. However, they were clearly not, showing that food-induced disgust is psychologically and culturally hardwired rather than a mere matter of fussiness.
Cultural beliefs persist even in extreme conditions, so we must take them into account when designing effective humanitarian aid. Even under a utilitarian worldview that prioritises physiological “needs” over “wants” in an attempt to save as many lives as possible, aid only has good consequences if it is accepted. When it incites physical revulsion, the intended benefits vanish, leaving behind not only wasted resources but also preventable lifelong medical consequences. In order to truly “feed the most people,” providers of aid are ethically obligated to ensure that it aligns with cultural expectations.
However, this example also highlights a deeper moral problem. By ranking “needs” over “wants,” we send the message that people in need don’t deserve to have their preferences or cultures considered. When we treat the defining parts of someone’s identity as secondary, we risk dehumanising them — reducing them to interchangeable bodies to be fed, instead of people with dignity. Treating aid as a one-size-fits-all endeavour also renders the recipient’s cultural context, like the Bangladeshi aversion to peanuts, an inconvenient obstacle rather than essential knowledge. This perpetuates the core power imbalance of aid: the giver defines the problem and solution, while the receiver is stripped of agency, reduced to a passive vessel for Western benevolence, resulting in a reinforcement of dependency under the guise of charity rather than any true empowerment.
As philosopher Martha Nussbaum argues in her book Creating Capabilities (2011), true wellbeing isn’t merely about fulfilling basic biological requirements like calories. It’s about expanding the substantive freedoms and capabilities people have to live lives they value, including the ability to use their senses without revulsion, to participate in cultural practices, and to make choices about their own nourishment. Forcing a child to eat something they do not culturally see as food, despite its nutritional value, actively damages this capability.
This hierarchy of needs and wants therefore doesn’t alleviate suffering holistically — it trades one form of deprivation (hunger) for another (the denial of autonomy).
Even though research has now expanded into culturally appropriate RUTFs, such as a mung bean cake called “hebi” for use in Vietnam, it is revealing that these initiatives only began after the failure of Plumpy’Nut. When it comes to for-profit enterprises targeting wealthier consumers, market research is an essential part of preparation — think KFC rice and congee in China, or the Teriyaki McBurger in Japan. We know people have different palates across the world, and usually consider it. So why assume Plumpy’Nut would succeed unchanged in both Malawi and Bangladesh, two places with completely different cuisines?
We cannot simply rely on trial and error to improve the ways we distribute humanitarian aid. To truly help people — people, not just bodies to be sustained — we must consider the full picture of their identities. Dignity is the foundation upon which effective, lasting help is built because ultimately, humanitarianism that ignores the human is a contradiction. As citizens in a world where humanitarian crises dominate headlines, understanding these dynamics matters not just for policymakers, but for anyone who donates, protests, or speaks out in response to global events.

BY Sophie Yu
Sophie Yu is a Year 12 student at Redlands, Sydney, where she studies the International Baccalaureate. She is interested in philosophy, culture, and international affairs, and explores these through the mediums of public speaking, writing and the visual arts.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Is it wrong to care about Ukraine more than other wars?
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
An angry electorate
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Science + Technology
The value of a human life
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
COP26: The choice of our lives
3 things we learnt from The Ethics of AI
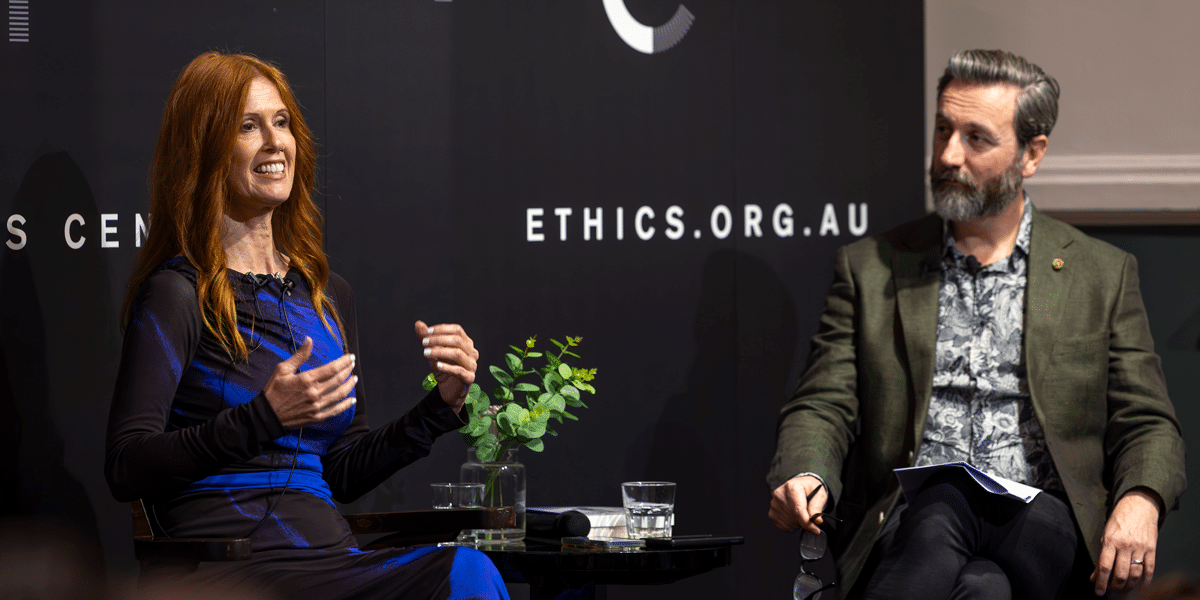

3 things we learnt from The Ethics of AI
Opinion + AnalysisScience + TechnologyBusiness + Leadership
BY The Ethics Centre 17 SEP 2025
As artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly accessible and integrated into our daily lives, what responsibilities do we bear when engaging with and designing this technology? Is it just a tool? Will it take our jobs? In The Ethics of AI, philosopher Dr Tim Dean and global ethicist and trailblazer in AI, Dr Catriona Wallace, sat down to explore the ethical challenges posed by this rapidly evolving technology and its costs on both a global and personal level.
Missed the session? No worries, we’ve got you covered. Here are 3 things we learnt from the event, The Ethics of AI:
We need to think about AI in a way we haven’t thought about other tools or technology
In 2023, The CEO of Google, Sundar Pichai described AI as more important than the invention of fire, claiming it even surpassed great leaps in technology such as electricity. Catriona takes this further, calling AI “a new species”, because “we don’t really know where it’s all going”.
So is AI just another tool, or an entirely new entity?
When AI is designed, it’s programmed with algorithms and fed with data. But as Catriona explains, AI begins to mirror users’ inputs and make autonomous decisions – often in ways even the original coders can’t fully explain.
Tim points out that we tend to think of technology instrumentally, as a value neutral tool at our disposal. But drawing from German philosopher Martin Heidegger, he reminds us that we’re already underthinking tools and what they can do – tools have affordances, they shape our environment and steer our behaviour. So “when we add in this idea of agency and intentionality” Tim says, “it’s no longer the fusion of you and the tool having intentionality – the tool itself might have its own intentions, goals and interests”.
AI will force us to reevaluate our relationship with work
The 2025 Future of Jobs Report from The World Economic Forum estimates that by 2030, AI will replace 92 million current jobs but 170 million new jobs will be created. While we’ve already seen this kind of displacement during technological revolutions, Catriona warns that the unemployed workers most likely won’t be retrained into the new roles.
“We’re looking at mass unemployment for front line entry-level positions which is a real problem.”
A universal basic income might be necessary to alleviate the effects of automation-driven unemployment.
So if we all were to receive a foundational payment, what does the world look like when we’re liberated from work? Since many of us tie our identity to our jobs and what we do, who are we if we find fulfilment in other types of meaning?
Tim explains, “work is often viewed as paid employment, and we know – particularly women – that not all work is paid, recognised or acknowledged. Anyone who has a hobby knows that some work can be deeply meaningful, particularly if you have no expectation of being paid”.
Catriona agrees, “done well, AI could free us from the tie to labour that we’ve had for so long, and allow a freedom for leisure, philosophy, art, creativity, supporting others, caring for loving, and connection to nature”.
Tech companies have a responsibility to embed human-centred values at their core
From harmful health advice to fabricating vital information, the implications of AI hallucinations have been widely reported.
The Responsible AI Index reveals a huge disconnect between businesses leaders’ understanding of AI ethics, with only 30% of organisations knowing how to implement ethical and responsible AI. Catriona explains this is a problem because “if we can’t create an AI agent or tool that is always going to make ethical recommendations, then when an AI tool makes a decision, there will always be somebody who’s held accountable”.
She points out that within organisations, executives, investors, and directors often don’t understand ethics deeply and pass decision making down to engineers and coders — who then have to draw the ethical lines. “It can’t just be a top-down approach; we have to be training everybody in the organisation.”
So what can businesses do?
AI must be carefully designed with purpose, developed to be ethical and regulated responsibly. The Ethics Centre’s Ethical by Design framework can guide the development of any kind of technology to ensure it conforms to essential ethical standards. This framework can be used by those developing AI, by governments to guide AI regulation, and by the general public as a benchmark to assess whether AI conforms to the ethical standards they have every right to expect.
The Ethics of AI can be streamed On Demand until 25 September, book your ticket here. For a deeper dive into AI, visit our range of articles here.

BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Why we can’t learn from our past (and shouldn’t try to)
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
Facing tough decisions around redundancies? Here are some things to consider
Reports
Business + Leadership
A Guide to Purpose, Values, Principles
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Between frenzy and despair: navigating our new political era
Ask an ethicist: Should I use AI for work?
Ask an ethicist: Should I use AI for work?
Opinion + AnalysisScience + TechnologyBusiness + Leadership
BY Daniel Finlay 8 SEP 2025
My workplace is starting to implement AI usage in a lot of ways. I’ve heard so many mixed messages about how good or bad it is. I don’t know whether I should use it, or to what extent. What should I do?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is quickly becoming unavoidable in our daily lives. Google something, and you’ll be met with an “AI overview” before you’re able to read the first result. Open up almost any social media platform and you’ll be met with an AI chat bot or prompted to use their proprietary AI to help you write your message or create an image.
Unsurprisingly, this ubiquity has rapidly extended to the workplace. So, what do you do if AI tools are becoming the norm but you’re not sure how you feel about it? Maybe you’re part of the 36% of Australians who aren’t sure if the benefits of AI outweigh the harms. Luckily, there’s a few ethical frameworks to help guide your reasoning.
Outcomes
A lot of people care about what AI is going to do for them, or conversely how it will harm them or those they care about. Consequentialism is a framework that tells us to think about ethics in terms of outcomes – often the outcomes of our actions, but really there are lots of types of consequentialism.
Some tell us to care about the outcomes of rules we make, beliefs or attitudes we hold, habits we develop or preferences we have (or all of the above!). The common thread is the idea that we should base our ethics around trying to make good things happen.
This might seem simple enough, but ethics is rarely simple.
AI usage is having and is likely to have many different competing consequences, short and long-term, direct and indirect.
Say your workplace is starting to use AI tools. Maybe they’re using email and document summaries, or using AI to create images, or using ChatGPT like they would use Google. Should you follow suit?
If you look at the direct consequences, you might decide yes. Plenty of AI tools give you an edge in the workplace or give businesses a leg up over others. Being able to analyse data more quickly, get assistance writing a document or generate images out of thin air has a pretty big impact on our quality of life at work.
On the other hand, there are some potentially serious direct consequences of relying on AI too. Most public large language model (LLM) chatbots have had countless issues with hallucinations. This is the phenomenon where AI perceives patterns that cause it to confidently produce false or inaccurate information. Given how anthropomorphised chatbots are, which lends them an even higher degree of our confidence and trust, these hallucinations can be very damaging to people on both a personal and business level.
Indirect consequences need to be considered too. The exponential increase in AI use, particularly LLM generative AI like ChatGPT, threatens to undo the work of climate change solutions by more than doubling our electricity needs, increasing our water footprint, greenhouse gas emissions and putting unneeded pressure on the transition to renewable energy. This energy usage is predicted to double or triple again over the next few years.
How would you weigh up those consequences against the personal consequences for yourself or your work?
Rights and responsibilities
A different way of looking at things, that can often help us bridge the gap between comparing different sets of consequences, is deontology. This is an ethical framework that focuses on rights (ways we should be treated) and duties (ways we should treat others).
One of the major challenges that generative AI has brought to the fore is how to protect creative rights while still being able to innovate this technology on a large scale. AI isn’t capable of creating ‘new’ things in the same way that humans can use their personal experiences to shape their creations. Generative AI is ‘trained’ by giving the models access to trillions of data points. In the case of generative AI, these data points are real people’s writing, artwork, music, etc. OpenAI (creator of ChatGPT) has explicitly said that it would be impossible to create these tools without the access to and use of copyrighted material.
In 2023, the Writers Guild of America went on a five-month strike to secure better pay and protections against the exploitation of their material in AI model training and subsequent job replacement or pay decreases. In 2025, Anthropic settled for $1.5 billion in a lawsuit over their illegal piracy of over 500,000 books used to train their AI model.
Creative rights present a fundamental challenge to the ethics of using generative AI, especially at work. The ability to create imagery for free or at a very low cost with AI means businesses now have the choice to sidestep hiring or commissioning real artists – an especially fraught decision point if the imagery is being used with a profit motive, as it is arguably being made with the labour of hundreds or thousands of uncompensated artists.
What kind of person do you want to be?
Maybe you’re not in an office, though. Maybe your work is in a lab or field research, where AI tools are being used to do things like speed up the development of life-changing drugs or enable better climate change solutions.
Intuitively, these uses might feel more ethically salient, and a virtue ethics point of view could help make sense of that. Virtue ethics is about finding the valuable middle ground between extreme sets of characteristics – the virtues that a good person, or the best version of yourself, would embody.
On the one hand, it’s easy to see how this framework would encourage use of AI that helps others. A strong sense of purpose, altruism, compassion, care, justice – these are all virtues that can be lived out by using AI to make life-changing developments in science and medicine for the benefit of society.
On the other hand, generative AI puts another spanner in the works. There is an increasing body of research looking at the negative effects of generative AI on our ability to think critically. Overreliance and overconfidence in AI chatbots can lead to the erosion of critical thinking, problem solving and independent decision making skills. With this in mind, virtue ethics could also lead us to be wary of the way that we use particular kinds of AI, lest we become intellectually lazy or incompetent.
The devil in the detail
AI, in all its various capacities, is revolutionising the way we work and is clearly here to stay. Whether you opt in or not is hopefully still up to you in your workplace, but using a few different ethical frameworks, you can prioritise your values and principles and decide whether and what type of AI usage feels right to you and your purpose.
Whether you’re looking at the short and long-term impacts of frequent AI chatbot usage, the rights people have to their intellectual property, the good you can do with AI tools or the type of person you want to be, maintaining a level of critical reflection is integral to making your decision ethical.

BY Daniel Finlay
Daniel is a philosopher, writer and editor. He works at The Ethics Centre as Youth Engagement Coordinator, supporting and developing the futures of young Australians through exposure to ethics.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Ethics Explainer: Dirty Hands
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing
Make an impact, or earn money? The ethics of the graduate job
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Relationships, Science + Technology
From NEG to Finkel and the Paris Accord – what’s what in the energy debate
Opinion + Analysis
Science + Technology, Health + Wellbeing
Does your therapy bot really care about you? The risks of offloading emotional work to machines
What happens when the progressive idea of cultural ‘safety’ turns on itself?

What happens when the progressive idea of cultural ‘safety’ turns on itself?
Opinion + AnalysisSociety + CulturePolitics + Human Rights
BY Hugh Breakey 4 SEP 2025
In mid-August, controversy enveloped the Bendigo Writers Festival. Just days before it began, festival organisers sent a code of conduct to its speakers – a code that drove more than 50 authors to make the difficult decision to pull out.
The code was intended to ensure the event’s safety, with a requirement to “avoid language or topics that could be considered inflammatory, divisive, or disrespectful”. Yet distressed speakers argued it made them feel culturally unsafe. Speakers on panels presented by La Trobe university were also required to employ a contested definition of antisemitism.
The incident is the most recent in a series of controversies in which progressive writers and artists have faced restrictions and cancellations, with organisations citing “safety” as the reason. They include libraries cancelling invited speakers and asking writers to avoid discussing Gaza, Palestine and Israel.
How did speech rules developed and promoted by the progressive left – rules promoting cultural safety and safe spaces – become tools that could be wielded against it?
Applying ‘safety’ to speech
Over recent years, “safety” – including in terms like “safe spaces” and “cultural safety” – has become a commonly raised ethical concern. Safe-speech norms often arise in the context of public deliberation, education and political speech.
“Safe spaces” are places where marginalised groups are protected against harassment, oppression and discrimination, including through speech like microaggressions, unthinking stereotypes and misgendering. Within safe spaces, protected groups are encouraged and empowered to speak about their experiences and needs.
Similarly, “cultural safety” refers to environments where there is no challenge or denial of people’s identities, allowing them to be genuinely heard. This can be crucial for First Nations communities, especially in health and legal contexts.
Safe-speech norms are therefore complex. They involve the freedom to speak, but also freedom from speech.
This way of thinking takes a broad view of the kinds of speech that can be interpreted as harmful or violent. Harmful speech does not just include hate speech and incitement. It also includes speech with unintended consequences and speech that challenges a person’s perceived identity.
These safe-speech norms, increasingly adopted in universities and other broadly progressive organisations, should be distinguished from “psychological safety”. This earlier concept refers to creating environments – such as workplaces – where it is safe to speak up, including to raise concerns or ask questions.
While psychological safety is a general norm protecting all parties, the more recent safe-speech norms protect specific marginalised groups. They aim to push back against larger systemic forces like racism or misogyny that would otherwise render those groups oppressed or unsafe. In some cases, the prioritisation of safety has led to deplatforming of speakers at universities.
With this special focus on oppressed minorities and heightened sensitivity to speech’s negative impacts, applying these norms has become a familiar part of progressive social justice efforts (sometimes pejoratively called “wokism”). Now, conservatives and others are employing the language of cultural safety to close down discussion of topics such as the war in Gaza.
Are safe-speech norms controversial?
By constraining what can be said, safe speech norms impinge on other potentially relevant ethical norms, such as those of public deliberation. These “town square” norms aim to encourage a diversity of views and allow space for a robust dialogue between different perspectives.
Public deliberation norms might be defended as part of the human right to free speech, or because arguing and deliberating with other people can be an important way of respecting them.
Alternatively, public deliberation can be defended by appeal to democracy, which requires more than merely casting votes. Citizens must be able to hear and voice different perspectives and arguments.
Those in favour of free speech and the public square will look suspiciously at safe-speech norms, worrying that they give rise to the well known risks of political censorship. Thinkers like Jonathan Haidt and Greg Lukianoff explicitly criticise “safetyism”, arguing the prioritisation of emotional safety inappropriately coddles young people.
Supporters of safe-speech norms might respond in different ways to these objections. One response might be that safety doesn’t intrude very much on dialogue anyway (at least, not on the type of dialogue worth having). Another response might be to challenge the value of public debate itself, seeing any system that does not explicitly work to support the marginalised as inherently oppressive.
Yet another response might be to query whether writers festivals are an apt place for public debate. Most speakers want an enjoyable experience and to promote their book (even when such books explore contentious ideas). Many in the audience will be supportive of the authors’ ideas and positions. Some will even be fans. Maybe it’s not so bad if most festival sessions are “love-ins”.
Prohibited vs. protected
In order to protect and empower specific marginalised groups, safe-speech norms both support and restrain speech. So long as the views of these protected groups are relatively aligned with each other, these norms work coherently. The speech that is being prohibited doesn’t overlap with the speech that is being protected.
But what happens when members of two marginalised groups have stridently opposed views and the words they use to decry injustice are called unsafe by their opponents? Once this happens, the speech that one group needs to be protected is the same speech that the other group needs prohibited.
Perhaps it was inevitable that the internal contradictions of safe-speech norms would eventually create such problems. In Australia, like many countries, this was triggered by the October 7 Hamas atrocity and Israel’s unrelenting and brutal military response. Jews and Palestinians are both vulnerable minorities who face the well known bigotries of antisemitism and Islamophobia respectively. They both can reasonably demand the protection of safe-speech norms.
However, is each side interested in respecting the other’s right to such norms? Author and academic Randa Abdel-Fattah has reportedly alleged on social media, that if you are a Zionist, “you have no claim or right to cultural safety”. In turn, she says she has been harrassed and threatened over her views on the war in Gaza, and public institutions hosting her “have been targeted with letters defaming me and demanding I be disinvited”.
Perhaps the time has come to acknowledge that safe speech norms were never as straightforward or innocuous as they first appeared. They require a form of censorship that not only involves choosing political sides, but inevitably making fine-grained judgements between which opposing minority deserves protection at the expense of the other.
Indeed, safe speech norms may themselves be exclusionary. The US organisation “Third Way” advocates for moderation and centre left policies. In a recent memo it said research among focus groups had consistently found ordinary people interpreted key terms from progressive political language as alienating and arrogant.
According to Third Way, the term “safe space” (among others) communicates the sense that, “I’m more empathetic than you, and you are callous to hurting others’ feelings.”
With all this in mind, I find it hard to disagree with author Waleed Aly’s recent reflection that “in arenas dedicated to public debate, safety makes a poor organising principle”. Efforts to support and include marginalised voices are laudable. However, safe-speech norms are a deeply problematic – and perhaps ultimately contradictory – tool to use in pursuing that worthy goal.
This article was originally published in The Conversation.

BY Hugh Breakey
Hugh is Deputy Director at Griffith University’s Institute for Ethics, Governance and Law. His research spans the philosophical subdisciplines of political philosophy, normative ethics, moral psychology, governance studies and applied philosophy. His works explore the ethical challenges arising in such diverse fields as peacekeeping, institutional governance, climate change, sustainable tourism, safety industries, private property, medicine, and international law, published in journals including The Philosophical Quarterly, The Modern Law Review and Political Studies. He has taught philosophy and ethics at the University of Queensland, Queensland University of Technology and Bond University. Since 2013, Hugh has served as President of the Australian Association for Professional and Applied Ethics.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Reports
Politics + Human Rights
Ethical by Design: Evaluating Outcomes
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
If you don’t like politicians appealing to voters’ more base emotions, there is something you can do about it
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
What money and power makes you do: The craven morality of The White Lotus
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Free speech is not enough to have a good conversation
AI and rediscovering our humanity

AI and rediscovering our humanity
Opinion + AnalysisScience + TechnologyBusiness + LeadershipSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff 2 SEP 2025
With each passing day, advances in artificial intelligence (AI) bring us closer to a world of general automation.
In many cases, this will be the realisation of utopian dreams that stretch back millennia – imagined worlds, like the Garden of Eden, in which all of humanity’s needs are provided for without reliance on the ‘sweat of our brows’. Indeed, it was with the explicit hope that humans would recover our dominion over nature that, in 1620, Sir Francis Bacon published his Novum Organum. It was here that Bacon laid the foundations for modern science – the fountainhead of AI, robotics and a stack of related technologies that are set to revolutionise the way we live.
It is easy to underestimate the impact that AI will have on the way people will work and live in societies able to afford its services. Since the Industrial Revolution, there has been a tendency to make humans accommodate the demands of industry. In many cases, this has led to people being treated as just another ‘resource’ to be deployed in service of profitable enterprise – often regarded as little more than ‘cogs in the machine’. In turn, this has prompted an affirmation of the ‘dignity of labour’, the rise of Labor unions and with the extension of the voting franchise in liberal democracies, to legislation regulating working hours, standards of safety, etc. Even so, in an economy that relies on humans to provide the majority of labour required to drive a productive economy, too much work still exposes people to dirt, danger and mind-numbing drudgery.
We should celebrate the reassignment of such work to machines that cannot ‘suffer’ as we do. However, the economic drivers behind the widescale adoption of AI will not stop at alleviating human suffering arising out of burdensome employment. The pressing need for greater efficiency and effectiveness will also lead to a wholesale displacement of people from any task that can be done better by an expert system. Many of those tasks have been well-remunerated, ‘white collar’ jobs in professions and industries like banking, insurance, and so on. So, the change to come will probably have an even larger effect on the middle class rather than working class people. And that will be a very significant challenge to liberal democracies around the world.
Change to the extent I foresee, does not need to be a source of disquiet. With effective planning and broad community engagement, it should be possible to use increasingly powerful technologies in a constructive manner that is for the common good. However, to achieve this, I think we will need to rediscover what is unique about the human condition. That is, what is it that cannot be done by a machine – no matter how sophisticated? It is beyond the scope of this article to offer a comprehensive answer to this question. However, I can offer a starting point by way of an example.
As things stand today, AI can diagnose the presence of some cancers with a speed and effectiveness that exceeds anything that can be done by a human doctor. In fact, radiologists, pathologists, etc are amongst the earliest of those who will be made redundant by the application of expert systems. However, what AI cannot do replace a human when it comes to conveying to a patient news of an illness. This is because the consoling touch of a doctor has a special meaning due to the doctor knowing what it means to be mortal. A machine might be able to offer a convincing simulation of such understanding – but it cannot really know. That is because the machine inhabits a digital world whereas we humans are wholly analogue. No matter how close a digital approximation of the analogue might be, it is never complete. So, one obvious place where humans might retain their edge is in the area of personal care – where the performance of even an apparently routine function might take on special meaning precisely because another human has chosen to care. Something as simple as a touch, a smile, or the willingness to listen could be transformative.
Moving from the profound to the apparently trivial, more generally one can imagine a growing preference for things that bear the mark of their human maker. For example, such preferences are revealed in purchases of goods made by artisanal brewers, bakers, etc. Even the humble potato has been affected by this trend – as evidenced by the rise of the ‘hand-cut chip’.
In order to ‘unlock’ latent human potential, we may need to make a much sharper distinction between ‘work’ and ‘jobs’.
That is, there may be a considerable amount of work that people can do – even if there are very few opportunities to be employed in a job for that purpose. This is not an unfamiliar state of affairs. For many centuries, people (usually women) have performed the work of child-rearing without being employed to do so. Elders and artists, in diverse communities, have done the work of sustaining culture – without their doing so being part of a ‘job’ in any traditional sense. The need for a ‘job’ is not so that we can engage in meaningful work. Rather, jobs are needed primarily in order to earn the income we need to go about our lives.
And this gives rise to what may turn out to be the greatest challenge posed by the widescale adoption of AI. How, as a society, will we fund the work that only humans can do once the vast majority of jobs are being done by machines?

BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
Ask an ethicist: Is it OK to steal during a cost of living crisis?
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Business + Leadership
Teachers, moral injury and a cry for fierce compassion
Opinion + Analysis
Science + Technology, Society + Culture
AI is not the real enemy of artists
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
The ethics of pets: Ownership, abolitionism and the free-roaming model
We can raise children who think before they prompt

We can raise children who think before they prompt
Opinion + AnalysisScience + Technology
BY Emma Wilkins 26 AUG 2025
We may not be able to steer completely clear of AI, or we may not want to, but we can help our kids to understand what it is and isn’t good for, and make intentional decisions about when and how to use it.
ChatGPT and other artificial “help” is already so widely used that even parents and educators who worry about the ways it might interfere with children’s learning and development, seem to accept that it’s a tool their kids will have to learn to use.
In her forthcoming book The Human Edge, critical thinking specialist Bethan Winn says that because AI is already embedded in our world, the questions to ask now are around which human skills we need to preserve and strengthen, and where we draw the line between assistance and dependence.
By taking time to “play, experiment, test hypotheses, and explore”, Winn suggests we can equip our kids and ourselves with the tools to think critically. This will help us “adapt intelligently” and set our own boundaries, rather than defaulting lazily and unthinkingly to what “most people” seem okay with.
What we view as “good”, what decisions we make, and encourage, and discourage, our children to make, will depend on what we value. One of the reasons corporations and governments have been so quick to embrace AI is that they prize efficiency, productivity and profit; and fear falling behind. But in the private sphere, we can make different decisions based on different values.
If, for example, we value learning and creativity, the desire to build up skills and knowledge will help us to resist using AI to brainstorm and create on our behalf. We’ll need to help our kids to see that how they produce something can matter just as much as what they produce, because it’s natural to value success too. We’ll also need to make learning fun and satisfying, and discourage short-term wins over long-term gains.
Myself and my husband are quick to share cautionary tales – from the news, books, podcasts, our own experiences and those of our friends – about less than ideal uses of AI. He tells funny stories about the way candidates he interviews misuse it, I tell funny stories about how disastrously I’d misquote people if I relied on generated transcripts. I also talk about why I’m not tempted to rely on AI to write for me – I want to keep using my brain, developing my skills, choosing my sources; I want to arrive at understanding and insight, not generate it, even if that takes time and energy. (I also can’t imagine prompting would be nearly as fun).
Concern for the environment can also offer incentive to use our brains, or other less energy-intensive tools, before turning to AI. And if we value truth and accuracy, the reality that AI often presents information that’s false as fact will provide incentive to think twice before using it, or strong motivation to verify its claims when we do. Just because an “AI overview” is the first result in an internet search, doesn’t mean we can’t scroll past it to a reputable source. Tech companies encourage one habit, but we can choose to develop another.
And if we’ve developed a habit of keeping a clear conscience, and if we value honesty and integrity, we’ll find it easier to resist using AI to cheat, no matter how easy or “normal” it becomes. We’ll also be concerned by the unethical ways in which large language models have been trained using people’s intellectual property without their consent.
As our kids grow more independent, they might not retain the same values, or make the same decisions, as we do. But if they’ve formed a habit of using their values to guide their decisions, there’s a good chance they’ll continue it.
In addition to hoping my children adopt values that will make them wise, caring, loving, human beings, I hope they’ll understand their unique value, and the unique value all humans have. It’s the existential threat AI poses, when it seems to outperform us not only intellectually but relationally, that might be the most concerning one of all.
In a world where chatbots are designed to flatter, befriend, even seduce, we can’t assume the next generation will value human relationships – even human life and human rights – in the way previous generations did. Already, some prefer a chatbot’s company to that of their own friends and family.
Parents teaching their children about values is nothing new. Nor is contradicting our speech with our actions in ways our children are bound to notice. We know we should set the example we want our kids to follow, but how often do we fall short of our own standards? In our defense, we’re only human.
We’re “only” human. In other words, we’re not divine. And AI is neither human nor divine. Whether or not we agree that humans are made in the image of God – are “the work of his hands” – I hope we can agree that we’re more valuable than the work of our hands, no matter how incredible that work might be.
Of all the opportunities AI affords us and our children, the prompt to consider what it means to be human, to ask ourselves deep questions about who we are and why we’re here, may be the most exciting one of all.

BY Emma Wilkins
Emma Wilkins is a journalist and freelance writer with a particular interest in exploring meaning and value through the lenses of literature and life. You can find her at: https://emmahwilkins.com/
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships, Science + Technology, Society + Culture
Who does work make you? Severance and the etiquette of labour
Opinion + Analysis
Science + Technology, Business + Leadership
Ask an ethicist: Should I use AI for work?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Science + Technology
5 dangerous ideas: Talking dirty politics, disruptive behaviour and death
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships, Science + Technology