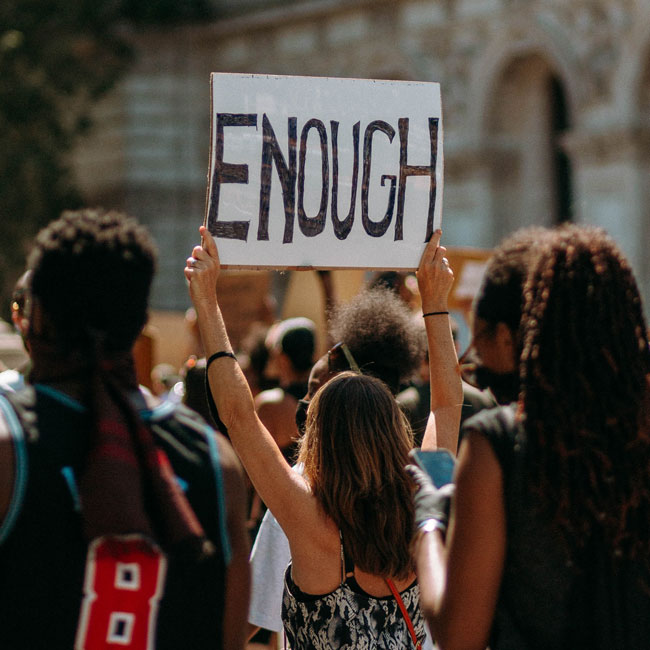We're being too hard on hypocrites and it’s causing us to lose out

We’re being too hard on hypocrites and it’s causing us to lose out
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Dr Cressida Gaukroger 19 MAY 2022
Everyone hates a hypocrite. And apparently they are everywhere.
In the last week alone British Labour leader Keir Starmer has been accused of hypocrisy for having a beer and curry with colleagues in violation of lockdown rules; feminist social commentator and writer (and election candidate) Jane Caro has been labelled a hypocrite for advocating action on climate change, but also flying a lot; teal independents have been called hypocrites for their sources of funding after criticising Australia’s donation rules; the president of the Solomon Islands has accused Australia of hypocrisy for criticising their security pact with China while pursuing its own AUKUS agreement…
Hypocrisy is a sin regularly and loudly identified in politics and the media. And not without cause. However, this discourse regularly goes too far, to no good end.
We should be less critical of hypocrisy. Our obsession with hypocrisy prevents us from engaging in reasoned debate, it robs us of the tools to identify and express what others are doing wrong, and it risks leading us and others to becoming worse people.
What is the problem with hypocrites?
Though the term ‘hypocrite’ is often used as a catch-all term of moral condemnation, vaguely pointing to people whose actions appear to be inconsistent with their words, it is worth distinguishing between different types of hypocrites.
First there are insincere hypocrites – people who lie to gain advantage. Their actions, however, reveal that they genuinely do not hold the convictions they espouse. They are intentionally mis-leading and using others. Which is particularly egregious when they hold significant power over others as is in the case of politicians. But note that, here, the lying and manipulation are typically far more serious offences than the inconsistency and hypocrisy.
There are also exceptionalist hypocrites – those who make or police rules which they have no qualms about violating themselves. At the heart of it, this feels really unfair. However, it is not a universal wrong. Think of parents who make rules for their children that they do not follow – “you are not allowed to drink”, they say, while nursing a glass of wine; “it is always wrong to lie”, they say, while putting out mince pies for Father Christmas.
Such exceptionalist hypocrisy can sometimes reveal a greater wrong, or potential for wrong. For example, Boris Johnson made laws that kept large parts of his country in lockdown, but was breaking social distancing rules and attending parties. His actions demonstrated a lack of respect for others and, importantly, for those people whose interests he is meant to represent. The hypocrite hater could also point out that Johnson’s actions likely contributed to less adherence to the rules as people looked at his actions and felt “if he gets to do that, why shouldn’t I?”. However, modelling bad behaviour can encourage bad behaviour in others whether or not it is exhibited by a hypocrite. In this respect, the hypocrisy does not worsen the situation.
And then there is the weak-willed or inadvertent hypocrite. This person fails to live up to their espoused rules or ethical principles, not due to malice or deep insincerity, or because they think the rules don’t apply to them, but because it can be hard to be really good all the time. Think of the Christian who believes in the sanctity of marriage but finds themself desperate to leave a loveless marriage. The animal rights advocate who cares passionately about protecting native wildlife, but can’t bring themself to give up their beloved cat that steadfastly resists being kept indoors.
Inadvertent hypocrites may do better to reflect on their own experiences of struggle before harshly criticising others for not living up to their principles. But if they are unempathetic or overly aggressive in their attacks on others who violate their ethical rules, isn’t that the greater crime than not fully living up to those rules themselves? Wouldn’t that be problematic whether or not they lived according to those rules? And is it unempathetic of us to demonise the inadvertent hypocrite for an understandable weakness of will?
We shouldn’t just dismiss hypocrites
As soon as someone is called a hypocrite we feel licence to ignore them. But just because someone is bad, that doesn’t mean what they are saying is incorrect. Rather than shutting hypocrites down it is rational to ask if their hypocrisy is relevant to their argument.
Consider the smoker suffering from lung cancer who tells young people not to smoke because it can ruin their lives. Is their testimony any less reliable because they did not listen to their own advice? Or an environmental activist who flies to climate action conferences. Does this mean that they are any less right when they say we need to take action on climate change?
Our focus on hypocrisy can distract attention from the real issues or moral problems with a person (or institution) or their actions, such as: Are they lying to or manipulating people? Are they showing that they don’t respect the people they are meant to represent? Are they being aggressive or unsympathetic to others? Are they espousing something false or acting in a way that is morally wrong – whether or not their actions and words match up?
This should not dissuade people from rationally engaging in discussions with others about whether their moral principles are consistent. Highlighting ethical inconsistencies is the bread and butter of contemporary moral philosophy. If holding one principle should entail another but your friend holds the first while rejecting the second, talking through this can shed light on their values: help them realise the connection between the two. But throwing around the term ‘hypocrisy’ when you do it can turn a potentially neutral observation that they should reflect more on whether their ethical principles are consistent (shouldn’t we all?) to simply telling them that they are bad.
Being inconsistent is better than being consistently bad
A hypocrite says one thing and does another: so at least they are getting something right. Would we prefer someone who is all bad?
An obsession with hypocrisy can lead us to expect moral perfection in everyone. But inconsistency is part of moral life. There is nothing wrong with having high moral standards while recognising that we won’t always meet them.
Our desire for consistency can lead to unachievably high expectations that, when unmet, lead us to rejecting an entire principle or endeavour rather than living with our moral imperfections and trying to gradually improve our actions next time. Like the dieter who fasts for a week and then immediately gives up because of one slip with a slice of cake, or the long-time vegetarians or vegans who returned to eating meat after an extended stint in a country where vegetarian options were extremely limited. It is not surprising that they broke with their vegetarian principles while in those countries. It may well have been inconsistent with the view that all else being equal it is wrong to eat meat, but that makes it no less understandable an action to take. Rather, it is surprising that they continued to eat meat once they returned to a country where vegetarians were once again well catered for. Their actions changed first and their values followed. They ended up being more consistent perhaps, but (at least for those who believe that it is wrong to eat meat) things went the wrong way.
We are all hypocrites sometimes. The desperate desire to avoid hypocrisy can lead us to strive to be all good and, when that fails, to be all bad, rather than trying to be ‘good enough’ – being guided by moral principles we will likely never fully live up to.
My recommendation is to take it easy on hypocrisy. If you are in a debate, attack arguments not people. Where people are bad the wrongness of their actions or words should speak for themselves, and you should focus on pointing out the actual problem with them, rather than using a catch-all term. When it comes to yourself it may also help to start by aiming for the good, not the perfect. Improving incrementally is still improvement, even if it sometimes means you will be inconstant.
And if all of that doesn’t convince you, then you better hope that you have never exhibited inconsistency in your own principles and your actions. Because if you have, judging others for being hypocritical would be, well, very hypocritical of you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
I’d like to talk to you: ‘The Rehearsal’ and the impossibility of planning for the right thing
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Five dangerous ideas to ponder over the break
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
He said, she said: Investigating the Christian Porter Case
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A new era of reckoning: Teela Reid on The Voice to Parliament
BY Dr Cressida Gaukroger
Dr Cressida Gaukroger is a former lecturer in Ethics at Oxford University now a Senior Policy Advisor focusing on wellbeing-led approaches to government.
Housing affordability crisis: The elephant in the room stomping young Australians

Housing affordability crisis: The elephant in the room stomping young Australians
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Intifar Chowdhury 16 MAY 2022
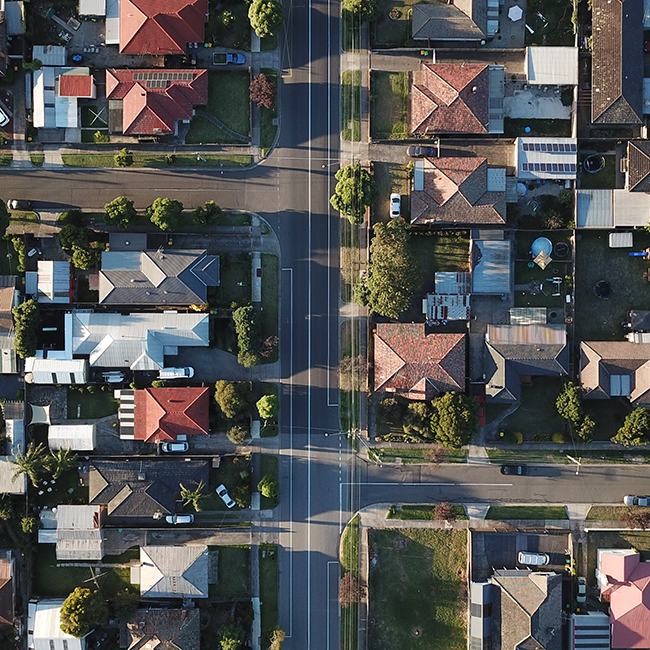
Affordably housing its peoples is a hallmark of a developed society. Yet, Australia’s housing system has been failing young people, argues Intifar Chowdhury.
Squeezed by rising rents and aggressive increase in property prices, young Australians are increasingly being locked out of the housing market, and thus are being denied the stability and financial security that was taken for granted by previous generations.
The housing affordability crisis deepens as inflation, cost of living and housing prices rise at a faster rate than wages. Similarly, Australia’s rental crisis worsens with natural disasters such as flooding and increased competition as the country reopens to international students.
The backdrop to the COVID-19 pandemic will also exacerbate this growing economic inequality across generations. In fact, those in their late 20s and early 30s have now known two crises: the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) of 2008-2009 and the COVID-19 crisis of 2020-2021. This puts them at unique risk and financial disadvantage compared to other members of society.
The reality on the ground is that, compared to their parents and grandparents, today’s young people are not only poor homeowners but also poor renters. The reality is an intergenerational theft.
While some have argued that housing should be at the front and centre of the upcoming federal election, housing affordability has not taken on a sufficient degree of importance in the policy narratives of the two major parties.
In fact, I’d agree that young Australians have been betrayed by both parties. Although the youth need a proper national plan for housing affordability and supply, their situation is sometimes met with rather condescending comments from the political leadership.
Prime Minister Scott Morrison’s comment – that “if you can’t afford rent, buy a house” is both comical and disturbing at first reading. As the PM flaunted in the first 2022 leader’s debate, first home buyer loan schemes allowed 160, 000 Australians to gain access to the property ladder last year. And his recent proposal to allow young people to tap into their superannuation has a similar ambition.
But what he neglects is how housing affordability concerns 67 per cent of Australians, many of whom are young people with low wealth and heavily taxed incomes. And government subsidies for a relative minority put upward pressure on prices for the many, presenting a trade-off of where it is more difficult to save a deposit for a home. Therefore, such comments are disturbing reflections of how far removed Australian political leaders are from the reality on the ground.
Housing affordability: a sticky problem?
Housing unaffordability has been identified as a pressing problem for more than decade now, so why then does it remain unresolved? The simple answer to this is that the politics around the problem prevents a permanent solution.
The housing affordability crisis persists because of two political reasons. First, more voters have an incentive to maintain the status quo compared to those who could benefit from a more equitable housing system. Although the growth in property prices entrenches economic inequality, it is a positive for incumbent homeowners who want to capitalise on their investment.
Further, impenetrable, cumbersome and ambiguous policies spook those with property. They fall into the status quo bias. For example, Labor’s 2019 election slogan to tone down investment incentives and introduce the housing tax upset property and construction industries and offended a large constituency of property owners. These radical proposals cost Labor the election.
Existing housing policies also fail to address the root cause of the problem. Most efforts to deal with unaffordability aim to cool housing demand rather than increasing supply. Pete Wargent, co-founder of BuyersBuyers, believes this approach would “make a marginal difference to affordability over time”.
Although investment incentives like CGT discounts and negative gearing are touted as the key drivers, recent review of six economic papers revealed that the combination of both contributed only a small 1 per cent to 4 per cent increase in dwelling prices. Whereas zoning restrictions, which limit the supply of land on which to build homes, contribute to almost half the rise of average detached house prices in major metropolitans, like Sydney and Melbourne. Centre for Independent Studies’ chief economist and a former RBA official, Peter Tulip, suggests increasing supply and lifting zoning restrictions can have huge benefits.
Yet, these are difficult to attain. The politics of improving housing affordability is determined by whether there are more voters who are property owners than not.
That is, whether there are more beneficiaries of unaffordability who will vote in their self-interest and support policies and parties that will keep prices high and rising, even if that compromises the future security of young people.
According to the Australian Electoral Commission, in 2022, there are 4.2 million voters aged over 65 compared to 3.1 million voters under 29. That is a difference of 1.1 million between lightly taxed, asset-rich older Australians, and younger wage earners. This intergenerational inequality is therefore a function of the classic headlock between the older haves and the younger have-nots.
Simple fix: increase supply?
Housing unaffordability is a complex structural issue that can’t be viewed through a simplistic lens.
Despite a plethora of issues influencing the housing market, the imbalance in supply and demand is at the crux of the matter. Rather unsurprisingly, the Property Council of Australia, recommends major parties to address supply shortages to improve affordability.
But adequate supply of housing doesn’t just mean constructing a certain number of dwellings on greenfield sites. It needs to be well-located and well-serviced with job, social and community infrastructures.
At both federal and state level, more commitment is requited to increase urgent need for more social housing. With a historically low level of social housing, (i.e. a non market rental housing sector), this would be more affordable and secure for low-income earners. Both major parties, however, fall short on public housing investment this election.
Supply of affordable housing can be increased by institutional investments, but investors show relatively little interest in affordable housing largely due to perceptions of risk and comparatively low returns. This is where government incentives and the introduction of some form of financial instrument (similar to the discontinued National Rental Affordability Scheme) could work.
However, evidence from Europe and Britain, suggest that government intervention may decline as affordability worsens. There is a major challenge to rolling out reforms: homeowners want to protect their properties from being undermined by growing housing supply, resulting in less support for government intervention. This feeds into inequality.
Another option is rent control. But opponents suggest that more limitations in the rental property make owning far less appealing. This again points to the headlocks between homeowners and renters; as the classic adage from former PM John Howard goes: no one is complaining in the streets about their house value going up.
Under the current structure, young people are common losers of the housing system. A change in government won’t be a silver bullet for housing affordability in Australia. What is needed is a structural change which is hard to attain given competing interests, imbalanced power and wealth dynamics among stakeholders.
Explore the role that ownership plays in our lives. Join Executive Director of The Ethics Centre Dr Simon Longstaff AO for The Ethics of Ownership on the 17th of August 6:30pm AEST. Tickets on sale now.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
It’s time to talk about life and debt
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Where do ethics and politics meet?
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Is every billionaire a policy failure?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Climate + Environment, Relationships
ESG is not just about ticking boxes, it’s about earning the public’s trust
BY Intifar Chowdhury
Intifar is an Associate Lecturer at the ANU School of Politics and International Relations. Her doctoral research tackles the important question of whether young people are turning away from democracy. Her political commentary on the engagement of young people in politics and issues affecting youth voters has been published in The Conversation, ABC, The Guardian, The Canberra Times and ANU's Policy Forum.
Antisocial media: Should we be judging the private lives of politicians?

Antisocial media: Should we be judging the private lives of politicians?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY Isabella Vacaflores 13 MAY 2022
The footage was grainy, but the man stepping out of the gay sex club was easily recognisable.
David Campbell, then transport minister of the New South Wales Government, was outed in the evening news, prompting his resignation the following day. His sexuality was the subject of intense media coverage, not least because of the impact it would have on his wife and children.
As headline grabbing and salacious as such personal scandals might be, one might question whether we should have the right to know about the private lives of politicians in the first place. After all, the fact of being queer alone bears little relevance to one’s ability to speak for their constituents, therefore arguably falling outside the realm of the public interest.
Yet, the journalist who broke the story felt differently, noting that the politician in question had “purported to be a family man”. As such, some might see this as an act of exposing hypocrisy, speaking to a deeper issue of character that is highly problematic for representative democracy.
So when it comes to dealing with information about the private lives of public officials, how morally justified are we in caring about what is done outside of parliament?
When rights collide
Although privacy is beneficial for human well-being and flourishing, it is not unequivocally good because such a claim can equally be used to hide information. This poses a significant threat when we consider how the personal lives of those wielding political power might influence their decision-making abilities, negatively impacting those that they claim to represent.
This tension between the claims to privacy of public officials and the rights of the public and the media to freedom of information is an undeniably hard one to resolve.
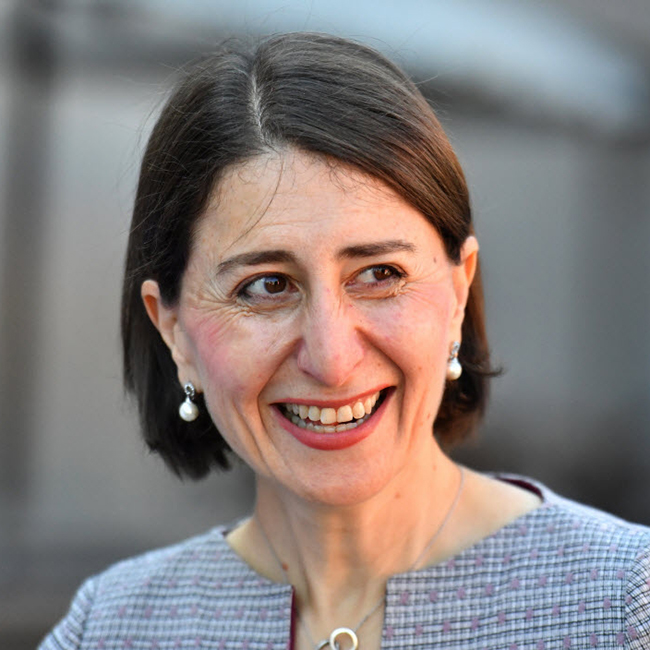
On the one hand, the revelation of Gladys Berejiklian’s relationship with Daryl Maguire and her subsequent resignation over accusations of corruption vindicate the idea that we should hold the private lives of politicians under constant scrutiny.
Yet, on the other, the case of David Campbell highlights the murky waters in which public interest claims lurk, with a person being pressured to end their political career over a seemingly inconsequential fact about their personal lives.
Are we morally justified in paying attention to and seeking out private information about public officials? After all, prima facie, all individuals have morally and legally robust claims to privacy.
Nevertheless, we generally consider it reasonable for interviewers to enquire about a potential employee’s prior working history to ensure that they are a good fit, or for a detective to ask someone questions about their private life to solve a crime. This is because privacy can and sometimes should be forfeited (with our knowing consent) for other rights or purposes, such as safety and transparency.
On a similar note, many citizens would see certain information about the private lives of politicians as relevant to their decision of who to vote for. This interest is warranted because public officials attain their legitimacy and authority from being entrusted to represent their constituents.
Ultimately, serving in government is ethically demanding – to avoid the corruption of power, we must elect individuals who have a track record of not abusing such privileges. According to the perpetually relevant ‘unity of virtues’ theory of the ancient Greeks, individual morality exists across both public and private spheres of decision-making.
As such, an absence or excess of good behaviour in one’s personal life may be illuminating with regard to professional conduct.
For instance, the media has recently reported that Boris Johnson, in his previous job as a motoring correspondent, accrued over £4000 in parking tickets. This fact, whilst seemingly trite, implies a historical pattern of rule flouting behaviour by the British Prime Minister, suggesting that we ought not be surprised by his involvement in the Partygate scandal.
Such cases highlight the often-blurry public/private divide and justify why we might look to politicians’ personal lives for clues as to how they might fulfil their moral duty to represent their constituents and their interests – even if this conflicts with their own.
Social media and the personalisation of politics
Furthermore, many politicians willingly open themselves up to public scrutiny by using their personal virtues and achievements to appeal to voters. We need not look further than Scott Morrison’s Twitter and Facebook feeds, which regularly feature pictures of the politician cooking up a curry in Kirribilli House and donning blue in support of the Cronulla-Sutherland Sharks, to see how political figures selectively reveal aspects of their private life to project a likeable image.
For as long as public officials advertise themselves and attack others on the basis of irrelevant personal characteristics and decisions (see criticisms recently directed at Anthony Albanese for everything from his weight loss efforts to having a “quiet week” of campaigning despite being in isolation for Covid) they cannot also claim to be innocent victims of the press, particularly when journalists are merely reporting on these assertions.
Nevertheless, politicians often resort to the refrain that ‘the media goes too far’ to divert attention away from their more questionable acts. When it was revealed that self-proclaimed family man and current Deputy Prime Minister Barnaby Joyce was having an extramarital affair with a staffer, a formal complaint about news coverage of the incident was made despite the couple accepting $150,000 to do a tell-all interview about it on live television.
The omnipresent pressure for news outlets to turn a profit leads them to sensationalist reporting and a rather liberal stance as to what information falls into the purview of the public interest.
However, political journalism acts as an irreplaceable check on power, and we ought to be wary of solutions that involve stifling it more than it already is under Australia’s extremely rigid defamation laws.
Towards a better discourse
Instead, content relating to the private lives of politicians needs to be understood in terms of its relevance to their ability to execute their role. We should actively dismiss and avoid searching for details that tell us nothing about the honesty, accountability, competence, integrity, judgement, and self-discipline of a public official, no matter how salacious. However, we can feel justified in pursuing information that reveals their historic performance in such areas.
Admittedly, this is a long laundry list that leaves few areas off-limits. It is important to note here that judgements about protected characteristics alone – such as race, sexuality, religion and gender – are not morally acceptable ways in which to judge the competence of an individual, as established under anti-discrimination laws.
That said, we cannot shy away from investigating how public officials have acted when they thought nobody was looking, particularly when such actions reveal how they use (and abuse) power or contradict their espoused values.
Because the relevance of this information can only be ascertained once it has been made publicly available, there will always be some politicians that have their privacy unjustly violated. This is a trade-off that can be easily defended when we consider the immense number of people that benefit from having a government composed of honest and accountable representatives.
Additionally, anyone entering a public-facing role knowingly places their privacy in a position of vulnerability. If they have something to hide, politics is probably not the place for them, practically and principally speaking.
Furthermore, we can limit the collateral damage of this proposal by encouraging journalists to prioritise reporting on facts that expose political corruption and speak truth to power. By choosing not to indulge in amusing but inconsequential gossip about the private lives of politicians, we can help change the incentive structure of the media system whilst simultaneously promoting enlightened attitudes towards sex and other areas of intense, but often illegitimate, public interest.
The democratic function of the press falters when trivial details about the lives of politicians consume all the resources of our finite attention economy. As such, it is a moral imperative for news outlets to maintain strong ethical standards when it comes to their reporting on the private lives of politicians, focusing their coverage on that which is relevant to their ability to bear office.
Finally, as public ethicist Patrick Dobel writes, “we should judge as mortals judging other mortals”. Public officials are not perfect people, but if they can recover from a fall from grace by regaining trust and legitimacy in the eyes of the people then we should leave them (and their sex scandals) be.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Survivors are talking, but what’s changing?
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights
Constructing an ethical healthcare system
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
An angry electorate
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Society + Culture
The youth are rising. Will we listen?
BY Isabella Vacaflores
Isabella is currently working as a research assistant at the Global Institute for Women’s Leadership. She has previously held research positions at Grattan Institute, Department of Prime Minister & Cabinet and the School of Politics and International Relations at the Australian National University. She has won multiple awards and scholarships, including recently being named the 2023 Australia New Zealand Boston Consulting Group Women’s Scholar, for her efforts to improve gender, racial and socio-economic equality in politics and education.
Yellowjackets and the way we hunger

Yellowjackets and the way we hunger
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Joseph Earp 10 MAY 2022
Yellowjackets, with its widely acclaimed first season, has a more disturbing element than its surface of considerable violence and horror.
Sure, the Showtime series, which follows a group of young athletes as they crash-land following a disastrous plane trip in the middle of the wilderness and turn, with visceral, enjoyable brevity, to cannibalism and taboo-shattering behaviour, contains a lot in the way of gore. There are broken limbs; bodies eating up bodies; physically construed nightmares which the protagonists cannot escape.
But underneath that immediate level of violence is a claim, considerably more unsettling than fractured calcium, that our ethical systems are far from stable and robust. We’re not bent towards virtue. We seem to be shaped in the opposite way. Yellowjackets knows that. And more than that, the show loves it.
Corruption Seeps In, Naturally
Yellowjacket’s “heroes” – a word which only means to indicate those characters who are applied with a particular, and frequently intense, narrative scrutiny – are the stereotypes of “ordinary” people. The show, which flips back and forth between the present and the deep, traumatic past, makes a great deal of effort to depict that. There are extended shots of the central characters, moving their way through the world, not even thinking about the trauma they inflicted on others, deep in their pasts.
Indeed, the flashback structure of proceedings, one that allows the central mystery to unfurl slowly – who ate who, following that terrible plane crash? – mines much from the main characters’ attempts to live their lives freely in the aftermath of their great collectively-constructed horror.
In the show’s temporal present, these plane crash survivors are all people who wake up every day, and apply themselves to their jobs, and are loved and love in turn. You’d meet them, and catch their eyes in a shopping centre, and smile, astonishingly oblivious of their histories. It’s only when we get painful stabs of their past, unfolded in flashback, that we come to understand that there is something hiding here; a history streaked by vicious behaviour.
That “something” can’t be pinned down to the specifics of our heroes’ lives, either. We can’t shirk the implication that we’d fail to avoid the same behaviour – it is nothing less than the human capacity for violence. We are all confronted, more frequently than we would like to admit, with the idea that we have a potential for evil.
Remember that time you stood on the train platform, and considered, all of a sudden, pushing a stranger onto the tracks? Not for any reason – just because you could. Because, despite what we hope ethics might teach us, there’s something actively joyful about vicious behaviour.
Yellowjackets doesn’t make anything extraordinary out of its central characters. These are just human beings, ones who happen to have been freed – predictably, almost boringly – from the social code of morality, and plunged into horror. We all could be there. All that Yellowjackets tells us is that, most worrying of all, we would enjoy it.

So Why?
The philosopher David Hume constructed his ethical system out of twin poles: pleasure and pain. Hume believed that we all have a natural repulsion to pain, and an attraction to pleasure. That, for him, was the foundation of all ethical behaviour, the starting point that explains empathy, charity, and goodness.
Yellowjackets tells us that’s not true. The show’s spark of originality is not to prove that we all have a propensity for inflicting suffering. That’s already been explored through multiple works of art – consider, for example, the Netflix smash hit Squid Game, which should be considered the contemporary final word on what happens when you guide desperate people towards viciousness.
No. What makes Yellowjackets special is that its central characters have spent the rest of their lives following the plane crash pursuing the highs of gnawing on another human being. They’re not tortured – they’re hungry.
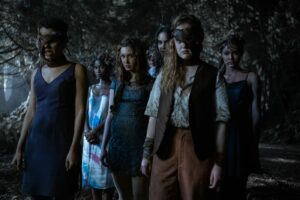
We Do What We Want – Thank God
If that sounds horrifically bleak, it’s because, despite its considerable vein of humour, Yellowjackets is horrifically bleak. We are inundated with art that aims to provide us with a moral compass, designating bad and good behaviour, and telling us how to navigate both. The thematic work, quite often, in these pieces of popular culture, is to condition us emotionally – to train us to be repulsed by horror, and drawn to goodness.
Yellowjackets does not do this. It makes the horrendous appear attractive: “look at these regular people, who ate one another, and defied the social norm, and found themselves in the process.” And it makes the virtuous seem weak: “look at those fools who let their sense of goodness stop them from doing what they want to do.”
If there’s any hope here, then, it’s our capacity to understand pleasure and pain in a more complicated way than Hume did, and that much contemporary art concerned with morality encourages us to do so. Rather than monoliths of feeling – this is pleasurable, and thus morally good; this is not pleasurable, and thus morally bad – Yellowjackets encourages us to mine the depth of our affect, and see it as being filled with nuance.
As Yellowjackets teaches us, we can’t hope that we will have an intrinsic and affective pull away from vicious behaviour, and a pull towards virtuous behaviour. What we can hope, instead, is that we understand our emotional states of pleasure and pain as containing more complexity than mere repulsion and attraction. We should become the experts in our own emotional states – not merely how they feel, but how they tell us to act.
After all, as plane crash victims who begin gnawing on each other’s bones tell us – not to mention addicts, or those who hurt the people they love – we can sink, pleasurably, into horror, and feel good about things that we don’t like, or no longer want to do.
We will never extinguish the joy of doing something we know we shouldn’t do. That’s the kid peeking at the Christmas presents before he should; of turning to our friend, maimed in a plane crash, and eyeing up their naked leg, considering our teeth in it. But what we can do is explore those feelings, and truly feel their complexity, and understand that no affect leads us more closely to one conclusion than any other. It’s up to us. That’s scary. But it’s also beautiful.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: The Harm Principle
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
What money and power makes you do: The craven morality of The White Lotus
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Are there limits to forgiveness?
LISTEN
Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Life and Debt
BY Joseph Earp
Joseph Earp is a poet, journalist and philosophy student. He is currently undertaking his PhD at the University of Sydney, studying the work of David Hume.
Let the sunshine in: The pitfalls of radical transparency

Let the sunshine in: The pitfalls of radical transparency
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + Leadership
BY Dr Tim Dean 3 MAY 2022
“Sunlight is said to be the best of disinfectants.” So wrote United States Supreme Court Justice Louis Brandeis, in his 1914 book critical of the concentration of power in banks and financial institutions, Other People’s Money and How the Bankers Use It.
Over a century later, sunlight is experiencing a resurgence in popularity as a disinfectant through the concept of radical transparency. This movement towards greater transparency is increasingly being adopted by a wide range of businesses from the technology, legal and environmental sectors as well as the banking and finance sector that motivated Brandeis’ book.
The movement has received a surge of attention in recent years due to policies promoted by pioneers like Ray Dalio, the founder of asset management firm Bridgewater Associates. Dalio sought to improve decision making by encouraging all employees to express their opinions freely about all aspects of the business, creating what he calls an “idea meritocracy”, where the best ideas rise to the surface.
Other pioneers include the US media streaming company, Netflix, and Finnish software consultancy, Reaktor, both of which have implemented wide ranging radical transparency policies covering everything from wage transparency to radical candour in internal communications to releasing employee emails to the public.
And the idea is growing in its appeal. The 2018 Future of Work Study, commissioned by online communications platform Slack, found that “80% of workers want to know more about how decisions are made in their organization and 87% want their future company to be transparent”.
However, there’s no single definition or implementation of radical transparency and it is employed in different ways in different contexts, and each has its own ethical implications.
The virtue of openness
In its broadest sense, transparency simply means openness, especially when it comes to revealing and sharing information. What makes it “radical” is when information that was previously closely guarded is systematically opened up to a wider audience, whether that’s within the organisation or without.
The primary ethical virtues of radical transparency are that it improves accountability and prevents corruption, in the sense of the improper use of power.
A culture of radical transparency not only makes it harder to conceal wrongdoing or compromising information, it also encourages a greater sense of honesty in dealings with others because of the anticipation that all information about those dealings will be revealed.
Radical transparency can also help counteract some of the power dynamics that influence decision making within organisations, whereby individuals might be reluctant to challenge the ideas and opinions of their leaders. A culture of radical transparency can improve decision making, as is claimed by Bridgewater, but also encourage people to speak up if they see something they believe is inappropriate.
Another form is wage transparency, which can promote fairness by giving employees more bargaining power in negotiations, placing them on a more even informational playing field with the employers. This is especially beneficial for those who are less inclined towards aggressive negotiation and can help counteract biases based on gender, racialisation and disability.
In an environment where trust in institutions, government and business is increasingly strained, radical transparency directed towards the public can serve to rebuild some of that trust. More organisations are laying bare information such as their employee diversity data, the results of internal or independent reviews – such as conducted by The Ethics Centre on behalf of the Australian Olympic Committee in 2017 – or details of their supply chains and environmental record.
Virtues and vices
Openness is a virtue. However, as Aristotle pointed out, any virtue taken to extreme can become a vice, and pushing transparency into “radical” territory steers it towards several ethical pitfalls and trade-offs that can easily be overlooked.
For a start, transparency sits in natural tension with privacy. Privacy is not just about restricting access to information but it can be thought of as the right of each individual to exercise some control over their personal information. This means they should have some power to choose whether or not to reveal their personal information. Some examples of radical transparency, such as wage transparency or the sharing of internal emails, can violate that right to privacy.
Privacy also enables us to protect ourselves from those who might use our personal information in bad faith to exclude, discriminate or persecute us. Radical transparency risks bleeding over into the personal space, such as if health, sexuality or religious attitudes are revealed that have no bearing on someone’s professional performance but which could expose them to unjust persecution.
One of the goals of radical transparency is to promote trust, but ironically it can also work to undermine it.
There are many kinds of special trusted relationships that are dependent on privacy, such as the relationship between patient and doctor or priest and parishioner. Should these conversations be made open, many people would end up concealing information for fear that it would be made public.
While no-one is suggesting radical transparency in the doctor’s surgery quite yet, it underscores that transparency in inappropriate contexts can actually cause people to suppress information rather than share it. There is already evidence that some workers in radically transparent workplaces change their behaviour to conceal information from their peers and act in a performative way that will be seen in a favourable light by others even if it’s not productive.
Trust in others is something that is learnt and must be cultivated through experience and practice. Should radical transparency seek to make trust redundant by making all information public, there is a risk that the virtue of trust will atrophy. This represents a real ethical risk should those individuals return to a less transparent environment where the virtue of trust is required once again.
Respectfully disagree
Radical transparency also requires an organisation to establish appropriate norms and culture in order to execute it in a safe and non-toxic way. In many instances, we modulate how we speak, how honest we are and what information we share on the basis of the relationships we have and the respect we owe to the other parties. In many contexts, deference, sensitivity or an ethic of care – or just the norms of good manners – trump candour, such as when we are speaking to a senior or vulnerable individual.
If we have implicit norms that promote deference to senior management, for example, or that encourage us to be sensitive towards a colleague who has just lost their job, these can come into conflict with the norms of radical transparency. There are accounts of employees feeling tremendous awkwardness when they’re thrust into radically transparent meetings where they’re expected to criticise managers or give reasons why a colleague should be fired.
It can take considerable time and effort to change the norms of discourse within the workplace to enable something like Dalio’s “meritocracy of ideas” in a way that is not overly confronting, where people feel like disagreement is tantamount to a personal attack.
These norms require that people feel respected, secure and safe to speak, which can also be threatened if radical transparency is executed poorly.
If implemented in a targeted and systemic way, radical transparency can deliver considerable ethical benefits in terms of elevating trust, improving decision making and encouraging constructive disagreement. But the most radical and hasty implementations carry serious ethical risks. Arguably, the point of the radical transparency movement is not to continually drive towards ever greater levels of transparency in every domain but to make openness an ethical norm that is, itself, no longer radical.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Capitalism is global, but is it ethical?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Society + Culture
Banking royal commission: The world of loopholes has ended
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Holly Kramer on diversity in hiring
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Do Australian corporations have the courage to rebuild public trust?
BY Dr Tim Dean
Dr Tim Dean is Philosopher in Residence at The Ethics Centre and author of How We Became Human: And Why We Need to Change.
A foot in the door: The ethics of internships

A foot in the door: The ethics of internships
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Althea Kuzman 2 MAY 2022
It’s just to get my foot in the door, I tell myself for the fifth time today as I offer my brain, my degrees and time to someone for free.
It’s a phrase that I’ve always found to be so incredibly visceral. I picture a door just about to slam shut in my face, that I have to hastily shove my foot in before it swings to a heavy close. Or a door that is slightly ajar, an unknown little me comes knocking and I have to slip my foot in and pry the thing open – to beg for an opportunity.
A foot in the door to do tasks which by now should be compensated. Because somehow in my years of trying to find a suitable job, no-one deems my skills to be transferable.
None of these scenarios really paint a picture for a healthy work foundation.
One would think that multiple arts degrees and years of casual jobs following instructions, would qualify me for an “entry level position”.
But it doesn’t. It leaves me cold emailing organisations, asking if they can send their off cuts to me so that I can get exposure. So that I can build a portfolio. So that I can earn a living and build my career.
But in my thinly veiled bitterness I digress. I chose the arts. I chose the creative field where getting your foot in the door is seen as a ‘privilege’. Having worked actual entry level jobs such as gallery host, our role was held up on a pedestal, yet we were not. We were made to simultaneously feel so lucky to have this job and yet so small and very replaceable. Why? Well, because it looks so good on the CV.
But in reality, it hasn’t really done anything to help my long-term career. And while I’ve had some wonderful bosses who have helped mentor me to learn and grow, this no longer seems like valid proof that I can, in fact, progress my career. It also doesn’t help that the pandemic cut arts positions in half.
The issue that lies here is often the refusal in hiring processes to acknowledge transferable skills. Which leaves you wondering, where do you gain these industry specific skills if no one will hire you for entry level jobs? Internships, of course.
Internship or Indenture?
Internships are fascinating mostly because of their prevalence, lack of regulation and lack of overall purpose. A report for the Fair Work Ombudsman by Adelaide Law School in 2013 states that “In Australia, as elsewhere, the term ‘internship’ is without fixed content. It has a broad and uncertain meaning covering everything from unpaid or paid entry level jobs to volunteer work in the not-for-profit sector”. This covers such a breadth of options that no wonder those starting out in their careers can fall into the trap of being exploited.
Internships are rife, particularly in the arts and on a global scale. Note when referring to the arts I include any creative industry, because they all bleed into each other – skills intersect and majority of skills learned are transferrable. There would be no issue with internships… if they were paid, but they rarely are.
In the UK, Sutton Trust is a non-for-profit organisation that fights for youth social mobility. Their work spans research on the prevalence and the social impact that internships have on recent graduates or those looking to change their career. Their 2018 report found that that 86% of arts internships are unpaid. The issue with unpaid internships is that life isn’t free.
Putting numbers on this, to live in London for a month whilst doing an unpaid internship costs £1,019 (about AUD$1800). And to make matters worse, due to the lack of legal clarity surrounding internships, there are concerns that some employers are exploiting this grey area. A harrowing ethical dilemma – getting an extra pair of hands without even attempting to understand their own responsibilities towards interns.
Due to the lack of legal clarity surrounding internships, there are concerns that some employers are exploiting this grey area.
It’s interesting to note that internships are always perceived as a stepping-stone. The Australian National Association for the Visual Arts (NAVA) has a fact sheet on internships and what to expect, stating that they can be either paid or unpaid but the ‘crux of the situation is that it is an educational exchange’. NAVA go further to highlight the Fair Work Ombudsman’s criteria of an internship as a ‘meaningful learning experience, training or skill development’. This sounds completely reasonable, except when there is a precarious edge that tips easily into exploitation.
Researcher at the University of Montreal, Mirjam Gollmitzer recently detailed the precarious entryways into journalism. Often internships are seen as a socialisation into an industry or workplace, but Gollmitzer states that whilst that is ideal, research shows the opposite.
Through interviews with interns within the journalism industry, she finds interns who are ‘starved of mentorship and training’ and often left to their own devices. She highlights a powerful observation arguing that ‘the tacit assumption is that workers, not employers, are tasked with making the internship a success’.
How do we determine the success or value of an internship? To be seen as a meaningful learning experience, interns require mentorship, an environment to gain confidence and an understanding of how an industry works. Instead, Gollmitzer finds interns are often merely an extra pair of hands doing menial tasks, “with their experiences marred by haphazard interactions with time-strapped colleagues and arbitrary decisions by supervisors.”
The onus should be with employers to ensure interns are offered a valuable and structured experience where they can come out having truly learnt something and be given a genuine leg up in their career.
Instead many interns are left with a bitter taste in their mouth. They’re overworked, under paid (or not at all) and don’t walk away with skills or tangible experience they can take into an entry level job, which seems barely adequate. Which leads to the questions… when did jobs stop being a place of meaningful learning experiences and skill development? And how did we palm this off onto unpaid internships?
How did you get your start?
The above two questions are integral in understanding the shift that has occurred in the workplace. When listening to boomers talk about their start in the industry, often we hear those anecdotes about how they started in the photocopy room and someone noticed their intelligence and they were given a chance. Or how they were internally trained and given qualifications within the organisation.
The fact of the matter is that entering the workforce has been increasingly difficult for young people. The latest statistics from the HILDA Survey by The Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic & Social Research shows that only about 40% of graduates find full-time work in the first year out of full-time education. Their median hourly earnings are about two-thirds of median earnings of all workers, which is abysmal since our cost of living is ever on the rise. But this is certainly part of the discussion surrounding internships. With more and more people unable to find full-time work, we turn to casual work, to subsidise rent and to simply make a living, despite these casual jobs often not actually having relevance to one’s degree or career aspirations.
Casual work is the backbone of all unpaid internships. We all know someone who has worked in a pub whilst doing an unpaid internship in their desired creative field. But this leaves young people with burnout, and a distaste for a particular industry. Imagine that – already having doubts about something you studied just because from the get go you’re told you’re lucky to be working for free.
Nothing in life is free, therefore internships shouldn’t be. Making internships unpaid ‘learning’ experiences often leaves out entire demographics of people who simple cannot afford to work for free. It perpetuates the elite nature of industry, and the idea of the grind straight off the diving block. It’s cruel and unnecessary. Particularly because it wasn’t quite as brutal in different generations. For the first time ever, gen Z are running the risk of earning LESS than their parents, something that has never happened in the course of history.
How do we fix this? While I’m not well versed in economics or capitalism, I do know that people need to be paid for their work. Don’t take on an employee if you don’t have the bandwidth to mentor or financially compensate them. We need to start treating entry level jobs as a first stepping stone into an industry and leave the exploitation of young workers in the past, where it belongs.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
How far should you go for what you believe in?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Corruption in sport: From the playing field to the field of ethics
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights
Thought Experiment: The famous violinist
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
What it means to love your country
BY Althea Kuzman
Althea Kuzman is an emerging curator and arts writer. She holds a Master of Curating and a BA in Communications and International Studies.
How to have a conversation about politics without losing friends

How to have a conversation about politics without losing friends
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Dr Tim Dean 21 APR 2022
There’s a reason our parents told us to steer clear of discussing politics (along with sex and religion) in polite company. Because as soon as politics is raised, there’s a very real chance that the company will become significantly less polite.
One reason political disagreements can be so divisive is that, unlike other contentious topics, like whether pineapple belongs on pizza, politics taps into our deeply held moral values and emotions: taxation policy isn’t just about the budget’s bottom line, it’s fundamentally about fairness; climate policy isn’t just about decarbonisation, it’s about the harm that our society is inflicting on future generations.
The moral dimension of politics can make us less tolerant of disagreement and more likely to see other views as not just different but mistaken, and perhaps dangerously so. It’s easier to shrug off someone’s opinion about the latest episode of The Bachelor than it is to let their views on asylum seekers pass without rebuttal.
The good news is that there are ways to have fruitful conversations about political differences if you approach them with care.
Before you start
Disagreements don’t have to be corrosive to our relationships or wellbeing. In fact, genuine disagreements give us an opportunity to learn, grow and share our perspectives with others. But they take time and effort to set up.
So before you utter a contrary opinion to a friend or family member about a political issue, first reflect on the strength of your own views and how open you are to new perspectives and evidence.
In today’s heated political environment there can be a great deal of pressure on us to form an opinion and take a side before we’ve had a chance to digest all the relevant information. There’s also a strong tribal element to politics that makes us more likely to adopt the views of ‘our side’ and oppose anything said by the ‘other side’. Many of us might even admit we hold opinions that we would struggle to justify if pressed.
Ideally, the strength of our convictions should be proportional to the strength of the reasons and evidence we can muster in their support. It’s still OK to form an opinion without doing a Masters degree on it first, but it does mean we should remain open to new information and perspectives that could change our mind. As a rule of thumb, if there are no reasons or evidence that could even hypothetically change your mind, then you’re being dogmatic and will likely receive no joy arguing about your views with others.
Before deciding to engage in a political disagreement, it’s also worth pausing to consider whether it’s worth arguing at all. It’s natural to feel compelled to correct a view you believe is harmful or wrong. But if it is likely that a disagreement could get heated or emotional, or it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to influence the other person at all, then getting into a debate might end up being entirely fruitless. All you might achieve is damaging the relationship, even if you’re in the right.
Sometimes relationships matter more than being right. If you’re arguing with someone close to you, someone you care for or depend on, it may not be worth eroding that relationship for the sake of a political argument, especially if it’s almost certain to go nowhere.
And if you do want to actually change someone’s mind, you need to establish a base of trust and respect first. Foregoing one heated conversation in order to strengthen a relationship means you can build enough trust and respect so that you can have a constructive disagreement sometime in the future. Once you’re sure they’re willing to listen to you, you might even have a shot at changing their mind.
Where to start
If you do decide to wade in, the very first thing to do is keep your mouth shut! At least at the start of the conversation.
When we hear someone say something we disagree with, our first impulse is often to express our own contrary opinion. The problem is that this immediately frames the conversation as a ‘war of ideas,’ which can trigger all the baggage this metaphor implies. We see our conversation partner as our ‘opponent,’ we become focused on ‘winning,’ on ‘undermining’ and ‘outflanking’ their position. And absurdly, if we do learn something and change our mind, that’s considered ‘losing’.
It’s better to frame the conversation in terms of fellow travellers exploring an issue together. You might have different perspectives, but you have the same ultimate goal: improving your understanding of the world.
In order to avoid slipping into the argument-as-war frame, instead of expressing your opinion up front, start by asking questions. Ask why your conversation partner believes what they do. Get them to elaborate on what they mean by various terms. Then listen carefully, paying special attention to both the content of what they say as well as their emotional state when saying it.
Once they’ve had a chance to express themselves uninterrupted, summarise their view back to them and validate how they feel. You can do this without necessarily validating the content of their beliefs, even if you disagree with them. You might say something like “I see you’re really concerned about the economic impact of climate policy”, which acknowledges how they feel but doesn’t commit you to agreeing or disagreeing with them.
This kind of reflective listening achieves two crucial things. First, it gives you a fighting chance of actually understanding their view in detail rather than assuming you know what it is. This is important because people often mean different things when they use terms like ‘freedom’ in a political context, which can lead to confusion and crossed wires unless you probe them on what they mean.
Secondly, reflective listening helps people feel heard, which signals respect and can lower the temperature of a conversation. In fact, a lot of defensiveness can simply be a result of people wanting to be heard and feeling like no-one is listening.
Common ground
If you want to progress the conversation, the next stage is to seek out common ground, especially around values or goals that you both agree upon. For example, you might both care about taxes not being wasted, or you both care about the wellbeing of the next generation. At this point you can start to frame your difference in perspective as being different strategies to achieve common goals. This can take a lot of the edge out of arguments, making them feel less like you’re fundamentally at odds and show that you’re only disagreeing about the means to achieving shared ends.
Crucially, if you ever feel the conversation getting heated to the point where it’s difficult for either of you to engage constructively, then it can be wise to back out and change the subject before it’s too late. You can always revisit the topic once things have cooled down.
It’s also important to not let the conversation drag out. It’s unlikely that you’ll be able to fully grasp someone’s views or change their mind in a single conversation. But even a short conversation can help you better understand their views and allow you to offer up a different perspective. And if it’s done with patience and respect, it can open the door to future constructive conversations. After a few such chats, you might even find you change their mind – or find that your own view has changed. That’s not a bad thing.
The highly charged moral dimension to politics is why conversations about it are so fraught. But if we engage thoughtfully and respectfully we can have a rich conversation about politics, and still have a fighting chance of making it to dessert with friendships and family relationships intact.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Berejiklian Conflict
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Particularism
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Hey liberals, do you like this hegemony of ours? Then you’d better damn well act like it
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Australia’s paid parental leave reform is only one step in addressing gender-based disadvantage
BY Dr Tim Dean
Dr Tim Dean is Philosopher in Residence at The Ethics Centre and author of How We Became Human: And Why We Need to Change.
Big Thinker: Tyson Yunkaporta

Tyson Yunkaporta is a researcher, arts critic, poet, and traditional wood carver. He works as a senior lecturer in Indigenous Knowledges and is the founder of the Indigenous Knowledge Systems Lab at Deakin University.
A scholar of free-ranging ideas
Yunkaporta is not your typical academic. In a recent interview, he said:
“I try to avoid naming anything. And I try to avoid making too much sense, and I try to say things a bit differently every time and to mix it up. And I’ll make points that you can’t put together. I do that quite deliberately because I don’t want the things I’m thinking or working on to become an ideology or a brand, or something that people can use as a name… you’ve got to avoid that packaging and repackaging of ideas and let these things be free-range.”
Yunkaporta tries to keep his writing and discussions “free-range” because he doesn’t want to give complex ideas or concepts an “artificial simplicity.”
According to Yunkaporta, when we simplify complex ideas, they can become easily distorted or manipulated and the original intention behind them can become lost. But more problematically, when we simplify complex ideas, we fail to see how they connect to the larger patterns of creation at work.
“There is a pattern to the universe and everything in it.”
Nothing is really created or destroyed, it merely moves and changes. When we start to pay attention to the way that things move and change, and take note of the patterns that they make, we gain a better understanding of the world around us.
This is important, Yunkaporta states, because “future survival of all life on this planet will be dependent on humans being able to perceive and be the custodians of the patterns of creation again.”
Indigenous thinking can save the world
Yunkaporta’s recent book Sand Talk: How Indigenous Thinking Can Save the World, is all about identifying and learning from the patterns of creation.
Sand Talk has sometimes been described as an exercise in “reverse-anthropology”, because rather than looking at Indigenous knowledge systems and practices from a Western perspective, Yunkaporta examines Western knowledge systems and practices from an Indigenous perspective.
He is careful about what knowledge he shares in the process, explaining that symbolic knowledge is often restricted (for example, by age or birth order) or is only appropriate for a specific places or groups (for example, members of particular clans).
However, he shares enough to help his readers start to recognise patterns in the world around them and to “come into Aboriginal ways of thinking and knowing, as a framework for the understandings needed in the co-creation of sustainable systems.”
Although Yunkaporta believes that sustainable systems cannot be manufactured by individuals (this is something that we must undertake collectively), he does think that each of us plays an important role as an agent of sustainability.
Agents of sustainability have four main protocols or guidelines, according to Yunkaporta: diversify, connect, interact, and adapt.
These guidelines tell us that we should diversify our interactions, so that we engage with people and systems that are dissimilar to ourselves and what we’re used to.
We should also aim to expand the networks of people that we currently engage with, so that we connect with as many new people and engage with as many new systems as we can.
Through these connections, we should also share knowledge, energy, and resources. But most importantly, we should allow ourselves to be transformed by the knowledge, energy and resources that are shared with us.
Ironically, Yunkaporta believes that frameworks are nothing more than “window dressing.” Yet, as he himself highlights, the four main protocols for sustainability agents are a kind of framework for sustainability.
This contradiction is, however, just part of Yunkaporta’s style. He describes his work as a “free-range ramble that should never be taken at face value.”
He writes to provoke thought and reflection in his audience, not to give them all the answers. After all, he muses, “perhaps the worst possible outcome of this work would be civilisation embracing these ideas.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
But how do you know? Hijack and the ethics of risk
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Do Australia’s adoption policies act in the best interests of children?
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Living well or comfortably waiting to die?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
I’d like to talk to you: ‘The Rehearsal’ and the impossibility of planning for the right thing
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Agree to disagree: 7 lessons on the ethics of disagreement

Agree to disagree: 7 lessons on the ethics of disagreement
Opinion + AnalysisRelationships
BY Dr Luara Ferracioli Dr Sam Shpall 12 APR 2022
Senior Lecturers in Philosophy at the University of Sydney, Dr Luara Ferracioli and Dr Sam Shpall, participated in a live Ethics Centre conversation last year, discussing: how do we respectfully disagree? Ferracioli and Shpall concluded the following seven lessons, and how there can be value in disagreeing.
It often feels like we’ve lost a sense of principled disagreement – the idea that it’s OK if reasonable people think differently about something that matters.
In part, this is because we’ve changed the boundaries on what it’s OK to disagree about. Today, disagreement and debate about sensitive issues is seen by some as harmful or violent.
This can be interpreted as both attempts to de-platform bigoted ideologies, and also as those upholding the status quo having their power threatened and hiding behind a veil of civil society. It’s why subjects like Black Lives Matter and Critical Race Theory attract so much opprobrium – they speak directly to and challenge power, particularly latent and overt power dynamics.
We can all be guilty of treating disagreement as something that must have a winner and a loser. Whilst in other times disagreement has been used as a tool for everyone to learn; today, we disagree without any readiness to be persuaded.
When should we respectfully disagree? Should we always be open to having our mind changed? Can we remain friends with someone who we disagree with about things that really matter?
1. Genuine disagreement is not a bad thing.
There is value in good disagreement. Arguing well helps to flesh out all sides of an issue, bring to light underrepresented perspectives and contribute to solutions that benefit the most people; as in a true, functioning democracy and political system.
People occasionally conflate disagreement over an idea with a personal attack. This is a mistake, because disagreeing over issues and rationally debating the outcome – whether it’s who will do the dishes or how to allocate the national budget – is the best way to ensure a measured outcome that is in the best interests of the greatest majority. The more diversity of opinion there is in the discussion, the better the chance that the outcome will be balanced and representative of the greatest range of points of view.
The trouble lies in ensuring that the debate is measured, rational and charitable, and does not resort to humiliation and point scoring, as it often does in politics and personal disagreements. It’s important, also, to consider whether some disagreements of opinion are so fundamental that they license strong non-engagement moves like cancellation, de-platforming, and defriending; for example, boycotting a festival because of the presence on the bill of an act or speaker with whose ideas you disagree, or demanding their invitation to speak be withdrawn, such as in the recent case of Sydney Festival.
2. Genuine disagreement is often positively necessary for intellectual and emotional development.
Hopefully it’s already clear that cancelling and de-platforming people’s voices is not the way to stimulate a healthy culture of disagreement. Imagine I disagree with my partner about the wisdom of buying an apartment. One of us could simply acquiesce to make things more comfortable. This seems dangerous and unproductive. It makes it more likely that we will make the wrong decision, and it makes it more likely that at least one of us will feel ignored, disrespected and resentful. Notice how familiar the gendered dynamic is here in heterosexual romantic relationships: the controlling, all too often abusive man makes the decisions and expects or enforces compliance.
To make the right decision we both need to express our needs, wants and arguments clearly, and treat each other’s opinions with respect, working our way through the pros and cons to eventually reach a compromise based on mutual respect, not on one person overpowering the other.
In the case of the marriage equality debate in Australia, it came down to a national referendum, where the majority voted in favour of same sex marriage, proving pointless all the misleading ad campaigns and snarky media baiting of politicians and pundits.
3. Sometimes what people call “disagreement” is not disagreement at all.
Rather than disagreeing over philosophical ideas, sometimes people resort to the tactics of personal attack and outright hostility. If your aim is to humiliate a political opponent or win an election, you might well find that genuine disagreement and a contest of ideas is a less effective strategy than belittling them and misrepresenting their policies. (This goes partway to explaining political apathy, because it appears that many politicians are more interested in humiliating their opponent and scoring a point than having a real battle of ideas.)
Similarly, if your aim is to “win” a fight with your partner (and make yourself feel good, humiliate them, and put them in their place), you might find that genuine disagreement is a less effective strategy than personal attack. How often in a personal disagreement have you found yourself wanting to bring up a time in the past when the person has wronged you, that has no bearing on the current situation?
These analogies run quite deep, involving posturing, self-absorption, strong rhetoric, a lack of charity, no engagement with the “opponent’s” perspective, and so on. It’s not a true “disagreement” and contest of ideas, though, but a personal attack motivated by ego.
4. Sometimes what people call “offensive” and “hostile” is in fact disagreement.
In any interlocution, the first interaction always sets the tone: if it starts off hostile, that hostility will only escalate. You need to ask yourself: are you attempting a good faith engagement, or are you being defensive and stereotyping and categorising your opponent’s argument points?
Take, for example, the disagreement in the media and social media between podcaster Joe Rogan and musician Neil Young. Young removed his music from streaming service Spotify to protest its hosting of Rogan’s podcast, accusing The Joe Rogan Experience of spreading misleading information about Covid-19 vaccines.
Young followed up with a plea for Spotify employees to leave the company before it “eats up [their] souls”. Other prominent social media users then posted clips of Rogan using racial slurs. Rogan apologised for the slurs and said he will try, “in the future, to balance things out” with information on Covid. Spotify CEO Daniel Ek wrote, “based on the feedback over the last several weeks, it’s become clear to me that we have an obligation to do more to provide balance.”
5. Contemporary technologies (text messaging, emailing, social media) can make it harder to disagree well.
Communicating through the brevity of screens does not do much to help the art of good disagreement. With social media we’re getting less charitable with our opponents’ points of view and not always assuming the best version of their views. The way social media enables discussion is counter-productive – it’s so short, often anonymous, and you’re not looking at each other so you can’t see that your opponent is generally trying to have a good faith discussion.
Sarcasm and irony do not translate over text – consider how many times you’ve been misunderstood over email or text message. Abbreviating our vocabulary down into the bite size shapes of an emoji also engenders a poverty of language and ideas that benefits nobody. Consider Godwin’s law, that the longer an online discussion grows, the more the probability of a reference to the Nazis or Adolf Hitler reduces to zero.
6. Philosophical-collegial disagreement is a useful model for productive transformations of disagreement, from the personal to the political.
The philosophical model of disagreement has some valuable tools that should be exported for use in everything from intimate relationships, work environments and political culture to anonymous social interaction. One of the hallmarks of bad disagreement is a lack of charity – presenting your interlocutor in an unflattering light.
One of the things philosophers try to do at a university level is to reconstruct the best, most plausible, compelling version of the argument that one’s opponent is presenting. The principle of charity is related to a lot of other principles of agreeing well, such as the principle of intellectual humility, understanding that even one’s most cherished beliefs could be improved or better justified.
You want to win not because you put your opponent down but because you’ve made the best argument and your opponent can see why it should go your way.
7. Some disagreements are not worth having
The phrase ‘agree to disagree’ is a funny one that’s worth thinking about – it’s usually employed in the same way as phrases such as ‘it’s all subjective anyway’ or ‘everyone has their opinion’, not as a real move in a conversation but more as an ending to the conversation. Sometimes we need to end a conversation because it’s not getting anywhere, but sometimes we employ phrases like that to paper over the fact that we don’t have anything more to add to our argument.
But what about when one party to a disagreement rejects the foundational presuppositions of liberalism? For example, if someone thinks that men and women are fundamentally different and women deserve to be paid less than men, it might be very difficult to have a reasonable conversation with them when your foundational viewpoints are so radically different.
We have laws that prohibit certain forms of hate speech, of course, but these are hard to enforce and do not really help to answer many of the practical questions about how to interact with people who have these views.
We can’t give an overall theory about what to do in such cases, but we want to suggest that we steer clear of two dangers:
- failing to confront the genuinely inegalitarian, illiberal views; pretending that such views deserve the same sorts of consideration as liberal ones;
- and overstretching this response to illiberal exceptions.
Maybe you disagree with us about some of the things we’ve written, but hopefully you agree that there is value in disagreeing well.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Mary Wollstonecraft
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Plato’s Cave
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Your child might die: the right to defy doctors orders
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics explainer: Cultural Pluralism
BY Dr Luara Ferracioli
Luara Ferracioli is Associate Professor in Political Philosophy at the University of Sydney and ARC DECRA fellow. She was awarded her PhD from the Australian National University in 2013, and has held appointments at the University of Oxford, Princeton University, and the University of Amsterdam. Her first book Liberal Self-Determination in a World of Migration was published in 2022 with Oxford University Press, and her new book Parenting and the Goods of Childhood is forthcoming (with Oxford University Press).
BY Dr Sam Shpall
Dr Sam Shpall is Senior Lecturer in the Department of Philosophy at The University of Sydney. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Southern California in 2011, and was a Postdoctoral Fellow there from 2011-2013. From 2013-2015 he was the Postdoctoral Associate in Law and Philosophy at Yale University, and a Lecturer at the Yale Law School. He also taught philosophy in four New York State Correctional Facilities from 2014-2015 as a faculty member of the Bard Prison Initiative. He works mostly in ethics, moral psychology, and the philosophy of art.
Ethics Explainer: Teleology

Often, when we try to understand something, we ask questions like “What is it for?”. Knowing something’s purpose or end-goal is commonly seen as integral to comprehending or constructing it. This is the practice or viewpoint of teleology.
Teleology comes from two Greek words: telos, meaning “end, purpose or goal”, and logos, meaning “explanation or reason”.
From this, we get teleology: an explanation of something that refers to its end, purpose or goal.
For example, take a kitchen knife. We might ask why a knife takes the form and features that it does. If we referred to the past – to the process of its making, for example – that would be a causal (etiological) explanation. But a teleological explanation would be something that refers to its end, like: “Its purpose is to cut”. Someone might then ask: “But what makes a good knife?”, and the answer would be: “A good knife is a knife that cuts well.” It’s this guiding principle – knowing and focusing on the purpose – that allows knife-makers to make confident decisions in the smithing process and know that their knife is good, even if it’s never used.
What once was an acorn…
In Western philosophy, teleology originated in the writings and ideas of Plato and then Aristotle. For the Ancient Greeks, telos was a bit more grounded in the inherent nature of things compared to the man-made example of a knife.
For example, a seed’s telos is to grow into an adult plant. An acorn’s telos is to grow into an oak tree. A chair’s telos is to be sat on. For Aristotle, a telos didn’t necessarily need to involve any deliberation, intention or intelligence.
However, this is where teleological explanations have caused issue.
Teleological explanations are sometimes used in evolutionary biology as a kind of shorthand, much to the dismay of many scientists. This is because the teleological phrasing of biological traits can falsely present the facts as supporting some kind of intelligent design.
For example, take the long neck of giraffes. A shorthand teleological explanation of this trait might be that “evolution gave giraffes long necks for the purpose of reaching less competitive food sources”. However, this explanation wrongly implies some kind of forward-looking purpose for evolved traits, or that there is some kind of intention baked into evolution.
Instead, evolutionary biology suggests that giraffes with short necks were less likely to survive, leaving the longer-necked giraffes to breed and pass on their long-neck genes, eventually increasing the average length of their necks.
Notice how the accurate explanation doesn’t refer to any purpose or goal. This kind of description is needed when talking about things like nature or people (at least, if you don’t believe in gods), though teleological explanations can still be useful elsewhere.
Ethics and decision-making
Teleology is more helpful and impactful in ethics, or decision-making in general.
Aristotle was a big proponent of human teleology, seen in the concept of eudaimonia (flourishing). He believed that human flourishing was the goal or purpose of each person, and that we could all strive towards this “life well-lived” by living in moderation, according to various virtues.
Teleology is also often compared or confused with consequentialism, but they are not the same. If you were to take a business that specialises in home security, for example, a consequentialist would tell you to look at the consequences of your service to see if it is effective and good. Sometimes, though, it will be hard to tell if the outcome (e.g., fewer break-ins or attempted break-ins) can be attributed to your business and not other factors, like changes in laws, policing, homelessness, etc., or you might not yet have any outcomes to analyse.
Instead, teleological approaches to business decision-making would have you focus on the purpose of your service i.e., to prevent home intrusion and ensure security. With that in mind, you could construct your services to meet these goals in a variety of ways, keeping this purpose in mind when making hiring decisions, planning redundancies, etc., and be confident that your service would fulfil its purpose well (even if it is never needed!).
But how do we decide what a good purpose is?
Simply using a teleological lens doesn’t make us ethical. If we’re trying to be ethical, we want to make sure that our purpose itself is good. One option to do this is to find a purpose that is intrinsically good – things like justice, security, health and happiness, rather than things that are a means to an end, like profit or personal gain.
This viewpoint needn’t only apply to business. In trying to be better, more ethical people, we can employ these same teleological views and principles to inform our own decisions and actions. Rather than thinking about the consequences of our actions, we can instead think about what purpose we’re trying to achieve, and then form our decisions based on whether they align with that purpose.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
How to deal with people who aren’t doing their bit to flatten the curve
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Want men to stop hitting women? Stop talking about “real men”
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The historical struggle at the heart of Hanukkah
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships