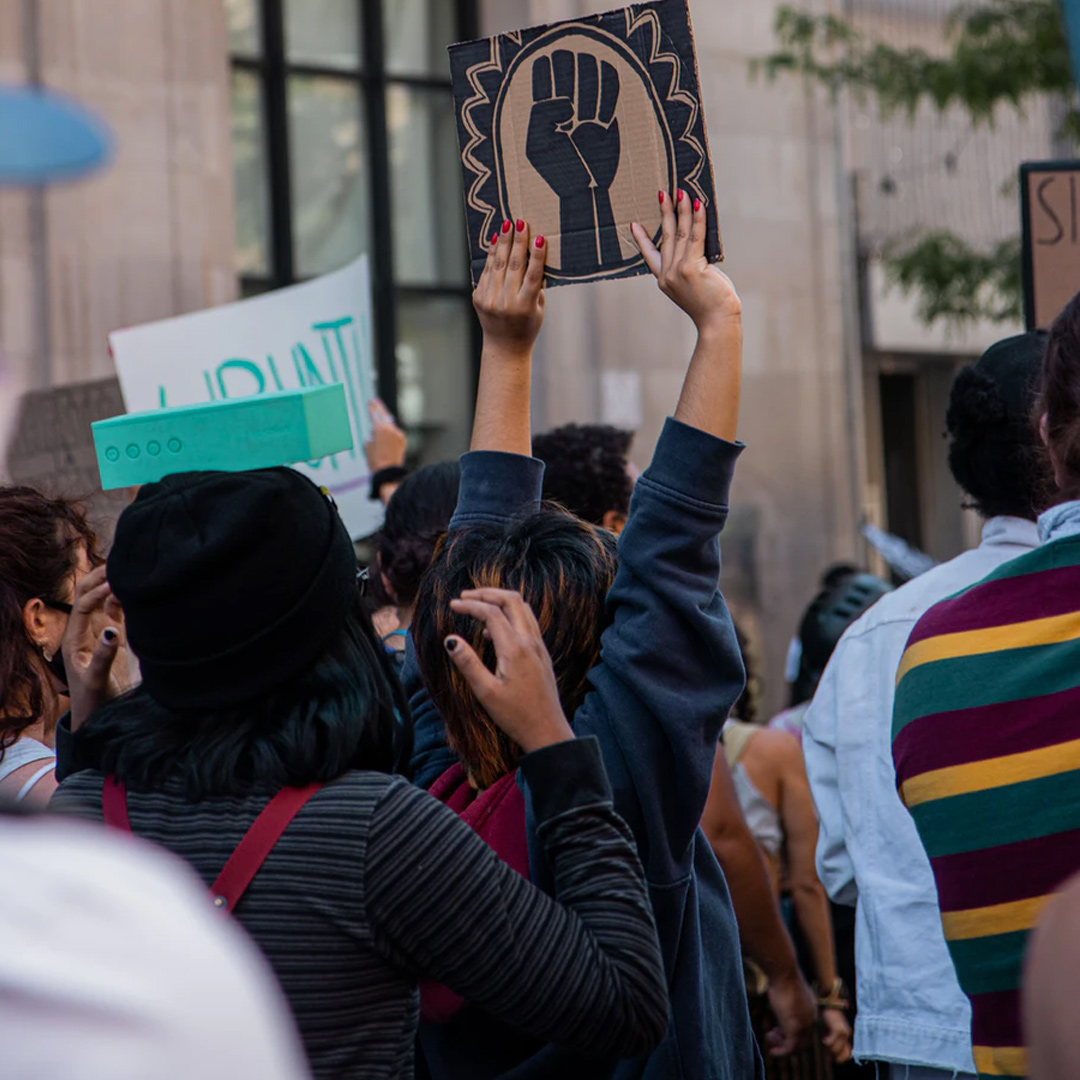The sticky ethics of protests in a pandemic
The sticky ethics of protests in a pandemic
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 31 JUL 2020
[Video Transcript]
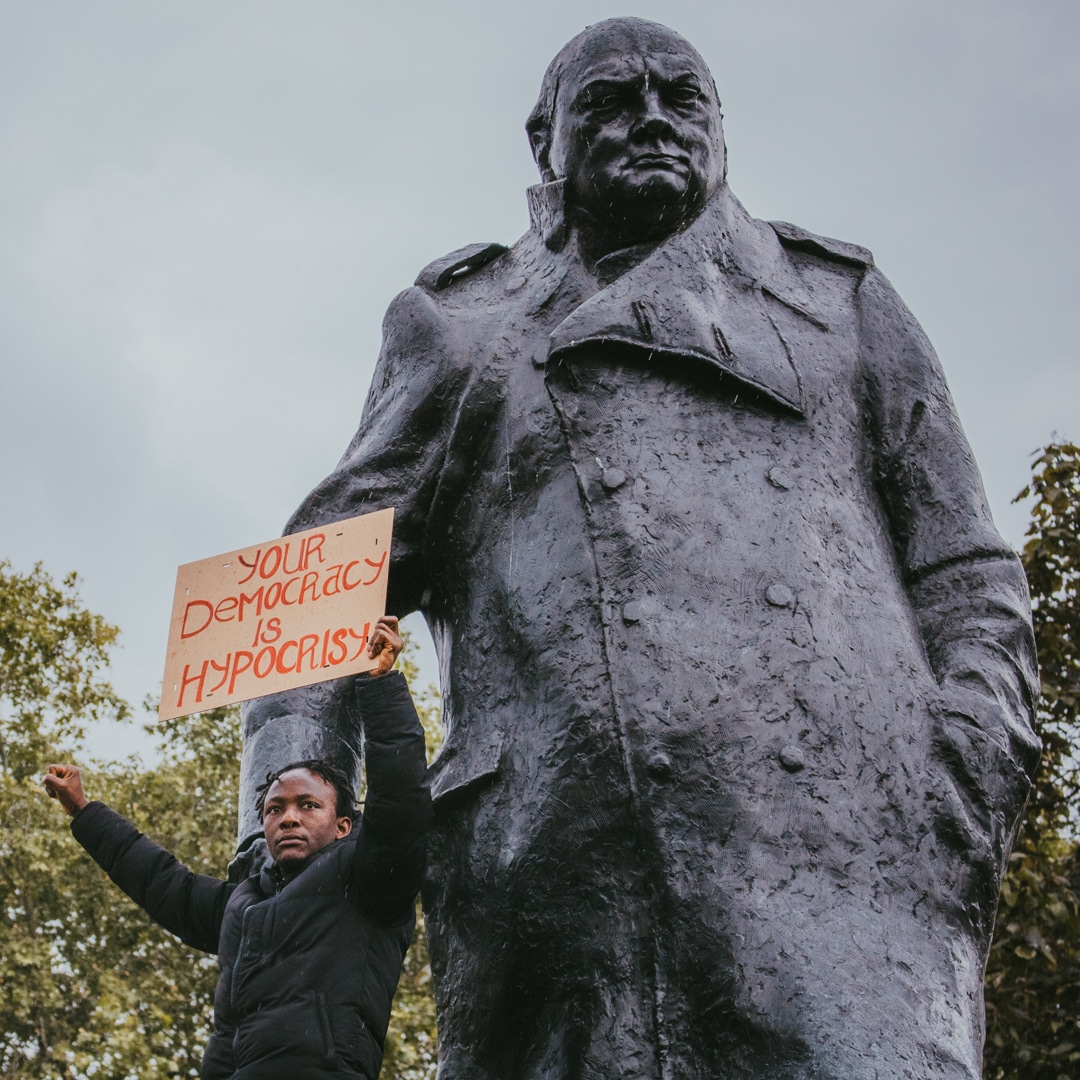
This week has seen the unfolding of a classic ethical dilemma.
A clash between the ethics of peaceful citizens wishing to exercise their democratic right to gather in support of the Black Lives Matter movement and the ethics of medical experts, the NSW Government, the Supreme Court and the NSW Police Force – all of whom combined to prevent these same citizens from gathering together in numbers thought to represent a risk to human health and safety.
The strangest thing of all was that people on both sides of this dilemma supported the objectives of the protesters – with the Deputy Chief Medical Officer, Dr Nick Coatsworth, saying that on any other day, and in any other circumstance, he would be in the ranks of the protesters – championing their cause. Even the NSW Police Commissioner, Mick Fuller, sounded genuinely sympathetic.
So, how did people sharing so much in terms of good will find themselves so divided … and what are we to make of the merits of each side of the argument?
To say that these are extraordinary times is the understatement of the year. The second wave of infections, in Victoria, has ramped up the pressure as we witness the infection spread like wildfire. What started off as a lazy spark is now a growing conflagration – burning up the lives of the vulnerable as it spreads from hotel, to tower block, to abattoir, to aged care homes. The medical fraternity is seeing frontline staff having to withdraw to quarantine as the beds begin to fill. Meanwhile, lockdown and mounting concern is further depressing economic activity.
Is there any wonder that the authorities in NSW are desperate to prevent the same sparks from igniting here? Already, we know that the tinder is dry … with minor outbreaks flaring up across the city. Infection rates in Sydney are on the knife-edge. So when the best available medical advice was that it is too dangerous for a mass gathering of those who support the proposition that Black Lives Matter, a Supreme Court Judge ordered that the protests not proceed – not to suppress the free expression of political opinion but instead to protect the vulnerable many from the risk posed by the sincere and committed few.
Against this, the protest organisers argued that they would guarantee a safe event with people masked and physically distant. They charged the authorities with hypocrisy, pointing out that if people are allowed to travel to work or gather for church services or engage in any one of a number of other types of permitted activity, why single out and ban a protest to condemn the deaths in custody of First Nations people? It’s a good question.
Opponents to the gathering could argue that a protest is, by its very nature, an unruly venture. No one can ever know, in advance, who will turn up, in what numbers, in what mood, with what motives? Even the best organised political gathering can get out of control. It is at least arguable that there is a valid distinction to be made between protest marches and other gatherings.
Even so, it’s hard not to think that it might have been better to set clear guidelines for the gathering, and only then intervene if they were not followed. As noted above, the protest organisers were publicly committing to an event in which every person wore a mask and maintained proper distancing in a large, open air environment.
One wonders what might have been possible had the police and organisers been able to work together to uphold such standards. In those circumstances I reckon that the organisers might have been just as willing, as the police, to close down the event if their supporters failed to observe the rules.
However, we shall now never know.
Some might suggest an ulterior motive in curbing a protest about black lives and Indigenous deaths in custody. If you belong to one of the marginalised groups who have lost loved ones to the criminal justice system due to racism and prejudice, it would be easy to believe that the cancellation of a protest march is just the latest example of unjust oppression.
However, in this case, I do not think that would be a fair or accurate judgment. As I noted above, there was a palpable air of good will in support of the protesters’ objectives, if not their chosen means on this occasion.
Instead, fear of what might have happened seems to have won the day. In part, this is because the public is merciless and unforgiving whenever public officials make the slightest mistake. Again, Victoria is a case in point, with the Andrews government being hauled over the coals for its evidently ineffective management of the pandemic. I very much doubt that Daniel Andrews, or his colleagues, would be cut any slack, by the Victorian public, if they invoked arguments about democracy and free speech to defend their decision making.
NSW Premier, Gladys Berejiklian, would have this example in mind, concluding that few politicians are ever punished for going overboard on public health and safety. More’s the pity.
In my opinion, politicians should be held to equal account for going further than is reasonable or proportionate -especially because of the implications on civil liberties, not least for especially vulnerable and disenfranchised groups. Governments that curb the liberty of citizens should only do so for reasons of necessity, and then only in a manner that is reasonable, proportionate and equitable. Yet, rarely do we see such standards being invoked by a fearful public.
There is a fine line between genuinely protecting the public from harm and constraining the democratic rights of citizens; there is a fine line between exercising those rights and avoiding preventable harm to others.
Ideally, one limits those rights to the bare minimum necessary to secure the public good. It is an open question as to whether or not that occurred in this case.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
There is something very revealing about #ToiletPaperGate
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
The right to connect
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Michel Foucault
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Are there any powerful swear words left?
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Stop giving air to bullies for clicks

Stop giving air to bullies for clicks
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 31 JUL 2020
By now, most people will have heard of the antics of the person who berated staff at Bunnings – simply because the staff insisted that she wear a mask before entering the store.
As is common these days, the altercation was filmed on someone’s phone and uploaded to social media channels. However, the story also captured the attention of mainstream media. What would normally have been an incident of minor importance soon became a topic of the national conversation – bringing fame (or infamy) to the antagonist.
I do not want to add to this person’s unwarranted celebrity. In part, this is because I do not think people should be rewarded for being rude and aggressive. In part, it is because I do not want to fuel further interest in ideas that are not just wrong – but dangerously so.
Instead, I want to focus on two issues of relevance to the media. First, should oxygen be given to people and ideas that do not deserve the public’s attention? Second, how can we avoid causing unintended harm done to people who have legitimate reasons for not wearing face masks – but who are made to feel like a pariah for not doing so?
The first of these issues is one of general concern. Naturally enough, the media is keen to cover stories that engage the interest of their audience. This is perfectly understandable in a context where maintaining audience numbers is critical to survival. People want to hear about the extraordinary. However, there are times when giving people what they want is not in their interest – a principle that holds for individuals as it does for wider society. An alcoholic might want another drink – but it is not in their interest to give them one!
The world abounds with crackpots, conspiracy theorists – and the like. At one level, it is easy to dismiss them as a part of a radical fringe whose ludicrous beliefs are merely entertaining. However, we should never underestimate the ability of such groups to wheedle their way into the public consciousness – even to the point where what seems to be extreme on one day eventually becomes commonplace … just part of the background beliefs of our time. We have seen this in the case of anti-vaxxers, or the people who believe that infection rates for COVID-19 are linked to 5G telephone towers, or that one’s gender or race determines character … and so on.
As noted above, some of these ideas can be explosive in their effects … with the potential for damage easily predicted. Yet, if the proponents are sufficiently weird, wonderful or compelling, then there is a chance that their views might be amplified by a media seduced by the novelty of what is being presented. This is not to suggest that the media approves of the ideas it promotes. If anything, most outlets probably assume that wacky ideas are pure entertainment – that no one will actually be seduced by ridiculous ideas. Unfortunately, history is full of examples of improbable beliefs becoming embedded in ‘mainstream’ ideologies.
This is not to suggest that the media should never cover stories like the incident at Bunnings. However, I think a decision to tell such a story comes with an additional obligation explicitly to discount the validity of claims that are false and misleading. That is, there are times when just reporting the facts will not be enough. Instead, editorial judgement needs to be brought to bear.
The application of judgement is also required in minimising the unintended, adverse effects of moderating opinion about matters like the wearing of face masks during a rampant pandemic. The person at Bunnings objected to wearing a mask as if to do so was some kind of violation of basic human rights. Those arguments were singularly poor – and potentially dangerous – as they uncritically undercut most efforts to preserve the health and safety of the community. However, there could have been another person – perhaps suffering from a medical condition – for whom not wearing a mask is a matter of necessity (not choice). The arguments of that person deserve to be taken seriously.
While it is important to repudiate the crackpots, we should do so with a care not to inflame public prejudice of a kind that discounts every objection as invalid. Some people have perfectly good reasons for not conforming to accepted norms that are justifiable in general.
The bully at the Bunnings door did little to advance the public debate about the rights and responsibilities of citizens and the community. But perhaps she has done some good – in prompting further reflection about what, when and how the media chooses to amplify through its channels.
This article was first written for, and published by Crikey. It has been republished here with permission.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Academia’s wicked problem
WATCH
Relationships
Unconscious bias
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
The ‘good ones’ aren’t always kind
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
But how do you know? Hijack and the ethics of risk
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
It takes a village to raise resilience

It takes a village to raise resilience
Opinion + AnalysisRelationships
BY Matthew Beard The Ethics Centre 28 JUL 2020
Several years ago, I was participating in a workshop around moral injury and war trauma in veterans.
A veteran detailed a horrific experience where through a combination of fatigue, bureaucracy and bad decision-making, he had left a reported IED to be defused by local forces, knowing full well it wouldn’t happen. His team had just come in after a long stint and were due for leave that day. He wanted to protect them from further burnout.
Tragically, a civilian convoy hit the IED, and this soldier suddenly saw his base flooded with injured, dying and dead civilians – harmed by an IED he ordered his team to leave for someone else.
The soldier detailed how his life had subsequently progressed. He was discharged from the army, became homeless, turned to substance abuse and lost just about everything before slowly rebuilding the broken pieces of his life. He was in a stable relationship, had secure work and was working with therapists to process what had happened.
After his presentation, the man left and the academics did what academics do: they debriefed and discussed his situation. The direction of the conversation was largely around what we could do to ensure that what happened to this person didn’t happen to other people. How could we provide a level of mental and moral resilience, such that these things wouldn’t be so damaging to warfighters?
For me, this question completely misunderstood the problem. This wasn’t a story about a lack of individual resilience. It was a conspiracy of systemic errors, tragedy and moral complexity.
Look at the systemic factors at play. First, there were problems with the local military operations that meant this soldier’s team were shouldering too much of the load. Second, deployment times and handovers weren’t designed in a way to ensure that teams were refreshed or replaced in a timely enough fashion to ensure they could do their jobs. Third, a lack of adequate mental health support on re-entry led to the soldier being dishonourably discharged. Fourth, bureaucratic issues in the funding for discharged veterans meant enormous loads of paperwork for a man suffering PTSD and therefore unlikely to be able to get through the tedium of such tasks. This is before we consider the moral and political complexities of the war in Afghanistan, where the soldier was deployed.
It is often said of PTSD that it is an ordinary response to extraordinary circumstances. I would argue that similar can be said for the kind of moral distress this soldier was feeling – his sense of responsibility, guilt and complicity was painful, but in some ways normal – even healthy.
His suffering is a recognition that he was caught up in events that mattered, and that his role in them also mattered. To suggest that what he needed was moral resilience seems to miss the point: his feelings weren’t the primary problem. The failure of his environment to support him during those feelings was.
I found myself thinking back to this conversation last week, when ABC Chair Ita Buttrose’s comments about millennial workers went public. In a Chatham House Rule conversation, Buttrose allegedly said that millennial workers “seem to lack the resilience that I remember from my younger days.”
“They’re very keen on being thanked and they almost need hugging – that’s before COVID of course, we can’t hug any more – but they almost need hugging.”
These comments are consistent with a particularly individualistic view of resilience that has become commonplace in workplace training, some forms of mental health coaching and – yes – in parenting circles. It’s an approach that treats resilience as a virtue – a character trait that marks a person as morally good.
To some extent, resilience is a virtue. A range of traditions, most notably Buddhism and Stoicism – recognise that a great deal of suffering is the product of the way we think about problems. We can be too attached to things that don’t matter and tend to catastrophise when things go wrong.
Overcoming this tendency is important. In an era where we face persistent, large-scale challenges like climate change, we need to be resilient. At times, we aren’t, through nothing more than what Aristotle called akrasia – weakness of will. However, we make a mistake when we see any evidence of a lack of resilience as an individual failing. In blaming the individual, we excuse the system.
For example, millennials working at Buttrose’s ABC have faced round after round of redundancies, intense political scrutiny and a heavily disrupted industry in recent years. As former ABC journalist Sophie McNeill wrote, “Lack resilience? How insulting. Us millennials at the ABC were usually paid less but expected to do so much more than many of our older colleagues, plus many are on insecure contracts for years.”
Lack resilience? How insulting. Us millennials at the ABC were usually paid less but expected to do so much more than many of our older colleagues, plus many are on insecure contracts for years – @ItaButtrose clearly needs to go & meet more of them https://t.co/TFf2SW5xFg
— Sophie McNeill (@Sophiemcneill) July 22, 2020
Resilience is a conditional good. Whether or not resilience is a good thing depends on what we’re being resilient to. If an employee is experiencing workplace harassment, is routinely looked over for promotion because of their race or gender, or has their labour rights undermined, we shouldn’t tell them to be resilient to it. We should encourage them to feel let down, wronged and betrayed – and to use those feelings as a spur to demand better treatment.
Just like the story of the soldier, we can see that young workers today face a complex system of different forces. Asking them to be more resilient or painting their struggles as a lack of resilience – a kind of moral failing – paints over the underlying problems rather than addressing them.
This isn’t to undercut or eliminate the importance of personal virtue and individual resilience. Sometimes, people will get comfortable. They may need to push a bit harder or learn to deal with hardship, and they should be encouraged to do so. Good leadership will help them in that project. In other cases, systems might be so oppressive as to prevent people from speaking out or demanding redress. Here, there is a very different role for resilience – it becomes a crucial survival tool, but one we should feel ashamed is necessary.
Framing resilience as an individual virtue also misses a range of things we can do to support people in difficult situations. Rather than expecting people to tough it out alone, seeing resilience as a systemic problem means understanding that it will need a collective solution.
It requires – as it always has – for people to lean on one another, to build supportive environments and, yes, the occasional hug. Requiring these things doesn’t demonstrate a lack of resilience – they are themselves acts of resilience. They are ways of enduring in situations that are challenging, stressful and difficult.
When we think of resilient communities, cities and workplaces, the people who are struggling aren’t problems that need to be fixed, they’re the canaries in the coal mine. When people aren’t flourishing, it’s not a sign they’re weak or broken. It’s usually a sign the environment they’re in is generating feelings of stress and burnout rather than helping them to cope.
Solving that problem doesn’t look like a pointed finger, it looks like a helping hand.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Plato
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Confirmation bias: ignoring the facts we don’t fancy
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Adoption without parental consent: kidnapping or putting children first?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The danger of a single view
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Ethics Explainer: Ethical judgement and moral intuition

Ethics Explainer: Ethical judgement and moral intuition
ExplainerRelationships
BY Matthew Beard The Ethics Centre 28 JUL 2020
Have you ever seen a situation that seems flatly wrong, but when asked to explain why you find yourself struggling for words? Perhaps you’ve got a strong sense that something is wrong – an immediate, powerful instinct about what should or shouldn’t happen. In ethics, we refer to these as moral intuitions.
Moral intuitions go by a number of different names. Some of us talk about ‘gut instinct’ or whether something passes the ‘sniff test’. Both terms suggest that there is some strong, basic belief about right and wrong that we can use to ground our judgements.
The problem is, despite the speed and strength of these intuitions, they are only as valuable as their source. Our intuitions can come from a range of sources: personal and family history, unconscious biases, custom, culture or a strong, stable and well-founded sense of what’s right.
Opinions differ on what we should do with our moral intuitions. Should we follow them, trusting them as a different kind of knowledge that draws on subconscious, non-rational and emotional cues? Should we ignore them, seeing them as irrational, unjustifiable claims about what’s right or wrong? Or should we treat them as one piece of evidence among many when we’re making a decision?
Resolving these questions requires us to work out what kind of intuitions we’re having. Some of our judgements about ethics can be based in a sense of disgust or ideas about what’s taboo (for instance, thinking about lab-grown meat), they can be the product of psychological biases like availability bias or halo effect, or social prejudices like racism, sexism, ableism or class-based moralities.
However, other intuitions may be based in our emotional response to a situation. Many of our emotions can reflect and inform our rational judgements. If something makes us angry, that’s information worthy of considering. If something makes us proud, that’s data we can use to help shape an opinion. Standing alone, ‘this made me feel sick’ isn’t sufficient information to form a moral judgement. But, the fact that learning about or witnessing something made you feel physically ill also isn’t something you should ignore lightly.
From the Nazis to ISIS, history is littered with groups who have encouraged their members to dismiss the evidence of their minds and bodies – such as feeling of disgust or shame at committing acts of murder – in order to serve some ‘higher’ goal. Dismissing the morally informative role of emotions can be used as a tool to pave the way to atrocity.
Whilst emotions alone should not be taken as sufficient for forming judgement, some believe there are kinds of intuitions that can, in and of themselves, reveal something ethically important to us.
For instance, we might have an intuition that all people are to be treated fairly, that it is wrong to intentionally harm an innocent person for no reason or that all people are to be treated with dignity. These are beliefs that moral intuitionists claim to be self-evident. These ideas don’t need to be justified or proven true, they just are. A moral intuitionist would argue that any person who disputes them is simply wrong.
Of course, not everyone accepts that there are self-evident principles on which to build an ethical system. These people, who are often associated with a philosophical school of thought known as rationalism, prioritise analytic reason, and hold that intuitions should be ignored. The only basis on which we should make ethical judgements is a rationally constructed argument. If, for instance, we think all people should be treated equally, we should make an argument to that effect. If we can’t, we don’t have good reasons to hold that belief.
What intuitionists and rationalists agree on is that making an ethical judgement is distinct from having a moral intuition. Our strong, immediate judgements about a situation are rarely – if ever – enough for us to make a decent appraisal of a situation.
However, the rationalist goal of eliminating emotion and intuition from the realm of ethical judgement is also false. Critical feminist and race scholars have highlighted the way that rationalists tend to paint a male, Western approach to thinking as a ‘universal’ rationality. In doing so, they tend to understate and invalidate other knowledge traditions and sources of moral judgement, including emotion.
For example, psychologist Laurence Kohlberg used a rationalist model of ethical decision-making to develop a stage theory of moral development. He thought rational, theoretical decision-making was more mature than decisions based on emotion, care and relationships. As a result, he concluded that boys tended to be more morally mature than their same-age female peers.
It took his student, feminist scholar Carol Gilligan, to point out that not only was Kohlberg’s assumption about rationality unjustified (it ignored, for example, the work of scholars like David Hume), it painted the difference between male and female moral reasoning as a deficiency in women rather than as a simple difference.
Perhaps we should take guidance from both rationalists and intuitionists. From the rationalist we can learn the understanding that our first judgement of a situation should not be our last. However, intuitionists remind us not to dismiss our initial judgements out of hand, but to interrogate and understand them. That way, next time, our intuitions will be a little closer to the mark.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Want men to stop hitting women? Stop talking about “real men”
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Plato’s Cave
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Want #MeToo to serve justice? Use it responsibly.
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Male suicide is a global health issue in need of understanding
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Punching up: Who does it serve?

Punching up: Who does it serve?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff 24 JUL 2020
I recently watched Hannah Gadsby’s comedic tour-de-force, Douglas. It is sharp and provocative – but wonderfully insightful. In the course of her performance, Hannah explains that she applies to her humour the principle of ‘punching up’.
It is an approach employed by comics when deciding who is a legitimate target for ridicule and satire. The idea is pretty simple, it’s fine to take aim at someone who is more powerful than you – but never those who are relatively weaker. The operating assumption is that the powerful are unlikely to be harmed by a bit of fun at their expense, while the weaker have suffered enough without having to cope with a comic’s insults.
The idea of ‘punching up’ seems to have taken on a life beyond the world of comedy. More generally, those who stand higher up the ladder of power and privilege are now expected to accept, without retaliation or reproach, whatever comes their way from those located on lower rungs of the ladder. Sitting at the top are cis-gendered, white men, like me. If we complain, then this is just evidence of our ‘thin skin’ and an inability to take a serving of what we have been dishing out for millennia.
It is easy to identify who is currently at the top of the ladder. However, beyond that point, working out the relativities of who is ‘up’ or ‘down’ becomes increasingly difficult. After all, there is no natural hierarchy of power, privilege, disadvantage or subjugation.
Instead, positions change as the wheel of history turns – with some groups ascending at one point only to see their position reversed at another. For example, consider the case of the Aztecs. Prior to the arrival of the Spaniards, they commanded an empire built on the conquest, enslavement and ritual sacrifice of those who fell under their sway. Yet, today, their descendants are a dispossessed people with an extraordinarily resilient culture that has survived centuries of attempted suppression by their colonisers.
So, who gets to ‘punch up’ (or be ‘punched’) is relative to time and culture. The role of being a priestess can be at the apex of power and influence in one setting but marginalised in another. A banker can be reviled as a ‘usurer’ in the past only to be celebrated by future generations.
However, that’s not where the relativities end. Conduct that is condoned in one case will be condemned in another – even though the things done are identical. For example, what is praised as being ‘forthright’ in a man has often been criticised as ‘aggression’ in a woman. Asymmetry of judgement also applies in the context of ‘punching up’. Behaviour that is justifiably condemned in a powerful person is often excused or ignored if practiced by a relatively powerless individual.
So, what are we to make of this? First, let’s acknowledge that there are some individuals and groups who have been systematically marginalised, over such a long period of time, as to deserve the opportunity to ‘even things up’ in any contest. Only those blinded by prejudice would deny this to be so.
However, this is not to say that relative historical disadvantage should excuse anything done – just as long as it is directed at the relatively powerful. A person fighting a stronger adversary may pick up a stick to ‘even the odds’ – but it would be wrong for them to attack an unarmed person with a firearm. To do so would involve a disproportionate use of force.
Likewise, I think it wrong to belittle or vilify a person (any person) in a deliberate attempt to wound them with words. That is not comedy – it is abuse. Comics make a person uncomfortable as a way of drawing attention to an issue of underlying importance – but their aim is not (and should not be) to harm. To do otherwise is to adopt the stance of the bully … which is wrong whatever one’s relative position in life.
I realise that it is easy to recommend restraint when one belongs to a powerful or privileged group – as I do. However, I am not a supporter of relativism in ethics (or elsewhere). To wound another – willfully or recklessly – is wrong.
The fact that it occurs as a result of anger or frustration might explain such behaviour – but it does not justify it. I know that this will be a view unpopular with those who have a taste for revenge – who believe in the proverbial ‘eye for an eye, tooth for a tooth’. However, I prefer the position of the Reverend Dr Martin Luther King Jr. who wrote that:
“Violence as a way of achieving racial justice is both impractical and immoral. It is impractical because it is a descending spiral ending in destruction for all. The old law of an eye for an eye leaves everybody blind. It is immoral because it seeks to humiliate the opponent rather than win his understanding; it seeks to annihilate rather than to convert.”
Yes, great wrongs need to be made right – but justice cannot be produced by injustice.
So, does this load the greater obligation onto the shoulders of those who have traditionally been on the wrong end of the stick? On the contrary, those of us who enjoy the greatest power and privilege should accept the greatest obligation to act ethically … not least because we have the capacity to do so.
We should begin by recognising and redressing the disparities of our day; we should acknowledge that we did not earn our privileged position – but were simply lucky enough to be born blessed with opportunity. It is not out of guilt, but with a sense of justice, that we should seek to redress historical and contemporary sources of inequity.
Perhaps then the urge to punch will eventually be assuaged, and something better – that could never have grown in the soil of anger and resentment – can emerge to see the light of day.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
The Ethics Centre Nominated for a UNAA Media Peace Award
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The danger of a single view
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
What it means to love your country
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Education is more than an employment outcome
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
The dilemma of ethical consumption: how much are your ethics worth to you?

The dilemma of ethical consumption: how much are your ethics worth to you?
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentHealth + WellbeingRelationships
BY Matthew Beard The Ethics Centre 21 JUL 2020
Everyone, rich and poor alike, should be able to buy the cheapest product with a clean conscience.
This article was written for, and first published by The Guardian.
In the lead-up to a recent buck’s party, the group chat turned to the age-old question: will there be strippers? After some back and forth (for the record, I was opposed), the groom-to-be stepped in with the veto. “No strippers!” he declared.
His reasoning demonstrated a remarkable level of self-knowledge. He explained that he was planning on the weekend being filled with inhibition-reducing substances and didn’t trust his addled self to make smart decisions.
In doing so, he gave voice to a basic moral principle: better to avoid temptation than to overcome it. From Mufasa to Gandalf – and the Lord’s Prayer – we’re told that while it’s good to be able to resist vice when it calls to us, there’s wisdom in arranging our lives in a way that minimises our exposure to vice altogether.
Unfortunately, that advice is nearly impossible to follow when it comes to participating in the market. Increasingly our decisions around what we buy come with a trade-off: the more sustainable, ethical, fair trade option or the cheaper, potentially dodgier one.
Take an easy example: eggs. Do you want to buy them from the farms that give the chooks the best quality of life (comparably speaking)? Free range, organic and more than twice the price of the quick-and-dirty caged eggs stashed at the bottom of the shelves. For many of us, this is a fairly straightforward choice – the price to put our money where our morals are is relatively low, though even here, the lower your budget, the harder the ethical choice becomes. What happens when we increase the costs?
If we stop thinking with our stomachs, the problems get even larger. I recently informed my financial planner that I wanted to move my superannuation to an ethical investment fund. He did his job and showed me the comparison. If fees and returns for each fund performed as they had been, in 30 years’ time my superannuation would be $300,000 worse off investing in an ethical fund. Lead us not into temptation indeed.
There are a few perversities here. The most galling to me is that pitting money against morality is a regressive dilemma. The people who can most afford to pay their ethical way are the uber rich; those battling against the poverty line don’t have the option but to become complicit in animal wellbeing issues and clothing made in questionable conditions. They certainly can’t justify moving to a higher-fee fund just because it doesn’t invest in coal or tobacco.
There seems to be something uniquely cruel about creating a system that determines ethical seriousness by purchasing behaviour, thereby stigmatising the poor and lightening the load on the wealthy.
This only becomes more egregious when you consider the various ways in which wealth is accumulated under capitalism – often on the backs of the same workers who can’t afford not to be complicit in the ethical missteps that often end up lining the pockets of the very same elites who can then afford a clean conscience.
However, the choice remains difficult even for those who ostensibly can afford to take the financial hit for their ethics. It’s easy to compare the immediate, measurable and tangible cost difference of two products. Making a judgement regarding the vague, unquantifiable moral value of not investing in unethical practices or investing in exemplary ones is ambiguous. There’s no obvious benefit and thanks to the anonymity of the global market, we usually don’t see the harms inherent in the products we’re being offered. That’s a recipe for rationalising the choice that’s better for us and ours, no matter what the costs are to anonymous people, animals and ecosystems.
There appears to be little out for those wanting to be ethical consumers on a budget. Compromises and trade-offs will need to be made. You’ll likely need to benefit from practices that don’t align with what you think is right. However, the lie at the heart of the ethical consumption movement is to tell you this is your fault. It’s not. It’s the fault of a much larger system offering you choices that, in many cases, you simply shouldn’t be permitted to make.
I don’t want to be given the choice between forfeiting hundreds of thousands of dollars and compromising on my values. I don’t want to be offered the opportunity to buy clothes that are cheaper for me because disempowered workers paid the price in underpayment and subjugation. It’s too easy to justify the worse option. It’s too easy to be tempted.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
How to help your kid flex their ethical muscle
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A critical thinker’s guide to voting
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
A parade of vices: Which Succession horror story are you?
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
The Dark Side of Honour
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
If we’re going to build a better world, we need a better kind of ethics

If we’re going to build a better world, we need a better kind of ethics
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Matthew Beard The Ethics Centre 17 JUN 2020
At times of global crisis, it’s very tempting for moral philosophers to get an over-inflated sense of self-importance. Those who have dedicated their life to reasoning through matters of complexity – justice, rights, liberty and the rest – suddenly feel uniquely placed to make sense of what’s happening.
When philosophers intervene effectively in public debate, it’s often lauded as a breath of fresh air. If I had a dollar for every time someone had suggested I teach ethics to politicians, I wouldn’t need to teach anyone ever again.
Last week, Jared Field, a University of Melbourne mathematician and Gomeroi man argued in The Guardian that the recent destruction of the Juukan Gorge cave by Rio Tinto revealed the need for students of STEM to be trained in ethical reasoning.
Having myself argued for the need to include ethics within STEM, I desperately want to agree with Field. But in order for ethicists to provide the kind of education he hopes for, one in which scientists ask “am I being a good ancestor?”, the field of ethics first needs to reckon with its own history. Moral philosophers, as it turns out, don’t have the best ancestors.
Ethics, a branch of philosophy, is an intellectual tradition and an academic discipline that, like any other, has a history of sexism, racism and complicity with oppressive systems and regimes.
In the wake of the protests and riots following the killing of George Floyd, the solidarity that has been sparked across the globe, and the more targeted protests regarding Aboriginal deaths in custody here in Australia, I’ve started wondering about the legacy of the discipline. To follow Field’s line of questioning – what do ethicists have to do to ensure they’re being good ancestors?
I’m beginning to worry that some of the most basic ways we think and ‘reason’ (more on that word soon) about ethics, has a role in legitimising the very violence that ethicists and moral philosophers then seek to condemn.
This isn’t true of all philosophy – but it is typical of an approach that holds a lot of traction today because of its association with some of the most widely-known (and more importantly, widely taught) philosophers in history. It’s a notion of philosophy that sees it as an entirely rational exercise of developing and applying theories, ideas and frameworks in a vacuum.
This vacuum is meant to be liberating. It’s designed to be transcendental – elevating our ideas above what things appear to be so that we can articulate things as they really are, or as they should be. It’s from this vacuum that we get thought experiments and concepts like the trolley dilemma, the state of nature and the veil of ignorance. It’s also where we get a whole lot of applied ethical frameworks, like just war theory in military ethics, quality-adjusted life yields (QALY’s) in medical ethics and ‘use of force’ doctrines in policing ethics.
These theoretical frameworks provide us with a universal sense of what, for example, the ‘just’ use of police force looks like. To be considered ‘just’ (in Australia, at least) the use of force needs to be necessary, proportionate, reasonable, in pursuit of a legitimate goal and must aim to de-escalate or minimise harm.
When you run through these criteria as a list, it gives the sense of something comprehensive – that we could apply this framework to all cases and make some kind of reasonable judgement about whether the use of force is ethical or not. These approaches provide consistency, impartiality and at their best, capture something essential about the moral considerations at the heart of what’s at stake.
However, they also risk pulling the wool over our eyes, because they ask us to assume that when two people walk into this neat thought experiment, they too are transcendent. Their historical baggage, political status, social standing and whatever else defines their lived experience isn’t something to be wrestled with. Instead, the particularities of their lives and histories are something to be transcended.
What this means in the context of policing is that the very question of whether the police – as they have come to operate and function in a society – are legitimate or not is outside the scope of questioning. It means it falls to us to determine whether someone’s previous criminal status – itself likely intertwined with systemic injustices, social disadvantage and oppression – justifies a greater level of force, you know, because it’s proportional to the ‘greater threat’. The question ends, by accident or design, before we ask what role the colour of a person’s skin might have played in determining that use of force.
Philosopher and health researcher Bryan Mukandi describes this as a tendency to treat ethical decisions as an “atemporal phenomenon,” removing ethical decisions from the history that must inform them. It’s a phenomenon we have seen play out in the COVID-19 pandemic. Two patients arrive in need of a ventilator – one has promising health outcomes, the other doesn’t. The ventilator goes, according to many medical ethicists, to the one who promises better outcomes.
However, Mukandi points out that this, by design, overlooks the potential that the reason one person faces worse outcomes is because of a series of injustices they have experienced over the course of their life. Injustices that are not merely ignored at the moment of crisis, but which are relitigated against the person by denying them the same healthcare they have been denied again and again.
The false belief that ethics is an atemporal phenomenon has also been at work in the backlash against the Black Lives Matter protests around the globe. Conditioned to compare instances of violence only in the present, critics look at two instances of violence and treat them as equivalent. They have, by design, removed the most relevant factor – a history of deliberate, systemic violence and racism inflicted by one party on the other.
In so doing, they simultaneously rewrite the reality of the situation and claim some intellectual high ground, because they are the ones playing by the rules of rational thinking and reason. They are all too quick to spot an apparent contradiction in the logic of the other side after they’ve framed the terms of the debate and defined what matters and what doesn’t in their own way.
This is not a new tactic. It’s perhaps the earliest strategy in the colonial tool kit. Perhaps the best-known thought experiment in political philosophy concerns the ‘state of nature’, where we consider what life would be like if human society existed with no laws, no government, no organised systems of co-operation whatsoever.
The state of nature is meant to reveal how and why humans might wish to enter into society at all. Conveniently, most accounts of the state of nature – written by white men from European and British backgrounds – revealed the natural society to emerge from a state of nature to be a distinctly Eurocentric one.
The British philosopher John Locke developed his influential account of property ownership, based on European agricultural practices and the idea that land had to be tilled and settled to be owned. This way of thinking played a role in allowing colonists to see lands like Australia as unowned – as terra nullius. Philosopher Olly Thorn describes this as the practice of interpreting difference as absence. Different approaches to property, government and society were interpreted as lesser, or non-existent.
Far from discovering some universal truths by transcending the world, the philosophers I idolised as an undergrad (and to an extent, still do) simply gave their own world view the veneer of universality and in doing so, became available to launder white supremacy, colonialism and genocide.
They weren’t alone in this. Colonialism wasn’t invented by the British Empire. Nor was racism discovered during the Enlightenment. Other cultures and times have been guilty of similar crimes. However, what is distinct is the tendency to look for answers in the European thinkers who gave intellectual cover and license to the very evils we are now trying to address.
Jamaican political philosopher Charles Mills, wrote famously that at the end of the day, “a lot of philosophy is just white guys jerking off”. Often it fails to address real issues, and when it does, “the emphases are in the wrong place; or crucial facts are omitted, making the whole discussion pointless.”
If philosophers are to be good ancestors, we need to be honest about the legacy we’ve inherited from our own. We need to reckon with our unspoken tendency to accept an approach that is comfortable with erasing history. That requires a conscious choice to reconsider methods that focus on what’s happening now and what might happen in the future at the expense of the past. It means ensuring that we no longer overlook, or forgive, the racism, sexism and other moral failings of almost all the giants of our field.
Protestors and rioters have been criticised for destroying private property, invoking the very same intellectual concepts that were used to justify stealing Indigenous lands in the first place. They have been told to prosecute their arguments in a ‘marketplace of ideas’, invoking notions of liberty from John Stuart Mill, a man who believed only white people were truly capable of liberty. Failing to address the history of these ideas has seen us relitigating them in the same old ways, denying opportunities to refine, repurpose or replace these ideas with better ones.
Philosopher Kate Manne recently tweeted that “It is really striking at this moment how little talk there’s been of reforming philosophy departments. Our whiteness is overwhelming and deeply problematic.” I think Jared Field is right to think that a better curriculum might give us some hope looking forward.
But if we are going to start addressing social change in the curriculum, we first need to address the people writing it, and the thinkers in it.
Image credit: WikiCommons
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The tyranny of righteous indignation
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Melbourne Cup: The Ethical Form Guide
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
10 films to make you highbrow this summer
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
To live well, make peace with death
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
In the face of such generosity, how can racism still exist?

In the face of such generosity, how can racism still exist?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 12 JUN 2020
Is there any polite or moderate way to condemn racism? I think not. Nor should there be. As the world has witnessed, on countless occasions, racism kills. It does so for the worst of all possible reasons – by denying the equal humanity of some people simply because of the colour of their skin.
The evil caused by racism is not ‘theoretical’. We do not need to speculate about the horrors that it has unleashed. We have only to listen to the evidence of the enslaved, the dispossessed and the murdered to know what follows when one group of people is thought to be ‘less fully human’ than another.
Some people are upset by the words ‘Black Lives Matter’. They assert an alternative proposition that, ‘All Lives Matter’. Well, of course they do. But that has never been denied by the BLM movement. BLM does not claim that only black lives matter. They do not say that black lives matter more than any other.
They simply state that black lives also matter – in a way that racism denies. And they are right. They might also ask, ‘where were the people chanting ‘All Lives Matter’ when the ‘original sin’ of racism was being visited on the world?’. Why has the ‘All Lives Matter’ brigade only found its voice now that the spotlight has been turned on the oppressors by the oppressed?
I come from a privileged background. So, I can barely imagine what it must be like to be on the wrong end of the racist scourge. I can only guess at my reaction – probably a burning rage at the sheer injustice of my treatment. Like the Rev’d. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr – I would demand to be judged for the quality of my character rather than the colour of my skin. Denied that right, I would let loose my rage on an unjust world and those who represent the system that denied me the most basic form of dignity.
So, it eclipses all understanding to find that, in my experience, the vast majority of Indigenous Australians who have experienced racism are, in fact, amongst the most generous and accepting of people. Yes, there are angry firebrands. However, rather than replicate the wrongs they have suffered or become like those who have denied their humanity, most of those affected choose to repudiate racism by accepting others for who they are and not how they seem.
I speak of this from direct experience. A few days after my seventeenth birthday, I arrived on Groote Eylandt – the home of the Anindilyakwa people of East Arnhem Land and the Gulf of Carpentaria. This was the mid-1970s and the racism directed towards the local mob was common, open and shameless. I doubt that those involved would consider themselves as deliberately being racist. If anything, their racism was almost ‘casual’ in character – a product of ignorance, prejudice and ingrained habits of mind.
It’s hard to explain exactly how and why my experience was so different – perhaps it was my young age or a lucky accident … I really do not know. Whatever the reasons, a few of the Aboriginal men took me under their wing. Friendships developed and eventually I was given a skin name and inducted into a network of kinship ties that I value to this day. The point is that if you were to meet me ‘in the flesh’ you would simply see a middle-aged, white male. As far as I know, I have no genetic ties to the people of Groote. Yet, their acceptance of me has been complete and unconditional.
I have often questioned my experience – wondering if I might have invented a narrative to match an idealized version of myself. However, improbable as it might seem, the connections are real. I will never forget spending an evening with two members of the Amagula Clan (a brother and sister) who explained their kinship connection to me (I carry a Lalara name). Eventually, they simply placed their hands over my heart – to tell me that the colour of my skin, my ‘outward form’, did not matter. That this is not what they saw when they looked at me … but something altogether different. Both are dead – dying far earlier than would have been the case if Australia had been settled on more just terms.
My experience is not unique. Indeed, I believe that our First Nations people are willing to embrace anyone who cares to be open to their doing so. All that is asked is that there be a recognition of simple truths about our relationship to each other and to all that belongs to and is part of the country of which we form equal parts.
In the face of such generosity of spirit – how can we possibly allow racism to persist?
IMAGE CREDIT: The image displayed in this article is a painting by Alfred Lalara (deceased), a talented Groote Eylandt artist. The title is Angurugu River.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Science + Technology, Society + Culture
AI is not the real enemy of artists
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics explainer: Nihilism
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
5 ethical life hacks
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Easter and the humility revolution
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
The ethics of tearing down monuments

The ethics of tearing down monuments
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 12 JUN 2020
In the UK and US and other nations around the world, public monuments dedicated to people who have profited from or perpetuated slavery and racism are being torn down by demonstrators and public authorities who sympathise with the justice of their cause.
Statues of Christopher Columbus, Edward Colston, King Leopold II and Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee are amongst those toppled in protest.
What are we to make of these acts? In particular, who should decide the fate of such monuments – and according to what criteria?
By their very nature, statues are intended to honour those they depict. They elevate both the likeness and the reputation of their subject – conferring a kind of immortality denied to those of us who simply fade away in both form and memory.
So, the decision to raise a statue in a public place is a serious matter. The choice reveals much about the ethical sensibilities of those who commission the work. Such a work is a public declaration that a particular person, through their character and deeds, is deserving of public commemoration.
There are six criteria that should be used to evaluate the public standing of a particular life. These can be applied at the time of commissioning a monument or retrospectively when determining if such a commemoration is justified.
-
They must not be associated with any gateway acts
Are there aspects of the person’s conduct that are so heinous as to rule them out, irrespective of any other achievement that might merit celebration? For example, one would not honour a genocidal mass murderer, even if the rest of their life was marked by the most profoundly positive achievements. There are some deeds that are so wrong as to be beyond rectification.
-
Their achievements must be exceptionally noteworthy
Did they significantly exceed the achievements of others in relevantly similar circumstances? For example, we should note that most statues recognise the achievements of people who were born into conditions of relative privilege. The outstanding achievements of the marginalised and oppressed are, for the most part, barely noticed, let alone celebrated.
-
Their work must have served the public good
Did the person pursue ends that were noble and directed to the public good? For example, was the person driven by greed and a desire for personal enrichment – but just happened to increase the common good along the way?
-
The means by which they achieved their work must be ethical
Were the means employed by the person ethically acceptable? For example, did the person benefit some by denying the intrinsic dignity of others (through enslavement, etc)?
-
They must be the principal driver of the outcomes associated with their deeds
Is the person responsible for the good and evil that flowed from their deeds? Are they a principal driver of change? Or have others taken their ideas and work and used them for good or ill? It is important that we neither praise nor blame people for outcomes that they would never have intended but were the inadvertent product of their work. In those cases, we should not gloss over the truth of what happened. But if they otherwise deserve to be honoured for their achievements, then these should not be deemed ‘tainted’ by the deeds of others.
-
The monument must contribute positively to the public commons
Would the creation of the monument be a positive contribution to the public commons, or is it likely to become a site of unproductive strife and dissension? In considering this, does the statue perform a role beyond celebrating a particular person and their life? Is it emblematic of some deeper truth in history that should be acknowledged and debated? Not every public monument should be a source of joy and consensus. Some play a useful role if they prompt debate and even remorse.
It will be noted that five of the six criteria relate to the life of the individual who is commemorated. Only the sixth criterion looks beyond the person to the wider good of society. However, this is an important consideration given that we are thinking, here, specifically about statues displayed in public places.
The retrospective application of this criteria is precisely what is happening ‘on the streets’ at the moment. The trouble is that the popular response is often more visceral than considered – and this sparks deeper concerns amongst citizens who are ready to embrace change … but only if it is principled and orderly.
Of course, asking frustrated and angry people to be ‘principled and orderly’ in their response to oppression is unlikely to produce a positive response. That’s why I think it important for civic authorities to take responsibility for addressing such questions, and to do so proactively.
This was recently demonstrated by the Borough of Tower Hamlets that removed the statue of slave owner Robert Milligan from its plinth at West India Quay in London’s Docklands. As the Mayor of London, Sadiq Khan, noted: “it’s a sad truth that much of our wealth was derived from the slave trade – but this does not have to be celebrated in our public spaces”.
UPDATE: The statue of slave trader Robert Milligan has now been removed from West India Quay.
It’s a sad truth that much of our wealth was derived from the slave trade – but this does not have to be celebrated in our public spaces. #BlackLivesMatterpic.twitter.com/ca98capgnQ
— Sadiq Khan (@SadiqKhan) June 9, 2020
What does all of this mean for Australia? There will be considerable debate about what statues should be removed. I will leave it to others to apply the criteria outlined above. However, the issue is not just about the statues we take down.
What of those we fail to erect? Who have we failed to honour? For example, have we missed an opportunity to recognise people like Aboriginal warrior Pemulwuy whose resistance to European occupation was every bit as heroic as that of the British Queen Boudica. Two warrior-leaders – the latter celebrated; the other not. The absence is eloquent.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Why you should change your habits for animals this year
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
A guide to ethical gift giving (without giving to charity)
Explainer
Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Ethics Explainer: Logical Fallacies
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The role of emotions in ethics according to six big thinkers
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Big tech's Trojan Horse to win your trust

Big tech’s Trojan Horse to win your trust
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsScience + Technology
BY Matthew Beard 26 MAY 2020
Technology has created bad trust habits in all of us. We shouldn’t be tricked into giving tech our trust, but that’s exactly what happens when everything is about making life easier.
During this lockdown period, I’ve been thinking a lot about the difference between states and habits. Since the outbreak of COVID-19, we’ve all learned what proper hand washing hygiene looks like, how to prevent the risk of spreading disease when we’re in public and what kinds of places to avoid.
For many of us, health used to be a state that we enjoyed without having to develop too many of the habits that help guarantee that health. We’ve had all the benefit without the effort. However, we’re now recognising that if we want the best chance of maintaining our health in a time of uncertainty, we need to be intentional about the habits and behaviours we develop.
I think it’s helpful to think about trust in the same way. For many people and organisations, being trusted is a state: we want to be in a situation where people have high confidence in us. What hasn’t always happened is to think about the intentional practices, behaviours and habits that are likely to secure trust in times of crisis.
This is particularly true for technology and tech companies, who have enjoyed a disproportionately high level of trust for a simple reason: they make our lives easier. The convenience we receive by interacting with technology means we’re likely to continue to engage with them, even when there are very good reasons not to.
Take Uber, for example. Uber is highly reliable and very convenient, which means people are willing to get into cars with complete strangers. Their behaviour indicates they trust the service, even if they say they don’t (surveys find that people find taxi drivers more trustworthy than Uber drivers). This kind of behavioural trust, born of convenience, holds even in situations where people have very good reasons not to ride.
In 2016, in Kalamazoo, Michigan, Jason Dalton – an Uber driver – murdered six people whilst working his nightly Uber driving route. As news broke that there was a suspected murderer picking up rides via Uber, people continued to use the service. One rider who caught a ride with Dalton (thankfully, he wasn’t murdered) actually asked him ‘you’re not the one whose been driving around killing people, are you?’. Despite being aware there was a real threat to life, the convenience of a cheap ride home secured consumer trust in Uber.
Of course, it’s only trust of a certain kind. The trust we confer on convenient technology isn’t genuine trust – where we rationally, consciously believe that our interests align to the tech developers and that they want to take care of us. It’s implied trust; whether we believe the technology will deliver, we act as though it will.
This is the kind of trust we show in large tech platforms like Facebook. A 2018 YouGov survey commissioned by the Huffington Post found 66% of Facebook users have little to no trust in the platforms use of their data. Despite this, those users have given Facebook their data, and continue to do so, which is the kind of trust we provide when there’s something convenient on offer.
We cannot understate the significance that convenience plays as a trust lubricant. Trust expert Rachel Botsman, author of Who Can You Trust?, argues that “Money is the currency of transactions. Trust is the currency of interactions.” We need to add another layer to this: trust is the currency of conscious interactions, but convenience is the currency of the unthinking consumer (and we are all, at times, unthinking consumers).
This generates some real challenges for tech companies. It’s easy to use convenience to secure behavioural trust – to be in the ‘state’ of trust with customers – so that they’ll use your services, hand over data or spend their money, without developing the habits that generate rational, genuine trust. It’s easier to be trusted than to be trustworthy, but it might also be less valuable in the long run.
Moreover, the tendency to reward the convenience-seeking part of ourselves might generate problems with a very long tail. Some problems are not easily solved, nor is there an app to solve wealth inequality, climate change or discrimination. Many of our problems require a willingness to persevere; whilst technology can help, and might help resolve the symptoms of some of these issues, the underlying causes require rethinking our social, political and economic beliefs. Technology alone cannot get us there.
And yet, we continually look to technology as a solution for these woes. The Australian government’s first response to climate change after the 2020 bushfires was a large-scale investment in new climate technologies. Several people have released ‘consent apps’, aimed at preventing rape and false rape claims by having people sign a waiver to confirm they’ve consented to sex. There is no app to solve misogyny; no one technology that will fix our approach to the environment.
The reality is, trading on convenience can make us lazy – not just as individuals, but as a society. It’s bad for us. Moreover, it’s bad for business.
Although people often make decisions based on convenience, they pass judgements based on trust. This means they will often feel duped, exploited or betrayed, feeling ‘tricked’ into signing up to something just because it was convenient at the time.
This makes for a fickle customer and is an unreliable basis on which to build a business. Recognising this, a number of successful organisations are now seeking to build genuine trust. Salesforce CEO Mark Benioff recently stated, “trust has to be the highest value in your company, and if it’s not, something bad is going to happen to you.”
However, for people to trust you, they need to be able to slow down, think, form an ethical judgement. Today, one of the major goals of technology is to be frictionless. Hopefully by now you can see why that’s an unwise goal. If you want people to genuinely trust you, then you can’t give them a seamless experience. You need to create some friction.
Remember, convenience can be a lubricant. It might help you get people through the door more quickly, but it makes them slippery and hard to hold on to.
If you found this article interesting, download our paper, Ethical By Design: Principles for Good Technology for free to further explore ethical tech. Learn the principles you need to consider when designing ethical technology, how to balance the intentions of design and use, and the rules of thumb to prevent ethical missteps. Understand how to break down some of the biggest challenges and explore a new way of thinking for creating purpose-based design.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
I’d like to talk to you: ‘The Rehearsal’ and the impossibility of planning for the right thing
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Science + Technology
The undeserved doubt of the anti-vaxxer
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Stopping domestic violence means rethinking masculinity
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships