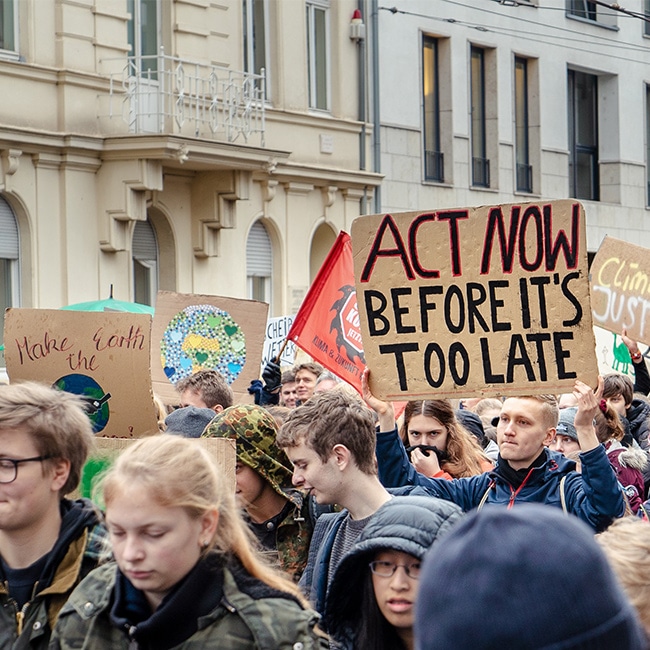Australia's ethical obligations in Afghanistan

Australia’s ethical obligations in Afghanistan
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY Simon Longstaff 1 SEP 2021
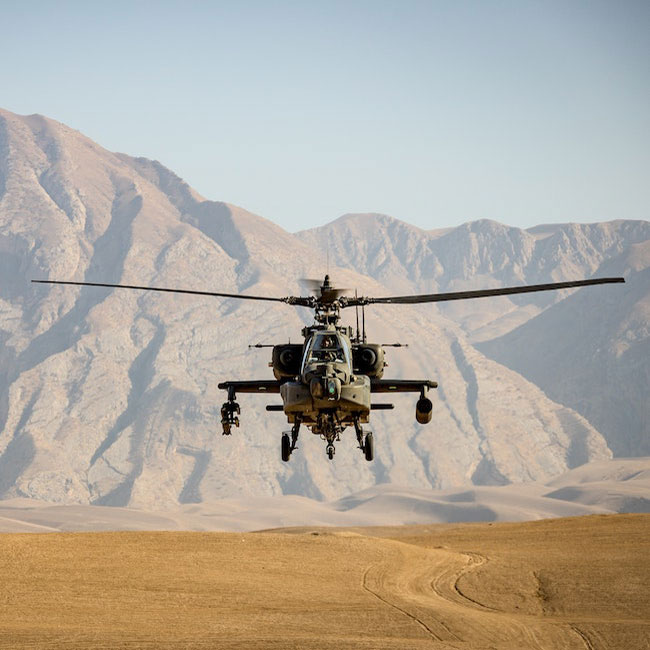
After 20 years of waging war in Afghanistan, the United States and its allies (including Australia) have withdrawn from the field – leaving the Taliban back in power.
The temptation is to label this outcome a resounding defeat. But how does one judge in such matters? Perhaps the Taliban of 2021 has learned, over the past 20 years, how to be better governors of Afghanistan – at least better than they were in the period leading up to 2001; and better than the series of governments that have muddled along in the interim. Perhaps the quality of the peace that will now prevail in Afghanistan will be better than that which would have otherwise existed if no war had been fought. If so, then the loss may not be as great as first thought.
Countries like Australia will need to act on their obligation to stay the course and help the Afghan people as best as they can.
Yet, if this possibility is ever to amount to something more than a feeble dream, then those who fought war need to do more than ‘hope for the best’. Rather, countries like Australia will need to act on their obligation to stay the course and help the Afghan people as best as they can.
Some might challenge the idea that Australia is bound by any obligation to the Afghans. After all, it might be said, have we not already invested a small fortune in treasure? Have we not already sent our sons and daughters to shed blood and to die under the Afghan sun?
My answer begins with the simple truth that, for the most part, we found ourselves expending blood and treasure for our own benefit – and not, primarily, for the good of Afghanistan. Much as we might be comforted by the rhetoric of ‘noble causes’ and ‘high ideals’, when it comes to the realpolitik of statecraft, our politicians send our forces into harm’s way in service of what they plainly believe to be the national interest. As has so often been the case, we went to war to support our most important ally, the United States of America. We went to war so that we could sleep more soundly in our beds – by blunting the edge of terrorism. So, our arrival in Afghanistan (and all that followed) was not driven by an overarching desire to improve the lives of Afghans.
Of course, we also aimed to do some good – and indeed we did. Many Afghans have led better lives due to Australia’s investment in aid and development. Indeed, I have first-hand knowledge of the efforts we have gone to in helping to improve, say, the circumstances of women and girls in Afghanistan. The good we did is real. However, let’s not pretend that it was the product of altruism alone.
I have made much of the self-interest of nations because I think it is key to our understanding the ethical obligation that still binds the Australian government – despite our withdrawal.
As we know, thousands of Afghans rallied to our cause. They served as locally engaged staff in our embassy. They worked as interpreters – both in civilian and military settings. They were our partners in aid and development projects. All of these people directly enabled Australia to realise – as far as possible – its strategic objectives. They did so at considerable personal risk – openly assisting a self-declared enemy of the Taliban (and even more extreme groups like ISIS-K). This risk was exacerbated by the work they did – on our behalf – not just in areas of conflict. For example, what would a hardline opponent to women’s empowerment think of those who have worked tirelessly to achieve that outcome? Surely, those who worked to help women now have a target on their back!
It’s not just specific individuals we need to think of. Large numbers of apparently unconnected Afghans have borne the brunt of 20 years of war waged for our benefit. They were the ones maimed and killed – whether as ‘collateral damage’ or as the intended victims of fundamentalists bent on dominating and pacifying through terror.
It was shameful that our response to the growing power of the Taliban was to do ‘too little, too late’.
Given all of this, it was shameful that our response to the growing power of the Taliban was to do ‘too little, too late’. In saying this, I acknowledge that very few people predicted the speed or comprehensive nature of the Taliban victory. However, I suspect that the larger problem was that too few in government truly understood the depth of our obligation to those Afghans who have assisted us. As much as anything else, it is the sense of indifference that has led many in our armed forces to feel that we have betrayed those left behind – and to express a sense of shame on behalf of our nation.
We should have had much to celebrate. Despite the dark shadow cast by the findings of the Brereton Report, there is much to be proud of in terms of Australia’s overall contribution. That legacy is at risk of being sullied by the manner of Australia’s departure and the sense that we will do the minimum that decency requires – and then wash our hands of the whole thing, leaving our faithful collaborators to pay the price of our failure.
I mentioned before that talk of defeat may turn out to be illusory; that there is a chance that 20 years of war has led to a better future than could otherwise have been hoped for. This brings to mind an old Islamic proverb, “Trust in Allah! … but tie the camel’s leg”.
If we are to find honour, then we must not abandon our Afghan colleagues – not even now when the evacuation has been declared ‘complete’. We need to make it easy for those we left behind to secure visas. We need to ease their passage to safety. We need to continue to invest – if at all possible – in programs that improve the plight of ordinary Afghans – even while they live under Taliban rule.
That much we owe them for bearing their share of the burdens arising out of our self-interested invasion of their country.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights
Big Thinker: Malcolm X
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Calling out for justice
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Settler rage and our inherited national guilt
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
Who gets heard? Media literacy and the politics of platforming
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
Vaccines: compulsory or conditional?

Vaccines: compulsory or conditional?
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingPolitics + Human Rights
BY Simon Longstaff 16 AUG 2021
One of the most significant ethical issues to confront the community in the current phase of the COVID-19 pandemic concerns the extent to which people should be required to achieve full vaccination.
The debate mirrors earlier discussions about where to set the balance between public safety and personal liberty. In the wake of events such as the 9/11 terrorist attack or the Bali bombing, successive governments introduced legislation to curb civil liberties that, in some cases, had been fought for centuries ago – with the shedding of much blood in the name of liberty.
However, there was scarcely a whimper of protest from conservatives at that time, or since. Former Prime Minister, Tony Abbott, spoke for many government leaders when, in February of 2015, he said that, “There is no greater responsibility – on me – on the government – than keeping you safe”.
That formula has been invoked time and time again in response to criticism from those who have questioned the erosion of civil liberties. Once again, Tony Abbott outlined the rationale for preferring public safety over personal liberty, noting that one or two people could pose a threat to the community. In the same national security statement quoted above, Mr Abbott when on to say, “But frankly, I’d rather lose a case, than lose a life.”
For the most part, the community has accepted this set of prescriptions. It is against this background that one needs to understand the approach of government to the menace posed by COVID – where lives can be threatened by the actions of just one or two individuals – including those who are free from malicious intent.
As noted above, I cannot think of single conservative commentator who took Mr Abbott (or other leaders) to task for their preference of public safety over personal liberty. Yet, many of these same commentators are lining up to condemn politicians who take an identical stance in response to the proportionately greater risk to life posed by COVID-19. In doing so, some have decided to oppose a range of government measures that they think identify as violating individual liberties – ranging from ‘lockdowns’ to vaccination.
Unhelpfully, the debate has been skewed by the failure to make a clear distinction between different types of restriction.
As far as I know, there has been no serious proposal – from government or the private sector – for ‘compulsory vaccinations’. Yet, this ‘red herring’ is causing widespread debate and a fair measure of concern.
So, how should we think about the issue of vaccinations?
It seems to me that the greatest source of confusion (and concern) lies in the failure to distinguish between three types of requirement: compulsory, optional and conditional.
Compulsory requirements are enforced – and those that contravene are subject to punishment. There are very few compulsory requirements in liberal democracies. Examples in Australia include: the requirement for children to be educated (e.g. attend school); and the requirement that adult citizens attend voting places and receive a ballot paper (whether they cast a valid vote or not is up to them). Most recently, we have had genuinely compulsory ‘lockdowns’. If you fail to abide by the rules, then you are subject to formal punishment by the state.
Optional requirements leave each person to decide whether or not to engage in the specified activity – without consequence. As such, they are generally held to be uncontroversial.
Conditional requirements are far more common. Typically, they are in the form of: ‘if … then’. For example, ‘if you wish to drive a car … then you must be licensed to do so’. Or, ‘if you wish to enter this mine … then you must wear safety equipment’. As will be evident, no person is required to drive a car or enter a mine site. To do so is a matter of choice. In this lies the principal difference between ‘conditional’ and ‘compulsory’ requirements.
I have not really heard anyone make the case for ‘compulsory’ vaccination. Rather, there are arguments being made in favour of vaccination as a ‘conditional requirement’. So, how might such a requirement be justified?
First, it is easy to justify such a requirement in order to protect the health and safety of a community or a workplace. This was the line of argument that Peter Singer attributed to John Stuart Mill, in his recent opinion piece in The Sydney Morning Herald. Second, one can also justify a conditional requirement as a precondition for being able to perform a function. Third, one can set a condition that requires a person not to render themselves either unsafe or unable to perform their role. For example, a mining company might require an employee to wear protective clothing or sunscreen. This is not solely to keep the employee safe. It also ensures that the person remains fit (physically able) to perform their role, free from injury.
The same thinking can also be extended to the idea that an employee should remain fit (physically able) to perform their role free from disease. As noted above, this conditional requirement could be seen as being directed towards the welfare of the employee. Or it could be a requirement for the benefit of the employer.
In either case, no person is compelled to work under such conditions. If they are not prepared to accept the condition, then they may choose not to work for an employer imposing such a requirement. As noted above, this is common and uncontroversial in many, many cases.
A final note: nothing here has any implications for what a person should or should not believe. For example, a person may have a ‘magical belief’ that they are protected from the risk of injury or disease, yet still be required to wear safety equipment. A person may believe that COVID-19 is a ‘hoax’ yet still have to meet the conditional requirement that they be vaccinated.
Governments, companies, etc. should not be in the business of imposing beliefs on others. They can seek to persuade – but nothing more. However, they have every right to set conditions on behaviour and then leave it to people to choose whether or not to meet the conditional requirements that have been set.
Of course, this leaves open one final possibility – that a person may be unable to meet the condition through no fault of their own. For example, some people cannot operate the pedals on a car – yet may still wish to drive. The fact that they cannot operate an unmodified vehicle is not a matter of choice (or an absence of will) – it is a physical impossibility. In such cases, society might try to develop mechanisms (e.g. modified control systems) to offset the limitations. However, this will not always be possible.
Should an employer set vaccination as a condition of employment?
The decision to undertake any kind of medical procedure is a serious one.
Normally, this would be a private matter – especially when it relates to the health of an individual. However, there are multiple precedents for setting conditional requirements of a kind that involve medical procedures, including vaccination. For example, as things stand, one cannot travel to certain countries without vaccination (yellow fever). But to what extent, if any, might the context of employment render a different ethical outcome? For example, should employers apply a ‘test of relevance’ (e.g. different requirements for people working in aged care/disability sectors than, say, for construction workers)?
Some might argue that there is room for conscientious objection – but it has always been a mark of genuine cases, of conscientious objection, that people be prepared to accept the consequences of acting in conformance with their conscience. Also, the duty is to act on a well-informed conscience. That is, one cannot claim the protections or validations of conscience when based in proven error (e.g. in the belief that vaccines do not work, that they contain micro-chips, etc.).
Thus, when it comes to balancing safety vs freedom it should be recognised that both values are of importance. However, good health is an enabler of freedom. Therefore, freedom from the risk of infection (e.g. amongst employees) should be given priority. This would allow for the establishment of ‘conditional requirements’ (such as in the case of a vaccine passport). But these requirements should be structured as the minimum necessary to secure safety. For example, if the job can be done while working from home, then that should be allowed amongst those who choose not to be vaccinated. On the other hand, if the job requires contact with others (if this is strictly necessary), then a refusal to be vaccinated would be equivalent to refusing to take an anti-doping blood test (in elite sports) or to wear safety equipment in a mine.
What questions should employers consider about vaccination?
- Does vaccination significantly reduce the risk of transmission to others? If so, does the employer have a duty to limit the risk of infection faced by its employees (as a whole), customers, etc.?
- Does COVID present a risk that an infected employee will be unable to perform their duties? If so, is the risk sufficient to justify a conditional requirement that the employee protect themselves from this harm?
- What exceptions (if any) can be made for people who are unable to meet the conditional requirement (e.g. medically unfit to be vaccinated)? To what extent can the person’s work practices be managed to take account of this limitation (e.g. special facilities, use of additional PPE, etc.) so as to balance the interests of the individual and the wider group?
Conditional requirements are an everyday occurrence. They range from clothing requirements (e.g. to enter certain places), to the possession of licences, to the need for vaccinations when travelling to certain countries overseas. Some of these requirements are established to reflect cultural preferences, or as indicators of respect for particular institutions or places or as being necessary to realise values like those of ‘safety’, ‘efficiency’, etc.
In the end, when values compete – as in the case of ‘public safety’ vs ‘personal liberty’ the best approach is to seek to make every effort to minimise the damage to one value to the greatest extent possible while realising the other. It’s an approach that I think we failed to heed when it came to our nation’s response to the threat posed by terrorism – sowing the seeds that we seem to be harvesting today.
Perhaps this time round, we can do better.
As a small beginning, I wonder if we can at least drop the reference to so-called ‘compulsory’ vaccinations and instead focus on what might count as a reasonable, conditional requirement.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Limiting immigration into Australia is doomed to fail
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing
Your kid’s favourite ethics podcast drops a new season to start 2021 right
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Are we prepared for climate change and the next migrant crisis?
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Why you should change your habits for animals this year
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
3 Questions, 2 jabs, 1 Millennial

3 Questions, 2 jabs, 1 Millennial
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingPolitics + Human Rights
BY Rebecca Blake 28 JUL 2021
What started out as a trip to get my flu shot turned into a quick, loaded political decision.
Fortunately, by stopping and reflecting, I left politics to the pollies and made my decision based on ethics.
When Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced that anyone under 40 could approach their GP to get the AstraZeneca vaccine, I decided to act. We were not long into Sydney’s second lockdown and already I was feeling the frustration of isolation. I called my GP and was told to book a consultation first before making any appointments for the jab. I decided to make a day of it and booked both my consultation and flu shot as one appointment. Any outing in Covid times is a highlight, am I right?
One week later I sat down in front of my GP. He said, “I know you’re here for your flu shot but given the situation we’re in, I strongly recommend you get the AstraZeneca. What do you want to do?” In the space of 30 seconds I had to decide whether to AZ now, or to Pfizer at some time in the future, date to be determined. The challenge? Putting aside the loaded politics and making an ethical choice.
I am aware I am privileged in being able to make this choice in the first place; I have the means to transport myself to and from the clinic, English is my first language so I can understand the information and make an informed consent. I am fit and healthy and being in a medical clinic, whilst not always comfortable, is not a traumatic experience for me. None the less given the bad rap the AZ vaccine has received, it was a little daunting.
So here are three questions this Millennial asked themself about getting the AZ vaccine now or waiting for Pfizer:
1. Who am I doing this for?
I am fully aware that the Pfizer vaccine is the preferred jab given there are some risks for young people when it comes to taking the AstraZeneca. A few friends have managed to somehow obtain a Pfizer vaccination through connections, either that or some back-alley vaccine deal (letting my imagination run wild). Black market fantasies aside, when it came to my decision making, I chose the non-preferred option as there was plenty of AZ supply to go around. This choice was my contribution to ensuring the small amounts of Pfizer are provided to those who need it most urgently.
Of course, I could wait until there is plenty of supply of Pfizer. But given that medical advice is that the vaccine reduces transmission, the decision to delay can impact the people around me, people who I love the most, such as my partner who is a teacher. I have friends who are immune-suppressed, and family members who are elderly. I feel, the more we all do to suppress transmission in the community, the safer they will be.
2. What does the best outcome look like? In the short term? In the long term?
Recently the government released an advertising campaign to encourage the public to get vaccinated. Most have seen the footage of a young woman, around my age, on a ventilator struggling to breathe and becoming increasingly distressed. There has been a lot of discussion concerning that this advert was aimed at young people, the very people who can’t get hold of the recommended vaccine for this age group. Like many, I find myself repeatedly frustrated about the vaccine roll out.
But there are actions I could do now to play my part in preventing this lockdown from lasting any longer. I have friends in the UK, many of whom have had the AZ vaccine. I want to do everything I can to help get life back to normal. I feel an overwhelming responsibility as a citizen to do what I can to prevent the spread, protect myself and fellow neighbour, and avoid the possibility of passing it on to someone I love. I channelled this frustration into an action that I as an individual can take. My decision to take the AstraZeneca was my way of contributing in some small way to increasing acceptance of a mass vaccination campaign that will improve the lives of the majority in the long term. Whilst it’s reported there are some small amounts of discomfort (fever, body aches and chills for the first 24 hours post vaccine) it’s a short-term pain for a long-term great gain.
3. What are the risks involved?
My anxiety does have its moments and I can catastrophise at the drop of a hat. The human brain likes to predict the future so it can be prepared. In moments where my anxiety flares up, I try and remember it’s just my body trying to protect itself. We tend to focus on the negatives – an easy thing to do during a global pandemic – particularly when combined with media reports of the risks and misinformation across social media.
Negativity bias is rife and it’s easy for us to be more motivated or affected by negative information than positive.
Faced with needing to make a quick decision I relied on the information given to me by my GP in the consultation.
The consultation involves your doctor thoroughly taking you through the potential risks of the AstraZeneca jab. The AZ vaccine has been associated with a rare side effect called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS). According to the Australian Government Department of Health website (www.health.gov.au), in every 1,000,000 cases there is a 3.1 chance of TTS for individuals under 50. Given the current situation in Sydney I felt the risks of COVID far outweighed the risks of adverse side effects from the vaccine. Sure, we do not know what the long-term vaccine effects could be, but it was a chance to consider the trade off between facts and knowledge and the assumptions that there might be some long-term effects from the vaccine. For now, I am sticking with my faith and trust in the medical industry. They have been working hard these past 18 months and have been right so far. Plus vaccines are not new, the first recorded use is from the 16th century in China for smallpox.
So what did I choose …
In the end, after weighing up these questions I was stoked to get poked. By the evening I was hit with the prewarned symptoms of fever and body aches but by the time 48 hours had passed, I was fit as a fiddle. I was surprised by how many work colleagues congratulated me saying how brave I was or how proud they were to know a young person playing their part to combat this disease.
One small disappointment. I didn’t get one of those, “I’ve been vaccinated stickers.” I may be 30 but the six-year-old in me was severely disappointed. Not even a lollipop… so if you choose to get the AZ vaccine… at least bring your own post poke treat.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Science + Technology
Big Thinker: Francesca Minerva
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
We are witnessing just how fragile liberal democracy is – it’s up to us to strengthen its foundations
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Science + Technology
Twitter made me do it!
Big thinker
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Big Thinker: Temple Grandin
BY Rebecca Blake
Rebecca is a writer, producer, director and theatre maker. Alongside their work with The Ethics Centre they are Artistic Associate and board member with Kings Cross Theatre. Prior to this, they were an Artist in Residence with the Barbican Centre and Rich Mix Theatre in London.
Thought Experiment: The famous violinist

Thought Experiment: The famous violinist
ExplainerPolitics + Human Rights
BY The Ethics Centre 23 JUL 2021
Imagine waking up in a bed, disoriented, bleary-eyed and confused.
You can’t remember how you got to there, and the bed you’re in doesn’t feel familiar. As you start to get a sense of your surroundings, you notice a bunch of medical equipment around. You notice plugs and tubes coming out of your body and realise you’re back-to-back with another person.
A glimpse in the mirror tells you the person you’re attached to is a world-famous violinist – one with a fatal kidney ailment. And now, you start to realise what’s happened. Last night, you were invited to be the guest of honour at an event hosted by the Society of Music Lovers. During the event, they told you about this violinist – whose prodigious talent would be taken from the world too soon if they couldn’t find a way to fix him.
It looks like, based on the medical records strewn around the room, the Society of Music Lovers have been scouring the globe for someone whose blood type and genetic markers are a match with the violinist.
A doctor enters the room, looking distressed. She informs you that the Society of Music Lovers drugged and kidnapped you, and had your circulatory system hooked you up to the violinist. That way, your healthy kidney can extract the poisons from the blood and the violinist will be cured – and you’ll be completely healthy at the end of the process. Unfortunately, the procedure is going to take approximately 40 weeks to complete.
“Look, we’re sorry the Society of Music Lovers did this to you–we would never have permitted it if we had known,” the doctor apologises to you. “But still, they did it, and the violinist is now plugged into you. To unplug you would be to kill him. But never mind, it’s only for nine months. By then he will have recovered from his ailment and can safely be unplugged from you.”
After all, the doctor explains, “all persons have a right to life, and violinists are persons. Granted you have a right to decide what happens in and to your body, but a person’s right to life outweighs your right to decide what happens in and to your body. So you cannot be unplugged from him.”
This thought experiment originates in American philosopher Judith Jarvis Thompson’s famous paper ‘In Defence of Abortion’ and, in case you hadn’t figured it out, aims to recreate some of the conditions of pregnancy in a different scenario. The goal is to test how some of the moral claims around abortion apply to a morally similar, contextually different situation.
Thomson’s question is simple: “Is it morally incumbent on you to accede to this situation?” Do you have to stay plugged in? “No doubt it would be very nice of you if you did, a great kindness. But do you have to accede to it?” Thomson asks.
Thomson believes most people would be outraged at the suggestion that someone could be subjected to nine months of medical interconnectedness as a result of being drugged and kidnapped. Yet, Thomson explains, this is more-or-less what people who object to abortion – even in cases where the pregnancy occurred as a result of rape – are claiming.
Part of what makes the thought experiment so compelling is that we can tweak the variables to mirror more closely a bunch of different situations – for instance, one where the person’s life is at risk by being attached to the violinist. Another where they are made to feel very unwell, or are bed-ridden for nine months… the list goes on.
But Thomson’s main goal isn’t to tweak an admittedly absurd scenario in a million different ways to decide on a case-by-case basis whether an abortion is OK or not. Instead, her thought experiment is intended to show the implausibility of the doctor’s final argument: that because the violinist has a right to life, you are therefore obligated to be bound to him for nine months.
“This argument treats the right to life as if it were unproblematic. It is not, and this seems to me to be precisely the source of the mistake,” she writes.
Instead, Thomson argues that the right to life is, actually, a right ‘not to be killed unjustly’.
Otherwise, as the thought experiment shows us, the right to life leads to a situation where we can make unjust claims on other people.
For example, if someone needs a kidney transplant and they have the absolute right to life – which Thomson understands as “a right to be given at least the bare minimum one needs for continued life” – then someone who refused to donate their kidney would be doing something wrong.
Thinking about a “right to life” leads us to weird conclusions, like that if my kidneys got sick, I might have some entitlement to someone else’s organs, which intuitively seems weird and wrong, though if I ever need a kidney, I reserve the right to change my mind.
Interestingly, Thomson’s argument – written in 1971 – does leave open the possibility of some ethical judgements around abortion. She tweaks her thought experiment so that instead of being connected to the violinist for nine months, you need only be connected for an hour. In this case, given the relatively minor inconvenience, wouldn’t it be wrong to let the violinist die?
Thomson thinks it would, but not because the violinist has a right to use your circulatory system. It would be wrong for reasons more familiar to virtue ethics – that it was selfish, callous, cruel etc…
Part of the power of Thomson’s thought experiment is to enable a sincere, careful discussion over a complex, loaded issue in a relatively safe environment. It gives us a sense of psychological distance from the real issue. Of course, this is only valuable if Thomson has created a meaningful analogy between the famous violinist and what an actual unwanted pregnancy is like. Lots of abortion critics and defenders alike would want to reject aspects of Thomson’s argument.
Nevertheless, Thomson’s paper continues to be taught not only as an important contribution to the ethical debate around abortion, but as an excellent example of how to build a careful, convincing argument.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Do states have a right to pre-emptive self-defence?
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
CoronaVirus reveals our sinophobic underbelly
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
A note on Anti-Semitism
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Ask an ethicist: Why should I vote when everyone sucks?
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Libertarianism and the limits of freedom

Libertarianism and the limits of freedom
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY Joshua Pearl 20 JUL 2021
Libertarianism is the political philosophy that champions individual freedom. But does it really love freedom as much as it claims?
Governments interfere with our lives all the time. They punish us when we say things that they (or others) consider offensive. They make us save money we can only access if we reach a certain age. They engage police that can stop us in the street. They require us to inoculate against disease – even if it is against our wishes. And they demand we give away some of our salaries and assets (in the form of taxes), to be spent on things that may neither benefit nor be agreeable to us.
These are all fairly standard government interferences, even before we consider the more extreme restrictions that we have seen imposed throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Most political philosophies permit state interference, with some permitting quite a lot. Social contract theories, from Hobbes in the 17th century to Rawls in the 20th century, contend that citizens have consented either implicitly or explicitly, to give up certain freedoms, in exchange for protection of their remaining freedoms. However, not all political philosophies are as sanguine.
Libertarianism, which champions individual freedom, argues government interference is not only a pesky annoyance, but a violation of our fundamental rights. Libertarians contend that government interference is unjust even if intervention benefits the person being interfered with. Extreme libertarians would even support the right of a person to sell themselves into slavery – and would object to any government that seeks to prevent this.
Libertarianism has its roots in the works of the seventeenth and eighteenth-century liberal philosophers: John Locke, David Hume and Adam Smith. However, modern libertarians find much of their inspiration from Robert Nozick’s Anarchy, State and Utopia (1974). Nozick argues that individuals have strong self-ownership and property rights, rights that cannot be violated. Freedom, the core tenet of libertarianism, is the fundamental good to be affirmed and protected. On this view, we are all free (and equal) individuals, with the uninhibited right to make individual decisions with regard to our lives, our liberty, and the ownership of our property.
Libertarians, however are not anarchists. They do believe in the existence of the state. A libertarian state is one that performs the strictly limited roles of protecting citizens’ self-ownership and property rights and rectifying past transgressions of those rights.
Government’s role is to protect people’s freedom to choose happiness of a kind that is defined by each individual, not as dictated by others. If an individual wants to follow a particular god, that is their choice. If a person wants to buy a particular good or service on the free market, so let them. If a woman wants to marry multiple husbands, that is up to her.
For most right-libertarians, original property ownership (that is staking an ownership on unowned natural resources) is allowable, subject to the somewhat ambiguous Lockean proviso, that “enough and is good” is left for others. Nozick also asserted that when staking an ownership claim, no-one else should be made worse-off than they would otherwise be, which allows for significant variation in original property ownership. Left-libertarians, distinguished from right-libertarians by the very feature of original property ownership, claim everyone has a pro rata right to natural resources such as land, air and minerals.
Libertarianism’s absolute focus on individual freedom is attractive and makes for a consistent and simple political philosophy. It also has broad appeal, attracting strange ideological bedfellows.
Social progressives find attractive the social freedom associated with libertarianism. Governments have no right to punish an individual for taking recreational drugs; it is impermissible for the state to ban marriage between same sex couples; wrong for a country to wage a foreign war or conscript people into the army; and forbidden for government to ban, say, assisted dying.
Economic conservatives are attracted to the libertarian stance that it is wrong for government to take away assets in the form of an inheritance tax; impermissible for the state to impose an income tax for the purpose of redistribution. Indeed, the argument that government has no right to interfere in transactions between consenting adults, underpins the fundamental argument for many free market economists. Those on both the left and right are attracted to the argument that governments have no right to censor free speech.
However, if you think that libertarianism maximises freedom, then you would be wrong. One criticism of libertarianism is that it allows for scenarios which substantially limit freedom. Libertarianism prohibits anything but the very minimum level of taxation. This stance permits gross inequalities across wealth and income, and prohibits the levying of taxes required to fund the provision of state-run services.
As long as people are not interfered with, libertarianism finds it fair for children to be born into a subsistent existence, without access to education or basic healthcare. While these children may be able to do whatever they want without interference, their options and possibilities are severely limited. It is difficult to argue that these children are free in any meaningful sense.
Libertarianism also struggles to deal with negative externalities – the negative effects that individuals’ actions have on unrelated third parties. Companies (and individuals) tend to ignore costs which are imposed on other people. When this occurs, the net total cost to society of the pursuit of individual production and consumption choices, are typically negative.
Emblematic of this problem is climate change. I might enjoy all the benefits of taking a holiday to London, but I impose certain costs associated with green-house emissions that contribute to global warming, on other Australians. Adani’s shareholders and executives may enjoy the higher dividends and salaries from its pursuit of coal mining, but ignore the pollution costs they impose on future generations.
In such cases, libertarians, with their strong insistence of individual freedom, have very little constructive criticism to contribute to considerations regarding potential government intervention mechanisms. A further example concerns COVID-19 vaccination. Should citizens be free to choose whether they are vaccinated, despite the costs a failure to vaccinate imposes on other people? The libertarian position is that forcing someone to be vaccinated is unjust.
Perhaps the most incisive criticism of libertarianism though, is that paradoxically, libertarianism interferes too much.
Property acquisition typically involves a whole suite of historical injustices and the rectification of past injustice is likely to require a great deal of interference. If you are a card-carrying Silicon Valley billionaire libertarian, then you are aware (or at least you should be) that your worldly possessions are contingent upon the injustice of Europeans taking somebody else’s (native Americans’) private property.
Libertarian fairness, requires appropriate rectification. And arguing past injustices do not require rectification is arguing for something quite different to libertarian rules of justice. Most likely, that’s just arguing for self-interest.
Libertarianism has many attractive features and is likely to remain the political philosophy of choice for those who claim to love freedom. However, libertarian freedom is conditional. A world where libertarian rules of justice reign, may in fact result in a world that is not very free at all.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights
Ethics Explainer: Just War Theory
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Science + Technology
Parent planning – we shouldn’t be allowed to choose our children’s sex
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Israel or Palestine: Do you have to pick a side?
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Why you should change your habits for animals this year
BY Joshua Pearl
Joshua Pearl is the head of Energy Transition at Iberdrola Australia. Josh has previously worked in government and political and corporate advisory. Josh studied economics and finance at the University of New South Wales and philosophy and economics at the London School of Economics.
What do we want from consent education?

What do we want from consent education?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Georgia Fagan 11 MAY 2021
In mid-April this year a government-funded video was released which aimed to teach high-school aged Australians about sexual consent.
The video, which attempted to emphasise the importance of sexual consent by discussing the forced consumption of milkshakes, was widely criticised around the globe. It has since been removed from ‘The Good Society’ site, with secretary of the Department of Education Dr Michele Bruniges citing “community and stakeholder feedback” as reason for the action.
Widespread criticism of the video can be found online about the video’s sole use of metaphor to describe consent. Less present in the discussions is consensus on what a good consent education video would look like.
The underlying assumption in the video released by The Good Society is that issues of sexual consent can be managed by teaching adolescents that the rights of an individual are violated when an aggressor forces a ‘no’, or a ‘maybe’, into a ‘yes’. And, the video tells us, “that’s NOT GOOD!“.
Is it sufficient to tell adolescents to respect the rights of their peers in order to overcome issues of sexual violence? While rights may help us discuss what it is we want our societies to look like, they fail to assist us in getting others to care for, or value, the rights of others.
Sally Haslanger, Ford Professor of Philosophy and Women’s and Gender Studies at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) argues that actions are shaped by culture, and that cultures are effectively networks of social meanings which work in a variety of ways to shape our social practices. To change undesirable social practices, cultural change must also occur.
For example, successfully managing traffic is not just achieved by passing traffic laws or telling drivers that breaking the law is ‘not good’. Instead, Haslanger tells us that it requires inculcating “public norms, meanings and skills in drivers”. That is, we need a particular type of culture for traffic laws to adequately do what it is we want them to do. Applying this idea to sexual consent, we see that we are required to educate populations about why violating the preferences of our peers is indeed ‘not good’, after all.
Skirting around the issue fails to provide resources to move our culture to better recognise the deep injustice and harms of sexual violence.
Vague, euphemistic videos will likely fail to play even a minor role in transforming our current culture into one with fewer instances of sexual violence. This is due largely to the fact that Australia is comprised of social and political systems which fail to take the violence experienced by women and girls seriously.
Haslanger suggests that interventions such as revised legislation and moral condemnation will be inadequate when enforced onto populations whose values are incompatible with the goals of such interventions.
Attempting to address issues of sexual misconduct indirectly – as seen by The Good Society video – are likely to be unsuccessful in creating long term behavioural change. Skirting around the issue fails to provide resources to move our culture to better recognise the deep injustice and harms of sexual violence.
As Haslanger tells us, so long as we are a culture which has misogyny embedded into it, social practices will continue to develop that cause people to act in misogynistic ways. We are required to reshape our culture in a way that changes the value and importance of women.
So long as we are a culture which has misogyny embedded into it, social practices will continue to develop that cause people to act in misogynistic ways.
So, what will shift and transform embedded cultural practices? A better approach advocates educating audiences why consent is valuable, not just how to go about getting it. A population which fails to value the bodily autonomy and preferences of each of its members equally is not a population that will go about acquiring consent in successful and desirable ways.
Quick fix solutions such as ambiguously worded videos on matters of consent are likely to do very little for adolescents in a school system absent of a comprehensive sexual education, and where conversations on sexual conduct and interpersonal relationships remain marginalised.
We need to aim to create a generation of adolescents who are taught why sexual consent is important and why they should value the preferences of their peers. A culture which continues to keep sex ‘taboo’ by failing to explicitly discuss sexual relationships and the reasons why disrespecting bodily autonomy is “NOT GOOD!” will be one which fails to resolve its endemic misogyny and disregard for the lives of women and girls.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
What makes a business honest and trustworthy?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships, Science + Technology, Society + Culture
Who does work make you? Severance and the etiquette of labour
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Dignity
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Ethics Explainer: Testimonial Injustice
BY Georgia Fagan
Georgia has an academic and professional background in applied ethics, feminism and humanitarian aid. They are currently completing a Masters of Philosophy at the University of Sydney on the topic of gender equality and pragmatic feminist ethics. Georgia also holds a degree in Psychology and undertakes research on cross-cultural feminist initiatives in Bangladeshi refugee camps.
He said, she said: Investigating the Christian Porter Case

He said, she said: Investigating the Christian Porter Case
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human Rights
BY Louise Richardson-Self 10 MAR 2021
On 4 March 2021 Attorney General Christian Porter identified himself as the unnamed Minister who had been accused of a 1988 rape in a letter sent to the Prime Minister and some senators.
He strenuously denies any wrongdoing and has refused to step down from his role.
ABC News reports that ‘the letter urges the Prime Minister to set up an independent parliamentary investigation into the matter’ — but should there be an investigation?
The Problem With Testimony
When it comes to accusations of sexual assault, it seems like the situation comes down to a clash of ‘testimony’ — she said, he said. But who is to be believed?
Testimony, to clarify, isn’t just any old speech act. Testimony is speech that is used as a declaration in support of a fact. “The sky is blue” is testimony; “I like strawberries” isn’t.
Generally, people are hesitant to accept testimony as good, or strong evidence for any sort of claim. This is not because testimony is always unreliable, but because we think that there are more reliable methods of attaining knowledge.
Other methods include direct experience (living through or witnessing something), material collection (looking for evidence to support the truth of a claim), or through the exercise of reason itself (for instance, by way of logic or deductive reasoning).
In this case, it seems like what would need to occur is a fact-finding mission which could add weight either to the testimony of either Porter or the alleged victim.
What is very surprising, then, is that only some people support such an investigation, while others have rejected the move as unnecessary, including Prime Minister Scott Morrison. These people deem Porter’s testimony credible. But should they?
Judging Credibility
It isn’t strange to find that people are willing to treat testimony as sufficient evidence for a claim. We often do. Testimony is used in trials. Every news report is testimony. The scientific truths we have learn from books or YouTube are testimony. You get the picture. We may think we are always sceptical of testimony, but we could hardly get by without it.
So, we do rely on testimony. Just not all testimony. When it comes to believing testimony, what we’re really doing is judging the speaker’s credibility. The question is thus: should we trust what a specific person says about a specific matter in a specific context?
The problem is that we’re actually not very good at working out which speakers are credible and which aren’t. Often we get it wrong. And sometimes we get it wrong because of implicit biases—biases about types of people, biases about institutions, and the sway of authority.
As philosopher Miranda Fricker has pointed out, when people do not receive the credibility they are due—whether because they receive too much (a credibility excess) or too little (a credibility deficit)—and the reason they do not receive it is because of such biases, then a testimonial injustice occurs.
“Being judged credible to some degree is being regarded as more credible than others, less credible than others, and equally credible as others,” explains philosopher José Medina.
In a she said, he said case, if we judge one person as credible, we’re also discrediting the other.
Fricker explains that testimonial injustice produces harms. First, there is a harm caused to the listener: because they didn’t believe testimony they should have, they failed to acquire some new knowledge, which is a kind of harm.
However, testimonial injustices also harms the speaker. When someone’s testimony is doubted without good reason, we disrespect them by doubting their ability to convey truth – which is part of what defines us as humans. This means testimonial injustices symbolically degrade us qua [as] human. Basically, to commit a testimonial injustice means we fail to treat people in a fundamentally respectful way. Instead, we treat them as less than fully human.
Is there a Credibility Deficit or Excess in Porter’s case?
Relevant to the issue of credibility attribution in the wake of a sexual assault allegations is the perception (and fear) shared by many that women lie about sexual assault.
In fact, approximately 95% of sexual assault allegations are true. This means it is highly improbable (but not impossible) that the alleged victim made a false claim.
It is not just stereotyping about lying and vindictive women that can interfere with correct credibility attribution. As Treasurer Josh Frydenberg has reminded us, Porter “is entitled to the presumption of innocence, as any citizen in this country is entitled.”
This commitment we share to presume innocence unless or until guilt is proven is a significant bulwark of our ethico-legal value system.
However, in a case of “she said, he said”, his entitlement to the presumption of innocence automatically generates the assumption that the victim is lying. Given that false rape allegations are so infrequent, the presumption of innocence unfairly undermines the credibility of the complainant almost every time.
This type of testimonial injustice may seem unavoidable because we cannot give up the presumption of innocence; it is too important. However, the insistence that Porter receive the presumption of innocence rather than insisting we believe the statistically likely allegations against him may point to another problem with the way assign credibility.
As philosopher Kate Manne has observed, particularly when it comes to allegations made by women of sexual assault by men, the accused are often received with himpathy—that is, they receive a greater outpouring of sympathy and concern over the complainants. She explains, “if someone sympathizes with the [accused] initially…he will come to figure as the victim of the story. And a victim narrative needs a villain…”
So here’s the rub.
If a great many people in a society share the view that women lie, then they tacitly see complainants as uncredible.
And if a great many people in a society feel sorry for certain men who are accused of sexual assault, then they are likely to side with the accused. In turn, those who are accused of sexual assault (usually, men) will automatically receive a credibility excess.
Is this what has happened in Porter’s case? Note that an investigation could lend credibility to either party’s claims. This is where the police would normally step in.
Didn’t the Police Investigate and Exonerate Porter?
You would be forgiven for thinking that NSW Police had conducted a thorough investigation and had cleared Porter’s name judging by the way some powerful parliamentary figures have responded to Porter’s case.
For example, in his dismissal of calls for an independent investigation, Scott Morrison said that it “would say the rule of law and our police are not competent to deal with these issues.” Likewise, Treasurer Josh Frydenberg said: “The police are the only body that are authorised to deal with such serious criminal matters.” Nationals Senator Susan MacDonald also opposed the investigation, saying: “We have a system of justice in this country [and] a police service that is well resourced and the most capable of understanding whether or not evidence needs to go to trial — and they have closed the matter.”
Case closed. This must mean that there’s no evidence and that an independent inquiry would be pointless, right?
Not quite. NSW Police stated that there was “insufficient admissible evidence” to proceed with an investigation. They did not say that there was no evidence of misconduct. Moreover, the issue for criminal proceedings is that the alleged victim did not make a formal statement before she took her own life.
In other words, the complainant’s testimony does not get to count as evidence because, technically, there is no testimony on the record.
Preventing Testimonial Injustice
Since the alleged victim had not made a formal statement to Police at the time of her death, the call for an investigation into Porter’s conduct can be seen as a means of ensuring Porter does not receive a testimonial credibility excess and the complainant a testimonial credibility deficit.
To stand by Porter’s testimony in a context where it is widely – and falsely – believed that women make false rape allegations, and where the police are seen as the only body capable of exercising an investigation (when in fact they are not), would be to commit a testimonial injustice.
As former Liberal staffer and lawyer Dhanya Mani says, “The fact that the police are not pursuing the matter for practical reasons does not preclude or prevent the Prime Minister from undertaking an inquiry into a very serious allegation… And that inquiry will either exonerate Christian Porter and prove his innocence or it will prove otherwise.”
It is important to understand that an independent investigation is not bound by the exact same evidentiary rules as are the police and courts. It may be possible for others to testify on her behalf. Other evidence which is inadmissible in court may be admissible here. An independent investigation at least offers the possibility that the complainant’s testimony will get a fair hearing.
Also worth noting is where the presumption of innocence would end. For a crime, guilt should be proved beyond a reasonable doubt. For civil cases, that standard is “on the balance of probabilities”. What standard should an independent investigation use? I would suggest the latter, precisely because testimony is likely to be all the evidence there is.
To prevent a testimonial injustice—attributing too much credibility, or too little, to someone undeserving of it—these allegations must be investigated.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Climate + Environment
What we owe each other: Intergenerational and intertemporal justice
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A new era of reckoning: Teela Reid on The Voice to Parliament
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Power without restraint: juvenile justice in the Northern Territory
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights
Thought Experiment: The famous violinist
BY Louise Richardson-Self
Louise Richardson-Self is a Lecturer in Philosophy and Gender Studies at the University of Tasmania and an Australian Research Council Discovery Early Career Researcher Awardee (2019). Her current research focuses are the problem online hate speech, and the tension between LGBT+ non-discrimination and religious freedom. She is the author of Justifying Same-Sex Marriage: A Philosophical Investigation (2015) and her second book, Hate Speech Against Women Online: Concepts and Countermeasures is due for publication in 2021.
Big Thinker: Aristotle

Big Thinker: Aristotle
Big thinkerPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY The Ethics Centre 3 MAR 2021
It is hard to overstate the impact that Aristotle (384 BCE—322 BCE) has had on Western philosophy.
He, along with his teacher Plato, set the tone for over two millennia of philosophical enquiry, with much subsequent work either building on or refuting his ideas.
His influence on philosophy has been unparalleled for over two thousand years, in fields including logic, metaphysics, science, ethics and politics.
Aristotle was born in the 4th century BC in Thrace, in the north of Greece. At around 18 years of age he moved south to Athens, the capital of philosophical thought, to study under Plato at his famous Academy. He spent around two decades there, absorbing – but not always agreeing with – Plato and his disciples.
After Plato’s death, he departed Athens and landed a gig tutoring the teenage Alexander of Macedon – soon to be Alexander the Great. However, it appears Aristotle summarily failed to imbue the budding general with a taste for either philosophy or ethics.
After Alexander was appointed regent of Macedon at the age of 16, Aristotle returned to Athens, where he established the Lyceum, his own philosophical school where he taught and wrote on a startling array of topics.
His followers became known as peripatetics, after the Greek word for “walking”, due to the walkways that surrounded the school and Aristotle’s reputed tendency to give lectures on the move.
Ethics and Eudaimonia
One of the areas of lasting impact was Aristotle’s work on ethics and politics, which he considered to be intimately related subjects (much to the surprise of modern folk).
His ethical theory was based on the idea that each of us ultimately seeks a concept he called eudaimonia, often translated as “happiness” but better rendered as “flourishing” or “wellbeing.”
The basic idea is that every (non-frivolous) thing we do is directed towards achieving some end. For example, you might fetch an apple from the fruit bowl to sate your hunger. But it doesn’t stop there. You might sate your hunger to promote your health, and you might promote your health because it enables you to do other things that you want to do – and so on.
Aristotle argued that if you follow this chain of ends all the way down, you’ll eventually reach something that you do because it’s an ‘end in itself’, not because it leads to some other end. He argued that the enlightened individual would inevitably arrive at the single ultimate end or good: eudaimonia.
Aristotle’s ethical theory is more like a theory of enlightened prudence or ‘practical wisdom’, which he called phronesis, that helps guide people towards achieving eudaimonia.
This sets Aristotle’s ethics apart from many modern ethical theories, such as utilitarianism, in that he’s not calling for us to maximise happiness or eudaimonia for all people but only helping us to live a good life.
Compared to more modern ethical theories, he is also less focused on explicit issues of preventing harm or preventing injustice than on the cultivation of good people.
Whereas the primary question guiding many ethical theories is ‘what should we do?’, Aristotle’s main concern is ‘how should we live?’.
Virtues and Friendship
This doesn’t mean Aristotle disregarded how we ought to behave towards others. Indeed, he argued that the best way to achieve eudaimonia was to embody certain virtues, such as honesty, courage and charity, which encourage us to be good to other people.
Each of these virtues occupies a “golden mean” between two extremes, which were considered vices. So too little courage was cowardice, and too much was recklessness, but just enough would lead to decisions that would promote eudaimonia.
He also lent us a useful term, akrasia, which means a kind of weakness of will, whereby people do the wrong thing not due to embodying vices, but by some inability to resist temptation.
We have all likely experienced akrasia from time to time, such as when we devour that last cookie or lie to escape blame, which we know is not conducive to our health or ethical flourishing.
While Aristotle’s “virtue ethics” fell out of favour for many centuries, it has enjoyed a resurgence since the mid-20th century and has a growing following today.
Aristotle also argued that one of the benefits of being a virtuous person was the kinds of friendships you could form.
The second reason is because you think they’re fun to be around, such as when two people simply enjoy each other’s company or enjoy shared activities like watching sport or playing board games, but don’t have any deeper connection when those activities are absent.
It’s the third type of friendship that Aristotle thought was the highest, which is when you like someone because they are a good person.
This is a mutual recognition of virtuous character, and you have reciprocal good will, where you genuinely care for them – even love them – and want the best for them. Aristotle argued that by cultivating virtues, and seeking out other virtuous people, we could form the strongest and most nourishing friendships.
Interestingly, modern science has vindicated the idea that one of the most important factors in living a happy and fulfilled life is the number of genuine and deep relationships one has, particularly with friends whom they care for and who care for them in return.
Artistotle on Politics
Aristotle’s political theory concerned how to structure a society in such a way that it enabled all its citizens to achieve eudaimonia.
His ancient Greek predilections – as well as the influence of Plato, who believed society should be ruled by ‘Philosopher Kings’ – are visible in his contempt for democracy in favour of rule by an enlightened aristocracy or monarchy.
However, Aristotle disagreed with his mentor in one important respect: Aristotle favoured private property, which he said promoted personal responsibility and fostered a kind of meritocracy that treated great achievers as being more morally worthy than the ‘lazy’.
The breadth, sophistication and influence of Aristotle’s thinking is formidable, especially considering that we only have access to 31 of the 200+ treatises that he wrote during his lifetime.
Tragically, the rest were lost in antiquity. While much of Aristotle’s philosophy is contested today given developments in logic and science over the last few centuries, arguably many of these developments were built on or were inspired by his work.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
If politicians can’t call out corruption, the virus has infected the entire body politic
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Blame
Big thinker
Climate + Environment, Relationships
Big Thinker: Ralph Waldo Emerson
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The danger of a single view
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Who's to blame for Facebook’s news ban?

Who’s to blame for Facebook’s news ban?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsScience + Technology
BY Matthew Beard 25 FEB 2021
News will soon return to Facebook, with the social media giant coming to an agreement with the Australian government. The deal means Facebook won’t be immediately subject to the News Media Bargaining Code, so long as it can strike enough private deals with media companies.
Facebook now has two months to mediate before the government gets involved in arbitration. Most notably, Facebook have held onto their right to strip news from the platform to avoid being forced into a negotiation.
Within a few days, your feed will return to normal, though media companies will soon be getting a better share of the profits. It would be easy to put this whole episode behind us, but there are some things that are worth dwelling on – especially if you don’t work in the media, or at a social platform but are, like most of us, a regular citizen and consumer of news. Because when we look closely at how this whole scenario came about, it’s because we’ve largely been forgotten in the process.
Announcing Facebook’s sudden ban on Australian news content last week, William Easton, Managing Director of Facebook Australia & New Zealand wrote a blog post outlining the companies’ reasons. Whilst he made a number of arguments (and you should read them for yourself), one of the stronger claims he makes is that Facebook, unlike Google Search, does not show any content that the publishers did not voluntarily put there. He writes:
“We understand many will ask why the platforms may respond differently. The answer is because our platforms have fundamentally different relationships with news. Google Search is inextricably intertwined with news and publishers do not voluntarily provide their content. On the other hand, publishers willingly choose to post news on Facebook, as it allows them to sell more subscriptions, grow their audiences and increase advertising revenue.”
The crux of the argument is this. Simply by existing online, a news story can be surfaced by Google Search. And when it is surfaced, a whole bunch of Google tools – previews, summaries from Google Home, one-line snippets and headlines – give you a watered-down version of the news article you search for. They give you the bare minimum info in an often-helpful way, but that means you never click the site or read the story, which means no advertising revenue or way of knowing the article was actually read.
But Facebook is different – at least, according to Facebook. Unless news media upload their stories to Facebook, which they do by choice, users won’t see news content on Facebook. And for this reason, treating Facebook and Google as analogous seems unfair.
Now, Facebook’s claims aren’t strictly true – until last week, we could see headlines, a preview of the article and an image from a news story posted on Facebook regardless of who posted it there. And that headline, image and snippet are free content for Facebook. That’s more or less the same as what Facebook says Google do: repurposing news content that can be viewed without ever having to leave the platform.
However, these link previews are nowhere near as comprehensive as what Google Search does to serve up their own version of news stories for the company’s own purpose and profit. Most of the news content you see on Facebook is there because it was uploaded there by media companies – who often design video or visual content explicitly to be uploaded to Facebook and to reach their audience.
However, on a deeper level, there seem to be more similarities between Google and Facebook than the latter wants to admit, because the size and audience base Facebook possesses makes it more-or-less essential for media organisations to have a presence there. In a sense, the decision to have a strategy on Facebook is ‘voluntary’, but it’s voluntary in the same way that it’s voluntary for people to own an attention-guzzling, data sucking smartphone. We might not like living with it, but we can’t afford to live without it. Like inviting your boss to your wedding, it’s voluntary, but only because the other options are worse.
Facebook would likely claim innocence of this. Can they really be blamed for having such an engaging, effective platform? If news publishers feel obligated to use Facebook or fall behind their competitors that’s not something Facebook should feel bad about or be punished for. If, as Facebook argue, publishers use them because they get huge value from doing so, it does seem genuinely voluntary – desirable, even.
Even if this is true, there are two complications here. First, if news media are seriously reliant on Facebook, it’s because Facebook deliberately cultivated that. For example, five years ago Facebook was a leading voice behind the ‘pivot to video’, where publishers started to invest heavily in developing video content. Many news outlets drastically reduced writing staff and investment in the written word, instead focussing on visual content.
Three years later, we learned that Facebook had totally overstated the value of video – the pivot to video, which served Facebook’s interests, was based on a self-serving deception. This isn’t the stuff of voluntary, consensual relationships.
Let’s give Facebook a little benefit of the doubt though. Let’s say they didn’t deliberately cultivate the media’s reliance on their platform. Still, it doesn’t follow obviously from this that they have no responsibility to the media for that reliance. Responsibility doesn’t always come with a sign-up sheet, as technology companies should know all too well.
French theorist Paul Virilio wrote that “When you invent the ship, you also invent the shipwreck; when you invent the plane you also invent the plane crash; and when you invent electricity, you invent electrocution.” Whilst Virilio had in mind technology’s dualistic nature, modern work in the ethics of technology invites us to interpret this another way.
If inventing a ship also invents shipwrecks, it might be up to you to find ways to stop people from drowning.
Technology companies – Facebook included – have wrung many a hand talking about the ‘unintended consequences’ of their design and accepting responsibility for them. In fact, speaking before a US Congress Committee, Mark Zuckerberg himself conceded as much, saying:
“It’s clear now that we didn’t do enough to prevent these tools from being used for harm, as well. And that goes for fake news, for foreign interference in elections, and hate speech, as well as developers and data privacy. We didn’t take a broad enough view of our responsibility, and that was a big mistake. And it was my mistake. And I’m sorry. I started Facebook, I run it, and I’m responsible for what happens here.”
It seems unclear why Facebook recognised their responsibility in one case, but seem to be denying it in another. Perhaps the news media are not reliant – or used by – Facebook in the same way as they are Google, but it’s not clear this goes far enough to free Facebook of responsibility.
At the same time, we should not go too far the other way, denying the news media any role in the current situation. The emergence of Facebook as a lucrative platform seems to have led the media to a Faustian pact – selling their soul for clicks, profit and longevity. In 2021 it seems tired to talk about how the media’s approach to news – demanding virality, speed, shareability – are a direct result of their reliance on platforms like Facebook.
The fourth estate – whose work relies on them serving the public interest – adopted a technological platform and in so doing, adopted its values as their own: values that served their own interests and those of Facebook rather than ours. For the media to now lament Facebook’s decision as anti-democratic denies the media’s own blameworthiness for what we’re witnessing.
But the big reveal is this: we can sketch out all the reasons why Facebook or the media might have the more reasonable claim here, or why they share responsibility for what went down, but in doing so, we miss the point. This shouldn’t be thought of as a beef between two industries, each of whom has good reasons to defend their patch.
What needs to be defended is us: the community whose functioning and flourishing depends on these groups figuring themselves out.
Facebook, like the other tech giants, have an extraordinary level of power and influence. So too do the media. Typically, we don’t to allow institutions to hold that kind of power without expecting something in return: a contribution to the common good. This understanding – that powerful institutions hold their power with the permission of a community they deliver value to – is known as a social license.
Unfortunately, Facebook have managed to accrue their power without needing a social license. All power, no permission.
This is in contrast to the news media, whose powers aren’t just determined by their users and market share, but by the special role we afford them in our democracy, the trust and status we afford their work isn’t a freebie: it needs to be earned. And the way it’s earned is by using that power in the interests of the community – ensuring we’re well-informed and able to make the decisions citizens need to make.
The media – now in a position to bargain with Facebook – have a choice to make. They can choose to negotiate in ways that make the most business sense for them, or they can choose to think about what arrangements will best serve the democracy that they, as the ‘fourth estate’, are meant to defend. However, at the very least they know that the latter is expected of them – even if the track record of many news publishers gives us reason to doubt.
Unfortunately, they’re negotiating with a company whose only logic is that of a private company. Facebook have enormous power, but unlike the media, they don’t have analogous mechanisms – formal or informal – to ensure they serve the community. And it’s not clear they need it to survive. Their product is ubiquitous, potentially addictive and – at least on the surface – free. They don’t need to be trusted because what they’re selling is so desirable.
This generates an ethical asymmetry. Facebook seem to have a different set of rules to the media. Imagine, for a moment, if the media chose to stop reporting for a fortnight to protest a new law. The rightful outrage we would feel as a community would be palpable. It would be nearly unforgivable. And yet we do not hold Facebook to the same standards. And yet, perhaps at this point, they’ve made themselves almost as influential.
There’s a lot that needs to happen to steady the ship – and one of the most frustrating things about it is that as individuals, there isn’t a lot we can do. But what we can do is use the actual license we have with Facebook in place of a social license.
If we don’t like the way a news organisation conducts themselves, we cancel our subscriptions; we change the channel. If you want to help hold technology companies to account, you need to let your account to the talking. Denying your data is the best weapon you’ve got. It might be time to think about using it – and if not, under what circumstances you might.
This project is supported by the Copyright Agency’s Cultural Fund.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights
Big Thinker: Kimberlé Crenshaw
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology
The ethics of exploration: We cannot discover what we cannot see
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Science + Technology
MIT Media Lab: look at the money and morality behind the machine
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Science + Technology
People first: How to make our digital services work for us rather than against us
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
Tim Soutphommasane on free speech, nationalism and civil society

Tim Soutphommasane on free speech, nationalism and civil society
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY The Ethics Centre 18 FEB 2021
We believe conversations matter. So when we had the opportunity to chat with Tim Soutphommasane we leapt at the chance to explore his ideas of a civil society. Tim is an academic, political theorist and human rights activist. A former public servant, he was Australia’s Race Discrimination Commissioner at the Australian Human Rights Commission from 2013 – 2018 and has been a guest speaker at the Festival of Dangerous Ideas. Now a professor at Sydney University, he shared with The Ethics Centre his thoughts on the role of the media, free speech, racism and national values.
What role should the media play in supporting a civil society?
The media is one place where our common life as a society comes into being. It helps project to us our common identity and traditions. But ideally media should permit multiple voices, rather than amplify only the voices of the powerful. When it is dominated by certain interests, it can destroy rather than empower civil society.
How should a civil society reckon with the historical injustices it benefits from today?
A mature society should be able to make sense of history, without resorting to distortion. Yet all societies are built on myths and traditions, so it’s not easy to achieve a reckoning with historical injustice. But, ultimately, a mature society should be able to take pride in its achievements and be critical of its failings – all while understanding it may be the beneficiary of past misdeeds, and that it may need to make amends in some way.
Should a civil society protect some level of intolerance or bigotry?
It’s important that society has the freedom to debate ideas, and to challenge received wisdom. But no freedom is ever absolute. We should be able to hold bigotry and intolerance to account when it does harm, including when it harms the ability of fellow citizens to exercise their individual freedoms.
What do you think we can do to prevent society from becoming a ‘tyranny of the majority’?
We need to ensure that we have more diverse voices represented in our institutions – whether it’s politics, government, business or media.
What is the right balance between free speech and censorship in a civil society?
Rights will always need to be balanced. We should be careful, though, to distinguish between censorship and holding others to account for harm. Too often, when people call out harmful speech, it can quickly be labelled censorship. In a society that values freedom, we naturally have an instinctive aversion to censorship.
How can a society support more constructive disagreement?
Through practice. We get better at everything through practice. Today, though, we seem to have less space or time to have constructive or civil disagreements.
What is one value you consider to be an ‘Australian value’?
Equality, or egalitarianism. As with any value, it’s contested. But it continues to resonate with many Australians.
Do you believe there’s a ‘grand narrative’ that Australians share?
I think a national identity and culture helps to provide meaning to civic values. What democracy means in Australia, for instance, will be different to what it means in Germany or the United States. There are nuances that bear the imprint of history. At the same time, a national identity and culture will never be frozen in time and will itself be the subject of contest.
And finally, what’s the one thing you’d encourage everyone to commit to in 2021?
Talk to strangers more.
To read more from Tim on civil society, check out his latest article here.
Tim Soutphommasane is a political theorist and Professor in the School of Social and Political Sciences, The University of Sydney, where he is also Director, Culture Strategy. From 2013 to 2018 he was Race Discrimination Commissioner at the Australian Human Rights Commission. He is the author of five books, including The Virtuous Citizen (2012) and most recently, On Hate (2019).
This project is supported by the Copyright Agency’s Cultural Fund.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Lessons from Los Angeles: Ethics in a declining democracy
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
James Hird In Conversation Q&A
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Banks now have an incentive to change
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Can philosophy help us when it comes to defining tax fairness?
Join our newsletter