Are we prepared for climate change and the next migrant crisis?

Are we prepared for climate change and the next migrant crisis?
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentPolitics + Human Rights
BY Kate Prendergast 7 MAY 2019
A powerful infographic published in 2014, predicted how many years it would take for a world city to drown.
It used data from NASA, Sea Level Explorer, and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Venice will be the first to go under apparently, its canals rising to wetly throttle the city of love. Amsterdam is set to follow, Hamburg next.
Other tools play out the encroachment of rising tides on our coasts. This one developed by EarthTime shows Sydney airport as a large puddle if temperatures increase by four degrees. There’s also research suggesting our ancestors may one day look down to see fish nibbling on the Opera House sails.
Climate change refugees will become reality
Sea level rise is just one effect of anthropogenic climate change that would make a place uninhabitable or inhospitable to humankind. It’s also relatively slow. Populations in climate vulnerable hotspots face a slew of other shove factors, too.
Already, we are seeing a rising frequency of extreme weather events. Climate change was linked to increasingly destructive tropical cyclones in a report published in Nature last year, and Australia’s Climate Council attributed the same to earlier and more dangerous fire seasons. Rapidly changing ecosystems will impact water resources, crop productivity, and patterns of familiar and unfamiliar disease. Famine, drought, poverty and illness are the horsemen saddling up.
Some will die as a result of these events. Others, if they are able, will choose to stay. The far sighted and privileged may pre-empt them, relocating in advance of crisis or discomfort.
These migrants can be expected to move through the ‘correct’ channels, under the radar of nativist suspicion. (‘When is an immigrant not an immigrant?’ asks Afua Hirsch. ‘When they’re rich’.)
But many more will become displaced peoples, forcibly de-homed. Research estimates this number could be anywhere between 50 million and 1 billion in the 21st century. This will prompt new waves of interstate and international flows, and a resultant redistribution and intensification of pressures and tensions on the global map.
How will the world respond?
Where will they go? What is the ethical obligation of states to welcome and provide for them? With gross denialism characterising global policies towards climate change, and intensifying hostility locking down national borders, how prepared are we to contend with this challenge to come?
“You can’t wall them out,” Obama recently told the BBC. “Not for long.”
While interstate climate migration (which may already be occurring in Tasmania) will incur infrastructural and cultural problems, international migration is a whole and humongous other ethical conundrum. Not least because currently, climate change migrants have almost no legal protections.
Is a person who moves because of a sudden, town levelling cyclone more entitled to the status of climate migrant or refugee (and the protection it affords) than someone who migrates as a result of the slow onset attrition of their livelihood due to climate change?
Who makes the rules?
Does sudden, violent circumstance carry a greater ethical demand for hospitality than if, after many years of struggle, a Mexican farmer can no longer put food on the table because his land has turned to dust? Does the latter qualify as a climate or economic migrant, or both?
Somewhat ironically (and certainly depressingly), the movement of people to climate ‘havens’ will place stress on those environmental sanctuaries themselves, potentially leading to concentrated degradation, pollution and threat to non-human nature. (On the other hand, climate migration could allow for nature to reclaim the places these migrants have left.)
There is also the argument that, once migrants from developing countries have been integrated into a host country, their carbon footprint will increase to resemble that of their new fellow citizenry – resulting in larger CO2 emissions. From this perspective, put forward by Philip Cafaro and Winthrop Staples, it is in the interests of the planet for prosperous countries to limit their welcome.
Not that privileged populations need much convincing. Jealous fear of future scarcity, a globalisation inflamed resentment towards the Other, a sense that modernity has failed to deliver on its promise of wholesale bounty: all these are conspiring to create increasingly tribalised societies that enable the xenophobic agendas of their governments. A recent poll showed that 46 percent of Australians believe immigration should be reduced, a percentage consistent with attitudes worldwide.
A divided world
In the US, there’s Trump’s grand ‘us vs them’ symbol of a wall. As reported in the Times, German lawmakers are comparing refugees to wolves. In Italy, tilting towards populism and the right, a mayor was arrested after transforming his small town into a migrant sanctuary.
Closer to home, in a country where the 27 years without recession could be linked to immigration, there’s Scott Morrison’s newly proposed immigration cuts. There’s Senator Anning blaming the Christchurch massacre on Muslim immigration. There’s the bipartisan support for the prospects, wellbeing and mental health of asylum seekers to deteriorate to such an extent, the UN human rights council described it as ‘massive abuse’.
Yet the local effects of climate change don’t have a local origin. Causality extends beyond borders, piling miles high at the feet of industrialised countries. Nations like the US and Australia enjoy high standards of living largely because we have been pillaging and burning fossil fuels for more than a century. Yet those least culpable will bear the heaviest cost.
This, argues the author of a paper published in Ethics, Policy and Environment, warrants a different ethical framework than that which applies to other kinds of migration. He concludes that industrialised nations “have a moral responsibility … to compensate for harms that their actions have caused”.
This responsibility may include investing in less developed countries to mitigate climate change effects, writes the author. But it also morally obliges giving access, security and residence to those with nowhere else to go.
MOST POPULAR
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
An ethical dilemma for accountants
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
The role of ethics in commercial and professional relationships
ArticleBeing Human
The problem with Australian identity
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
Understanding the nature of conflicts of interest
BY Kate Prendergast
Kate Prendergast is a writer, reviewer and artist based in Sydney. She's worked at the Festival of Dangerous Ideas, Broad Encounters and Giramondo Publishing. She's not terrible at marketing, but it makes her think of a famous bit by standup legend Bill Hicks.
Australia, it’s time to curb immigration

Australia, it’s time to curb immigration
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentPolitics + Human Rights
BY Satya Marar 3 MAY 2019
A majority of Australians welcome immigrants. So why then do opinion polls of young and old voters alike across the political divide, now find majority support for reducing our immigration intake?
Perhaps it could be for the same reason that faith in our political system is dwindling at a time of strong economic growth. Australia is the ‘lucky country’ that hasn’t had a recession in the last 28 years.
Yet we’ve actually had two recessions in this time if we consider GDP on a per-capita basis. This, combined with stagnant real wage growth and sharp increases in congestion and the price of housing and electricity in our major cities, could explain why the Australian success story is inconsistent with the lived experience of so many of us.
The decline of the Australian dream?
Our current intake means immigration now acts as a ponzi scheme.
The superficial figure of a growing headline GDP fuelled by an increasing population masks the reality of an Australian dream that is becoming increasingly out of reach for immigrants and native-born Australians alike.
We’ve been falsely told we’ve weathered economic calamities that have stunned the rest of the world. When taken on a per-capita basis, our economy has actually experienced negative growth periods that closely mirror patterns in the United States.
We’re rightly told we need hardworking immigrants to help foot the bill for our ageing population by raising productivity and tax revenue. Yet this cost is also offset when their ageing family members or other dependents are brought over. Since preventing them from doing so may be cruel, surely it’s fairer to lessen our dependence on their intake if we can?
A lack of infrastructure
Over 200,000 people settle in Australia every year, mostly in the major cities of Sydney and Melbourne. That’s the equivalent of one Canberra or greater Newcastle area a year.
Unlike the United States, most economic opportunities are concentrated in a few major cities dotting our shores. This combined with the failures of successive state and federal governments to build the infrastructure and invest in the services needed to cater for record population growth levels driven majorly by immigration.
A failure to rezone for an appropriate supply of land, mean our schools are becoming crowded, our real estate prohibitively expensive, our commutes are longer and more depressing, and our roads are badly congested.
Today, infrastructure is being built, land is finally being rezoned to accommodate higher population density and more housing stock in the outer suburbs, and the Prime Minister has made regional job growth one of his major priorities.
But these issues should have been fixed ten years ago and it’s increasingly unlikely that they will be executed efficiently and effectively enough to catch up to where they need to be should current immigration intake levels continue for the years to come.
Our governments have proven to be terrible central planners, often rejecting or watering down the advice of independent expert bodies like Infrastructure Australia and the Productivity Commission due to political factors.
Why would we trust them to not only get the answer right now, but to execute it correctly? Our newspapers are filled daily with stories about light rail and road link projects that are behind schedule.
All of it paid for by taxpayers like us.
Foreign workers or local graduates?
Consider also the perverse reality of foreign workers brought to our shores to fill supposed skill gaps who then struggle to find work in their field and end up in whatever job they can get.
Meanwhile, you’ll find two separate articles in the same week. One from industry groups cautioning against cutting skilled immigration due to shortages in the STEM fields. The other reporting that Australian STEM graduates are struggling to find work in their field.
Why would employers invest resources in training local graduates when there’s a ready supply of experienced foreign workers? What incentive do universities have to step in and fill this gap when their funding isn’t contingent on employability outcomes?
This isn’t about nativism. The immigrants coming here certainly have a stake in making sure their current or future children can find meaningful work and obtain education and training to make them job ready.
There’s only one way to hold our governments accountable so the correct and sometimes tough decisions needed to sustain our way of life and make the most of the boon that immigration has been for the country, are made. It’s to wean them off their addiction to record immigration levels.
Lest the ponzi scheme collapse.
And frank conversations about the quantity and quality of immigration that the sensible centre of politics once held, increasingly become the purview of populist minor parties who have experienced resurgence on the back of widespread, unanswered frustrations about unsustainable immigration that we are ill-prepared for.
This article was produced in association with IQ2: Should Australia curb immigration? With powerful arguments presented at both ends of the spectrum, it was a debate that raised issues from urban planning to government policy, environmental impacts to economic advantages and more.
MOST POPULAR
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
An ethical dilemma for accountants
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
The role of ethics in commercial and professional relationships
ArticleBeing Human
The problem with Australian identity
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
Understanding the nature of conflicts of interest
BY Satya Marar
Satya Marar is an Indian-born, Sydney based writer, public commentator and Director of Policy at the Australian Taxpayers’ Alliance. He took part in the IQ2 debate, ‘Curb Immigration’
How to build good technology
How to build good technology
WATCHBusiness + LeadershipClimate + EnvironmentScience + Technology
BY Matthew Beard 2 MAY 2019
Dr Matthew Beard explains the key principles to guide the development of ethical technology at the Atlassian 2019 conference in Las Vegas.
Find out why technology designers have a moral responsibility to design ethically, the unintended ethical consequences of designs such as Pokemon Go, and the the seven guiding principles designers need to consider when building new technology.
Whether editing a genome, building a driverless car or writing a social media algorithm, Dr Beard says these principles offer the guidance and tools to do so ethically.
Download ‘Ethical By Design: Principles For Good Technology ‘
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Climate + Environment
The business who cried ‘woke’: The ethics of corporate moral grandstanding
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Businesses can’t afford not to be good
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
The anti-diversity brigade is ruled by fear
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology
Big tech’s Trojan Horse to win your trust
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
Overcoming corruption in Papua New Guinea

Overcoming corruption in Papua New Guinea
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipClimate + EnvironmentSociety + Culture
BY David Burfoot 30 APR 2019
Papua New Guinea is known as one of the most corrupt countries in the world.
Yet through delivering ethical leadership training to public officials there, The Ethics Centre is seeing a natural aptitude for ethics that government and corporations are struggling to nurture in Australia.
It has one of the most diverse cultures with over 850 known languages spoken. It is rich in minerals, gas and forestry.
Yet despite its natural wealth, Papua New Guinea suffers the ‘paradox of plenty’ or ‘resource curse’. This is where countries endowed with rich natural resources struggle to make effective use of them and end up with lower levels of economic development than countries without those natural resources. How could this be?
PNG is plagued by what the United Nations Development Program claim to be the most crippling ethical failure in international development: corruption.
Transparency International ranks PNG as one of the most corrupt countries in the world. Its PNG chapter states, “There is massive disrespect for rule of law in Papua New Guinea. Public servants and citizens alike lack the integrity to adhere to proper processes and respectful ways of conduct”.
Such assessments may however overlook some important strengths amongst PNG’s people, ones which may in time prove instrumental in corruption control.
The Ethics Centre delivers a broad range of ethics educational programs, including one package being delivering to senior PNG Officials, funded by Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade.
Contrary to what some might guess, this training does not lecture participants about what is ‘right’ and ‘wrong’. Instead, it identifies what is meant by ‘ethics’, what gets in the way of ethical decision making and mechanisms to integrate ethics into the governance of organisations and their various activities.
More research is showing the power of ethical leadership in building strong organisational cultures that are able to resist ethical failure (like corruption) and enhance corporate performance.
The program links personal and organisational ethical frameworks. Different factors are identified as influential to the ‘PNG mindset’ and decision making of public officials:
- Christian values
- Clan values
- Government values
- Global values
At times the training also includes instruction on specific techniques, such as conflicts of interest management and probity reviewing.
Instruction in these skills is growing in demand in Australia and abroad as government and corporations alike search for ways of winning back public trust and confidence.
In contrast to the past problematic approach of corporate leaders to ethics in the West, that is, as non-essential and nice-to-have, PNG officials demonstrated a sophisticated appreciation of the instrumental and social value of ethics in administration.
As facilitators, we learnt much about the ethical dilemmas and challenges confronting PNG officials, often on a scale many Australians would have difficulty comprehending. A person’s relationship with a clan, family, profession and government at times present complex dilemmas.
Yet these officials’ enthusiasm for honouring all these duties and appreciating their tangible and intangible worth appears undiminished. They appear to have missed the economic rationalist memo. And this is a real strength for PNG, something some commentators may be overlooking.
To help preserve this strength and to take advantage of it in countering corruption and other PNG challenges, The Ethics Centre is talking to potential partners about co-designing content with local officials and developing a train-the-trainer program.
We know local officials are enthusiastic for more of this training, indeed, it was the PNG Department of Personnel Management who requested education in ethical decision making for public servants. The average Net Promotor Score from participants on the program is 88 (of a score between -100 and +100), indicating high levels of satisfaction. We look forward to continuing our work with the Australian Government and the Government and people of PNG on this important initiative.
Lead photo by Stefan Krasowski
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
10 films to make you highbrow this summer
Explainer, READ
Business + Leadership
Ethics Explainer: Moral hazards
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing
Feeling rules: Emotional scripts in the workplace
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Alpha dogs and the toughness trap: How we can redefine modern masculinity
BY David Burfoot
David has worked in the not-for-profit, public and private sectors domestically and internationally for organisations as diverse as the United Nations Development Program, Deloitte, the NSW Independent Commission Against Corruption and Sydney University. He has been an anti-corruption specialist with a number of government agencies and held senior positions responsible for corporate planning, change and internal communications.
Increase or reduce immigration? Recommended reads

Increase or reduce immigration? Recommended reads
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentPolitics + Human Rights
BY Kym Middleton 21 MAR 2019
Immigration is the hot election issue connecting everything from mismanaged water and mass fish deaths in the Murray Darling to congested cities and unaffordable housing.
The 2019 IQ2 season kicks off with ‘Curb Immigration’ on 26 March. It’s something Prime Minister Scott Morrison promised to do today if re-elected and opposition leader Bill Shorten has committed to considering.
Here’s a collection of ideas, research, articles and arguments covering the debate.
New migrants to go regional for permanent residency, under PM’s plan
Scott Morrison, SBS News / 20 March 2019
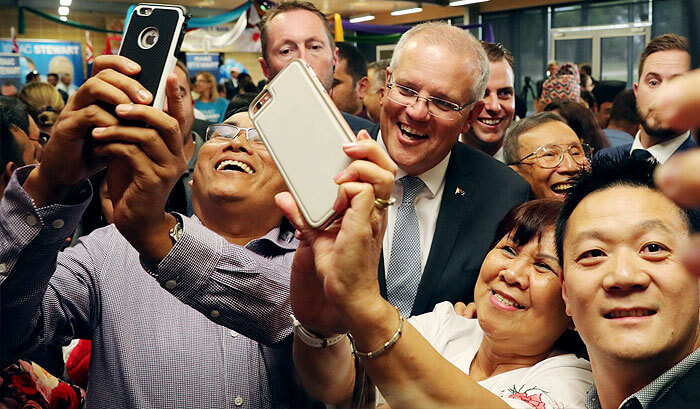

Prime Minister Scott Morrison revealed his immigration plan today. He confirmed reports he will lower the cap on Australia’s immigration intake from 190,000 to 160,000 for the next four years. He announced 23,000 visa places that require people to live and work in regional Australia for three years before they can apply for permanent residency. “It is about incentives to get people taking up the opportunities outside our big cities” and “it’s about busting congestion in our cities”, Morrison said.
————
Australian attitudes to immigration: a love / hate relationship
The Ethics Centre, The New Daily / 24 January 2019

You’ll hear Australians talk about our country as either a multicultural utopia or intolerant mess. This article charts many recent surveys on our attitudes to immigration. The results show almost equal majorities of us love and hate it for different reasons, suggesting individual people both support and reject immigration at the same time. We’re complex creatures.
————
Post Populism
Niall Ferguson, Festival of Dangerous Ideas / 4 November 2018

At the Festival of Dangerous Ideas on Cockatoo Island, Niall Ferguson presented his take on the five ingredients that have bred the nationalistic populism sweeping the western world today. Point one: increased immigration. Listen to the podcast or watch the video highlights. Elsewhere, Ferguson points to Brexit and the European migrant crisis and predicts, “the issue of migration will be seen by future historians as the fatal solvent of the EU”.
————
Human Flow movie
Ai Weiwei / 2017
Part documentary and part advocacy, Human Flow is a film by Chinese artist Ai Weiwei that “gives a powerful visual expression” to the 65 million people displaced from their homes by climate change, war or famine. It is not the story of ‘orderly migration’ based on skilled visas or spatial planning policies, but rather, one of mass flows across countries and continents.
————
Government needs to wake up to impact of population boom
PM, ABC RN / 23 February 2018

IQ2 guest and human geographer Dr Jonathan Sobels is interviewed by Linda Mottram on the impact of Australia’s population growth on the continent’s natural environment. He’s not the only person concerned about this. A 2019 study by ANU found 75 percent of Australians agree the environment is already under too much pressure with the current population size.
————
Counter-terrorism expert Anne Aly: ‘I dream of a future in which I’m no longer needed’
Greg Callaghan, The Sydney Morning Herald / 18 November 2016
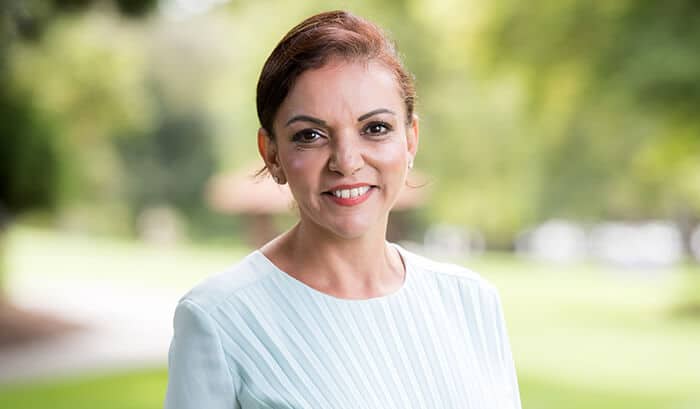

Dr Anne Aly is a counter terrorism expert come politician with “instant relatability”, according to this feature piece on her. Get to know more about her interesting life and career before catching her at IQ2 where she’ll argue against the motion ‘Curb Immigration’. Aly is the Labor Member for the West Australian electorate of Cowan and first female Muslim parliamentarian in Australia.
————
Event info
Get your IQ2 ‘Curb Immigration’ tickets here
Satya Marar & Jinathan Sobels vs Anne Aly & Nicole Gurran
27 March 2019 | Sydney Town Hall
MOST POPULAR
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
An ethical dilemma for accountants
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
The role of ethics in commercial and professional relationships
ArticleBeing Human
The problem with Australian identity
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
Understanding the nature of conflicts of interest
BY Kym Middleton
Former Head of Editorial & Events at TEC, Kym Middleton is a freelance writer, artistic producer, and multi award winning journalist with a background in long form TV, breaking news and digital documentary. Twitter @kymmidd
Australia Day: Change the date? Change the nation

Australia Day: Change the date? Change the nation
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentPolitics + Human Rights
BY Karen Wyld 24 JAN 2019
Like clockwork, every January Australians question when is, or even if there is, an appropriate time to celebrate the nationhood of Australia.
Each year, a growing number of Australians acknowledge that the 26thof January is not an appropriate date for an inclusive celebration.
There are no sound reasons why the date shouldn’t be changed but there are plenty of reasons why the nation needs to change.
I’ve written about that date before, its origins and forgotten stories and recent almost-comical attempts to protect a public holiday. I choose not to repeat myself, because the date will change.
For many, the jingoism behind Australia Day is representative of a settler colonialism state that should not be preserved. A nation that is not, and has never been fair, free or young. So, I choose to put my energy into changing the nation. And I am not alone.
People are catching up and contributing their voices to the call to change the nation, but this is not a new discussion. On 26 January 1938, on the 150thanniversary of the British invasion of this continent, a group of Aboriginal people in NSW wrote a letter of protest, calling it a Day of Mourning. They asked the government to consider what that day meant to them, the First Peoples, and called for equality and justice.
Since 1938, the 26thof January continues to be commemorated as a Day of Mourning. The date is also known as Survival Day or Invasion Day to many. Whatever people choose to call that day, it is not a date suitable for rejoicing.
It was inconsiderate to have changed the date in 1994 to the 26th January. And, now the insensitivity is well known, it’s selfish not to change the date again. The only reasons I can fathom for opposition to changing the date is white privilege, or perhaps even racism.
These antiquated worldviews of white superiority will continue to haunt Australia until a critical mass has self reflected on power and privilege and whiteness, and acknowledges past and present injustices. I believe we’re almost there – which explains the frantic push back.
A belief in white righteousness quietened the voices of reason and fairness when the first fleet landed on the shores of this continent. And it enabled colonisers and settlers to participate in and/or witness without objection decades of massacres, land and resource theft, rape, cultural genocide and other acts of violence towards First Peoples.
The voice of whiteness is also found in present arguments, like when the violence of settlement is justified by what the British introduced. It is white superiority to insist science, language, religion, law and social structures of an invading force are benevolent gifts.
First Peoples already had functioning, sophisticated social structures, law, spiritual beliefs, science and technology. Combining eons of their own advances in science with long standing trade relations with Muslim neighbours, First Peoples were already on an enviable trajectory.
Tales of white benevolence, whether real or imagined, will not obliterate stories of what was stolen or lost. Social structures implanted by the new arrivals were not beneficial for First Peoples, who were barred from economic participation and denied genuine access to education, health and justice until approximately the 1970s.
Due to systemic racism, power and privilege, and social determinants, these introduced systems of justice, education and health still have entrenched access and equity barriers for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
Changing the nation involves settler colonialists being more aware of the history of invasion and brutal settlement, as well as the continuing impact on Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. It involves an active commitment to reform, which includes paying the rent.
The frontier wars did not result in victory for settler colonialists, because the fight is not over. The sovereignty of approximately 600 distinctly different cultural/language groups was never ceded. Despite generations of violence and interference from settler colonialists, First Peoples have not been defeated.
“You came here only recently, and you took our land away from us by force. You have almost exterminated our people, but there are enough of us remaining to expose the humbug of your claim, as white Australians, to be a civilised, progressive, kindly and humane nation.”
‘Aborigines Claim Citizen Rights!: A Statement of the Case for the Aborigines Progressive Associations’, The Publicist, 1938, p.3
Having lived on this continent for close to 80,000 years and surviving the violence of colonisation and ongoing injustices of non-Indigenous settlement, the voices of First Peoples cannot be dismissed. The fight for rights is not over.
The date will change. And, although it will take longer, the nation will change. There are enough still standing to lead this change – so all Australians can finally access the freedoms, equality and justice that Australia so proudly espouses.
Karen Wyld is an author, living by the coast in South Australia
MOST POPULAR
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
An ethical dilemma for accountants
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
The role of ethics in commercial and professional relationships
ArticleBeing Human
The problem with Australian identity
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
Understanding the nature of conflicts of interest
Big Thinker: Henry Thoreau
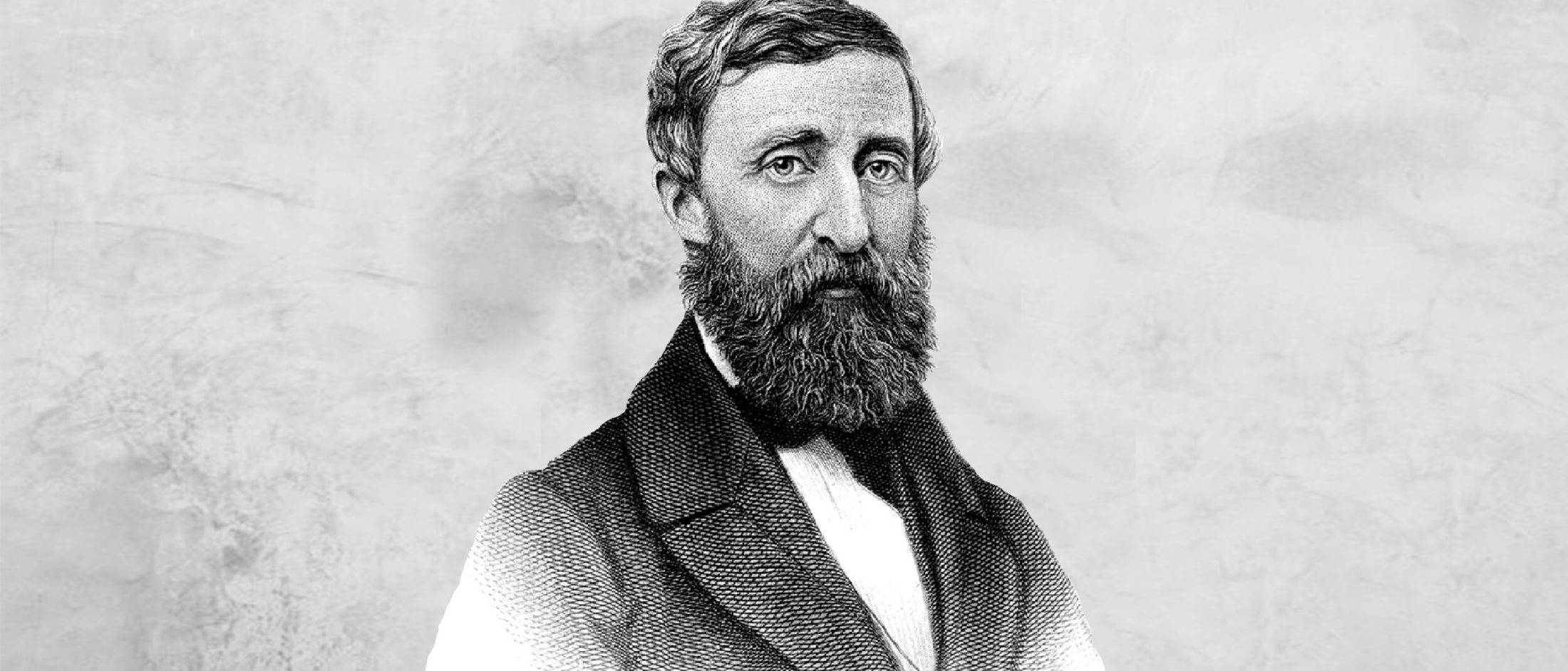

A tax evader, rebel philosopher and the grandfather of environmentalism, Henry Thoreau (1817—1862) practiced a back-to-nature experience of the natural world while opposing authority.
Though enjoying no great acclaim in his lifetime, today the name Henry David Thoreau resonates across philosophy, literature, political history, natural history and environmental science. His spirit of non-conformity, his rugged individualism and his ‘essentialist’ approach to living, have seen him mythologised as an American hero – and an ancestor of various ‘return to nature’ movements, too.
The son of a pencil maker, Thoreau was born in 1817 in Massachusetts, US. He demonstrated free minded dissent for institutions early in life. While at Harvard, he allegedly refused to pay for his diploma certificate. In his subsequent role as teacher, he rejected a recommendation for corporal punishment – by thrashing a random group of students to make a point, then resigning. Later, he would refuse to pay six years’ taxes. He saw it as surrendering his money to fund slavery and the government’s war in Mexico, both of which he vigorously opposed. For this, he was thrown in jail.
Civil Disobedience
Thoreau’s spirit of resistance coalesced in the libertarian manifesto Civil Disobedience. Unjust governments have no right bending citizens to their arbitrary laws and corrupt systems, he argued in the book. A free, enlightened state was only possible once that state “recognised the individual as a higher and independent power”, and enabled them to be “men first, and subject after”.
Rather than meekly obey, Thoreau said he was obliged “to do at any time what I think right” – even if that meant breaking the law. This idea of self-governance by individual conscience would later inspire Gandhi, Martin Luther King and others who took a principled stance against unjust rule.
It has also been widely critiqued. Violent and bigoted acts can, after all, easily be committed under the banner of self-righteousness. And what if two people divided on a matter by ideology or faith can’t settle their differences?
Lines in Civil Disobedience like, “That government is best which governs not at all” also make some question whether Thoreau’s libertarian politics tended towards anarchism.
Simple living, transcendentalism and the Walden experiment
A fellow resident of his home town, Ralph Waldo Emerson was a pivotal influence on Thoreau. He introduced Thoreau to transcendentalism – a movement which reacted against religious and intellectual trends, and enjoined each individual to forge their own “original relation to the universe”. Thoreau became a key figure in the movement. For him, solitude, simplicity, awareness and harmonious engagement with the wild were concrete ways to forge this relation. His philosophy as well as his science, insisted upon embodied understanding, rather than just a contemplative or discursive one.
In a forest cabin lent to him by Emerson, Thoreau conducted an experiment in simple living which would last two years and two months. His methods and reflections during this time became the classic work Walden – named after a pond which abutted the property. In it, with poetic eloquence, didacticism and free wheeling style, he lays out his view of a resigned, frivolous and wretched humanity, and how one is to instead rise above and “live deliberately”.
To achieve an existence which is pure and meaningful, Thoreau argued a life must be cultivated free from illusion and excess. He practiced a style of subsistence living through radical self-denial. Only essential needs were identified and met. A plausible misanthrope, he forswore conversation, sensuality, coffee, meat and alcohol, advising just one meal a day. To relinquish to the slightest temptation was to open the gates to moral disrepair. He even eschewed a doormat, “preferring to wipe my feet on the sod before my door.”
According to the American author John Updike, “Waldenhas become such a totem of the back-to-nature, preservationist, anti-business, civil-disobedience mindset, and Thoreau so vivid a protester, so perfect a crank and hermit saint, that the book risks being as revered and unread as the Bible”.
Kathryn Schulz reads Thoreau’s hermitage as rather a renunciation of responsibility, and categorises it as “original cabin porn”.
“Being forever on the alert”
Shorn of distractions, purged of indulgences, Thoreau believed a greater awareness of the universe can bloom. But more vital to his philosophy was an “ethics of perception” – requiring rigorous attentiveness to the outside world as it was uniquely registered on the senses. This could be observing a sunset’s reflection on glass, or the miniaturised battle of ants. Through this expanded and intensified focus, man was empowered to elevate his life, in “infinite expectation of the dawn”.
A surveyor by trade, Thoreau said we must consciously endeavour to practice “the discipline of looking […] at what is to be seen”.He was suspicious of orthodox forms of knowledge and believed the “essential facts of life” come to us through “the perpetual instilling and drenching of the reality that surrounds us”. Truth, then, was deeply individualised communion between self and world, and the product of intuition and revelation, rather than logic or reason.
Natural as intrinsically valuable
Thoreau’s ideas around nature’s intrinsic value have had significant bearing on modern conservationism. The sublime beauty and order that could be perceived in natural phenomena were not, he thought, qualities projected onto it by humans. They were immanent. What’s more, “Whatever we have perceived to be in the slightest degree beautiful is of infinitely more value to us than what we have only as yet discovered to be useful and to serve our purpose”.
In other words, nature cannot be commodified. Priceless, it must be viewed on its own terms, rather than as a resource to serve human agendas and needs. His view was diametrically opposed to the anthropocentricism that characterised the industrial revolution’s frenzied assault upon lands and oceans, which would culminate in the raft of ecological crises facing us today.
Thoreau also drew attention to the hidden benefits and invisible services of plant and animal species. In one example, he considered the squirrel. To the average American, they were a pest. But if we recognised squirrels in a broader ecosystem context, we could honour them as “planters of forests”, noble little workers whose free labour humans couldn’t do without.
Thoreau recognised, too, that our ignorance of these hidden benefits makes us careless. Trampling over nature’s bounty, upending its fragile balance, we are liable to do untold damage – for which we may ourselves pay a dear cost. In this sense, he was prescient.
“I should be glad if all the meadows on the earth were left in a wild state,” he wrote, “if that were the consequence of men’s beginning to redeem themselves.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Limiting immigration into Australia is doomed to fail
Big thinker
Climate + Environment, Relationships
Big Thinker: Ralph Waldo Emerson
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Climate + Environment, Society + Culture
Overcoming corruption in Papua New Guinea
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing
How can we travel more ethically?
BY Kate Prendergast
Kate Prendergast is a writer, reviewer and artist based in Sydney. She's worked at the Festival of Dangerous Ideas, Broad Encounters and Giramondo Publishing. She's not terrible at marketing, but it makes her think of a famous bit by standup legend Bill Hicks.
Is it time to curb immigration in Australia?

Is it time to curb immigration in Australia?
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentPolitics + Human Rights
BY The Ethics Centre 24 JAN 2019
To curb or not to curb immigration? It’s one of the more polarising questions Australia grapples with amid anxieties over a growing population and its impact on the infrastructure of cities.
Over the past decade, Australia’s population has grown by 2.5 million people. Just last year, it increased by almost 400,000, and the majority – about 61 percent net growth – were immigrants.
Different studies reveal vastly different attitudes.
While Australians have become progressively more concerned about a growing population, they still see the benefits of immigration, according to two different surveys.
Times are changing
In a new survey recently conducted by the Australian National University, only 30 percent of Australians – compared to 45 percent in 2010 – are in favour of population growth.
The 15 percent drop over the past decade is credited to concerns about congested and overcrowded cities, and an expensive and out-of-reach housing market.
Nearly 90 percent believed population growth should be parked because of the high price of housing, and 85 percent believed cities were far too congested and overcrowded. Pressure on the natural environment was also a concern.
But a Scanlon Foundation survey has revealed that despite alarm over population growth, the majority of Australians still appreciate the benefits of immigration.
In support of immigration
In the Mapping Social Cohesion survey from 2018, 80 percent believed “immigrants are generally good for Australia’s economy”.
Similarly, 82 percent of Australians saw immigration as beneficial to “bringing new ideas and cultures”.
The Centre for Independent Studies’ own polling has shown Australians who responded supported curbing immigration, at least until “key infrastructure has caught up”.
In polling by the Lowy Institute last year, 54 percent of respondents had anti-immigration sentiments. The result reflected a 14 percent rise compared to the previous year.
Respondents believed the “total number of migrants coming to Australia each year” was too high, and there were concerns over how immigration could be affecting Australia’s national identity.
While 54 percent believed “Australia’s openness to people from all over the world is essential to who we are as a nation”, trailing behind at 41 percent, Australians said “if [the nation is] too open to people from all over the world, we risk losing our identity as a nation”.
Next steps?
The question that remains is what will Australia do about it?
The Coalition government under Scott Morrison recently proposed to cap immigration to 190,000 immigrants per year. Whether such a proposition is the right course of action, and will placate anxieties over population growth, remains to be seen.
Join us
We’ll be debating IQ2: Immigration on March 26th at Sydney Town Hall, for the full line-up and ticket info click here.

MOST POPULAR
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
An ethical dilemma for accountants
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
The role of ethics in commercial and professional relationships
ArticleBeing Human
The problem with Australian identity
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
Understanding the nature of conflicts of interest
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Limiting immigration into Australia is doomed to fail

Limiting immigration into Australia is doomed to fail
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentPolitics + Human Rights
BY Gordon Young 17 JAN 2019
Few topics bridge the ever widening divide between both sides of politics quite like the need to manage population growth.
Whether it’s immigration or environmental sustainability, fiscal responsibility or social justice. That the global population breached 7.5 billion in 2017 has everyone concerned.
We are at the point where the sheer volume of people will start to put every system we rely on under very serious stress.
This is the key idea motivating the centrist political party Sustainable Australia. Led by William Bourke and joined by Dick Smith, the party advocates for a non-discriminatory annual immigration cap at 70,000 persons, down from the current figure of around 200,000 – aimed at a “better, not bigger” Australia.
Join the first IQ2 debate for 2019, “Curb Immigration”. Sydney Town Hall, 26 March. Tickets here.
While the party has been accused of xenophobic bigotry for this stance, their policy makes clear they are not concerned about an immigrant’s religion, culture, or race. Their concern is exclusively for the stress greater numbers of migrants will place on Australia’s infrastructure and environment.
It is a compelling argument. After all, what is the point of the state if not to protect the interests of its citizens?
A Looming Problem
We should be concerned with the needs and interests of our international neighbours, but such concerns must surely be strictly secondary to our own. When our nearest neighbour has approximately ten times our population, squeezed into a landmass twenty five per cent Australia’s size, and ranks 113 places behind us in the Human Development Index, one can be forgiven for believing that limited immigration is critical for ongoing Australian quality of life.
This stance is further bolstered by the highly isolated, and therefore vulnerable nature of Australia’s ecosystem. Australia has the fourth highest level of animal species extinction in the world, with 106 listed as Critically Endangered and significantly more as Endangered or Under Threat.
Much of this is due to habitat loss from human encroachment as suburbs and agricultural lands expand for our increasing needs. The introduction of foreign flora and fauna can be absolutely devastating to these species, greatly facilitated by increased movement between neighbour nations (hence the virtually unparalleled ferocity of our quarantine standards).
While the nation may be a considerable exporter of foodstuffs, many argue Australia is already well over its carrying capacity. Any additional production will be degrading the land and our ability to continue growing food into the future.
The combination of ecological threats and socio-economic pressure makes the argument for limiting immigration to sustainable numbers a powerful one.
But it is absolutely doomed to failure.
Fortress Australia
If the objective of limiting immigration to Australia is both to protect our environment and maintain high quality of life, “Fortress Australia” will fail on both fronts. Why?
Because it does nothing to address the fundamental problem at hand. Unsustainable population growth in a world of limited resources.
Immigration controls may indeed protect both the Australian quality of life and its environment for a time, but without effective strategic intervention, the population burden in neighbouring countries will only continue to grow.
As conditions worsen and resources dwindle, exacerbated by the impacts of anthropogenic climate change, citizens of those overpopulated nations will seek an alternative. What could be more appealing than the enormous, low-density nation with incredibly high quality of life, right next door to them?
If a mere 10 percent of Indonesians (the vast majority of which live on the coast and are exceptionally vulnerable to climate change impacts) decided to attempt the crossing to Australia, we would be confronted by a flotilla equivalent to our entire national population.
The Dilemma
At this point we have one of two choices: suffer through the impact of over a decade’s worth of immigration in one go or commit military action against twenty-five million human beings. Such a choice is a Utilitarian nightmare, an impossible choice between terrible options, with the best possible result still involving massive and sustained suffering for all involved. While ethics can provide us with the tools to make such apocalyptic decisions, the best response by far is to prevent such choices from emerging at all.
Population growth is a real and tangible threat to the quality of life for all human beings on the planet, and like all great strategic threats, can only be solved by proactively engaging in its entirety – not just its symptoms.
Significant progress has been made thus far through programs that promote contraception and female reproductive rights. There is a strong correlation between nations with lower income inequality and population growth, indicating that economic equity can also contribute towards the stabilisation of population growth. This is illustrated by the decreasing fertility rates in most developed nations like Australia, the UK and particularly Japan.
Cause and Effect
The addressing of aggravating factors such as climate change – a problem overwhelmingly caused by developed nations such as Australia, both historically and currently through our export of brown coal– and continued good-faith collaboration with these developing nations to establish renewable energy production, will greatly assist to prevent a crisis occurring.
When concepts such as immigration limitations seek to protect our nation by addressing the symptoms, we are better served by asking how the problem can be solved from its root.
Gordon Young is an ethicist, principal of Ethilogical Consulting and lecturer in professional ethics at RMIT University’s School of Design.
MOST POPULAR
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
An ethical dilemma for accountants
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
The role of ethics in commercial and professional relationships
ArticleBeing Human
The problem with Australian identity
EssayBUSINESS + LEADERSHIP
Understanding the nature of conflicts of interest
BY Gordon Young
Gordon Young is a lecturer on professional ethics at RMIT University and principal at Ethilogical Consulting.
The kiss of death: energy policies keep killing our PMs

The kiss of death: energy policies keep killing our PMs
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentScience + Technology
BY Kym Middleton The Ethics Centre 24 AUG 2018
If you were born in 1989 or after, you haven’t yet voted in an election that’s seen a Prime Minister serve a full term.
Some point to social media, the online stomping grounds of digital natives, as the cause of this. As Emma Alberici pointed out, Twitter launched in 2006, the year before Kevin ’07 became PM.
Some blame widening political polarisation, of which there is evidence social media plays a crucial role.
If we take a look though, the thing that keeps killing our PMs’ popularity in the polls and party room is climate and energy policy. It sounds completely anodyne until you realise what a deadly assassin it is.
Rudd
Kevin Rudd declared, “Climate change is the great moral challenge of our generation”. This strategic focus on global warming contributed to him defeating John Howard to become Prime Minister in December 2007. As soon as Rudd took office, he cemented his green brand by ratifying the Kyoto Protocol, something his predecessor refused to do.
There were two other major efforts by the Rudd government to address emissions and climate change. The first was the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme(CPRS) led by then environment minister Penny Wong. It was a ‘cap and trade’ system that had bi-partisan support from the Turnbull led opposition party… until Turnbull lost his shadow leadership to Abbott over it. More on this soon.
Then there was the December 2009 United Nations climate summit in Copenhagen, officially called COP15 (because it was the fifteenth session of the Conference of Parties). Rudd and Wong attended the summit and worked tirelessly with other nations to create a framework for reducing global energy consumption. But COP15 was unsuccessful in that no legally binding emissions limits were set.
Only a few months later, the CPRS was ditched by the Labor government who saw it would never be legislated due to a lack of support. Rudd was seen as ineffectual on climate change policy, the core issue he championed. His popularity plummeted.
Gillard
Enter Julia Gillard. She took poll position in the Labor party in June 2010 in what will be remembered as the “knifing of Kevin Rudd”.
Ahead of the election she said she would “tackle the challenge of climate change” with investments in renewables. She promised, “There will be no carbon tax under the government I lead”.
Had she known the election would result in the first federal hung parliament since 1940, when Menzies was PM, she may not have uttered those words. Gillard wheeled and dealed to form a minority government with the support of a motley crew – Adam Bandt, a Greens MP from Melbourne, and independents Andrew Wilkie from Hobart, and Rob Oakeshott and Tony Windsor from regional NSW. The compromises and negotiations required to please this diverse bunch would make passing legislation a challenging process.
To add to a further degree of difficulty, the Greens held the balance of power in the Senate. Gillard suggested they used this to force her hand to introduce the carbon tax. Then Greens leader Bob Brown denied that claim, saying it was a “mutual agreement”. A carbon price was legislated in November 2011 to much controversy.
Abbott went hard on this broken election promise, repeating his phrase “axe the tax” at every opportunity. Gillard became the unpopular one.
Rudd 2.0
Crouching tiger Rudd leapt up from his grassy foreign ministry portfolio and took the prime ministership back in June 2013. This second stint lasted three months until Labor lost the election.
Abbott
Prime Minister Abbott launched a cornerstone energy policy in December 2013 that might be described as the opposite of Labor’s carbon price. Instead of making polluters pay, it offered financial incentives to those that reduced emissions. It was called the Emissions Reduction Fund and was criticised for being “unclear”. The ERF was connected to the Coalition’s Direct Action Plan which they promoted in opposition.
Abbott stayed true to his “axe the tax” slogan and repealed the carbon price in 2014.
As time moved on, the Coalition government did not do well in news polls – they lost 30 in a row at one stage. Turnbull cited this and creating “strong business confidence” when he announced he would challenge the PM for his job.
Turnbull
After a summer of heatwaves and blackouts, Turnbull and environment minister Josh Frydenberg created the National Energy Guarantee. It aimed to ensure Australia had enough reliable energy in market, support both renewables and traditional power sources, and could meet the emissions reduction targets set by the Paris Agreement. Business, wanting certainty, backed the NEG. It was signed off 14 August.
But rumblings within the Coalition party room over the policy exploded into the epic leadership spill we just saw unfold. It was agitated by Abbott who said:
“This is by far the most important issue that the government confronts because this will shape our economy, this will determine our prosperity and the kind of industries we have for decades to come. That’s why this is so important and that’s why any attempt to try to snow this through … would be dead wrong.”
Turnbull tried to negotiate with the conservative MPs of his party on the NEG. When that failed and he saw his leadership was under serious threat, he killed it off himself. Little did he know he would go down with it.
Peter Dutton continued with a leadership challenge. Turnbull stepped back saying he would not contest and would resign no matter what. His supporters Scott Morrison and Julie Bishop stepped up.
Morrison
After a spat over the NEG, Scott Morrison has just won the prime ministership with 45 votes over Dutton’s 40.
Killers
We have a series of energy policies that were killed off with prime minister after prime minister. We are yet to see a policy attract bi-partisan support that aims to deliver reliable energy at lower emissions and affordable prices. And if you’re 29 or younger, you’re yet to vote in an election that will see a Prime Minister serve a full term.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology
Making friends with machines
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships, Science + Technology
When do we dumb down smart tech?
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Are we prepared for climate change and the next migrant crisis?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology, Society + Culture