From NEG to Finkel and the Paris Accord – what’s what in the energy debate

From NEG to Finkel and the Paris Accord – what’s what in the energy debate
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentRelationshipsScience + Technology
BY The Ethics Centre 20 AUG 2018
We’ve got NEGs, NEMs, and Finkels a-plenty. Here is a cheat sheet for this whole energy debate that’s speeding along like a coal train and undermining Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull’s authority. Let’s take it from the start…
UN Framework Convention on Climate Change – 1992
This Convention marked the first time combating climate change was seen as an international priority. It had near-universal membership, with countries including Australia all committed to curbing greenhouse gas emissions. The Kyoto Protocol was its operative arm (more on this below).
The Kyoto Protocol – December 1997
The Kyoto Protocol is an internationally binding agreement that sets emission reduction targets. It gets its name from the Japanese city it was ratified in and is linked to the aforementioned UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. The Protocol’s stance is that developed nations should shoulder the burden of reducing emissions because they have been creating the bulk of them for over 150 years of industrial activity. The US refused to sign the Protocol because the two largest CO2 emitters, China and India, were exempt for their “developing” status. When Canada withdrew in 2011, saving the country $14 billion in penalties, it became clear the Kyoto Protocol needed some rethinking.
Australia’s National Electricity Market (NEM) – 1998
Forget the fancy name. This is the grid. And Australia’s National Electricity Market is one of the world’s longest power grids. It connects suppliers and consumers down the entire east and south east coasts of the continent. It spans across six states and territories and hops over the Bass Strait connecting Tasmania. Western Australia and the Northern Territory aren’t connected to the NEM because of distance.
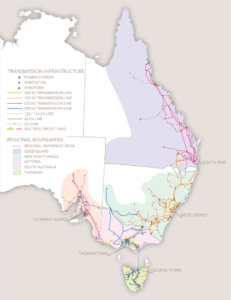 Source: Australian Energy Market Operator
Source: Australian Energy Market Operator
The NEM is made up of more than 300 organisations, including businesses and state government departments, that work to generate, transport and deliver electricity to Australian users. This is no mean feat. Before reliable batteries hit the market, which are still not widely rolled out, electricity has been difficult to store. We’ve needed to continuously generate it to meet our 24/7 demands. The NEM, formally established under the Keating Labor government, is an always operating complex grid.
The Paris Agreement aka the Paris Accord – November 2016
The Paris Agreement attempted to address the oversight of the Kyoto Protocol (that the largest emitters like China and India were exempt) with two fundamental differences – each country sets its own limits and developing countries be supported. The overarching aim of this agreement is to keep global temperatures “well below” an increase of two degrees and attempt to achieve a limit of one and a half degrees above pre-industrial levels (accounting for global population growth which drives demand for energy). Except Australia isn’t tracking well. We’ve already gone past the halfway mark and there’s more than a decade before the 2030 deadline. When US President Donald Trump denounced the Paris Agreement last year, there was concern this would influence other countries to pull out – including Australia. Former Prime Minister Tony Abbott suggested we signed up following the US’s lead. But Foreign Minister Julie Bishop rebutted this when she said: “When we signed up to the Paris Agreement it was in the full knowledge it would be an agreement Australia would be held to account for and it wasn’t an aspiration, it was a commitment … Australia plays by the rules — if we sign an agreement, we stick to the agreement.”
The Finkel Review – June 2017
Following the South Australian blackout of 2017 and rapidly increasing electricity costs, people began asking if our country’s entire energy system needs an overhaul. How do we get reliable, cheap energy to a growing population and reduce emissions? Dr Alan Finkel, Australia’s chief scientist, was commissioned by the federal government to review our energy market’s sustainability, environmental impact, and affordability. Here’s what the Review found:
Sustainability:
- A transition to low emission energy needs to be supported by a system-wide grid across the nation.
- Regular regional assessments will provide bespoke approaches to delivering energy to communities that have different needs to cities.
- Energy companies that want to close their power plants should give three years’ notice so other energy options can be built to service consumers.
Affordability:
- A new Energy Security Board (ESB) would deliver the Review’s recommendations, overseeing the monopolised energy market.
Environmental impact:
- Currently, our electricity is mostly generated by fossil fuels (87 percent), producing 35 percent of our total greenhouse gases.
- We’re can’t transition to renewables without a plan.
- A Clean Energy Target (CET), would force electricity companies to provide a set amount of power from “low emissions” generators, like wind and solar. This set amount would be determined by the government.
-
- The government rejected the CET on the basis that it would not do enough to reduce energy prices. This was one out of 50 recommendations posed in the Finkel Review.
ACCC Report – July 2018
The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission’s Retail Electricity Pricing Inquiry Report drove home the prices consumers and businesses were paying for electricity were unreasonably high. The market was too concentrated, its charges too confusing, and bad policy decisions by government have been adding significant costs to our electricity bills. The ACCC has backed the National Energy Guarantee, saying it should drive down prices but needs safeguards to ensure large incumbents do not gain more market control.
National Energy Guarantee (NEG)– present 20 August 2018
The NEG was the Turnbull government’s effort to make a national energy policy to deliver reliable, affordable energy and transition from fossil fuels to renewables. It aimed to ‘guarantee’ two obligations from energy retailers:
- To provide sufficient quantities of reliable energy to the market (so no more black outs).
- To meet the emissions reduction targets set by the Paris Agreement (so less coal powered electricity).
It was meant to lower energy prices and increase investment in clean energy generation, including wind, solar, batteries, and other renewables. The NEG is a big deal, not least because it has been threatening Malcolm Turnbull’s Prime Ministership. It is the latest in a long line of energy almost-policies. It attempted to do what the carbon tax, emissions intensity scheme, and clean energy target haven’t – integrate climate change targets, reduce energy prices, and improve energy reliability into a single policy with bipartisan support. Ambitious. And it seems to have been ditched by Turnbull because he has been pressured by his own party. Supporters of the NEG feel it is an overdue radical change to address the pressing issues of rising energy bills, unreliable power, and climate change. But its detractors on the left say the NEG is not ambitious enough, and on the right too cavalier because the complexity of the National Energy Market cannot be swiftly replaced.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Science + Technology
How will we teach the robots to behave themselves?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The tyranny of righteous indignation
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
There is something very revealing about #ToiletPaperGate
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Social philosophy
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
The energy debate to date – recommended reads

The energy debate to date – recommended reads
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + Environment
BY The Ethics Centre 18 AUG 2018
Australia, we put it to you. ‘Is it too soon to ditch fossil fuels?’ We’ve waded through political waters and presented our shiniest pearls for your perusal.
Cheat Sheet
From NEG to Finkel and the Paris Accord – what’s what in the energy debate
The Ethics Centre
18 October 2018
Before action must come knowledge. And before knowledge must come sorting through a heap of confusing, jargonistic, off-putting acronyms, reviews, and accords. Worry not, we’ve got your back and did it for you. Our cheat sheet will brush you up on all those names that keep getting dropped in the Australian energy debate like they’re hot coals.
Video
Australia’s energy crisis: “Absolute shambles, national embarrassment and a disgrace”
7.30, ABC News
Ian Verrender
13 Feb 2017
This 7.30 report is a perfect backgrounder to the mess that is Australia’s energy crisis. The NEM broke leaving hot and bothered South Australians without electricity (you read the cheat sheet so you know the NEM is a fancy acronym for the grid). A Victorian power plant that supplied 20 percent of the state’s energy simply closed shop. Renewables are unreliable but fossil fuels are killing the planet. Holy calamity!
Interactive
They Vote For You – How does your MP vote on the issues that matter to you?
Open Australia Foundation
If you’re rearing to parade your opinion, hold on. Haste makes waste. While we’re between elections, how about taking a look at how your local MP voted on energy? Did they champion a fast switch to renewables or continued support for fossil fuels like coal and gas? Forget what they said in the run up to an election and check out what they did.
Movie
And one for fun. Maybe a post-apocalyptic energy crisis isn’t so bad if we can also have double-necked flame guitars.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Climate + Environment
Big Thinker: Bill Mollison
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Climate + Environment
The business who cried ‘woke’: The ethics of corporate moral grandstanding
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
This is what comes after climate grief
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A burning question about the bushfires
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
The five biggest myths of ethical fashion

The five biggest myths of ethical fashion
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentHealth + WellbeingSociety + Culture
BY The Ethics Centre 18 APR 2018
We all know the way we shop is unsustainable.
Australians are the second biggest consumers of textiles worldwide. We throw more than 500,000 tonnes of the stuff into landfill every day. We only wear our garments seven times before throwing them away and still buy an average of twenty seven kilograms of new clothing each year.
The ethical fashion movement promotes a cull of fast fashion’s massive social and environmental impact. But why aren’t more people engaging in it?
We spoke to Clara Vuletich about the five biggest myths of ethical fashion – and if they’re keeping people out.
1. Ethical fashion has to be exclusive
It used to be the case that shopping ethically meant visiting tiny, hole-in-the-wall boutiques, which were either aggressively minimalist or bursting with colours a Crayola pack would be shy to wear. But it’s becoming mainstream.
Vuletich says big brands like H&M and Country Road are engaging with the ethical space in ways unique to their breadth and industry relationships. Another brand, Uniqlo, has introduced a recycling drive for customers to return their secondhand clothes. Though these actions are often met with a sceptical “But it’s just PR” comment, Vuletich says they are a step in the right direction.
‘The people that work in this space aren’t monsters’, she says. ‘They aren’t all ego-driven. It’s much more nuanced than that.’ The relationship a big brand like H&M has developed over decades with their primary garment supplier in Shanghai (for example) isn’t insignificant. They know their names, their families, their lives.
2. Ethical fashion has to be vegan, natural and eco-friendly
Catch-all phrases like natural, eco-friendly, or yes, ethical, are usually a sign to look further, warns Vuletich. Cotton, one of the most prolific materials worldwide, almost always produces toxic effluent from pesticides and dyes, and relies on infamously exploitative farming environments.
According to Levi’s, one denim pair of jeans is made with 2,600 litres of water. Polyester, a synthetic material derived from plastic, is far more easily recycled and reused than any other natural material.
But polyester can take up to 200 years to decompose. In landfill, wool creates methane gas. So which is better for the environment? The complexity of textile production makes it impossible to rank fabrics on a hierarchy of environmental sustainability.
3. Ethical fashion has to be local
Cutting down transport emissions does matter. But the fact is, unless we start growing cotton farms and erecting textile mills in our local communities, the creation of any piece of clothing will have some international process to it.
A ‘Made in Australia’ tag won’t always be the guarantor of quality and safe working conditions. Neither does a ‘Made in China’ tag mean poor workmanship and sweatshops (anymore).
For the quality, bulk, and turnaround the Australian fashion market wants, whether ethical or not, international processes are not an unfortunate by-product – they are crucial to its existence. Fabric manufacturing is one of the quickest ways for communities and countries to rise out of poverty and the solution isn’t to pull the rug out from under them.
4. Ethical fashion has to be expensive
If you’re looking for a new piece of clothing where every worker in the supply chain has been paid well, it stands to reason the final product will be expensive. If you don’t have money to burn, there are other clothing choices you can make that won’t exploit the earth and human race.
Vuletich is a big fan of secondhand shopping – think Salvos, Vinnies, U-Turn, Swop, Red Cross, Gumtree… Secondhand goods they may be, but that’s not a codeword for cheap, shoddy, or badly made. Instead of a fast fashion giant, your purchase funds a local charity, business, or market stall owner.
No extra resources were extracted for anyone to get that piece of clothing to you, nor was anyone enslaved to sew your new threads. It’s likely a local near the shop donated it, so transport emissions are low, and you’re also keeping something out of landfill.
5. Ethical fashion leads to social impact
Vuletich is wary of making huge claims. Slogans like ethical fashion will save the world are just that – slogans. The effectiveness of campaigns like the 1-for-1 business model have been thoroughly debunked, and it’s doubtful buying a pair of fair trade sandals will do as much good as a country changing their labour laws. But will it have some impact? She says yes.
For someone not in the industry, the complexity is overwhelming. Trying to track the supply chain of a polyester dress might take you to one factory in Turkey, while following the history of a pair of denim jeans will take you to China – if the clothing company even knows where their raw materials are sourced. The sheer scale of garment manufacturing is the main reason ethical fashion is intimidating, and that’s not taking into account consumer needs.
Fashion is personal. People want different things from their clothing – they might want it to be free of animal products, or for it to be breathable and comfortable, or for it to be made with as little impact to local communities as possible. They might want it to make them stand out, or to make them blend in.
They might want it to be easy and careless. But with the growing social, political and environmental consciousness around fashion, it’s difficult to stay unaware. Maybe it won’t change the world, but rest assured that the choices you make as a consumer do add up.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing
The virtues of Christmas
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
Rethinking the way we give
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Ethical concerns in sport: How to solve the crisis
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing
When you hire a philosopher as your ethicist, you are getting a unicorn
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Big Thinker: Bill Mollison

Bill Mollison (1928—2016) was an Australian ecologist and the ‘father of permaculture’, a type of agricultural design and practice he created, named and taught.
Having co-wrote Permaculture One with his student and colleague David Holmgrem, Mollison later founded the Permaculture Institute of Tasmania and taught his Permaculture Design Course and Certificate (PDCC) all around the world.
Today, his philosophy has reached millions. His commitment to ethics brings philosophy back into the marketplace and onto the farm – down to its earthworms and well-tilled soil.
What is permaculture?
Permaculture is an ethical design framework for sustainable farming. It combines traditional farming methods of Indigenous and Aboriginal communities with renewable technologies and low-energy materials. Masanobu Fukuoka, a Japanese farmer and creator of “Do-nothing Farming”, is cited as another influence on Mollison’s farming philosophy.
Mollison believed that farming monocultures, like corn, or wheat, was unsustainable. Instead, he called for ‘food forests’ – a varied collection of plant and tree species that support equally as diverse animal life.
Like a delicate structure of checks and balances, the little relationships formed in such an ecosystem would keep it self-sufficient. According to Mollison, once complete, a successful permaculture design wouldn’t need any human touch at all.
What’s wrong with what we’ve got now?
Because monocultures are more efficient, fast and easy to harvest, they’ve been the go-to for industrial farming. But, according to Mollison, their future is limited, with no means to reproduce the same healthy ecosystem it profits from. In fact, it’s often expected to meet the surplus demand of nations that already have enough food.
Mollison considered this form of agriculture as unethical, self-destructive and “temporary”. Rather than people being relied on to provide yields, he wanted to make us another part of the agricultural web. No more, no less.
This, along with permaculture’s three core ethics (earth care, people care and fair share), would transform how plants, animals and humans all interact with each other. People – not just farmers – would turn into active stewards of the earth. The social and economic needs of interdependent communities would be satisfied and looked after, with global surplus distributed to those most in need.
Some people find his views noble, but unrealistic. Indeed, his repositioning of farming as political might be novel. But applying ethics to fulfil basic needs of food and shelter, to Mollison, is essential:
“The greatest change we need to make is from consumption to production, even if on a small scale, in our own gardens. If only 10% of us can do this, there is enough for everyone. Hence the futility of revolutionaries who have no gardens, who depend on the very system they attack, and who produce words and bullets, not food and shelter.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Relationships
You can’t save the planet. But Dr. Seuss and your kids can.
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Who is to blame? Moral responsibility and the case for reparations
Big thinker
Climate + Environment, Relationships
Big Thinker: Ralph Waldo Emerson
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment
Why it was wrong to kill Harambe
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Ethics Explainer: Ownership

Ethics Explainer: Ownership
ExplainerBusiness + LeadershipClimate + Environment
BY The Ethics Centre 5 JUL 2017
Where lying is the abuse of truth and harm the abuse of dignity, philosophers associate theft with the abuse of ownership.
We tend to take property for granted. People own things, share things or have access to things that don’t belong to them. We rarely stop to think how we come to own things, whether there are some things we shouldn’t be allowed to own or whether our ideas of property and ownership are adequate for everybody.
This is where English philosopher John Locke comes in.
Locke believed that in a state of nature – before a government, human made laws or an established economic system – natural resources were shared by everyone. Similar to a shared cattle-grazing ground called the Commons, these were not privately owned and so accessible to all.
But this didn’t last forever. He believed common property naturally transformed into private property through ownership. Locke had some ideas as to how this should be done, and came up with three conditions:
- First, limit what you take from the Commons so everyone else can enjoy the shared resource.
- Second, take only what you can use.
- Third, that you can only own something if you’ve worked and exerted labour on it. (This is his labour theory of property).
Though his ideas form the bedrock of modern private property ownership, they come with their fair share of critics.
Ancient Greek philosopher Plato thought collective property was a more appropriate way to unite people behind shared goals. He thought it was better for everyone to celebrate or grieve together than have some people happy and others sad at the way events differently affect their privately-owned resources.
Others wonder if it is complex enough for the modern world, where the resource gap between rich companies and poor communities widens. Does this satisfy Locke’s criteria of leaving the Commons “enough and as good”? He might have a criticism of his own about our current property laws – that they’ve gone beyond what our natural rights allow.
Some critics also say his theory denies the cultivation techniques and land ownership of groups like the Native Americans or the Aboriginal Australians. While Locke’s work serves as a useful explanation of Western conceptions of property ownership, we should wonder if it is as natural as he thought it was.
On the other hand, it’s likely Locke simply had no idea of the way in which Indigenous people have managed the landscape over millennia. Had he understood this, then he may have recognised the way Indigenous groups use and relate to land as an example of property ownership.
Karl Marx, and the closely associated philosophies of socialism and communism, prioritise common or collective property over private forms of property. He thought humanity should – and does – move toward co-operative work and shared ownership of resources.
However, Marx’s work on alienation may be a common ground. This is when people’s work becomes meaningless because they can’t afford to buy the things they’re working to make. They can never see or enjoy the fruits of their labour – nor can they own them. Considering the importance Locke places on labour and ownership, he may have had a couple of things to say about that.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Why fairness is integral to tax policy
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Ethical concerns in sport: How to solve the crisis
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Climate + Environment
The business who cried ‘woke’: The ethics of corporate moral grandstanding
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
There’s no good reason to keep women off the front lines
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Melbourne Cup: The Ethical Form Guide

Melbourne Cup: The Ethical Form Guide
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentHealth + WellbeingSociety + Culture
BY The Ethics Centre 1 NOV 2016
The nation stops – and turns a blind eye.
The Melbourne Cup is the race that ‘convenes’ rather than ‘stops’ the nation. It’s a classic example of a moment when the abstraction that is the nation – large, sprawling, messy and diverse – is made temporarily and symbolically concrete. This is an illusion. But perhaps a necessary one.
The mega media sport spectacle is highly serviceable to the fantasy of the united nation because it is popular culture played out in real time. Sport is implicated in the idea of a singular Australian identity because it is apparently open and meritocratic, and also has operated historically as a vehicle for the projection of ‘Australianness’.
The Melbourne Cup represents the pros and cons of contemporary sport and society. It is devoted to pleasure as an interruption of the daily work routine that consumes more and more of our time. It is carnivalesque – fleetingly turning the world upside down.
But it is characterised by the range of excess demanded by consumer capitalism – risky financial expenditure, alcohol consumption and repressive co-optation. All of this activity is conducted using the body of the horse that is celebrated one minute and whipped the next, highly prized for sporting and breeding performance in some cases and turned into abattoir fodder in others.
National sporting spectacles are here to stay. The ‘people’, the state and the commercial complex demand them, but they should not be excuses for rampant collective self-delusion.
– David Rowe, Professor of Cultural Research at Western Sydney University.
If you loved horses, you wouldn’t treat them as commodities
We’re often told those involved in the horse racing industry truly love horses and treat them with the utmost respect. I have no doubt they believe that to be true, but their actions don’t support these claims.
If those working with horses truly loved them, they would spend time and money re-homing and appropriately retiring racehorses at the end of their careers. Instead, the evidence suggests racehorses are only loved when they have the potential to make money. When they’re injured or no longer able to race, they’re often sent off to the knackery without a second’s thought.
The racing industry pushes horses beyond their natural limits. This results in short careers and extensive injuries, such as those suffered by Admiral Rakti last year. Since Admiral Rakti’s death, 127 horses have died on Australian race tracks.
The ultimate image for this exploitative approach to racing is the whip, which desperately needs to be banned. In doing so, we would see horses performing at the peak of their natural ability rather than desperately running due to fear and pain.
– Elio Celotto, Campaign Director at the Coalition for the Protection of Racehorses.
The risks of horse racing are imposed on unwilling participants
Horse racing differs ethically from other sports. In other sports, it is the participant who freely decides to accept the risks. In horse racing, the risks are relatively low for the riders and extremely high for the animals.
It is not unethical to accept the risks of a given sport. Nor, in my view, is it always unethical to take the life of animals. The question is whether the costs of horse racing are reasonable, or whether they are unacceptably high.
Most Australians today would have ethical objections to entertainments such as bullfighting or dog fighting, or the use of non-domestic animals in circus acts. The number of horses slaughtered annually as a result of the racing industry far exceeds the number of animal deaths from most of these other entertainments.
The costs of the racing industry are unacceptably high. The situation is unlikely to improve as long as horse racing in Australia remains so closely tied to the enormous economic interests of the gambling industry.
– Ben Myers, Lecturer in Systematic Theology at United Theological College.
The Melbourne Cup sweep is harmless fun, but not in the classroom
The effects of gambling are an oft-discussed topic among my colleagues, but in the past week the discussion has been triggered by an all-staff email about the office’s annual Melbourne Cup Sweep. One staff member felt it was totally inappropriate for an organisation operating in mental health and wellbeing to be promoting in any way a day of socially acceptable statewide gambling.
I actually disagree, although not strongly. A sweep is a one-off, fixed price competition, not much different from a raffle. It’s in no way addictive in the way that poker machines and online betting can be.
The normalisation of gambling is certainly insidious. There is some evidence that the younger a person is when they have their first betting win, the more likely they are to develop problems down the track. So a sweep in a primary school does sound icky to me.
– Heather Grindley, Public Interest Manager at the Australian Psychological Society.
The spectacle is lost in a “feeding frenzy” of gambling
The Melbourne Cup is a genuine Australian icon. However, it’s now also a commodified hub for a gambling feeding frenzy. This is a tough time of year for people who are trying to restrain their gambling.
Effective regulation can undoubtedly reduce the harms associated with gambling. Cup Day should be a reminder that commercialised gambling corrupts sport and induces misery for many, including those who never gamble. Decent regulation might reduce super-profits but it would certainly help make Australia’s unique sporting and social environment safer, more fun and lot more enjoyable.
– Charles Livingstone, Senior Lecturer in Public Health and Preventive Medicine at Monash University.
The Melbourne Cup pits debauchery against dignity
As I write, many will be gathered in offices, pubs and racecourses around the country dressed to the nines. Fascinators, frocks, loud ties and sharp suits are the order of the day for the “world’s richest race”.
And yet by the end of it all, many punters will be staggeringly drunk – their state highlighted by its juxtaposition to their glamorous attire. Every year, tabloids gleefully post pictures of women in various stages of undress – simultaneously glorifying and shaming the debauchery that accompanies a race some revellers will likely miss, having already passed out.
Ultimately the Melbourne Cup is full of ethical polarities. It follows the highs and lows of the race itself. Fine champagne is popped in celebration as punters pass out from one too many drinks, horses are glorified as they are exploited, and once-off punters dress up and participate in the same gambling industry that destroys so many lives.
Racing Victoria were unavailable for comment but directed readers to their position on equine welfare.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
There is something very revealing about #ToiletPaperGate
Explainer
Society + Culture
Ethics Explainer: Aesthetics
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Beyond cynicism: The deeper ethical message of Ted Lasso
Big thinker
Relationships, Society + Culture
Five Australian female thinkers who have impacted our world
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Why it was wrong to kill Harambe

Why it was wrong to kill Harambe
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + Environment
BY Clive Phillips The Ethics Centre 2 JUN 2016
The killing of Harambe the gorilla at Cincinnati Zoo this week has aroused public sentiment in a way reminiscent of the public outrage caused by the killing of Cecil the lion.
This was not an isolated incident. On at least two previous occasions small children have accidentally fallen into gorilla pens. On both occasions the children were ‘protected’ by a prominent gorilla in the group, one female and one male, incidents which were heralded as examples of cross species animal altruism.
The incidents occurred in 1986 and 1991 in Jersey Zoo and Brookfield Zoo respectively – when rapid response teams would have been unknown. They demonstrate that gorillas are not dangerous animals.
This is further supported by the fact some witnesses’ reports said that Harambe was actually protecting the child and had not demonstrated any malevolence.
Animal behaviour expert, Professor Gisella Kaplan of the University of New England, has confirmed that gorillas are not inherently aggressive and would likely have not wanted to harm the child – a result of their social lifestyle and herbivorous diet.
Nowadays zoos have Dangerous Animal Response Teams, which in the ten minutes since the boy entered the enclosure made the decision to euthanise the gorilla. Members of this team are typically trained by the police to react to a dangerous animal threatening a member of the public.
Zoo animals already sacrifice many rights for the sake of human entertainment, education, conservation, and scientific endeavour.
Their first priority is for the safety of the public, then zoo staff. Only after these are assured is the animal’s wellbeing considered. As evidence of such a policy, Thayne Maynard, Director of Cincinnati Zoo, expressed public regret for the loss of Harambe as a future breeding male, a loss of genetic diversity, without any consideration for Harambe’s rights.
Zoos should have a policy based on an ethical appraisal of potential incidents based on higher level principles. These would include utilitarian, deontological, and virtue ethics principles.
From a utilitarian perspective, the harm caused by shooting Harambe, to him, his family, human witnesses, and the public generally, may have outweighed the small risk to the child. Harambe’s family will mourn his loss and may even have been traumatised by the event.
Deontologists would argue taking Harambe’s life would never be justified by the small risk to the child – the shooting constitutes a supreme example of a speciesist approach.
Insights from virtue ethics show how this incident has damaged the zoo’s reputation. Public outcry has accused the zoo of having little regard for the rights of its animal occupants – although the safeguarding of the child’s life may be welcomed by some future visitors. Is this the action we would expect of a ‘good’ zoo?
Instead, the zoo seems to have acted from self-interest, afraid of potential litigation should the child be harmed. From a commercial angle a seventeen year old gorilla is worth $100,000 to $200,000; a child’s life many millions. However, the zoo is likely to experience reduced visitor numbers for a prolonged period, as well as being responsible for damage to the reputation of American zoos more generally.
The zoo may also be liable for placing visitors in a dangerous situation, something not unheard of in zoos around the world. Owners of swimming pools in Australia could teach the zoos a lot about preventing small children entering facilities, with detailed regulations and strict monitoring minimising any risk to children.
Some zoos may have deliberately sacrificed safety for an enhanced visitor experience, with limited barriers between the public and apparently dangerous animals.
Harambe’s killing may yet prompt a renewed movement to provide legal recognition of the rights of great apes.
Zoo animals already sacrifice many rights for the sake of human entertainment, education, conservation and scientific endeavour. Our ‘contract’ with zoo animals, where we provide nutrition, good health, and companionship in return for the animals sacrificing their freedom, right to live, and reproduce naturally in a state of good welfare, stack the terms heavily in our favour.
Indeed, killing a defenceless animal that had not shown any aggression is tantamount to tearing up that contract.
The ethical dilemma over whether to shoot Harambe might have been avoided if a movement known as The Great Ape Project had succeeded. For over twenty years a group of philosophers, primatologists, and anthropologists have attempted to gain great apes, including gorillas, rights through the United Nations that would include the right to life.
The movement is based on overwhelming evidence for self-consciousness and other higher level cognitive abilities in great apes, which are undoubtedly greater than in some disabled humans who are adequately protected in law.
Although this has gained support in some minority states, it has yet to gain widespread acceptance, primarily because of determined opposition from scientists who reserve the right to use chimpanzees – another great ape – for medical research. Harambe’s killing may yet prompt a renewed movement to provide legal recognition of the rights of great apes.
Just like Cecil the lion, the killers of Harambe are being judged in the arena of social media. The pattern of argument there suggests members of the public would have preferred that the zoo accept some risk to the child before taking the extreme action of killing a harmless gorilla.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Who is to blame? Moral responsibility and the case for reparations
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Science + Technology
Space: the final ethical frontier
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Melbourne Cup: The Ethical Form Guide
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Relationships
“Animal rights should trump human interests” – what’s the debate?
BY Clive Phillips
Clive Phillips is Chair of Animal Welfare and Director of the Centre for Animal Welfare Ethics at the University of Queensland.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
“Animal rights should trump human interests” – what’s the debate?

“Animal rights should trump human interests” – what’s the debate?
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentRelationships
BY The Ethics Centre 22 MAR 2016
Are the ways humans subject animals to our own needs and wants justified?
Humans regularly impose our own demands on the animal world, whether it’s eating meat, scientific testing, keeping pets, sport, entertainment or protecting ourselves. But is it reasonable and ethical to do so?
Humans and animals
We often talk about humans and animals as though they are two separate categories of being. But aren’t humans just another kind of animal?
Many would say “no”, claiming humans have greater moral value than other animals. Humans possess the ability to use reason while animals act only on instinct, they say. This ability to think this way is held up as the key factor that makes humans uniquely worthy of protection and having greater moral value than animals.
“Animals are not self-conscious and are there merely as means to an end. That end is man.” – Immanuel Kant
Others argue that this is “speciesism” because it shows an unjustifiable bias for human beings. To prove this, they might point to cases where a particular animal shows more reason than a particular human being – for example, a chimpanzee might show more rational thought than a person in a coma. If we don’t grant greater moral value to the animal in these cases, it shows that our beliefs are prejudicial.
Some will go further and suggest that reason is not relevant to questions of moral value, because it measures the value of animals against human standards. In determining how a creature should be treated, philosopher Jeremy Bentham wrote, “… the question is not ‘Can they reason?’, nor ‘Can they talk?’, but ‘Can they suffer?’”
So in determining whether animal rights should trump human interests, we first need to figure out how we measure the value of animals and humans.
Rights and interests
What are rights and how do they correspond to interests? Generally speaking, you have a right when you are entitled to do something or prevent someone else from doing something to you. If humans have the right to free speech, this is because they are entitled to speak freely without anyone stopping them. The right protects an activity or status you are entitled to.
Rights come in a range of forms – natural, moral, legal and so on – but violating someone’s right is always a serious ethical matter.
“Animals are my friends. I don’t eat my friends.” – George Bernard Shaw
Interests are broader than rights and less serious from an ethical perspective. We have an interest in something when we have something to gain or lose by its success or failure. Humans have interests in a range of different projects because our lives are diverse. We have interests in art, medical research, education, leisure, health…
When we ask whether animal rights should trump human interests, we are asking a few questions. Do animals have rights? What are they? And if animals do have rights, are they more or less important than the interests of humans? We know human rights will always trump human interests, but what about animal rights?
Animal rights vs animal welfare
A crucial point in this debate is understanding the difference between animal rights and animal welfare. Animal rights advocates believe animals deserve rights to prevent them from being treated in certain ways. The exploitation of animals who have rights is, they say, always morally wrong – just like it would be for a human.
Animal welfare advocates, on the other hand, believe using animals can be either ethical or, in practice, unavoidable. These people aim to reduce any suffering inflicted on animals, but don’t seek to end altogether what others regard as exploitative practices.
As one widely used quote puts it, “Animal rights advocates are campaigning for no cages, while animal welfarists are campaigning for bigger cages”.
Are they mutually exclusive? What does taking a welfarist approach say about the moral value of animals?
‘Animal rights should trump human interests’ took place on 3 May 2016 at the City Recital Hall in Sydney.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The ethics of friendships: Are our values reflected in the people we spend time with?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
When identity is used as a weapon
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Naturalistic Fallacy
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Society + Culture
Stop giving air to bullies for clicks
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
How should vegans live?

How should vegans live?
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentHealth + Wellbeing
BY XAVIER COHEN The Ethics Centre 24 JAN 2016
Ethical vegans make a concerted lifestyle choice based on ethical – rather than, say, dietary – concerns. But what are the ethical concerns that lead them to practise veganism?
In this essay, I focus exclusively on that significant portion of vegans who believe consuming foods that contain animal products to be wrong because they care about harm to animals, perhaps insofar as they have rights, perhaps just because they are sentient beings who can suffer, or perhaps for some other reason.
Throughout the essay, I take this conviction as a given, that is, I do not evaluate it, but instead investigate what lifestyle is in fact consistent with caring about harm to animals, which I will begin by calling consistent veganism. I argue that the lifestyle that consistently follows from this underlying conviction behind many people’s veganism is in fact distinct from a vegan lifestyle.
It is probably the case that one cannot live without causing harm to animals due to the trade-off in welfare between other animals who are harmed by one’s own consumption.
Let us also begin by interpreting veganism in the way that many vegans – and most who are aware of veganism – would. A vegan consumes a diet containing no animal products. In conceiving of veganism in terms of what a diet contains, there seems to be an intuition about the moral relevance of directness, according to which it matters how direct the harm caused by the consumption of the food is with regards to the consumption of the food.
On this intuition, eating a piece of meat is worse than eating a certain amount of apples grown with pesticides that causes the same amount of harm, because the harm in the first case seems to be more directly related to the consumption of the food than in the second case. Harm from the pesticides seems to be a side-effect of eating the food, whereas the death of the animal for meat seems to be a means to the eating food.
Even if we grant this intuition to be a good in this case, it is not good in the case where the harm is greater from the apples than from the meat. To eat the apples in this case is to not put one’s care about harm to animals first, which means going against the only thing that should motivate a consistent vegan.
Here, our intuition about the amount of harm caused is what seems to matter; if what we care about is harm to animals, then we should cause less rather than more harm to animals, and therefore, from the moral point of view, it seems that it is better to eat the meat than the apples. Let the conviction in this intuition be called the ‘less-is-best’ thesis.
Therefore, the intuition about the directness of the harm is only potentially relevant in situations where one has to choose between alternatives that cause the same amount of harm, or in situations where one does not know which causes more harm. The rest of the time, it seems that consistent vegans should not care about the directness of the harm, but instead care only about causing less rather than more harm to animals.
Consistent vegans should not care about the directness of the harm, but instead care only about causing less rather than more harm to animals.
This requires an awareness of harm that extends further than relatively common considerations noted by vegans regarding animal products being used in the production process for—but not being contained in—foodstuffs like alcoholic drinks. Caring about harm to animals means caring about, less directly, accidental harm to (usually very small) animals from the harvesting process, and from products that have a significant carbon footprint, and thereby contribute to (and worsen) climate change, which is already starting to lead to countless deaths and harm to animals worldwide.
However, caring about harm to animals cannot plausibly require consistent vegans to cause no harm at all to animals. If it did, then in light of the last two examples given above, it seems it would require consistent veganism to be a particularly ascetic kind of prehistoric or Robinson Crusoe-type lifestyle, which would clearly be far too demanding.
In fact, it is probably the case that one cannot live without causing harm to animals due to the trade-off in welfare between other animals who are harmed by one’s own consumption, and oneself (an animal) who is harmed if one cannot consume what one needs to survive. But it is definitely the case that all humans could not survive if no harm to other animals could be caused; this means that either human animals or non-human animals will be harmed regardless of how we live.
We could not all be morally obligated to live in such a way that we could not in fact all live. Therefore, due to this argument and due to such a lifestyle being over-demanding, there are two sufficient arguments for why causing some harm to animals is morally permissible.
If it is the case that causing some harm to animals is morally permissible, then there is no clear reason why there should be a categorical difference in the moral status of acts – such as impermissibility, permissibility, and obligation – with regards to how they harm animals, apart from when these categorical differences arise only from vast differences in the amount of harm caused by different acts.
One’s care for animals should be further-reaching: rather than merely caring about harm one causes, a consistent vegan should care about acting or living in a way that leads to less rather than more harm to animals.
So, for example, shooting a vast number of animals merely for the pleasure of sport may well be impermissible, but only insofar as it causes a much greater amount of harm than alternative acts that one could reasonably do instead of hunting. It seems that the most reasonable position, then, which is in line with the less-is-best thesis, is that the morality of harm to animals is best viewed on a continuum on which causing less harm to animals is morally better and causing more harm to animals is morally worse, where the difference in morality is linked only to the difference in the amount of harm to animals.
Hitherto, I have said that it seems to be the case that consistent vegans care about causing less rather than more harm to animals. However, I claim that the less-is-best thesis should in fact be interpreted as having a wider application than merely harm caused by our actions or life lived. One’s care for animals should be further-reaching: rather than merely caring about harm one causes, a consistent vegan should care about acting or living in a way that leads to less rather than more harm to animals. The latter includes a concern about harm caused by others that one can prevent, which the former excludes as it is not harm caused by oneself.
The impact of social interaction on people’s lifestyles is an important way in which consistent vegans can act or live in a way that leads to less rather than more harm to animals. That nearly all vegans are in fact vegans because they were previously introduced to vegan ideas by others – rather than coming by them and becoming vegan through sheer introspection – is testimony to the impact of social interaction on people’s lifestyles, which in turn can be more or less harmful to animals.
If this recommended lifestyle is too demanding, many will reject it or simply not change, meaning that these people will continue to harm animals.
Consistent vegans have the potential to build a broad social movement that encourages many others to lead lives that cause less harm to animals. But in order to do this, consistent vegans will have to persuade those who do not care about harm to animals (or let care about harm to animals impact their lifestyle) to lead a different kind of lifestyle, and if this recommended lifestyle is too demanding, many will reject it or simply not change, meaning that these people will continue to harm animals.
The vegan lifestyle may seem too hard for many people
If these people are more likely to make lifestyle changes if the lifestyle suggested to them is less demanding, which for many – and probably a vast majority – will be the case, then consistent vegans could bring about less harm to animals if they try to persuade these people to live lifestyles that optimally satisfy the trade-off between demandingness and personal harm to animals. This lifestyle that consistent vegans should attempt to persuade others to follow I shall call “environmentarianism”.
Why ‘environmentarianism’? And what is the content of environmentarianism? Care about harm to animals can be framed in terms of care for the environment, as the environment is partially – and in a morally important way—constituted by animals. This can be easily – and I believe quite intuitively – communicated to those who do care about harm to animals, and those who do not are likely to be more swayed by arguments that are framed in terms of concern for the environment than for animals. Concern for oneself, one’s loved ones, and one’s species – things that most people care greatly about – may be more easily read into the former than the latter, especially in light of impending climate change.
Environmentarianism, then, is the set of lifestyles that seek to reduce harm done to the environment (which is conceived in terms of harm to animals for consistent vegans) – as this matters morally for environmentarians – regardless of which sphere of life this reduction of harm comes from. Be it rational or not, ascribing the title and social institution of ‘environmentarian’ to one’s life will, for many, make them more likely to lead a life that is more in line with caring about harm to animals; people often attach themselves to these titles, as the dogmatic behaviour of many vegans shows.
Some may prefer to reduce total harm to animals by a given amount by making the sacrifice of having a vegan diet, but not compromising on their regular car journey to work, whilst others may find taking on the latter easier than maintaining the strict vegan diet.
Moreover, environmentarianism can be practised to a more or less radical – and thus moral – extent. Some may prefer to reduce total harm to animals by a given amount by making the sacrifice of having a vegan diet, but not compromising on their regular car journey to work, or perhaps by opting out of what for them may be uncomfortable proselytising, whilst others may find taking on the latter two easier than maintaining the strict vegan diet (that they perhaps used to have). Some may reduce total harm by an even greater amount – and hence lead a morally better lifestyle – by having a vegan diet and by refraining from harmful transport and by actively suggesting environmentarianism to others.
As an environmentarian may begin by making very small changes, one can be welcomed into a social movement and be eased in to making further lifestyle changes over time, rather than being put off by the strictness of veganism or the antagonism typical of some vegans. Environmentarianism has the great advantage of making it easier for the many who cannot face the idea of never eating animal products again to live more ethically-driven lives.
It follows from all this, then, that consistent vegans should be (especially stringent) environmentarians. For the given impact they have on the total harm to animals, it does not matter if this comes from a totally vegan diet. In fact, to be fixated on dietary purity to the neglect of other spheres of one’s life – in the way that many vegans are – is to contradict a care about harms to animals. With this care given, what matters is lowering the level of harm to animals, regardless of how this harm is done.
This article was republished with permission from the Journal of Practical Ethics.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Moving on from the pandemic means letting go
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Australia Day: Change the date? Change the nation
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Science + Technology
Space: the final ethical frontier
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Exercising your moral muscle
BY XAVIER COHEN
Oxford student Xavier Cohen, was one of the two finalists in the undergraduate category of the inaugural Oxford Uehiro Prize in Practical Ethics.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
You can’t save the planet. But Dr. Seuss and your kids can.

You can’t save the planet. But Dr. Seuss and your kids can.
Opinion + AnalysisClimate + EnvironmentRelationships
BY Steve Vanderheiden The Ethics Centre 30 SEP 2015
Dr. Seuss’ The Lorax explores the consequences of deforestation and the environmental costs of development. It concludes with the Once-ler, the narrator of the story who is principally responsible for deforestation of the decimated Truffula tree, entrusting its final seed to a young boy. He implores the child, “Grow a forest. Protect it from axes that hack. Then the Lorax and all of his friends might come back.”
The Once-ler, wracked by guilt for his complicity in this environmental disaster, passes along responsibility for reversing damage done by his generation to a child. The Lorax suggests the young take on duties of planetary stewardship where adults have failed.
Is this fair? Perhaps the generation responsible for mucking up the planet has lost its moral authority to try and save it. So the task of conservation is inherited by those with a longer-term stake in its future.
That adults might vest hope for a better planet in our children is both edifying and deeply troubling. Edifying because the environmental record of the world’s children bests that of adults by default. The young have not yet begun to reproduce the patterns of behavior that implicate their parents – resource depletion, biodiversity loss, climate change…
Troubling because they may reproduce them in future. We cannot realistically expect young people socialised into a world of willful environmental neglect to behave much differently than their parents have. Adults cannot so easily absolve themselves of the responsibility of addressing environmental harm they have caused.
Rather than saving the planet, a more modest objective might be to refrain from making it much worse for our children. Even this is a daunting prospect. Patterns of energy use dependent on fossil fuels all but guarantee that global temperatures will continue to rise. For most, climate change is no longer a debate about “if” but “how severe?”
We may still hope to make the planet better for our children in other ways. For instance, by adding to the richness of human culture and the stock of beneficial technologies. When it comes to climate though, a more appropriate aim might be to refrain from chopping that last Truffula tree. To preserve our remaining forests so our children might be able to see the proverbial Brown Bar-ba-loots, Swomee-Swans or Humming Fish in their native habitats rather than natural history museums.
Doing this will be challenging. It will require an often uncomfortable reflection on what drives global environmental degradation. In Seuss’ tale the insatiable demand for thneeds – the ultimate commodity – drives the Truffula deforestation. This implicates our heedless consumerism in the causal chain of degradation alongside the Once-ler.
When we consume things we don’t need, and when the industry around these commodities is obviously unsustainable despite our obliviousness to this fact, we contribute to resource depletion. What’s more, we add to the attitudes and norms that suggest this is a private matter, answerable only to private consumer preferences and not larger public concerns for equity or sustainability.
Worst of all, we teach our children to do the same.
The first step in reducing our negative impact upon the planet must be to understand how and where we make the impact we do. We need to understand alternatives that yield comparable value to us with a lighter toll upon the planet. Consuming more conscientiously will leave our children a better planet and make them better citizens of it. Though it requires us to consume differently and less.
Thinking about the long-term consequences of our choices will also help. We cannot plausibly claim to value our children’s future while discounting the future value of current investments in sustainable infrastructure or future costs of unsustainable current practices.
To help make better children for our planet we must teach them that out of sight is not out of mind.
Our deeds announce our concern for the welfare of future generations more accurately than our words or thoughts. Thinking about such choices must be accompanied by some changes in course. Citizens must demand better public choices be made rather than acquiescing to worse ones as unavoidable products of political inertia or inviolable market forces.
The tendency to shift problems across borders is no less insidious than passing them to our children or grandchildren. To help make better children for our planet we must teach them that out of sight is not out of mind.
As role models for our children our success in stopping environmental harm will matter less than our sincerity in the efforts we make. If we honestly try to maintain the planet, our example will help make them into the kind of people our planet needs.
For as the Once-ler interprets the Lorax’s cryptic final word, “UNLESS someone like you cares a whole awful lot, nothing is going to get better. It’s not.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Beyond cynicism: The deeper ethical message of Ted Lasso
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Want #MeToo to serve justice? Use it responsibly.
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Agape
Explainer
Relationships