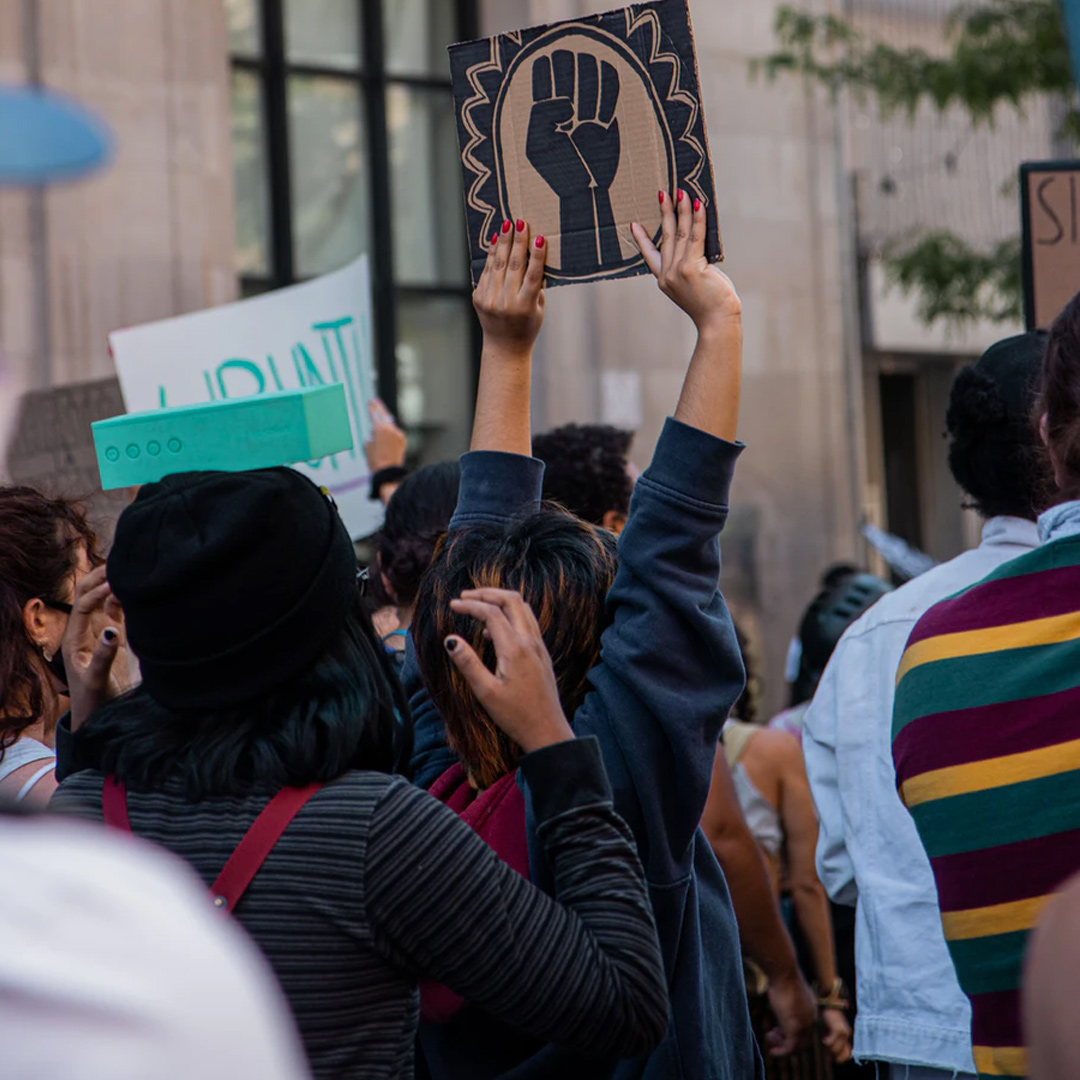Ethics Explainer: Liberalism

Ethics Explainer: Liberalism
ExplainerBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Dr Tim Dean 18 JAN 2021
Liberalism is founded on the belief that individual freedom should be the basis of a just society.
Who should decide how you live your life: where you reside; what career you choose; whom you can marry; and which gods you worship? Should it be your parents? Or your religious or community leaders? Should it be determined by the circumstances of your birth? Or perhaps by your government? Or should you ultimately be the one to decide these things for yourself?
If you answered the latter, then you’re endorsing the values of liberalism, at least in the broadest sense. Liberalism is, at its heart, the belief that each individual person has moral priority over their community or society when it comes to determining the course of their life.
This primacy of individual freedom and self-determination might seem self-evident to people living in modern liberal democracies, but it is actually a relatively recent innovation.
The Birth of Liberalism
In most societies throughout history and prehistory, one’s beliefs, values and social role were imposed on them by their community. Indeed, in many societies since agricultural times, people were considered to be the property of their parents or their rulers, with next to no-one having genuine freedom or the power of self-determination.
Brave (or foolhardy) was the medieval serf who took it upon themselves to defy their local church to practice their own religion, or defy their family tradition to seek out their dream job, or defy their clan to marry whomever their heart desired.
The seeds of modern liberalism were planted in England in the 13th century with the signing of the Magna Carta, which weakened the unilateral power of the King over his minions. This started a process that eventually enshrined a number of individual rights in English law, such as a right to trial by jury and equality before the law.
Soon even rulers – whether monarch or government – came to receive their legitimacy not from divine authority, tradition or fiat but from the will of the people. If the rulers didn’t operate in the interests of the people, the people had the right to strip that legitimacy from them. This made democracy a natural fit for nations with liberal sensibilities.
The other motivating force for liberalism was the horrifically destructive religious wars that wracked Europe after the Reformation, culminating in the Peace of Westphalia in 1648. Given the millions of lives lost due to religious and ideological differences, many people came to see that tolerance of different beliefs and religious practices might be a better alternative to imposing one’s beliefs on others by force.
Modern Liberalism
Liberalism was fleshed out as a comprehensive political philosophy by thinkers such as Thomas Hobbes, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, John Locke and John Stuart Mill, and more recently by John Rawls. While they differed in their emphases and recommendations, all liberal thinkers were committed to the core idea that individuals were – and ought to be – fundamentally free to live as they choose.
Philosopher John Locke argued that liberalism stemmed from our very nature, arguing that all people are essentially in “a state of perfect freedom to order their actions, and dispose of their possessions and persons as they think fit, within the bounds of the law of Nature, without asking leave or depending upon the will of any other man.”
Most liberal thinkers argued that individual freedom should only be limited in very special circumstances.
One of those limitations was not impinging upon the freedom of others to live according to their own beliefs and values, hence the importance of tolerance and preventing harm against others. As they say, your freedom to swing your arm ends where another person’s nose begins.
One common theme of liberalism is the importance of free speech. John Stuart Mill, for example, argued that each individual ought to be able to seek the truth for themselves rather than being obliged to accept the views imposed on them by authorities or tradition.
And in order to seek truth, they need to be able to explore, express and interrogate all beliefs and arguments. And the only way to do that was to allow wide-ranging free speech. “There ought to exist the fullest liberty of professing and discussing, as a matter of ethical conviction, any doctrine, however immoral it may be considered,” he wrote.
This freedom of speech should be limited only in very particular circumstances, such as when that speech is likely to cause direct harm to others. So shouting “fire” in a packed theatre when no such fire exists is an abuse of free speech.
This “harm principle” is still a topic of considerable debate amongst liberals and their opponents, especially around what ought to be considered sufficient harm to justify suppressing speech.
Other liberal thinkers emphasised the fact that not every person was equally able to exercise their freedom through no fault of their own. Poverty, sexism, racial discrimination and other systemic barriers mean that freedom and power are unequally distributed.
This led to what is often called “social justice” liberalism, which seeks to remove those social barriers and enable all people to exercise their freedom to the fullest extent. Some focused on economic redistribution, such as the liberal socialists, while others focused on social barriers, like feminists and anti-discrimination campaigners.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Volt Bank: Creating a lasting cultural impact
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
Freedom of expression, the art of…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing
Is your workplace turning into a cult?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
Ethical concerns in sport: How to solve the crisis
BY Dr Tim Dean
Dr Tim Dean is Philosopher in Residence at The Ethics Centre and author of How We Became Human: And Why We Need to Change.
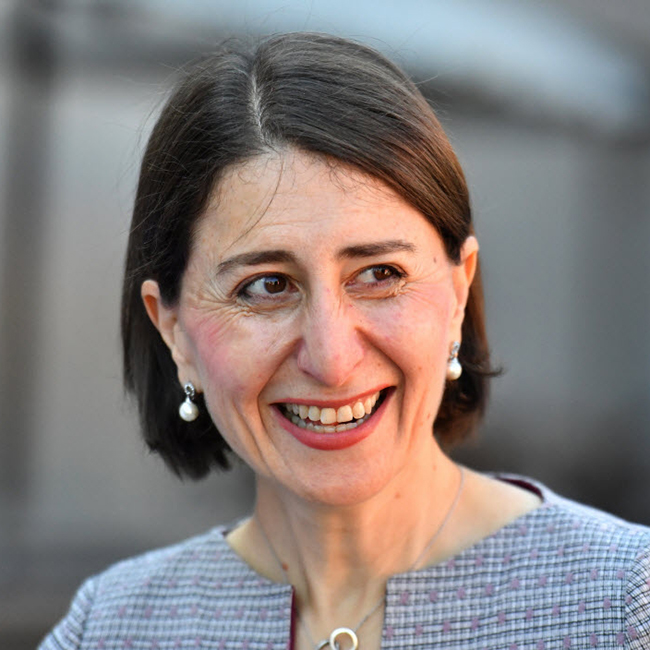
Berejiklian Conflict

Berejiklian Conflict
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Simon Longstaff 14 OCT 2020
The next phase in the political life of NSW Premier, Gladys Berejiklian, depends on answers to three questions.
First, was her former relationship with Daryl Maguire not just ‘close’ but, in fact, an “intimate personal relationship”? Second, did the Premier make or participate in any decisions that could reasonably be expected to confer a private benefit on Mr Maguire? Finally, if the answer is ‘yes’ to each of these questions, then did Ms Berejiklian declare her interest in the Ministerial Register of Interests and seek the permission of Cabinet to continue to act?
Nothing else matters – not the Premier’s choice of friends, not her judgement … only the answer to those three questions.
The reason for this can be found in the NSW Ministerial Code of Conduct (the Ministerial Code) which has the force of Law. As might be expected, the Ministerial Code imposes obligations that are in addition to and are more onerous than, those applying to Members of Parliament.
The Preamble to the Ministerial Code of Conduct says, amongst other things, that, “In particular, Ministers have a responsibility to avoid or otherwise manage appropriately conflicts of interest to ensure the maintenance of both the actuality and appearance of Ministerial integrity.” With that end in mind, the Code not only takes account of the personal interests of individual Ministers – but also those of members of their families. It is here that the precise nature of the Premier’s relationship with Mr Maguire risks becoming a matter of public, rather than personal, interest. This is because the Ministerial Code of Conduct defines a “family member”, in relation to a Minister, as including, “any other person with whom the Minister is in an intimate personal relationship”.
‘Intimate’ is not a word used in the ICAC hearing to describe the Premier’s relationship with Mr Maguire.
Instead, it was agreed that theirs had been a “close personal relationship” – the precise nature of which was never explained. However, the evidence suggested that the words ‘close’ and ‘intimate’ may have been synonymous. If so, then Mr Maguire will have fallen within the definition of ‘family member’ during the period of his relationship with the Premier.
However, this (in itself) is neither here nor there. The nature of Ms Berejiklian’s relationship with Mr Maguire was (and should have remained) an entirely private matter up until the point where the Premier became involved in any Ministerial decision that “could reasonably be expected to confer a private benefit” on Mr Maguire. Only then did the public interest become engaged.
So, did any such decisions come before the Premier (acting alone or in Cabinet) during the period of her relationship with Mr Maguire? And if so, did she declare her interest as she is required to do under the Ministerial Code? The matter would then have been in the hands of her Cabinet colleagues as the final provision of the Code states that, “a ruling in respect of the Premier may be given if approved by the Cabinet”.
The Premier obviously knew something of Mr Maguire’s hopes and plans – even if she thought them to be fanciful. She knew of his financial exposure and the material impact that NSW Government decisions might have on his personal wealth. We also know that, for a time, Mr Maguire was at the centre of the Premier’s private affections. The issue is not that the Premier would have acted against the public interest for the benefit of Mr Maguire. I sincerely doubt that she would ever do so. It is most importantly a question of what was done to ensure the maintenance of both the actuality and appearance of Ministerial integrity.
The Premier had a formal obligation to declare her relationship with Mr. Maguire if, a) it was intimate, b) she was involved in deciding any matter that could reasonably be expected to confer a private benefit on him. It was then up to her Cabinet colleagues to rule on how she should proceed from there. Beyond settling these questions, the public has no legitimate interest in the private life of Gladys Berejiklian – except, perhaps, to extend to her our sympathy if she has been drawn inadvertently into a web of grief spun by a former friend.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Standing up against discrimination
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Taking the bias out of recruitment
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Why Anzac Day’s soft power is so important to social cohesion
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights
Vaccines: compulsory or conditional?
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
Character and conflict: should Tony Abbott be advising the UK on trade? We asked some ethicists
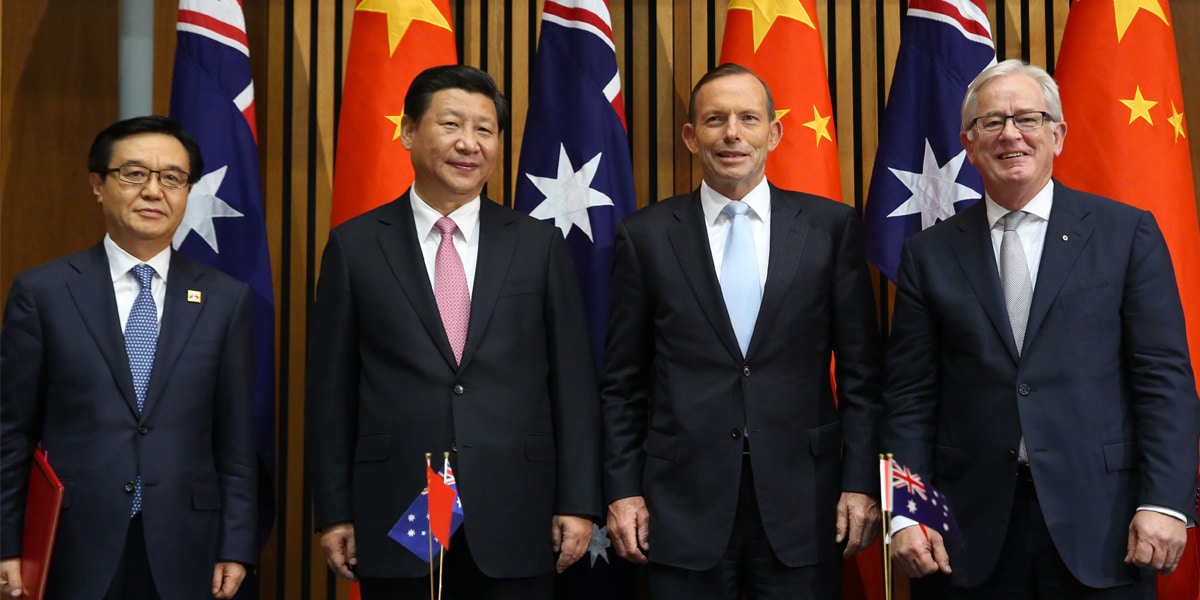

Character and conflict: should Tony Abbott be advising the UK on trade? We asked some ethicists
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human Rights
BY Matthew Beard 17 SEP 2020
Former Aussie PM Tony Abbott’s recent appointment to an unpaid role as a trade adviser to the Johnson government in the UK has sparked controversy in both countries.
UK government MPs have continually been asked what it means to have a man who is, by the judgement of many in both countries, “a misogynist and a homophobe”, as well as a climate change denier and – more recently – sceptical about coronavirus lockdown measures.
In Australia, politicians, journalists and citizens have all questioned the appropriateness of a former Prime Minister accepting a position that leaves him serving a foreign government. Whilst Abbott has obligations under the Foreign Influence Transparency Scheme that are designed to prevent conflicts of interest, there are many who believe Abbott is equipped with too much internal knowledge of Australia’s trade interests, internal party politics and regional issues in the Pacific – accrued as Prime Minister – for him to serve another government.
Given the range of questions that arise around both conflict and character, we made a list of some of the big ethical questions the Abbott situation brings up, and spoke to a few ethicists to help answer them.
1. Abbott is a private citizen now. Shouldn’t he be able to take any job he wants?
“Being Prime Minister isn’t like any other job,” says Hugh Breakey, a Senior Research Fellow at Griffith University’s Institute for Ethics, Governance and Law. “Abbott would have been privy to high level information and forward planning that he is obligated to hold secret.” If a potential employer of Abbott – whether in a paid role or not – would benefit from this situation, Breakey argues that it would give Abbott a conflict of interests.
But it’s not just a question of conflicts of interest. In situations like this, it is reasonable to consider whether this role was given as a “kind of payback for favourable treatment during his time in power,” Breakey says.
However, whilst Abbott’s appointment may generate potential conflicts of interest and are “legitimate lines of ethical inquiry”, Breakey believes they are not problems for Abbott’s appointment.
However, Simon Longstaff, executive director of The Ethics Centre, disagrees. “There just can be no guarantee that Britain’s interests will always coincide with Australia’s. Given this, the fact that one of our former Prime Ministers would ever serve a foreign power almost beggar’s belief,” he said.
2. If Abbott’s trade qualifications make him a good candidate, should we overlook his other beliefs and opinions?
“I believe that a representative of any country, in any honoured capacity like this one, should be a morally upstanding person. Tony Abbott is not that, given his history of misogyny, homophobia, and racism,” says Kate Manne, philosophy professor at Cornell University.
However, Hugh Breakey worries that an approach like this risks jeopardising our commitment to non-discrimination and supporting a diverse set of beliefs and ways of life. Sometimes, he says, ethics might require us to overlook the questionable beliefs of a potential political appointment.
“At least some of the views taken by Abbott on these matters have religious influences, and many similar (and, indeed, far more conservative) views are held by religious devotees across many of the world’s major faiths. Prohibiting from public offices and services all those who hold such views… would allow widespread religious discrimination.”
However, another complication arises when it comes to whose views and personality traits we tend to overlook. Cognitive biases, social norms and systemic beliefs like sexism and racism can mean we’re more likely to overlook controversial beliefs or difficult personalities when they belong to men, people who are straight or white.
Kate Manne suspects that “both women and non-binary people are far less likely to be viewed as truly qualified or competent, unless they’re also perceived as extraordinarily caring, kind, and what psychologists call ‘communal’.” She adds that the tendency to separate the professional and personal/political aspects of someone’s identity is “far less available to women and gender minorities.”
3. Should we label Abbott a misogynist or homophobe based only on his public comments and policies?
“The truth is, few people would know Tony Abbott well enough to say with any confidence what he truly feels or believes, and those who do know him paint a very different picture to the one sketched by his critics,” says Simon Longstaff. “A person can be opposed to same-sex marriage and yet not be a homophobe,” he adds.
However, for Kate Manne, the central question of misogyny or homophobia isn’t whether the person feels a certain way toward women or queer people, it’s what effect they have on those communities.
“Misogyny to me is not a personal failure or an individual belief system: it’s a system that polices and enforces a patriarchal order,” she says. “I define a misogynist in turn as someone who’s an ‘overachiever,’ or particularly active, in this system.”
Manne says, “misogyny on this view is less about what men like Abbott may or may not feel toward women, and more about what women face as a result of their toxic, obnoxious, and contemptuous behaviour.”
For Manne, this means Abbott can be reasonably called misogynist and homophobic on this basis. His status as a former PM and his very public comments have done considerable work to uphold a system that oppresses women and LGBTIQ+ people. She cites examples such as calling abortion the ‘easy way out’, standing next to a ‘ditch the witch’ sign or talking about feeling threatened by gay people as evidence of Abbott’s contributions.
4. How should we balance the need to reject some beliefs because they’re not morally acceptable or legitimate with our commitment to pluralism?
“Democracies gain critically in legitimacy by being able to conduct inclusive deliberations where diverse views can be raised and considered,” says Hugh Breakey.
“Naturally, no-one can or should expect immunity from social consequences for what they say in public discussion, Breakey adds. “The more that institutional sanctions are applied on the basis of positions taken in [controversial] debates the narrower the spectrum of positions that are likely to be defended, and the more that different views will fail to be represented.”
Kate Manne suggests a simple principle to test which voices we should accept as part of our political life: “It’s good to have a variety of voices, but those voices need not to silence or speak over the voices of other people,” she says.
“Abbott’s voice does not meet that simple test. “
Unlike Manne, Breakey doesn’t suggest Abbott’s views sit outside the realm of acceptable political opinions, he agrees with Manne’s principle. “If we want democracy to be more than the tyranny of the majority, or (worse still) rule by elites, then we need more civic tolerance afforded to those who think and speak in disagreeable ways.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Give them a piggy bank: Why every child should learn to navigate money with ethics
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Feel the burn: AustralianSuper CEO applies a blowtorch to encourage progress
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights
Disease in a Time of Uncertainty
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Trump and tyrannicide: Can political violence ever be justified?
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
What's the use in trying?

What’s the use in trying?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Eleanor Gordon Smith The Ethics Centre 24 AUG 2020
In early 2020 I sat in a friend’s house on the coast of New South Wales listening to smoke alarms go off in canon, triggered by the air itself, thick with smoke from the active fronts of the worst bushfire season in living memory.
The roads were lined with scorched animals and the climate crisis seemed as inevitable as it did cataclysmic. It was unthinkable then that this moment of apparently superlative awfulness would, in a matter of months, recede to just one more entry in a year-long list of suffering, death, and massive-scale crisis.
The lucky of us stayed inside afraid for months. The unlucky died, or lost loved ones and could not go to their funerals. There was widespread and systematic police violence against black people and against the people who protested it. USD $3.6 trillion was wiped off the stock market in one week.
The first six months of 2020 presented an unusually literal illustration of an old ethical question: why bother when the conclusion feels foregone?
What many of us felt about the climate in January was a well-known phenomenon: the fatigue of feeling useless when we felt we could not rely on the powerful to make changes or on other people to do their part. This feeling was quickly matched by parallels in resistance to systemic racism, in fighting an economic downturn and even in pandemic compliance.
Early on in the COVID-19 outbreak, data modelling revealed that social distancing would only work if 8 out of 10 of us followed the rules. If only 70% of us stood six feet apart, washed our hands, and stayed inside for weeks on end, it would be as though none of us had. To the misanthropist who felt that 30% of people would surely disregard the rules, a motivational gap loomed: why do what I can to help, when I’m not confident it will.
Even to the most resiliently motivated, parts of 2020 posed this problem. Hundred-thousand strong protests in the United States were not enough to prevent the deaths of more unarmed black people, nor to prevent protestors themselves from being pepper-sprayed at close range.
The indefatigability of the protests seemed met by the indefatigability of the problem. For many people it became impossible to feel calm or ordered anywhere as long as case numbers rose. So it seemed foregone that our homes would not feel calm or ordered either, and the motivation to improve them frayed in proportion to the dishes in the sink.
The philosopher and psychologist William James knew that certain beliefs can be self-validating; that confidence in outcomes, however, we come by it, can make itself well placed. The sailors who think they can pull the heavy rope are more likely to summon the gusto and collective coordination required to make it the case that they can. This first half of 2020 was a vivid illustration of the photonegative; the fact that uncertainty about outcomes can be enough to puncture our drive to pursue them.
So what is there to be done? Few of us believe that this pessimism or uncertainty in fact means that it is not worth protesting, or washing our hands, or doing the dishes. We still rationally endorse that we ought to do these things. But it becomes a wrench, an act of shepherding ourselves, parent-like, and it wears us down. It leads us to misanthropy.
An answer lies in looking more closely at one facet of what 2020 has cost us. We lost the most unthinking parts of our lives; the well-worn routine of the drive home or the setup at the gym, the clockwork Wednesday night choir, the disappearance into a team practicing a physical skill.
These were moments where what we did was not to achieve, or to think, but to be in a process. It was immaterial to us whether we achieved victory or even improvement, since our commitment to doing them was not dependent on whether we did. What we wanted was to be absorbed, to be a creature who acts.
We are, unavoidably, creatures who act. But as philosopher Mark Schroeder has noted, there is an asymmetry between our options in thought and our options in action. We have three options about what to think: we can believe what is on offer, reject it, or withhold judgement. But in action we have only two options; act or do not. There is no way to be in the world that avoids this two-prong choice.
When we realize this, we can shift our focus in a way that avoids futility fatigue. Our moral duty to act – and so too, our motivation – need not be entirely derived from what will happen once we do. It may be that what we owe each other is action itself, and effort itself.
In turn, this can release us from some pressure that comes with knowing that our goals will be difficult to achieve and fragile once we get them. We can simply aim at the action itself. We can find in resistance, in participation, and in care, a goal which is not about the altering of the world but about the observation of the act itself.
In this state, our uncertainty is no longer a threat to our motivation. With this as our focus and our source of energy, we may find that we are, in the end, more effective at altering the world.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
So your boss installed CCTV cameras
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Relationships
Stoicism on Tiktok promises happiness – but the ancient philosophers who came up with it had something very different in mind
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics explainer: Normativity
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Scepticism
BY Eleanor Gordon Smith
Eleanor Gordon-Smith is a resident ethicist at The Ethics Centre and radio producer working at the intersection of ethical theory and the chaos of everyday life. Currently at Princeton University, her work has appeared in The Australian, This American Life, and in a weekly advice column for Guardian Australia. Her debut book “Stop Being Reasonable”, a collection of non-fiction stories about the ways we change our minds, was released in 2019.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Whose home, and who’s home?

Whose home, and who’s home?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Eleanor Gordon Smith The Ethics Centre 17 AUG 2020
Australian citizens who live overseas and want to return to Australia, with some exceptions, now have to pay for their mandatory two-week hotel quarantine.
This new rule applies for those returning to New South Wales or Queensland. It means that a single adult returning home must have AUD $3000 to pay for their stay. Last week New Zealand announced a similar policy: citizens returning home to stay less than 90 days will be charged for their quarantine.
Announcing the policy, NSW Premier Gladys Berijiklian said “Australian residents have been given plenty of time to return home, and we feel it is only fair that they cover some of the costs of their hotel accommodation”.
The locution of having “been given” time to return home sounded curious to many of us who reside overseas. We were unaware that living elsewhere had been a matter of taking.
In the comments sections of news articles about the announcement, the Premier’s sentiment was echoed by other Australians. A recurring theme appeared: overseas Australians who returned home now are being selfish to expect taxpayer help
What could fairness require, in a pandemic? It is not fair that some people will get COVID and others will not. It is not fair that some will die while others survive. These are circumstances where a question about fairness is simply not askable; there is only tragedy, which does not have a possible equitable distribution.
One way to be unfair in a pandemic might be to expose other people to risk. People arriving from overseas certainly do that, and it is crucial to Australia’s efforts to contain the coronavirus that it curbs the risk from international travellers. Like many other countries, Australia was within its rights to close its borders early to international travellers in recognition of this risk.
The very concept of citizenship, however, prohibits closing borders entirely. No matter where citizens ordinarily live, their government has a duty to allow them to cross the border of their home. This is what it means to be a citizen.
There is a problem of incommensurability here. How does the need to mitigate a biothreat weigh against the standing rights of citizens to cross a border? One is a value of rights and obligations; the other is a value of consequences and threat reduction. Neither of these values presents itself in a standardised unit to be compared against the other.
The question is not quite “how do we make a good decision?” but “which kind of good should we be interested in?”. This is a fairly common problem.
Not all of the things we want governments to provide can be coherently measured against each other, so when they come into conflict, it’s not clear how to even begin making the trade. Privacy against safety, health against freedom, service provision against non-interference.
The Government appears to have chosen fairness as the value to adjudicate between the two. The Premier described the policy as “only fair”, since “Aussies overseas have had three or four months to figure out what they want to do”. Prime Minister Scott Morrison echoed this, saying overseas Australians “obviously delayed [their] decision”, and Winston Peters of the New Zealand First Party said that asking taxpayers to pay for fellow citizens’ quarantine was “grossly unfair”.
There are two features of the decision that challenge the terms of fairness here. One is that it seems only to apply to Australians overseas. We would not, for instance, describe it as “only fair” to deny Medicare coverage to an Australian at home who contracted COVID-19 after breaking quarantine rules, even though there is an argument that this is ‘only fair’. Like the quarantine fee, it would mean that those who had ‘plenty of time’ to follow the rules did not impose a burden on the taxpayer when an emergency befell them.
The second is that it is not clear that fairness is the value we should default to in the midst of a global pandemic. In an article for Guardian New Zealand, Elle Hunt suggested that these policies are a failure of empathy. “Discriminating against all but the most wealthy members of the diaspora is a rare failure of not just compassion but imagination – to reach a more equal solution, and to imagine the painful personal circumstances in which it might be warranted.”
Empathy asks different things of a government than fairness. It asks for mercy and the maximum provision of services to those who are suffering. It asks for an imaginative capaciousness about what life is like for citizens whose jobs, families, friends and visas would have been in peril if they had returned earlier. It asks for magnanimity, forgiveness, and generosity.
Empathy may not be a viable long term guiding principle for a political party. But in a pandemic, we may find that the alternative language of fairness and moralising either loses its footing entirely or forces us to absurd conclusions.
“Only fair” was how the Premier described the policy, but we have more values than only fairness. A global emergency may be the time to use some.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
The ‘good ones’ aren’t always kind
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
What we owe to our pets
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
We’re being too hard on hypocrites and it’s causing us to lose out
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Ask an ethicist: Should I tell my student’s parents what they’ve been confiding in me?
BY Eleanor Gordon Smith
Eleanor Gordon-Smith is a resident ethicist at The Ethics Centre and radio producer working at the intersection of ethical theory and the chaos of everyday life. Currently at Princeton University, her work has appeared in The Australian, This American Life, and in a weekly advice column for Guardian Australia. Her debut book “Stop Being Reasonable”, a collection of non-fiction stories about the ways we change our minds, was released in 2019.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
To deal with this crisis, we need to talk about ethics, not economics

To deal with this crisis, we need to talk about ethics, not economics
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Matthew Beard The Ethics Centre 6 AUG 2020
As Melbourne goes into the most intense lockdown measures we’ve seen during the Covid-19 pandemic, activity in the state grinds to a halt.
In media outlets around the country, contrarian commentators are running pell-mell to explain why the lockdowns are the wrong move, and why we should be hastening to open the economy, even if it means paying a price in lives.
Others have been sprinting at a similar speed to disprove them – perhaps moving too fast, and in so doing so, having the argument on their terms.
Consider two of the loudest critics of the purpose of the lockdown: UNSW Economics professor Gigi Forster and Adam Creighton, economics editor at the Australian newspaper. Forster has argued that the costs – measured in terms of overall wellbeing – are more greatly increased by our response to Covid-19 than by the virus itself.
Creighton’s arguments are related, though he has emphasised more the difference between quantity and quality of life. On the lockdowns in Melbourne, he recently tweeted “What’s the point in being alive if you can’t live?
Shameful what’s occurring in Victoria.
Effective dictatorship declared.
Devastating, destructive power of the state on full display.
Respect for the individual clearly irrelevant.
What’s the point in being alive if you can’t live?— Adam Creighton (@Adam_Creighton) August 2, 2020
Perhaps the loudest response to each of them has been to say that a successful economic exit from the COVID-19 pandemic relies on successfully controlling the virus through measures like lockdowns, social distancing and so on. Even on economic terms, it won’t work to allow the virus to run through the community. We can’t come back economically unless we succeed medically. It’s not a zero-sum game.
I’m not the right person to decide whether or not that argument is correct. But that’s not my primary concern either. Instead, my concern is that in arguing the facts on this particular issue – that economically we are better off by controlling the spread of the virus – we have granted them their first principle. Namely, that the correct course of action is whichever one makes the most sense economically and does the most work to maximise quality of life for the largest number of people.
In granting this principle, we’re rushing over a lot of controversial territory. For instance, we might want to take issue with Creighton’s argument on other grounds – that whilst it is important to be able to live fully, in order to so, we need to be alive. The idea that ‘life is for living’ only makes sense if we also say that some people shouldn’t be permitted to stay alive. And many people won’t want to say that.
The point is, the ‘maximise wellbeing’ argument implies a harsh form of utilitarianism. It suggests we accept that there are some people who will have to pay the price for our flourishing.
Maximising benefit still leaves some people to suffer. Usually, it means leaving the same people who have suffered before to suffer again. After all, the most vulnerable already have a low quality of life, so if they end up dying, statistically speaking, it doesn’t show up as much of a loss.
When we encounter arguments like those of Creighton and Forster, we have a choice to make: what matters most to us? Is our primary concern making as many people as possible as well off as we can? Or do we to stand in solidarity with those who are worst off, and refuse to flourish at their expense?
There are schools of thought and philosophers and arguments that will give you cover whichever way you make that choice. But it is a choice to be made. We can’t just interrogate the conclusions of these arguments, we need to question their starting (and often hidden) premises.
During this pandemic we have started to see some of the hidden premises bubble to the surface. Overwhelmingly, the result has been a discomfort at the idea that we get to decide who we are willing to sacrifice for our collective benefit.
I hope that’s an idea that we remember. Because that’s not a problem that started with COVID-19. Instead, it’s a trade-off that is hard–wired into our economic system. In many ways, it’s perfectly logical to suggest we let more people die from Covid-19 if it means we all benefit. After all, it’s what we’ve always done.
We need to recognise that it’s not just people who champion beliefs and values. It’s the very systems that inform and shape our world.
If we don’t want our collective benefit to be paid for by those who most need our care, we need to do more than debate the people floating this idea. We must interrogate the system that gave rise to those views at all. We need to recognise the ways in which it is our default setting and find the courage to imagine another way of doing things.
It’s often said there are no atheists in the foxholes. It feels like there are also few nihilists in a crisis. Circumstances like these sharpen our moral intuitions and surface underlying tensions in society.
Our responsibility, as well as getting through this and getting each other through this, is to ensure that in times of comfort we retain that ethical sharpness and continue to refuse to flourish when that requires others to fail.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
If politicians can’t call out corruption, the virus has infected the entire body politic
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Are we idolising youth? Recommended reads
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Friedrich Nietzsche
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
You’re the Voice: It’s our responsibility to vote wisely
BY Matthew Beard
Matt is a moral philosopher with a background in applied and military ethics. In 2016, Matt won the Australasian Association of Philosophy prize for media engagement. Formerly a fellow at The Ethics Centre, Matt is currently host on ABC’s Short & Curly podcast and the Vincent Fairfax Fellowship Program Director.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
The sticky ethics of protests in a pandemic
The sticky ethics of protests in a pandemic
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 31 JUL 2020
[Video Transcript]
This week has seen the unfolding of a classic ethical dilemma.
A clash between the ethics of peaceful citizens wishing to exercise their democratic right to gather in support of the Black Lives Matter movement and the ethics of medical experts, the NSW Government, the Supreme Court and the NSW Police Force – all of whom combined to prevent these same citizens from gathering together in numbers thought to represent a risk to human health and safety.
The strangest thing of all was that people on both sides of this dilemma supported the objectives of the protesters – with the Deputy Chief Medical Officer, Dr Nick Coatsworth, saying that on any other day, and in any other circumstance, he would be in the ranks of the protesters – championing their cause. Even the NSW Police Commissioner, Mick Fuller, sounded genuinely sympathetic.
So, how did people sharing so much in terms of good will find themselves so divided … and what are we to make of the merits of each side of the argument?
To say that these are extraordinary times is the understatement of the year. The second wave of infections, in Victoria, has ramped up the pressure as we witness the infection spread like wildfire. What started off as a lazy spark is now a growing conflagration – burning up the lives of the vulnerable as it spreads from hotel, to tower block, to abattoir, to aged care homes. The medical fraternity is seeing frontline staff having to withdraw to quarantine as the beds begin to fill. Meanwhile, lockdown and mounting concern is further depressing economic activity.
Is there any wonder that the authorities in NSW are desperate to prevent the same sparks from igniting here? Already, we know that the tinder is dry … with minor outbreaks flaring up across the city. Infection rates in Sydney are on the knife-edge. So when the best available medical advice was that it is too dangerous for a mass gathering of those who support the proposition that Black Lives Matter, a Supreme Court Judge ordered that the protests not proceed – not to suppress the free expression of political opinion but instead to protect the vulnerable many from the risk posed by the sincere and committed few.
Against this, the protest organisers argued that they would guarantee a safe event with people masked and physically distant. They charged the authorities with hypocrisy, pointing out that if people are allowed to travel to work or gather for church services or engage in any one of a number of other types of permitted activity, why single out and ban a protest to condemn the deaths in custody of First Nations people? It’s a good question.
Opponents to the gathering could argue that a protest is, by its very nature, an unruly venture. No one can ever know, in advance, who will turn up, in what numbers, in what mood, with what motives? Even the best organised political gathering can get out of control. It is at least arguable that there is a valid distinction to be made between protest marches and other gatherings.
Even so, it’s hard not to think that it might have been better to set clear guidelines for the gathering, and only then intervene if they were not followed. As noted above, the protest organisers were publicly committing to an event in which every person wore a mask and maintained proper distancing in a large, open air environment.
One wonders what might have been possible had the police and organisers been able to work together to uphold such standards. In those circumstances I reckon that the organisers might have been just as willing, as the police, to close down the event if their supporters failed to observe the rules.
However, we shall now never know.
Some might suggest an ulterior motive in curbing a protest about black lives and Indigenous deaths in custody. If you belong to one of the marginalised groups who have lost loved ones to the criminal justice system due to racism and prejudice, it would be easy to believe that the cancellation of a protest march is just the latest example of unjust oppression.
However, in this case, I do not think that would be a fair or accurate judgment. As I noted above, there was a palpable air of good will in support of the protesters’ objectives, if not their chosen means on this occasion.
Instead, fear of what might have happened seems to have won the day. In part, this is because the public is merciless and unforgiving whenever public officials make the slightest mistake. Again, Victoria is a case in point, with the Andrews government being hauled over the coals for its evidently ineffective management of the pandemic. I very much doubt that Daniel Andrews, or his colleagues, would be cut any slack, by the Victorian public, if they invoked arguments about democracy and free speech to defend their decision making.
NSW Premier, Gladys Berejiklian, would have this example in mind, concluding that few politicians are ever punished for going overboard on public health and safety. More’s the pity.
In my opinion, politicians should be held to equal account for going further than is reasonable or proportionate -especially because of the implications on civil liberties, not least for especially vulnerable and disenfranchised groups. Governments that curb the liberty of citizens should only do so for reasons of necessity, and then only in a manner that is reasonable, proportionate and equitable. Yet, rarely do we see such standards being invoked by a fearful public.
There is a fine line between genuinely protecting the public from harm and constraining the democratic rights of citizens; there is a fine line between exercising those rights and avoiding preventable harm to others.
Ideally, one limits those rights to the bare minimum necessary to secure the public good. It is an open question as to whether or not that occurred in this case.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Society + Culture
Ethics Explainer: Aesthetics
LISTEN
Society + Culture
Festival of Dangerous Ideas (FODI)
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
What we owe to our pets
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
There’s no good reason to keep women off the front lines
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Stop giving air to bullies for clicks

Stop giving air to bullies for clicks
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff The Ethics Centre 31 JUL 2020
By now, most people will have heard of the antics of the person who berated staff at Bunnings – simply because the staff insisted that she wear a mask before entering the store.
As is common these days, the altercation was filmed on someone’s phone and uploaded to social media channels. However, the story also captured the attention of mainstream media. What would normally have been an incident of minor importance soon became a topic of the national conversation – bringing fame (or infamy) to the antagonist.
I do not want to add to this person’s unwarranted celebrity. In part, this is because I do not think people should be rewarded for being rude and aggressive. In part, it is because I do not want to fuel further interest in ideas that are not just wrong – but dangerously so.
Instead, I want to focus on two issues of relevance to the media. First, should oxygen be given to people and ideas that do not deserve the public’s attention? Second, how can we avoid causing unintended harm done to people who have legitimate reasons for not wearing face masks – but who are made to feel like a pariah for not doing so?
The first of these issues is one of general concern. Naturally enough, the media is keen to cover stories that engage the interest of their audience. This is perfectly understandable in a context where maintaining audience numbers is critical to survival. People want to hear about the extraordinary. However, there are times when giving people what they want is not in their interest – a principle that holds for individuals as it does for wider society. An alcoholic might want another drink – but it is not in their interest to give them one!
The world abounds with crackpots, conspiracy theorists – and the like. At one level, it is easy to dismiss them as a part of a radical fringe whose ludicrous beliefs are merely entertaining. However, we should never underestimate the ability of such groups to wheedle their way into the public consciousness – even to the point where what seems to be extreme on one day eventually becomes commonplace … just part of the background beliefs of our time. We have seen this in the case of anti-vaxxers, or the people who believe that infection rates for COVID-19 are linked to 5G telephone towers, or that one’s gender or race determines character … and so on.
As noted above, some of these ideas can be explosive in their effects … with the potential for damage easily predicted. Yet, if the proponents are sufficiently weird, wonderful or compelling, then there is a chance that their views might be amplified by a media seduced by the novelty of what is being presented. This is not to suggest that the media approves of the ideas it promotes. If anything, most outlets probably assume that wacky ideas are pure entertainment – that no one will actually be seduced by ridiculous ideas. Unfortunately, history is full of examples of improbable beliefs becoming embedded in ‘mainstream’ ideologies.
This is not to suggest that the media should never cover stories like the incident at Bunnings. However, I think a decision to tell such a story comes with an additional obligation explicitly to discount the validity of claims that are false and misleading. That is, there are times when just reporting the facts will not be enough. Instead, editorial judgement needs to be brought to bear.
The application of judgement is also required in minimising the unintended, adverse effects of moderating opinion about matters like the wearing of face masks during a rampant pandemic. The person at Bunnings objected to wearing a mask as if to do so was some kind of violation of basic human rights. Those arguments were singularly poor – and potentially dangerous – as they uncritically undercut most efforts to preserve the health and safety of the community. However, there could have been another person – perhaps suffering from a medical condition – for whom not wearing a mask is a matter of necessity (not choice). The arguments of that person deserve to be taken seriously.
While it is important to repudiate the crackpots, we should do so with a care not to inflame public prejudice of a kind that discounts every objection as invalid. Some people have perfectly good reasons for not conforming to accepted norms that are justifiable in general.
The bully at the Bunnings door did little to advance the public debate about the rights and responsibilities of citizens and the community. But perhaps she has done some good – in prompting further reflection about what, when and how the media chooses to amplify through its channels.
This article was first written for, and published by Crikey. It has been republished here with permission.
You can contact The Ethics Centre about any of the issues discussed in this article. We offer free counselling for individuals via Ethi-call; professional fee-for-service consulting, leadership and development services; and as a non-profit charity we rely heavily on donations to continue our work, which can be made via our website. Thank you.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Blame
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
The ethics of pets: Ownership, abolitionism and the free-roaming model
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights
Disease in a Time of Uncertainty
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
What happens when the progressive idea of cultural ‘safety’ turns on itself?
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Punching up: Who does it serve?

Punching up: Who does it serve?
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff 24 JUL 2020
I recently watched Hannah Gadsby’s comedic tour-de-force, Douglas. It is sharp and provocative – but wonderfully insightful. In the course of her performance, Hannah explains that she applies to her humour the principle of ‘punching up’.
It is an approach employed by comics when deciding who is a legitimate target for ridicule and satire. The idea is pretty simple, it’s fine to take aim at someone who is more powerful than you – but never those who are relatively weaker. The operating assumption is that the powerful are unlikely to be harmed by a bit of fun at their expense, while the weaker have suffered enough without having to cope with a comic’s insults.
The idea of ‘punching up’ seems to have taken on a life beyond the world of comedy. More generally, those who stand higher up the ladder of power and privilege are now expected to accept, without retaliation or reproach, whatever comes their way from those located on lower rungs of the ladder. Sitting at the top are cis-gendered, white men, like me. If we complain, then this is just evidence of our ‘thin skin’ and an inability to take a serving of what we have been dishing out for millennia.
It is easy to identify who is currently at the top of the ladder. However, beyond that point, working out the relativities of who is ‘up’ or ‘down’ becomes increasingly difficult. After all, there is no natural hierarchy of power, privilege, disadvantage or subjugation.
Instead, positions change as the wheel of history turns – with some groups ascending at one point only to see their position reversed at another. For example, consider the case of the Aztecs. Prior to the arrival of the Spaniards, they commanded an empire built on the conquest, enslavement and ritual sacrifice of those who fell under their sway. Yet, today, their descendants are a dispossessed people with an extraordinarily resilient culture that has survived centuries of attempted suppression by their colonisers.
So, who gets to ‘punch up’ (or be ‘punched’) is relative to time and culture. The role of being a priestess can be at the apex of power and influence in one setting but marginalised in another. A banker can be reviled as a ‘usurer’ in the past only to be celebrated by future generations.
However, that’s not where the relativities end. Conduct that is condoned in one case will be condemned in another – even though the things done are identical. For example, what is praised as being ‘forthright’ in a man has often been criticised as ‘aggression’ in a woman. Asymmetry of judgement also applies in the context of ‘punching up’. Behaviour that is justifiably condemned in a powerful person is often excused or ignored if practiced by a relatively powerless individual.
So, what are we to make of this? First, let’s acknowledge that there are some individuals and groups who have been systematically marginalised, over such a long period of time, as to deserve the opportunity to ‘even things up’ in any contest. Only those blinded by prejudice would deny this to be so.
However, this is not to say that relative historical disadvantage should excuse anything done – just as long as it is directed at the relatively powerful. A person fighting a stronger adversary may pick up a stick to ‘even the odds’ – but it would be wrong for them to attack an unarmed person with a firearm. To do so would involve a disproportionate use of force.
Likewise, I think it wrong to belittle or vilify a person (any person) in a deliberate attempt to wound them with words. That is not comedy – it is abuse. Comics make a person uncomfortable as a way of drawing attention to an issue of underlying importance – but their aim is not (and should not be) to harm. To do otherwise is to adopt the stance of the bully … which is wrong whatever one’s relative position in life.
I realise that it is easy to recommend restraint when one belongs to a powerful or privileged group – as I do. However, I am not a supporter of relativism in ethics (or elsewhere). To wound another – willfully or recklessly – is wrong.
The fact that it occurs as a result of anger or frustration might explain such behaviour – but it does not justify it. I know that this will be a view unpopular with those who have a taste for revenge – who believe in the proverbial ‘eye for an eye, tooth for a tooth’. However, I prefer the position of the Reverend Dr Martin Luther King Jr. who wrote that:
“Violence as a way of achieving racial justice is both impractical and immoral. It is impractical because it is a descending spiral ending in destruction for all. The old law of an eye for an eye leaves everybody blind. It is immoral because it seeks to humiliate the opponent rather than win his understanding; it seeks to annihilate rather than to convert.”
Yes, great wrongs need to be made right – but justice cannot be produced by injustice.
So, does this load the greater obligation onto the shoulders of those who have traditionally been on the wrong end of the stick? On the contrary, those of us who enjoy the greatest power and privilege should accept the greatest obligation to act ethically … not least because we have the capacity to do so.
We should begin by recognising and redressing the disparities of our day; we should acknowledge that we did not earn our privileged position – but were simply lucky enough to be born blessed with opportunity. It is not out of guilt, but with a sense of justice, that we should seek to redress historical and contemporary sources of inequity.
Perhaps then the urge to punch will eventually be assuaged, and something better – that could never have grown in the soil of anger and resentment – can emerge to see the light of day.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics explainer: Cultural Pluralism
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
We shouldn’t assume bad intent from those we disagree with
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
Should corporate Australia have a voice?
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Settler rage and our inherited national guilt
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
Education is more than an employment outcome

Education is more than an employment outcome
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff 26 JUN 2020
The Federal Government recently announced university funding restructures that made a clear statement – to prioritise ‘useful’ degrees.
This decision is significant for a number of reasons. First, it has further shifted the cost of a university education away from government and onto students. It has done so on the assumption that education benefits the individual more than the society to which they contribute.
Second, the government has nominated some courses of study as being more likely to lead to employment than will others. Somewhat paradoxically, the government is reducing the cost of study for those most likely to get jobs, while increasing it for those it thinks will struggle to find employment due to their ill-considered choice of subjects. ‘Cost’ is deliberately unrelated to ‘ability to pay’ – and requires those with apparently poor employment prospects to subsidise the education of their more fortunate peers.
It’s clear that the government hopes market forces will encourage more people to take on ‘useful’ courses of study. However, in a further ironic twist, the new policy relies on the fact that many people will not. Otherwise, the economics won’t work. Fortunately (for the policy) there will be limited places available for the study of ‘useful’ courses in nursing, teaching and agriculture. This means that some of the students who rationally seek a ‘good deal’ will be forced to accept their ‘second choice’ – even to the point of having to suffer through a relatively expensive ‘dead-end’ degree in the Humanities.
However, this piece is not meant to be an examination of the paradoxes of government policy. Rather, I want to look at a deeper issue – the underlying assumption that resources are best invested in ‘useful’ things.
Demonstrating ‘usefulness’
This thinking stalks my waking hours – as it probably does anyone running an organisation that is not immediately and demonstratively ‘useful’. For those of us working in the not for profit world, the word ‘useful’ is never used. In its place is the notion of ‘impact’. Conventional wisdom dictates that one must demonstrate impact – or die!
The thinking that drives a demand to measure, report on and invest in ‘impact’ is the same thinking that leads a government to focus its investment in higher education on supporting courses that lead to the ‘jobs of the future’. With limited taxpayer and philanthropic dollars to spend, why not invest in those things that can prove themselves most effective? It’s easy to argue that this is the rational thing to do… but is it?
What is the ‘impact’ of Bell Shakespeare staging King Lear? What is the ‘impact’ of the National Gallery of Australia hanging Blue Poles? What is the impact of the Festival of Dangerous Ideas? I think it impossible to trace the impact of any of these works. We can measure outputs – the number of attendances, mentions in the media, donations received, and so on. But these numbers don’t identify the ideas or experiences seeded in the theatre, a gallery or at a festival that germinate – perhaps years later – and change the world.
Ideas can change the world
We underestimate the value of things like philosophy when assessed over the long term. Nearly every branch of knowledge that we draw on today including science, mathematics, economics, medicine and psychology were thought into existence by philosophers.
People motivated by nothing more than a love of wisdom (philo-sophia) have changed the world. The original concept of the atom came from Democritus. Pythagoras brought us the role of constants in mathematics. The classification of species began from Aristotle. Thomas Hobbes ideated the modern nation state. Adam Smith brought us the free market and Peter Singer animal rights. With the benefit of hindsight, their impact is obvious. But few of the world’s great philosophers could have demonstrated ‘impact’ while working on their seminal ideas.
I understand the strong desire to measure impact, to invest in making a tangible difference. I understand why governments want to fund ‘practical outcomes’ such as helping people to secure future employment. However, there is something deeply irrational about turning one’s back on forms of education and endeavour that emphatically shape the world – but at a pace and by means we cannot easily measure.
If ‘impact’ is the only measure of something’s worth, then we might as well close down the arts, the humanities, and a whole lot more. However, this would be to deny a fundamental truth that has informed all great societies: some things matter not because of their impact – but in and of themselves.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
He said, she said: Investigating the Christian Porter Case
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Australia Day: Change the date? Change the nation
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Confucius
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights