After Christchurch

After Christchurch
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY Simon Longstaff 19 MAR 2019
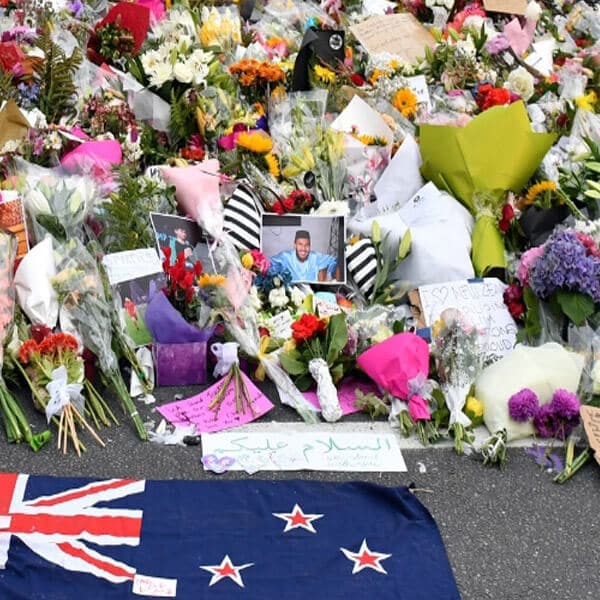
What is to be said about the murder of innocents?
That the ends never justify the means? That no religion or ideology transmutes evil into good? That the victims are never to blame? That despicable, cowardly violence is as much the product of reason as it is of madness?
What is to be said?
Sometimes… mute, sorrowful silence must suffice. Sometimes… words fail and philosophy has nothing to add to our intuitive, gut-wrenching response to unspeakable horror.
Thus, we bow our heads in silence… to honour the dead, to console the living, to be as one for the sake of others.
In that silence… what is to be said?
Nothing.
Yet, I feel compelled to speak. To offer some glimmer of insight that might hold off the dark — the dark shades of vengeance, the dark tides of despair, the dark pools of resignation.
So, I offer this. Even in the midst of the greatest evil there are people who deny its power. They are rare individuals who perform ‘redemptive’ acts that affirm what we could be. Some call them saints or heroes. They are both and neither. They are ordinary people who act with pure altruism – solely for the sake of others, with nothing to gain.
One such person is with me every day. The Polish doctor and children’s author, Janusz Korczak, cared for orphaned Jewish children confined to the Warsaw Ghetto. At last, the time came when the children were to be transported to their place of extermination. Korczak led his children to the railway station — but was stopped along the way by German officers. Despite being a Jew, Korczak was so revered as to be offered safe passage.
To choose life, all he need do was abandon the children. At the height of the Nazi ascendancy, Korczak had no reason to think that he would be remembered for a heroic but futile death. He had nothing to gain. Yet, he remained with the children and with them went to his death. He did so for their sake — and none other. In that decision, he redeemed all humanity — because what he showed is the other face of our being, the face that repudiates the murderer, the terrorist, the racist…the likes of Brenton Tarrant.
I know that many people do not believe in altruism. They will offer all manner of reasons to explain it away, finding knotholes of self-interest that deny the nobility of Janusz Korczak’s final act. They are wrong. I have seen enough of the world to know that pure acts of altruism are rare — but real. And it only takes one such act to speak to us of our better selves.
We will never know precisely what happened in those mosques targeted in Christchurch. However, I believe that, in the midst of the terror, there were people who performed acts of bravery, born out of altruism, of a kind that should inspire and ultimately comfort us all.
Most of these stories will be untold — lost to the silence. Of a few, we may hear faint whispers. But believe me, the acts behind those stories are every bit as real as the savagery they confronted and confounded. And even when whispered, they are more powerful.
Evil born of hate can never prevail. It offers nothing and consumes all — eventually eating its own. That is why good born of love must win the ultimate victory. Where hate takes, love gives — ensuring that, in the end, even a morsel of good will tip the balance.
You might say to me that this is not philosophy. Where is the crisp edge of logic? Where is the disinterested and dispassionate voice of reason? Today, that voice is silent. Yet, I hope you can hear the truth all the same.
Dr Simon Longstaff AO is Executive Director of The Ethics Centre.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Why businesses need to have difficult conversations
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
In the court of public opinion, consistency matters most
Big thinker
Relationships, Society + Culture
Big Thinker: Simone de Beauvoir
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Free speech is not enough to have a good conversation
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
Workplace romances, dead or just hidden from view?

Workplace romances, dead or just hidden from view?
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipRelationships
BY Fiona Smith 17 MAR 2019
Falling in love at work seems kind of quaint in the age of Tinder. But it still happens, despite the convenience of “swiping right” on strangers via dating sites.
The practice of getting to know someone before asking them out to dinner may intrigue some of your younger colleagues, but it still had its attractions for the 11 per cent of heterosexual couples who met through work in 2017.
So dating apps have not yet killed the office romance, but they have put the squeeze on it. At the “birth” of the internet, in 1995, 19 per cent of heterosexual couples said they met as, or through, colleagues, according to research by Stanford University in the US.
If fewer people are “coupling up” at work, the reasons should be pretty obvious. Negotiating a romance at work has always been somewhat tricky but has become even more so as employers tighten their human resources policies around how such relationships should be conducted.
Just like the “bonking ban” in Federal Parliament, which now rules out affairs between Ministers and their staff, many companies now have policies about when relationships must be declared and that prevent couples from being in charge of each other at work.
Employers are also mindful of the lessons learned from the #Metoo anti-sexual harassment movement, which has raised awareness that people can be deeply hurt by repeated and unwanted sexualised attention – especially from their bosses.
Trouble starts when ‘no’ is ignored
There will always be people who resist social change. However, the CEO of Relationships Australia, Elisabeth Shaw, quickly dismisses protestations by those who say morality-policing has gone too far in interfering in employees’ personal lives.
“The reality is: the sort of examples that make it into the public domain are those who haven’t taken no for an answer. They have kept up a level of sexual banter or flirtation that isn’t wanted,” she says.
Shaw says relationships become troublesome when the couple have an unequal power relationship. In practice, this usually means a male boss and a female who reports to him. Someone is often required to give up their job.
“The repercussions are that it is the woman who suffers. It is usually the woman who has the less valuable job and can be the one who people think should leave,” she says.
“The person in the subordinate job is the most vulnerable.”
‘None of us are islands’
If the relationship is an affair, that adds another layer of difficulty. The necessary secrecy leads to suspicion about how and why people are favoured by the boss.People in the midst of an affair tend to get lost in their own experience and forget that “none of us are islands”, she says. “What they do does affect the group.”
This is especially the case when the spouses of the couple are known to the group and onlookers start to feel morally compromised, as if they are colluding in the affair.
How colleagues view office romances can also depend on whether the people involved are well-liked and respected. Another factor is whether onlookers believe that they will be adversely affected – they may be shut out of work-related conversations between the pair and, if one of the couple is a boss, there may be favouritism towards their lover.
“There could be pillow talk, they could feel their own career is disadvantaged, that will also turn the heat up,” says Shaw.
When to tell
Deciding when to disclose the relationship is difficult – even when things seem straightforward. Should it be after the second date, when you agree to see each other exclusively, or after you tell your families?
“Everyone would pick a different moment where they would call it a relationship,” says Shaw. “When do they have a right to privacy as adults and when do they have a duty to others?“Some would argue if they keep it discreet and it doesn’t impact anybody, should they ever have to tell anybody?”
The CEO of human resources consultancy, mwah (Making Working Absolutely Human), Rhonda Brighton-Hall, has spent her career in large organisations and says that it is unfortunate that the relationships that most need to be reported are also the least likely to be reported.
These are the boss-subordinate romances.“I think the ones that don’t get reported are where the power difference is massive. There is something about that that creates gossip, puts people on tenterhooks, upsets the people around them,” she says.
“If you a very senior leader, your integrity and ethics of relationships are visible to people. You attract more judgement and that is probably not unfair if you are holding yourself up as a role model of good behaviour and honesty and integrity.”
“However, if they are not in a reporting line, they don’t need to notify anyone.”
In the absence of a handy app, Shaw offers a few guidelines to ensure lovers end up on the right side of the HR department (and out of the headlines).
Yes, you can find romance at work.
5 Easy steps:
- No means no: You can ask once, but take no for an answer
- Right place, right time: When indicating your non-work-related interest, make sure you are not at work. Ask them out for a coffee or a walk.
- Who’s on top?: Be aware of power imbalances between the two of you. The person with less power at work tends to be most adversely affected if things go sour.
- Create distance: Once the relationship looks like it may be ongoing, ideally one of the two would transfer to another department or employer. It is better for the relationship and better for the workplace.
- Tell someone: Once you consider yourself “dating” a colleague, you need to tell someone at work. That could be your manager or HR. It could even be a “critical friend” at work, who is likely to tell you if your relationship is affecting others.
MOST POPULAR
ArticleBeing Human
Putting the ‘identity’ into identity politics
ArticleHEALTH + WELLBEING
Parent planning – we should be allowed to choose our children’s sex
Article
Ethics Explainer: Respect
ArticleBeing Human
Praying for Paris doesn’t make you racist
BY Fiona Smith
Fiona Smith is a freelance journalist who writes about people, workplaces and social equity. Follow her on Twitter @fionaatwork
Blockchain: Some ethical considerations

Blockchain: Some ethical considerations
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipScience + Technology
BY Simon Longstaff 16 MAR 2019
The development and application of blockchain technologies gives rise to two major ethical issues to do with:
- Meeting expectations – in terms of security, privacy, efficiency and the integrity of the system, and
- The need to avoid the inadvertent facilitation of unconscionable conduct: crime and oppressive conduct that would otherwise be offset by a mediating institution
Neither issue is unique to blockchain. Neither is likely to be fatal to its application. However, both involve considerable risks if not anticipated and proactively addressed.
At the core of blockchain technology lies the operation of a distributed ledger in which multiple nodes independently record and verify changes on the block. Those changes can signify anything – a change in ownership, an advance in understanding or consensus, an exchange of information. That is, the coding of the blockchain is independent and ‘symbolic’ of a change in a separate and distinct real-world artefact (a physical object, a social fact – such as an agreement, a state of affairs, etc.).
The potential power of blockchain technology lies in a form of distribution associated with a technically valid equivalent of ‘intersubjective agreement’. Just as in language the meaning of a word remains stable because the agreement of multiple users of that word, so blockchain ‘democratises’ agreement that a certain state of affairs exists. Prior to the evolution of blockchain, the process of verification was undertaken by one (or a few) sources of authority – exchanges and the like. They were the equivalent of the old mainframe computers that formerly dominated the computing landscape until challenged by PC enabled by the internet and world wide web.
Blockchain promises greater efficiency (perhaps), security, privacy and integrity by removing the risk (and friction) that arises out of dependence on just one or a few nodes of authority. Indeed, at least some of the appeal of blockchain is its essentially ‘anti-authoritarian’ character.
However, the first ethical risk to be managed by blockchain advocates is that they not over-hype the technology’s potential and then over-promise in terms of what it can deliver. The risk of doing either can be seen at work in an analogous field – that of medical research. Scientists and technologists often feel compelled to announce ‘breakthroughs’ that, on closer inspection, barely merit that description. Money, ego, peer group pressure – these and other factors contribute to the tendency for the ‘new’ to claim more than can be delivered.
“However, the first ethical risk to be managed by blockchain advocates is that they not over-hype the technology’s potential and then over-promise in terms of what it can deliver.”
It’s not just that this can lead to disappointment – very real harm can befall the gullible. One can foresee an indeterminate period of time during which the potential of blockchain is out of step with what is technically possible. It all depends on the scope of blockchain’s ambitions – and the ability of the distributed architecture to maintain the communications and processing power needed to manage and process an explosion in blockchain related information.
Yet, this is the lesser of blockchain’s two major ethical challenges. The greater problem arises in conditions of asymmetry of power (bargaining power, information, kinetic force, etc.) – where blockchain might enable ‘transactions’ that are the product of force, fear and fraud. All three ‘evils’ destroy the efficiency of free markets – and from an ethical point of view, that is the least of the problems.
“The greater problem arises in conditions of asymmetry of power (bargaining power, information, kinetic force, etc.) – where blockchain might enable ‘transactions’ that are the product of force, fear and fraud.”
One advantage of mediating institutions is that they can provide a measure of supervision intended to identify and constrain the misuse of markets. They can limit exploitation or the use of systems for criminal or anti-social activity. The ‘dark web’ shows what can happen when there is no mediation. Libertarians applaud the degree of freedom it accords. However, others are justifiably concerned by the facilitation of conduct that violates the fundamental norms on which any functional society must be based. It is instructive that crypto-currencies (based on blockchain) are the media of exchange in the rankest regions of the dark web.
So, how do the designers and developers of blockchain avoid becoming complicit in evil? Can they do better than existing mediating institutions? May they ‘wash their hands’ even when their tools are used in the worst of human deeds?
This article was first published here. Dr Simon Longstaff presented at The ADC Global Blockchain Summit in Adelaide on Monday 18 March on the issue of trust and the preservation of ethics in the transition to a digital world.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing, Science + Technology
Can robots solve our aged care crisis?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Survivor bias: Is hardship the only way to show dedication?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships, Society + Culture
Renewing the culture of cricket
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing
Why ethical leadership needs to be practiced before a crisis
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
Not too late: regaining control of your data

Not too late: regaining control of your data
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human RightsScience + Technology
BY The Ethics Centre 15 MAR 2019
IT entrepreneur Joanne Cooper wants consumers to be able to decide who holds – and uses – their data. This is why Alexa and Siri are not welcome in her home.
Joanne won’t go to bed with her mobile phone on the bedside table. It is not that she is worried about sleep disturbances – she is more concerned about the potential of hackers to use it as a listening device.
“Because I would be horrified if people heard how loud I snore,” she says.
She is only half-joking. As an entrepreneur in the field of data privacy, she has heard enough horror stories about the hijacking of devices to make her wary of things that most of us now take for granted.
“If my device, just because it happened to be plugged in my room, became a listening device, or a filming device, would that put me in a compromising position? Could I have a ransomware attack?”
(It can happen and has happened. Spyware and Stalkerware are openly advertised for sale.)
Taking back control
Cooper is the founder of ID Exchange – an Australian start-up aiming to allow users to control if, when and to whom they will share their data. The idea is to simplify the process so that people will be able to visit one platform to control access.
This is important because, at present, it is impossible to keep track of who has your data and how much access you have agreed to and whether you have allowed it to be used by third parties. If you decide to revoke that access, the process is difficult and time-consuming.
Big data is big business
The data that belongs to you is liquid gold for businesses wanting to improve their offerings and pinpoint potential customers. It is also vital information for government agencies and a cash pot for hackers.
Apart from the basic name, address, age details, that data can reveal the people to whom you are connected, your finances, health, personality, preferences and where you are located at any point in time.
That information is harvested from everyday interactions with social media, service providers and retailers. For instance, every time you answer a free quiz on Facebook, you are providing someone with data.
Google Assistant uses your data to book appointments
With digital identity and personal data-related services expected to be worth $1.58 trillion in the EU alone by 2020, Cooper asks whether we have consciously given permission for that data to be shared and used.
A lack of understanding
Do we realise what we have done when we tick a permission box among screens of densely-worded legalese? When we sign up to a loyalty program?
A study by the Consumer Policy Research Centre finds that 94 per cent of those surveyed did not read privacy policies. Of those that did, two-thirds said they still signed up despite feeling uncomfortable and, of those, 73 per cent said they would not otherwise have been able to access the service.
And, what we are getting in return for that data? Do we really want advertisers to know our weak points, such as when we are in a low mood and susceptible to “retail therapy”? Do we want them to conclude we are expecting a new baby before we have had a chance to announce it to our own families?
Even without criminal intent, limited control over the use of our data can have life-altering consequences when it is used against us in deciding whether we may qualify for insurance, a loan, or a job.
“It is not my intention to create fear or doubt or uncertainty about the future,” explains Cooper. “My passion is to drive education about how we have to become “self-accountable” about the access to our data that will drive a trillion-dollar market,” she says.
“Privacy is a Human Right.”
Cooper was schooled in technology and entrepreneurialism by her father, Tom Cooper, who was one of the Australian IT industry’s pioneers. In the 1980s, he introduced the first IBM Compatible DOS-based computers into this country.
She started working in her father’s company at the age of 15 and has spent the past three decades in a variety of IT sectors, including the PC market, consulting for The Yankee Group, as a cloud specialist for Optus Australia, and financial services with Allianz Australia.
Starting ID Exchange in 2015, Cooper partnered with UK-based platform Digi.me, which aims to round up all the information that companies have collected on individuals, then hand it over those individuals for safekeeping on a cloud storage service of their choosing. Cooper is planning to add in her own business, which would provide the technology to allow people to opt in and opt out of sharing their data easily.
Cooper says she became passionate about the issue of data privacy in 2015, after watching a 60 Minutes television segment about hackers using mobile phones to bug, track and hack people through a “security hole” in the SS7 signaling system.
This “hole” was most recently used to drain bank accounts at Metro Bank in the UK, it was revealed in February.
Lawmakers aim to strengthen data protection
The new European General Data Protection Regulation is a step forward in regaining control of the use of data. Any Australian business that collects data on a person in the EU or has a presence in Europe must comply with the legislation that ensures customers can refuse to give away non-essential information.
If that company then refuses service, it can be fined up to 4 per cent of its global revenue. Companies are required to get clear consent to collect personal data, allows individuals to access the data stored about them, fix it if it is wrong, and have it deleted if they want.
The advance of the “internet of things” means that everyday objects are being computerised and are capable of collecting and transmitting data about us and how we use them. A robotic vacuum cleaner can, for instance, record the dimensions of your home. Smart lighting can take note of when you are home. Your car knows exactly where you have gone.
For this reason, Cooper says she will not have voice-activated assistants – such as Google’s Home, Amazon Echo’s Alexa or Facebook’s Portal – in her home. “It has crossed over the creepy line,” she says.
“All that data can be used in machine learning. They know what time you are in the house, what room you are in, how many people are in the conversation, keywords.”
Your data can be compromised
Speculation that Alexa is spying on us by storing our private conversations has been dismissed by fact-checking website Politifact, although researchers have found the device can be hacked.
The devices are “always-on” to listen for an activating keyword, but the ambient noise is recorded one second at a time, with each second dumped and replaced until it hears a keyword like “Alexa”.
However, direct commands to those two assistants are recorded and stored on company servers. That data, which can be reviewed and deleted by users, is used to a different extent by the manufacturers.
Google uses the data to build out your profile, which helps advertisers target you. Amazon keeps the data to itself but may use that to sell you products and services through its own businesses. For instance, the company has been granted a patent to recommend cough sweets and soup to those who cough or sniff while speaking to their Echo.
In discussions about rising concerns about the use and misuse of our data, Cooper says she is frustrated by those who tell her that “privacy is dead” or “the horse has bolted”. She says it is not too late to regain control of our data.
“It is hard to fix, it is complex, it is a u-turn in some areas, but that doesn’t mean that you don’t do it.”
It was not that long ago that publicly disagreeing with your employer’s business strategy or staging a protest without the protection of a union, would have been a sackable offence.
But not today – if you are among the business “elite”.
Last year, 4,000 Google employees signed a letter of protest about an artificial intelligence project with the Department of Defense. Google agreed not to renew the contract. No-one was fired.
Also at Google, employees won concessions after 20,000 of them walked out protesting the company’s handling of sexual harassment cases. Everyone kept their jobs.
Consulting firms Deloitte and McKinsey & Company and Microsoft have come under pressure from employees to end their work with the US Department of Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), because of concerns about the separation of children from their illegal immigrant parents.
Amazon workers demanded the company stop selling its Rekognition facial recognition software to law enforcement.
Examples like these show that collective action at work can still take place, despite the decline of unionism, if the employees are considered valuable enough and the employer cares about its social standing.
The power shift
Charles Wookey, CEO of not-for-profit organisation A Blueprint for Better Business says workers in these kinds of protests have “significant agency”.
“Coders and other technology specialists can demand high pay and have some power, as they hold skills in which the demand far outstrips the supply,” he told CEO Magazine.
Individual protesters and whistle-blowers, however, do not enjoy the same freedom to protest. Without a mass of colleagues behind them, they can face legal sanction or be fired for violating the company’s code of conduct – as was Google engineer James Damore when he wrote a memo criticising the company’s affirmative action policies in 2017.
Head of Society and Innovation at the World Economic Forum, Nicholas Davis, says technology has enabled employees to organise via message boards and email.
“These factors have empowered employee activism, organisation and, indeed, massive walkouts –not just around tech, by the way, but around gender and about rights and values in other areas,” he said at a forum for The Ethics Alliance in March.
Change coming from within
Davis, a former lawyer from Sydney, now based in Geneva, says even companies with stellar reputations in human rights, such as Salesforce, can face protests from within – in this case, also due to its work with ICE.
“There were protesters at [Salesforce annual conference] Dreamforce saying: ‘Guys, you’re providing your technology to customs and border control to separate kids from their parents?,” he said.
Staff engagement and transparency
Salesforce responded by creating Silicon Valley’s first-ever Office of Ethical and Humane Use of Technology as a vehicle to engage employees and stakeholders.
“I think the most important thing is to treat it as an opportunity for employee engagement,” says Davis, adding that listening to employee concerns is a large part of dealing with these clashes.
“Ninety per cent of the problem was not [what they were doing] so much as the lack of response to employee concerns,” he says. Employers should talk about why the company is doing the work in question and respond promptly.
“After 72 hours, people think you are not taking this seriously and they say ‘I can get another job, you know’, start tweeting, contact someone in the ABC, the story is out and then suddenly there is a different crisis conversation.”
Davis says it is difficult to have a conversation about corporate social activism in Australia, where business leaders say they are getting resistance from shareholders.
“There’s a lot more space to talk about, debate, and being politically engaged as a management and leadership team on these issues. And there is a wider variety of ability to invest and partner on these topics than I perceive in Australia,” says Davis, who is also an adjunct professor with Swinburne University’s Institute for Social Innovation.
“It’s not an issue of courage. I think it’s an issue with openness and demand and shifting culture in those markets. This is a hard conversation to have in Australia. It seems more structurally difficult,” he says.
“From where I stand, Australia has far greater fractures in terms of the distance between the public, private and civil society sectors than any other country I work in regularly. The levels of distrust here in this country are far higher than average globally, which makes for huge challenges if we are to have productive conversations across sectors.”
MOST POPULAR
ArticleBeing Human
Putting the ‘identity’ into identity politics
ArticleHEALTH + WELLBEING
Parent planning – we should be allowed to choose our children’s sex
Article
Ethics Explainer: Respect
ArticleBeing Human
Praying for Paris doesn’t make you racist
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
If humans bully robots there will be dire consequences

If humans bully robots there will be dire consequences
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsScience + Technology
BY Fiona Smith 13 MAR 2019
HitchBOT was a cute hitchhiking robot made up of odds and ends as an experiment to see how humans respond to new technology. Two weeks into its journey across the United States, it was beheaded in an act of vandalism.
For most of its year-long “world tour” in 2015, the Wellington-boot wearing robot was met with kindness, appearing in “selfies” with the people who had picked it up by the side of the road, taking it to football games and art galleries.
However, the destruction of HitchBOT points to a darker side of human psychology – where some people will act out their more violent and anti-social instincts on a piece of human-like technology.
A target for violence
Manufacturers of robots are well aware that their products can become a target, with plenty of reports of wilful damage. Here’s a brief timeline of the types of bullying human’s have inflicted on our robotic counterparts in recent years.
- The makers of a wheeled robot that delivers takeaway food in business parks reported that people kick or flip over the machines for no apparent reason.
- Homeless people in the US threw a tarpaulin over a patrolling security robot in a carpark and smeared barbeque sauce over its lenses.
- Google’s self-driving cars have been attacked. Children in Japan have reportedly attacked robots in shopping malls, leading their designers to write programs to help them avoid small people.
- In less than 24 hours after its launch, Microsoft’s chatbot “Tay” had been corrupted into a racist by social media users who encouraged its antisocial pronouncements.
Researchers speculated to the Boston Globe that the motives for these attacks could be boredom or annoyance at how the technology was being used. When you look at those examples together, is it fair to say we are we becoming brutes?
Programming for human behaviour
While manufacturers want us to be kind to their robots, researchers are examining the ways human behaviour is changing in response to the use of technology.
Take the style of discourse on social media, for example. You don’t have to spend long on a Facebook or Twitter discussion before you are confronted with an example of written aggression.
“I think people’s communications skills have deteriorated enormously because of the digital age,” says Tania de Jong, founder and executive producer of the Creative Innovation summit, which will be held in Melbourne in April.
“It is like people slapping each other – slap, slap slap. It is like common courtesies that we took for granted as human beings are being bypassed in some way.”
Clinical psychologist Louise Remond says words typed online are easily misinterpreted. “The verbal component is only 7 per cent of the whole message and the other components are the tone and the body language and those things you get from interacting with a person.”
The dark power of anonymity
“The disinhibition of anonymity, where people will say things they would never utter if they knew they were being identified and observed, is another factor in poor online behaviour. But, even when people are identifiable, they sometimes lose sight of how many people can see their messages.” says Remond, who works at the Kidman Centre in Sydney.
Text messaging is abbreviated communication, says Dr Robyn Johns, Senior Lecturer in Human Resource Management at the University of Technology, Sydney. “So you lose that tone and the intention around it and it can come across as being quite coarse,” she says.
Is civility at risk?
If we are rude to machines, will we be rude to each other?
If you drop your usual polite attitude when dealing with a taxi-ordering chatbot are you more likely to treat a human the same way? Possibly, says de Jong. The experience of call centre workers could be a bad omen: “A lot of people are rude to those workers, but polite to the people who work with them.”
“Perhaps there is a case to be made that we all need to be a lot more respectful,” says Jong, who founded the non-profit Creativity Australia, which aims to unlock the creativity of employees.
“A general rule, if we are going to act with integrity as whole human beings, we are not going to have different ways of talking to different things.”
The COO of “empathetic AI” company Sensum, Ben Bland, recently wrote that his company’s rule-of-thumb is to apply the principle of “don’t be a dick” to its interactions with AI.
“ … we should consider if being mean to machines will encourage us to become meaner people in general. But whether or not treating [digital personal assistant] Alexa like a disobedient slave will cause us to become bad neighbours, there’s a stickier aspect to this problem. What happens when AI is blended with ourselves?,” he asks in a column published on Medium.com.
“With the adoption of tools such as intelligent prosthetics, the line between human and machine is increasingly blurry. We may have to consider the social consequences of every interaction, between both natural and artificial entities, because it might soon be difficult or unethical to tell the difference.”
Research Specialist at the MIT Media Lab, Dr Kate Darling, told CBC news in 2016 that research shows a relationship between people’s tendencies for empathy and the way they treat a robot.
“You know how it’s a red flag if your date is nice to you, but rude to the waiter? Maybe if your date is mean to Siri, you should not go on another date with that person.”
Research fellow at MIT Sloan School’s Center for Digital Business, Michael Schrage, has forecast that “ … being bad to bots will become professionally and socially taboo in tomorrow’s workplace”.
“When “deep learning” devices emotionally resonate with their users, mistreating them feels less like breaking one’s mobile phone than kicking a kitten. The former earns a reprimand; the latter gets you fired, he writes in the Harvard Business Review.
Need to practise human-to-human skills
Johns says we are starting to get to a “tipping point” where that online style of behaviour is bleeding into the face-to-face interactions.
“There seems to be a lot more discussion around people not being able to communicate face-to-face,” she says.
When she was consulting to a large fast food provider recently, managers told her they had trouble getting young workers to interact with older customers who wanted help with the automated ordering system.
“They [the workers] hate that. They don’t want to talk to anyone. They run and hide behind the counter,” says Johns, a doctor of Philosophy with a background in human resources.
The young workers vie for positions “behind the scenes” whereas, previously, the serving positions were the most sought-after.
Johns says she expects to see etiquette classes making a comeback as employers and universities take responsibility for training people to communicate clearly, confidently and politely.
“I see it with graduating students, those who are able to communicate and present well are the first to get the jobs,” she says.
We watch and learn
Remond specialises in dealing with young people – immersed in cyber worlds since a very young age – and says there is a human instinct to connect with others, but the skills have to be practised.
“There is an element of hardwiring in all of us to be empathetic and respond to social cues,” she says.
Young people can practice social skills in a variety of real-life environments, rather than merely absorbing the poor role models they find of reality television shows.
“There are a lot of other influences. We learn so much from the social modelling of other people. You can walk into a work environment and watch how other people interact with each other at lunchtime.”
Remond says employers should ensure people who work remotely have opportunities to reconnect face-to-face. “If you are part of a team, you are going to work at your best when you feel a genuine connection with these people and you feel like you trust them and you feel like you can engage with them.”
This article was originally written for The Ethics Alliance. Find out more about this corporate membership program. Already a member? Log in to the membership portal for more content and tools here.
MOST POPULAR
ArticleBeing Human
Putting the ‘identity’ into identity politics
ArticleHEALTH + WELLBEING
Parent planning – we should be allowed to choose our children’s sex
Article
Ethics Explainer: Respect
ArticleBeing Human
Praying for Paris doesn’t make you racist
BY Fiona Smith
Fiona Smith is a freelance journalist who writes about people, workplaces and social equity. Follow her on Twitter @fionaatwork
Employee activism is forcing business to adapt quickly

Employee activism is forcing business to adapt quickly
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipRelationships
BY The Ethics Centre 12 MAR 2019
It was not that long ago that publicly disagreeing with your employer’s business strategy or staging a protest without the protection of a union, would have been a sackable offence.
But not today – if you are among the business “elite”.
Last year, 4,000 Google employees signed a letter of protest about an artificial intelligence project with the Department of Defense. Google agreed not to renew the contract. No-one was fired.
Also at Google, employees won concessions after 20,000 of them walked out protesting the company’s handling of sexual harassment cases. Everyone kept their jobs.
Consulting firms Deloitte and McKinsey & Company and Microsoft have come under pressure from employees to end their work with the US Department of Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), because of concerns about the separation of children from their illegal immigrant parents.
Amazon workers demanded the company stop selling its Rekognition facial recognition software to law enforcement.
Examples like these show that collective action at work can still take place, despite the decline of unionism, if the employees are considered valuable enough and the employer cares about its social standing.
The power shift
Charles Wookey, CEO of not-for-profit organisation A Blueprint for Better Business says workers in these kinds of protests have “significant agency”.
“Coders and other technology specialists can demand high pay and have some power, as they hold skills in which the demand far outstrips the supply,” he told CEO Magazine.
Individual protesters and whistle-blowers, however, do not enjoy the same freedom to protest. Without a mass of colleagues behind them, they can face legal sanction or be fired for violating the company’s code of conduct – as was Google engineer James Damore when he wrote a memo criticising the company’s affirmative action policies in 2017.
Head of Society and Innovation at the World Economic Forum, Nicholas Davis, says technology has enabled employees to organise via message boards and email.
“These factors have empowered employee activism, organisation and, indeed, massive walkouts –not just around tech, by the way, but around gender and about rights and values in other areas,” he said at a forum for The Ethics Alliance in March.
Change coming from within
Davis, a former lawyer from Sydney, now based in Geneva, says even companies with stellar reputations in human rights, such as Salesforce, can face protests from within – in this case, also due to its work with ICE.
“There were protesters at [Salesforce annual conference] Dreamforce saying: ‘Guys, you’re providing your technology to customs and border control to separate kids from their parents?,” he said.
Staff engagement and transparency
Salesforce responded by creating Silicon Valley’s first-ever Office of Ethical and Humane Use of Technology as a vehicle to engage employees and stakeholders.
“I think the most important thing is to treat it as an opportunity for employee engagement,” says Davis, adding that listening to employee concerns is a large part of dealing with these clashes.
“Ninety per cent of the problem was not [what they were doing] so much as the lack of response to employee concerns,” he says. Employers should talk about why the company is doing the work in question and respond promptly.
“After 72 hours, people think you are not taking this seriously and they say ‘I can get another job, you know’, start tweeting, contact someone in the ABC, the story is out and then suddenly there is a different crisis conversation.”
Davis says it is difficult to have a conversation about corporate social activism in Australia, where business leaders say they are getting resistance from shareholders.
“There’s a lot more space to talk about, debate, and being politically engaged as a management and leadership team on these issues. And there is a wider variety of ability to invest and partner on these topics than I perceive in Australia,” says Davis, who is also an adjunct professor with Swinburne University’s Institute for Social Innovation.
“It’s not an issue of courage. I think it’s an issue with openness and demand and shifting culture in those markets. This is a hard conversation to have in Australia. It seems more structurally difficult,” he says.
“From where I stand, Australia has far greater fractures in terms of the distance between the public, private and civil society sectors than any other country I work in regularly. The levels of distrust here in this country are far higher than average globally, which makes for huge challenges if we are to have productive conversations across sectors.”
This article was originally written for The Ethics Alliance. Find out more about this corporate membership program. Already a member? Log in to the membership portal for more content and tools here.
MOST POPULAR
ArticleBeing Human
Putting the ‘identity’ into identity politics
ArticleHEALTH + WELLBEING
Parent planning – we should be allowed to choose our children’s sex
Article
Ethics Explainer: Respect
ArticleBeing Human
Praying for Paris doesn’t make you racist
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
What ethics should athletes live by?
What ethics should athletes live by?
Opinion + AnalysisHealth + WellbeingRelationships
BY The Ethics Centre 10 MAR 2019
Athletes are bound by multiple codes – including the formal rules of the games they play and the informal conventions that define what is deemed to be acceptable conduct.
Professional athletes are often bound by a more stringent code that governs many aspects of their public and private lives. In an era of social media and phone cameras, lucrative sponsorships and media rights, online sports betting and performance enhancing drugs, there is very little that isn’t regulated, measured or scrutinised.
The culture of sport
The formal rules of any game establish the minimum standards that bind players and officials equally in order to ensure a fair contest. Not surprisingly, the formal rules are relative to the sports that they define: you can tackle someone to the ground in a rugby match (provided they’re holding the ball), but it would be deemed unacceptable in tennis.
But there are also conventions and informal obligations that define the culture of sport. For example, most sports establish informal boundaries that seek to capture a spirit of good sportsmanship. The cricketer who refuses to “walk” after losing their wicket – or who delivers a ball under-arm – may not be breaking any formal rule, but they’ll be offending the so-called spirit of cricket.
The sanctions for such an offence may be informal, but may blight that player’s career.
A question of trust
In sport, the bottom line is trust. Sportspeople are stewards for the games they play – with an obligation not to destroy the integrity of the sports in which they participate. Athletes tend to be intensely competitive, seeking victory for themselves, for their team or sometimes their nation.
Professional sports sell themselves to the public on the basis that the contests are real and, hopefully, fair. Every time two teams or competitors walk out onto the field of play, they place so much at stake – far more than just the result of one game.
That is why evidence of match fixing, doping or cheating is so destructive – it destroys public trust in the veracity of the competition that people pay to watch. It damages the reputation of the sport. And it is ultimately self-defeating – always leaving doubt in the dishonest victor’s mind, denying forever the satisfaction of a honest win.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Virtue Ethics
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Meet Joseph, our new Fellow exploring society through pop culture
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
How can you love someone you don’t know? ‘Swarm’ and the price of obsession
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Relationships
“Animal rights should trump human interests” – what’s the debate?
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
How will we teach the robots to behave themselves?

How will we teach the robots to behave themselves?
Opinion + AnalysisScience + Technology
BY Simon Longstaff 5 MAR 2019
The era of artificial intelligence (AI) is upon us. On one hand it is heralded as the technology that will reshape society, making many of our occupations redundant.
On the other, it’s talked about as the solution that will unlock an unfathomable level of processing efficiency, giving rise to widespread societal benefits and enhanced intellectual opportunity for our workforce.
Either way, one thing is clear – AI has an ability to deliver insights and knowledge at a velocity that would be impossible for humans to match and it’s altering the fabric of our societies.
The impact that comes with this wave of change is remarkable. For example, IBM Watson has been used for early detection of melanoma, something very close to home considering Australians and New Zealanders have the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. Watson’s diagnostic capacity exceeds that of most (if not all) human doctors.
Technologists in the AI space around the world are breaking new ground weekly – that is an exciting testament to humankind’s ability. In addition to advancements in healthcare, 2018 included milestones in AI being used for autonomous vehicles, with the Australian government announcing the creation of a new national office for future transport technologies in October.
However, the power to innovate creates proportionately equal risk and opportunity – technology with the power to do good can, in almost every case, be applied for bad. And in 2019 we must move this conversation from an interesting dinner-party conversation to a central debate in businesses, government and society.
AI is a major area of ethical risk. It is being driven by technological design processes that are mostly void of robust ethical consideration – a concern that should be the top of the agenda for all of us. When technical mastery of any kind is divorced from ethical restraint the result is tyranny.
The knowledge that’s generated by AI will only ever be the cold logic of the machine. It lacks the nuanced judgment that humans have. Unless AI’s great processing power is met and matched with an equal degree of ethical restraint, the good it creates is not only lost but potentially damaging.The lesson we need to learn is this: just because we can do something doesn’t mean that we should.
Ethical knowledge
As citizens, our priority must be to ensure that AI works in the interests of the many rather than the few.
Currently, we’re naively assuming that the AI coders and developers have the ethical knowledge, understanding and skills to navigate the challenges that their technological innovations create.
In these circumstances, sound ethical judgment is just as important a skill as the ability to code effectively. It is a skill that must be learned, practised and deployed. Yet, very little ethical progress or development has been made in the curriculum to inform the design and development of AI.
This is a “human challenge” not a “technology challenge”. The role of people is only becoming more important in the era of AI. We must invest in teaching ethics as applied to technological innovation.
Building a platform of trust
In Australia, trust is at an all-time low because the ethical infrastructure of our society is largely damaged – from politics to sport to religious institutions to business. Trust is created when values and principles are explicitly integrated into the foundations of what is being designed and built. Whatever AI solution is developed and deployed, ethics must be at the core – consciously built into the solutions themselves, not added as an afterthought.
Creating an ethical technologically advanced culture requires proactive and intentional collaboration from those who participate in society: academia, businesses and governments. Although we’re seeing some positive early signs, such as the forums that IBM is creating to bring stakeholders from these communities together to debate and collaborate on this issue, we need much more of the same – all driven by an increased sense of urgency.
To ensure responsible stewardship is at the centre of the AI era, we need to deploy a framework that encourages creativity and supports innovation, while holding people accountable.
This story first appeared on Australian Financial Review – republished with permission.
MOST POPULAR
ArticleBeing Human
Putting the ‘identity’ into identity politics
ArticleHEALTH + WELLBEING
Parent planning – we should be allowed to choose our children’s sex
Article
Ethics Explainer: Respect
ArticleBeing Human
Praying for Paris doesn’t make you racist
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
Film Review: If Beale Street Could Talk

Film Review: If Beale Street Could Talk
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY The Ethics Centre 14 FEB 2019
James Baldwin was one of the great American writers of the twentieth century.
His elegant, articulate and keenly perceptive work bore witness to the hostile, day-to-day realities in which African Americans lived, and the psychological implications of racism for society as a whole.
His fifth novel, If Beale Street Could Talk, is no exception. Forty-four years after it was published, Moonlight director Barry Jenkins has adapted it for the screen.
A different type of love story
A hypnotic, visually sumptuous and intimate love story, Beale Street has little of the structure of a traditional romance. The film begins, for instance, with the generic arc of courtship already complete. We first see the two young protagonists – Tish Rivers and her boyfriend Alfonzo ‘Fonny’ Hunt – walking slowly together in a park, their affections clear and perfectly mirrored. Growing up as childhood friends in the Bronx, there was never a time they did not love each other.
The story instead bears testimony to the resilience of love, and the strength it endows those who have faith in it. Here, we witness its many forms arrayed against a vast, malicious and coldly impersonal system which is rigged to destroy black lives and fracture the most precious of bonds.
Barely a minute into screen time, the plot throws Fonny (Stephan James) behind a glass wall. He’s in jail after being accused of rape. To his accuser and certainly the police, his innocence is irrelevant. As a black man, his identity in the white cultural imagination is as a violent savage – he was always-already condemned, regardless of his actions. It is through this transparent barrier that Tish (KiKi Layne) tells him that she is carrying his child.
When the past and present merge
Following this revelation, the story diverges in two interweaving streams of past and present. One, filled with hope and secret joys, sees the young couple come to understand each other as man and woman, while nursing dreams of a future together. In the second narrative, hope is not a simple impulse but an inviolable duty, as their baby swells in Tish’s womb, Fonny’s case stagnates and despair threatens. Each scene is freighted with the viewer’s knowledge that the lovers’ destiny is not their own.
Tish’s tale
This second narrative is also very much Tish’s story, and shifts its focus to a different kind of love. Beale Street is most affecting in its portrait of the Rivers family, who support Tish wholly and will do whatever they must to fight for her and the new life within her. Regina King won a Golden Globe for her portrayal of Tish’s mother Sharon, who embodies a fierce, calm and indominable maternal courage. Her father Joseph (played with a rich, growling warmth by Colman Domingo) and older sister Ernestine (Teyonah Parris) readily take on the role of advocate and defender.
Their unity has its foil in Fonny’s family, the Hunts, who refuse to partake in any struggle they did not ask for. Headed by a spiteful and Godfearing mother, who curses her unborn grandchild and rationalises prison as a place in which Fonny can find the Lord, theirs is a pride born of self-serving weakness. The Rivers’ contrasting pride is one born of unassailable dignity and a determination to act, in spite of the odds arrayed against them.
“What do you think is going to happen?” asks Mr Hunt when Joseph lays out a plan for them to steal from their workplaces to help their children.
“What we make happen.”
“Easy to say,” Hunt protests.
“Not if you mean it,” Joseph levelly responds.
Emotional explotation
Through these characters, Beale Street puts forward the case for love as the single most steadfast bastion against the dehumanising machine of systemic oppression. Those characters without this vital force are vulnerable to emotional exploitation – betraying family and friends to protect themselves. Hunt’s mother sacrifices her son rather than align herself with his fate.
Fonny’s old friend Daniel also deserts him when his words could have saved him, his integrity broken by the terror of returning to a prison that broke him. And Fonny’s accuser is so traumatised, she is locked in a prison of her own pain, insensible and insensitive the suffering of others.
None of these individuals are free. Living in a constant wash of fear without refuge or reprieve has deprived them of their integrity, transforming them into actively complicit agents in the perpetuation of a racist structure. This, Baldwin’s story reveals, is perhaps the most wretched and insidiously effective mechanism of tyranny.
Racial tensions
Daniel is sure that white man is the devil. But Beale Street itself doesn’t espouse this view. At crucial junctures, white allies take risks to intercede against social, economic, police and court racial injustice. A Jewish real estate agent grants the lovers a path to an affordable home. An old storekeeper stands up to a reptilian policeman. And Fonny’s lawyer is a ‘white boy just out of college’.
At two hours, the film is languid and poetic, with gorgeous cinematography by James Laxton. The deliberate slow pacing and the use of frequent close-ups demands of the viewer they recognise the central (and very beautiful) characters as subjects. In a culture which frequently effaces black bodies, fetishises them, or arbitrarily fashions them into villains, these images are quietly radical. The film plays out between the steady gaze of the two lovers, and plays within the gaze of an audience that can’t look away.
Quietly significant too, is the film’s inclusion of moments which are superfluous to the plot, but vital to the immersive legacy of Beale Street. One, impossible to forget: Tish’s parents swaying before a jazz record in the family loungeroom, holding each other close, smiling in the new knowledge of themselves as grandparents to be.
Final thoughts
Opening in Australia on Valentine’s Day, Jenkins’ film is a tender dream of two lovers trapped in a too-real nightmare. It is not difficult to remember that this nightmare still torments the freedoms of racial minorities in America, ‘the land of the free’, and other nations too – whether they characterise themselves as progressive democracies or not.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis, READ
Society + Culture
Read me once, shame on you: 10 books, films and podcasts about shame
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Ethical judgement and moral intuition
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: The Sunlight Test
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Come join the Circle of Chairs
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Banking royal commission: The world of loopholes has ended

Banking royal commission: The world of loopholes has ended
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipSociety + Culture
BY Simon Longstaff 6 FEB 2019
Following the release of Commissioner Hayne’s royal commission final report on the banking and financial services sector, our Executive Director shares his take on the findings for the Australian Financial Review.
The Final Report of the Hayne Royal Commission is both unsparing and inspired.
Mr Hayne casts a wide net in his analysis of what went wrong in Australia’s banking and finance industry. However, there is one group on whom he pins ultimate accountability; the boards and senior executives of the entities whom he found to be at fault, “Nothing that is said in this Report should be understood as diminishing that responsibility. Everything that is said in this Report is to be understood in the light of that one undeniable fact …”
That is the unsparing part of the Report.
Kenneth Hayne is inspired in his injunction to all Australian business that it must apply some underlying principles, “These norms of conduct are fundamental precepts. Each is well-established, widely accepted, and easily understood.”
- Obey the law;
- Do not mislead or deceive;
- Act fairly;
- Provide services that are fit for purpose;
- Deliver services with reasonable care and skill; and
- When acting for another, act in the best interests of that other.
A dominant theme in Mr Hayne’s final report is that it is time to eliminate the law’s own exceptions to these principles – a series of ‘loopholes’ – often the product of political convenience – that allow the underlying principles to be violated by those with the wit, means and licence to do so.
There is a subtle quality to Mr Hayne’s arguments on this point. At no time does he suggest that ethical commitments should be elevated above compliance with the law. Indeed, he is clear that he opposes that approach. However, he makes it clear that the Law must conform with ethics – in the form of ‘underlying principle’.
The implications of this for the targets of his harshest criticism – boards and senior executives – are profound. For too long, it has been possible to ease through a loophole and take comfort from the fact that questionable (and profitable) conduct was ‘strictly legal’. That approach has cost us all dearly.
The fact that a loophole was available to be exploited does not mean that it should have been. The capacity to exercise ethical restraint (not to do everything that is possible) was always latent within the ranks of boards and senior management.
To be fair, we should acknowledge that boards and senior management have often exercised that capacity. We will never know (and credit will never be given) for the many cases of good judgement that have prevailed. Unfortunately, in the current environment, a multitude of good decisions counts for little when compared to the relatively few, but emblematic, cases of ethical failure – some of which may also have been unlawful.
Ethical failure occurs when core purposes, values and principles are betrayed. On some occasions this is done in a knowing and deliberate manner. More often, the cause is a failure of culture and governance (both intimately linked) that leads an organisation to ‘sleep walk’ into an ethical ‘death pit’.
Recognising this, Commissioner Hayne recommends that:
All financial services entities should, as often as reasonably possible, take proper steps to:
- Assess the entity’s culture and its governance
- Identify any problems with that culture and governance
- Deal with those problems, and
- Determine whether the changes it has made have been effective
In doing so, Hayne supports and extends the approach already adopted by APRA and ASIC by looking beyond ‘risk culture’ to evaluate the whole.
The Ethics Centre is a pioneer in the development and application of world-class tools for undertaking precisely the kind of evaluation being recommended by Hayne. This approach should not be limited to banking and financial services. It is essential for all organisations – whether in the private or public sectors.
The trouble is that boards and senior managers are often deeply reluctant to look into a well-polished mirror that reveals the truth about their organisation. Instead, they look to those who offer a ‘magic mirror’ that always reflects the comforting myth that you are the ‘fairest of them all’. It takes a certain kind of moral courage to ask for the truth. Perhaps Kenneth Hayne has strengthened the sinews of corporate Australia.
We will see!
Australia was one of the first countries to develop an ethical framework for banking and finance. The Banking + Finance Oath was created in the aftermath of the global financial crisis – at a time when all seemed to be relatively rosy on the domestic front.
The great disappointment was that so few people took up the opportunity to commit to the ‘underlying principles’ on which the BFO is based. Perhaps too many people saw that reality fell too short of the ideal.
If ever there was a time to make something better, it is now. In the wake of the Hayne royal commission, it is time for the ethical majority, working within banking and finance, to step up. Whatever your role or seniority – it’s time to own what is noble in the aims of banking and finance and to give life to its ideals.
Embrace underlying principle, measure and achieve alignment, exercise ethical restraint, regain trust. Do so in the expectation of profit and to earn that most elusive of rewards: a good name.
That is the opportunity that lies latent in the recommendations of the Hayne Report.
Dr Simon Longstaff is executive director of The Ethics Centre
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
What money and power makes you do: The craven morality of The White Lotus
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Holly Kramer on diversity in hiring
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Despite codes of conduct, unethical behaviour happens: why bother?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
































