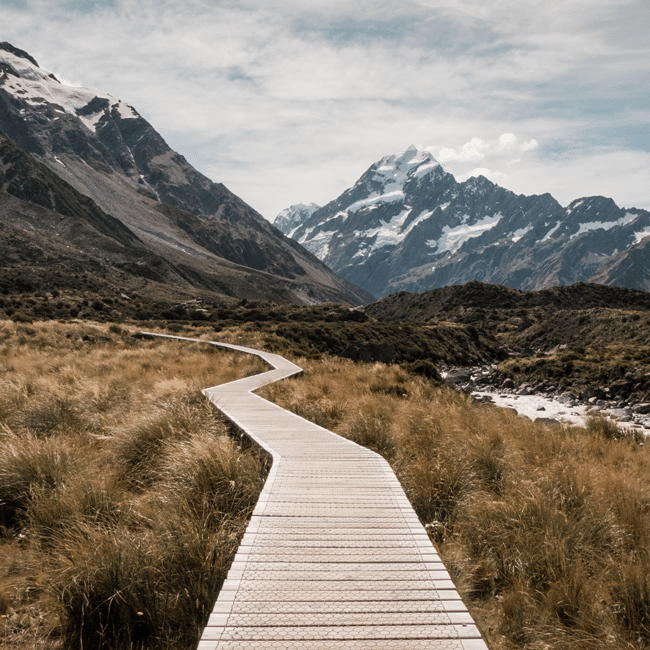
The future does not just happen. It is made. And we are its authors.

The future does not just happen. It is made. And we are its authors.
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipRelationships
BY Simon Longstaff 5 JUN 2023
Of late, I have been thinking about how to describe the impact of the work done by The Ethics Centre. It’s a surprisingly difficult thing to do because our greatest impact typically lies in our influence on what does NOT happen.
For example, when we assist or inspire a person to step back from making a disastrous decision, there is nothing to measure. We can measure the cost of disasters. We can measure the impact of the response to disasters. However, how do we measure the impact of a disaster averted?
Let’s consider this in a wider context. My abiding sense of today’s world is that we remain on the cusp of epoch-defining change. The sense of what is before us has led me back to binge-reading vast swathes of science fiction – and the worlds I encounter there are recognisably connected to our own. Yet, the unbounded power of the authors’ imagination invites the reader to be equally bold in contemplating ‘what might be’. Wondering about ‘what might be’ leads us to the realisation that we are each responsible, at least in part, for the future that actually emerges.
The future does not just happen. It is made. And we are its authors.
And that is why ethics matters. It is humanity’s best tool for the avoidance of disastrously bad decisions – and the nightmare worlds that emerge from them. More optimistically, ethics equips us to make brilliantly good decisions – and the wonderous possibilities that they entail.
We can see this at work in one topical example; the rise and rise of CHATGPT – the most famous of a growing suite of expert systems that already have the capacity to transform our lives. Predictably, there has been a slew of prophecies about the likelihood of both utopian and dystopian futures. The emergence of new technology is always accompanied by excessively optimistic and pessimistic views about its likely effects.
Less predictably, some of the architects of this technology have urged caution. Their call for a measure of self-restraint is not grounded in fear. They simply argue that it is irresponsible to unleash a powerful, transformative force without understanding what we do. In essence, we need to set the ethical parameters within which AI should be developed and deployed. If we get this right, then sound ethics will inform policy and practice that averts all manner of mischief. Yet, the impact of ethical restraint will go unmeasured. Despite this, The Ethics Centre remains actively engaged in work to support the development of ‘responsible AI’ – as evidenced by our joining the Responsible AI Network (RAIN) being led by the CSIRO.
The Centre’s work is aligned to three strategic priorities. First, we seek to exemplify and support good decision making. Second, we work to maintain an open civic space within which the issues facing our society can be discussed – even when there is much room for disagreement. Finally, we seek to strengthen the ‘ethical infrastructure’ of our society – so that they become trustworthy to the extent that the community will rely on its key institutions to exercise good judgement in the public interest. This is especially important to any society that faces major change. For example, the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy raises the spectre that some communities (typically linked to older forms of power generation) will bear a disproportionate share of the burdens, while others reap the benefits. If we cannot trust our governments, businesses, regulators, or other institutions to get the balance right, then reform will be slowed or halted – to the detriment of all.
The economic cost of broken ‘ethical infrastructure’ is immense. As Deloitte Access Economics has estimated, a mere ten percent increase in ethics would, by itself, generate an additional $45 Billion dollars per annum in improved GDP. Even more remarkable is that this economic return could be generated, over time, with a one-off investment of only $30 Million in funds. It’s hard to think of a better return on investment. Yet, it remains elusive.
What Australia needs is a truly national institution to help the nation lean into the challenges we face. It needs to become a trusted source of advice for governments and other key decision makers. It needs to build the capacity of our nation’s leaders, in the public and private sectors, to make good decisions – across the board. It needs to support our institutions in their efforts to regain public trust. Only then, will the community allow itself to accept the fundamental reforms that will be necessary to make the most of the future.
The establishment of such an institution will be especially important in its implications for the generations of younger Australians who so readily embrace ethics – in a way that surpasses earlier generations who looked to organised religion for guidance. That is why the Centre is investing in a new youth strategy to engage, at an early stage, with the ethical leaders of the future.
The immediate effects of a significant investment in ethics will be impossible to see. The increase in prosperity will inevitably be attributed to the wisdom of those in power. What will remain invisible are the many acts of folly that sound ethics will have prevented.
That is our conundrum. It is also why we are so deeply grateful for the support provided to us by the individuals, foundations and organisations who support our work. The Ethics Centre begins every financial year without a cent of income ‘locked in’. Nobody ‘needs’ ethics … until they do. So, we remain vulnerable. But, perhaps, that might be one of our greatest strengths – because it keeps the Centre attuned to the fundamental needs of society. Irrelevance is not an option.
So, next time things go better than expected, spare a thought for the possibility that it was the invisible hand of ethics (and not the market) that produced the result. With luck – and the generous support of our donors – we can strengthen that hand for a better future.
With your support, The Ethics Centre can continue to be the leading, independent advocate for bringing ethics to the centre of everyday life in Australia. Click here to make a tax deductible donation today.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
It’s easy to ignore the people we can’t see
Big thinker
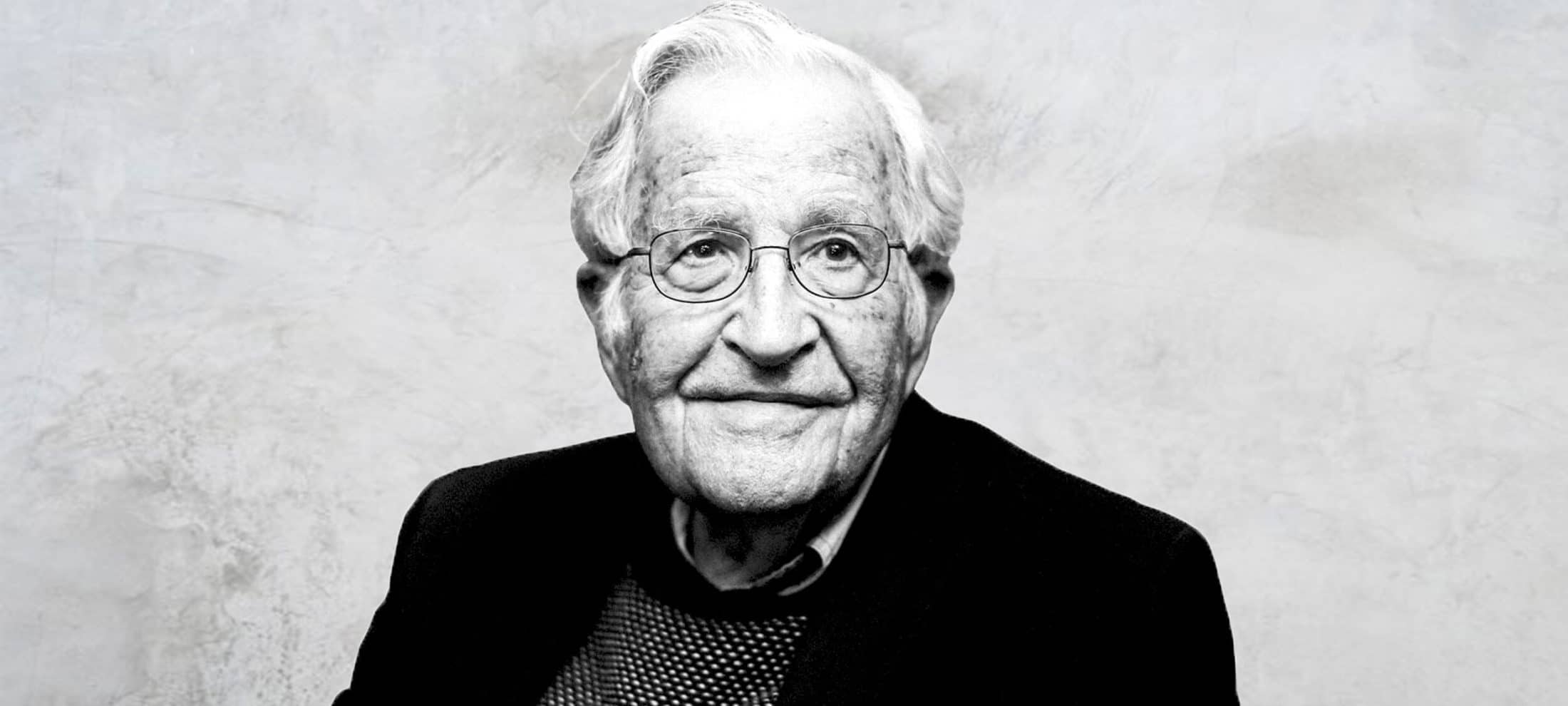
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Noam Chomsky
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
The truth isn’t in the numbers
Opinion + Analysis
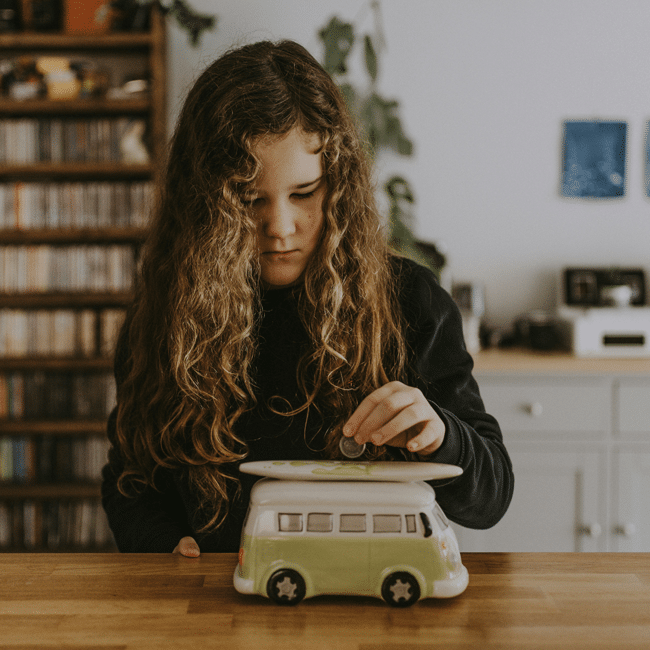
Business + Leadership
Give them a piggy bank: Why every child should learn to navigate money with ethics
BY Simon Longstaff
Simon Longstaff began his working life on Groote Eylandt in the Northern Territory of Australia. He is proud of his kinship ties to the Anindilyakwa people. After a period studying law in Sydney and teaching in Tasmania, he pursued postgraduate studies as a Member of Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1991, Simon commenced his work as the first Executive Director of The Ethics Centre. In 2013, he was made an officer of the Order of Australia (AO) for “distinguished service to the community through the promotion of ethical standards in governance and business, to improving corporate responsibility, and to philosophy.” Simon is an Adjunct Professor of the Australian Graduate School of Management at UNSW, a Fellow of CPA Australia, the Royal Society of NSW and the Australian Risk Policy Institute.
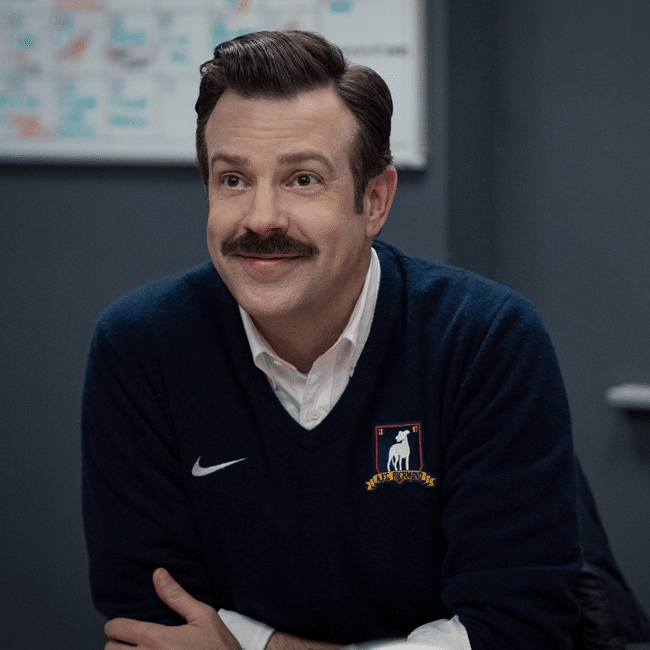
Beyond cynicism: The deeper ethical message of Ted Lasso

Beyond cynicism: The deeper ethical message of Ted Lasso
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Dr Tim Dean 1 JUN 2023
A truly ethical life requires that we let go of cynicism and strive for a better world.
Long after we’ve forgotten the gags, the on- and off-field shenanigans, and even most of the characters’ names, I suspect we’ll still remember how watching Ted Lasso made us feel.
That’s what makes this American sitcom about an endlessly optimistic NFL coach making the most of an English football team so remarkable today. It’s a show that subverts our expectations about what a typical TV show is all about. Instead of commenting on the ills of the world, or just making fun of them, Ted Lasso – both the character and the show – is devoid of cynicism.
Besides being a refreshing break from the bleak TV that populates our streams, there’s an important ethical message lurking behind Ted’s blunt moustache: in order to become better people and make the world a better place, we need to let go of cynicism.
Cynicism is rife these days. Largely for good reason. It’s easy to feel overwhelmed at the sheer number and scale of the problems we face today. And it’s easy to lapse into despondency when those in power repeatedly fail to address them. Add to this the increasingly polarised political atmosphere, and the growing sense that the “other side” is not just wrong but is morally bankrupt, and it’s easy to lose faith in human goodness altogether.
Given that popular storytelling is often a reflection of the time we’re living in, it’s no coincidence that it, too, has given over to cynicism. Series like Game of Thrones, White Lotus, Succession, House of Cards and Curb Your Enthusiasm depict duplicitous individuals who are far more consumed by expanding their power and/or covering up their insecurities than changing the world for the better or lifting up those around them.
We relate to these shows. We love to hate the Machiavellian villains. But this kind of storytelling comes at a moral cost. When art only acts as an exaggerated mirror, and only reflects back the worst of our nature, it’s no wonder that we have come to regard any magnanimous gesture with suspicion and any appeal to right the world’s wrongs as being naïve or in vain.
This is the heart of cynicism: a fundamental lack of faith in others’ intentions, an abandonment of hope that the world can be made better, as well as a tacit acknowledgement that we’re powerless to fix any of this ourselves.

The first Cynical age
Cynicism is not unique to our time. There have been other cynical ages, including the one in which the term was coined.
In the late fourth century BCE, corresponding with the rise to power of Alexander of Macedon, Greece also slipped into an age of cynicism. Prior to Alexander, Greece was a land of innovation, progress and (at least for a certain class of Greeks) seemingly boundless possibilities, driven by greater political participation by the people in city states like Athens.
Greek philosophy in the times before Alexander reflected that sense of empowerment and optimism. Thinkers from Pythagoras to Plato debated topics like justice, love, virtue and how to build the perfect state. They acknowledged human failings, but they believed we could – and should – rise above them.
But when Alexander and his successors shifted political power from individuals to concentrate it in the hands of a glory-seeking elite, philosophy shifted also. As Bertrand Russell put it in his History of Western Philosophy, philosophers “no longer asked: how can men create a good State? They asked instead: how can men be virtuous in a wicked world, or happy in a world of suffering?”
During this post-Classical era, four main schools of thought emerged from Greek thinkers, each with its own spin on how to cope in a corrupt world. Epicurus taught that happiness comes from diminishing our desires and learning to accept mortality. The Stoics believed that liberation from suffering came from within, cultivated by personal wisdom and self-control. The Sceptics gave up on the idea of truth altogether. And the Cynics – from whom we get the modern term – rejected all social conventions, including wealth, status or even basic material goods, in favour of living in accordance with raw nature.
It’s probably no coincidence that during our own time, when many of us feel a growing sense of powerlessness to fix the world’s ills, utopian visions have given way to a resurgence of these views. Indeed, Stoicism is undergoing a boom today. It seems many of us have given up trying to change the world for the better. Instead, we’re trying to adapt ourselves to cope with the way it is.
In walks Ted
Ted Lasso represents the peak in a growing trend against cynicism in media, the vanguard of which were Parks and Recreation, Schitt’s Creek and The Good Place. These are shows that subvert the typical formula of modern storytelling. Instead of depicting exaggerated versions of people at their worst, they show us exaggerated versions of people at their best. They tell stories where virtues like positivity, charity and forgiveness are not weaknesses that will be exploited by others but are strengths that help overcome the challenges we face.
That takes courage on behalf of the showrunners. It risks people dismissing uncynical shows as being unrealistic. And of course they are unrealistic, but no more so than the cynical series. But where many shows today are purely about illuminating and critiquing the ills of the world, they have little interest in offering solutions. Non-cynical shows, on the other hand, accept the critique has been made but offer us something ambitious to aim for.

Ethics requires moral imagination, which is the ability to picture the full range of possible choices open to us. And cynicism kills moral imagination. As author Sean P. Carlin puts it, “the stories we tell about the world in which we live are only as aspirational—and inspirational—as the moral imagination of our storytellers.”
Ted Lasso expands our moral imagination. Instead of dismissing people as only being self-interested or cruel, we can picture them as struggling with their own demons and offer them help.
Rather than only seeing the bleakest version of our future, moral imagination encourages us to see the world we want to live in and work towards making it happen, not ignoring the challenges we face but motivating us to overcome them.
While Ted Lasso is paradigmatically non-cynical in the modern sense, there is an interesting hint of the original philosophical Cynicism in the character of Ted. Like Diogenes, the paragon of Cynicism in the ancient world, Ted rejects the conventional metrics of success defined by the society around him. He’s uninterested in wealth or status, and justice to him means more than revenge. He repeatedly, and seemingly authentically, asserts that it’s not winning or losing that matters to him, it’s helping his players be the best versions of themselves they can be.
He also goes through his own arc to embrace another aspect of ancient Cynicism: shamelessness. The Cynics believed that conventions and social norms were bunk. Thus, they felt no shame, because they felt no discomfort in violating social expectations that they dismissed as vacuous. Likewise, Ted goes through his own journey with his anxiety, eventually opening up about it and demonstrating his contempt for norms that would shame him for it.
But Ted Lasso also transcends ancient Cynicism, just as it illustrates a better path than ancient Stoicism. It’s not just about how individuals can come to thrive by learning to cope in a disappointing world. It’s about how assuming the worst about others, and falling into the trap of suspicion and defensiveness, contributes to making the world even more disappointing.
Ted Lasso is not just entertaining. It carries an important ethical message about the virtue of releasing ourselves from cynicism. Yes, it’s unrealistic, but it reminds us that it’s worth having something to aim for, even if it’s likely to forever remain just out of reach.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics explainer: Cultural Pluralism
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Beyond consent: The ambiguity surrounding sex
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Ozi Batla: Fatherhood is the hardest work I’ve ever done
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Authenticity
BY Dr Tim Dean
Dr Tim Dean is Philosopher in Residence at The Ethics Centre and author of How We Became Human: And Why We Need to Change.
It’s time to increase racial literacy within our organisations

It’s time to increase racial literacy within our organisations
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY The Ethics Alliance 29 MAY 2023
In order establish more culturally diverse and inclusive workplaces, we need to increase our racial literacy.
We only need to look at the pay gap and underrepresentation in leadership to identify systemic racial issues within our organisations. In 2022, the Everyday Respect Report released from EB & Co identified racism as one of the factors impacting psychological safety and workplace culture. While new research from diversity and consultancy firm, MindTribes uncovered a non-Anglo pay gap within Australian organisations.
Workplace norms, systems and biases have sanitised racism to the point where not only it can affect individual’s mental wellbeing, pay and career progression, but also an organisation’s productivity, culture and consumer response. As ethical leaders we have a responsibility to unveil how racial discrimination plays out in our businesses and what strategies we can use to combat them.
An Ethics Exchange gathering in May 2023, welcomed Diversity Council of Australia (DCA) CEO Lisa Annese and Ethics Alliance members as they shared personal experiences and strategies used when developing Diversity and Inclusion (D&I) programs, and how they recognise and tackle racism within their workplaces.
The DCA has evolved over the last 40 years to become a leading entity which promotes and advances more diverse and inclusive workplaces for the benefit of individuals, organisations and the broader community. Annese says to build strategies that tackle racism in our organisations, we need to start with language.
Let’s start with language
It’s important to understand the difference in language when it comes race and culture, particularly within the Australian D&I context. Culture is defined as a combination of characteristics including ethnicity, ancestry, language, and place of origin, whereas race is generally seen as a social construct related to physical characteristics and group identity.
In response to the White Australian policy there was an effort by Gough Whitlam in the late 1960s to remove “race” from common language in order to reduce racism. This shift resulted in a focus on culture over race, and the country adopted terms such as “non-English speaking background”, embracing the concept of multiculturalism. For instance, since the United Nations created their Elimination of Racial Discrimination Day, Australia is the only country globally that doesn’t use the word race. We instead call it Harmony Day with a focus on harmony for the week. That is what is taught in our public schools and celebrated in our workplaces.
Annese suggests this avoidance of the term “race” in favour of “culture” was also an effort to maintain an existing Eurocentric power structure. For example, the term “culturally and linguistically diverse” was introduced, which broadly referred to anyone who couldn’t trace their origins back to Britain – essentially anyone non-Anglo Celtic. This excludes a large group of people with different experiences and perpetuates a sense of “otherness.”
Once we identify the other it can become easy to treat people differently and not afford them the same respect we would expect ourselves.
While understanding people’s culture is useful, it’s crucial to talk about race and to acknowledge the lived experiences of Australians who experience racism.
DCA research suggests that in Australia today, those who experience racism and racial marginalisation are people from non-European backgrounds, and the main cause of racism has less to do with language and culture and focuses more on race – features such as phenotype, visible difference, religious dress, skin tone, and hair texture.
If we want to build more inclusive and diverse businesses, we need to talk about race. And to do so, we must know what it is.
By developing an understanding of how history has sanitised our language and normalised racism in our workplace, we are able to discuss the concept of race in a way that avoids unnecessary distress. It’s important not to make assumptions that the harm felt by malintent, or overt racism is any different from the racism embedded in well-meaning or curious comments about an individual’s appearance or background.
Principles and a framework that emerged from The Ethics Exchange and DCA research to bring racial literacy to the workplace included:
- Build Racial Literacy: Before tackling racism, businesses must first educate their employees about the concept of race. They should understand what race is, how racialisation occurs, and the impact it has on people. This is important because most people have low levels of racial literacy.
- Build Confidence: The second step involves helping employees become confident in their understanding of race and racial issues. This stage ensures employees feel comfortable discussing these topics and are prepared for the next step.
- Talk About Anti-Racism: The final stage is to discuss what it means to be actively anti-racist. It is important that employees understand how they can contribute to an anti-racist environment. This stage of the process can only be effectively implemented once employees have a clear understanding of race and are confident discussing it.
One of the most impactful ways of understanding racism is to hear it from those who have been subject to it, however this carries a huge burden or cultural load. How can their voices be included to develop strategies to combat racism?
- Centre Voices: The experiences and perspectives of those affected by racism must be central to any initiatives addressing it. For instance, if a business is developing a Reconciliation Action Plan (RAP) in Australia, it should involve Indigenous employees in the process.
- Respect Cultural Labour: Organisations should acknowledge the cultural emotional and intellectual labour of employees with different social identities involved in initiatives addressing racism.
- Remunerate Appropriately: If individuals are asked to participate in initiatives to combat racism, particularly if they’re asked to share personal experiences or provide additional insights, they should be appropriately compensated.
- Respect Personal Choice: Not everyone will want to be involved in such initiatives, and that choice should be respected.
- Avoid Overgeneralisation and Presumption: One individual cannot represent an entire group. Avoid making assumptions about an entire race or culture based on the perspectives or experiences of one individual.
- Use Available Resources: In an age where information is readily available, it’s possible to educate oneself about different cultures and races without overly relying on individuals from those backgrounds to teach others.
We’d like to thank Lisa Annese and the Ethics Alliance members who contributed to this important conversation.
Find out more about the DCA’s research here.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Pulling the plug: an ethical decision for businesses as well as hospitals
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
What ethics should athletes live by?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
The pivot: Mopping up after a boss from hell
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Health + Wellbeing
Tips on how to find meaningful work
BY The Ethics Alliance
The Ethics Alliance is a community of organisations sharing insights and learning together, to find a better way of doing business. The Alliance is an initiative of The Ethics Centre.
Corporate whistleblowing: Balancing moral courage with moral responsibility

Corporate whistleblowing: Balancing moral courage with moral responsibility
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipRelationships
BY Kristina Novakovic 23 MAY 2023
Calling out corporate wrongdoing requires the moral courage to stand up for what you believe in, but also involves recognising the moral agency of others.
The story of Jeff Morris is both inspiring and daunting; inspiring because he decided to take on one of the largest banks in Australia alone by exposing corrupt practices that placed customers in financial danger, and daunting because of the fate that he suffered as a result.
Commonwealth Bank Australia’s (CBA) financial planners knowingly gave harmful financial advice to elderly and vulnerable customers that led them to severe financial losses and emotional distress. Morris spent five years trying to get the CBA and ASIC to confront the wrongdoing and set it right, attempting to force a Parliamentary Inquiry before he finally decided that the only way to protect customers from these practices was to go to the media with his story in 2013. This led to the firing of rogue CBA financial planners involved in these practices and triggered the landmark financial services royal commission.
Today, Jeff Morris stands as an admirable figure, having been awarded the Order of Australia for blowing the whistle on his employer. However, in the immediate aftermath of blowing the whistle on CBA, Morris was fired from the bank, his family left him due to the financial stress his actions put them under, he was diagnosed with PTSD and suffered constant surveillance and harassment.
The whistleblower’s moral dilemma
Corporate whistleblowers, like Morris, face a moral dilemma of balancing competing responsibilities to the organisation they work for and the responsibility they have to the consumer.
As an employee of the CBA, Morris was presumably hired with the condition that he must keep confidential information about the bank’s internal practices. This is often non-controversial. Corporations have valid reasons for not wanting their internal practices revealed, like wanting to protect their unique products and services from competitor corporations. When signing an employment contract, we often find that we’re being asked to sign a confidentiality agreement. We’re essentially promising to keep the organisation’s secrets secret.
By blowing the whistle on corporate wrongdoing, we are breaking this very promise. While promise-breaking itself is not necessarily morally wrong, often there is “moral residue” left over. What this means is, we might be justified in breaking a promise, but it might incur an obligation to remedy, say in apologising for breaking the promise, or making up for the broken promise in some compensatory way. This indicates that the breach of contract, in such a sense, does not necessarily leave us “morally clean”.
This is the first moral transgression: the breach of promissory obligation.
When we work for an organisation or corporation, we may find that there is an internal culture of loyalty or expected loyalty to both the organisation itself and to our fellow employees. By blowing the whistle on corporate wrongdoing, we could potentially be harming our fellow colleagues who may be out of work as a result of the disclosures. The organisational culture might be harmed in that we have introduced dissent into a culture that benefits from employee solidarity; the result, a sense of broader distrust.
This is the second moral transgression: a breach of loyalty.
However, as a member of an organisation or corporation that delivers products and services to the public, we also have an obligation toward the public consumer. If, like in Morris’ case, the corporation is delivering a service that is harming the consumer, we might feel an obligation to protect the broader public from these harmful practices.
To not publicly disclose the wrongdoing, we might be committing a third transgression: a breach of a natural duty to not cause harm to others.
A corporate whistleblower’s framework for harm minimisation
If there is sufficient wrongdoing that needs to be called out, it’s important to take appropriate steps to produce the best outcome. The best outcome, in these circumstances, would be one in which harm is minimised to all relevant stakeholders. Business ethicist, Richard T. De George developed, what the field of business ethics today considers the standard ethics framework for responsibly blowing the whistle on corporate wrongdoing.
He sets out the following conditions that suggest when we are morally permitted to blow the whistle and what moral consideration we ought to keep in mind before we do so:
- The firm, through its product or policy, will do serious or considerable harm, to employees or to the public, whether in the person of the user of its product, an innocent bystander or the general public.
- Once the employees identify a serious threat to the user of its product or to the general public, they should report it to their immediate supervisor and make their moral concern known. Unless they do so, their act of whistleblowing is not clearly justifiable.
- If one’s immediate supervisor does nothing effective about the concern or complaint, the employee should exhaust the internal procedures and possibilities within the firm. This usually will involve taking the matter up the managerial ladder, and if necessary – and possible – to the board of directors.
- The whistleblower must have, or have accessible, documented evidence that would convince a reasonable, impartial observer that one’s view of the situation is correct, and that the company’s product or practice poses a serious and likely danger to the public or to the user of the product.
Before we take action, we need moral courage
What De George does not account for, however, is that to follow his guidelines, we must have the moral courage to take action in the first place.
Associate Professor of Philosophy at Eastern Kentucky University, Matthew Pianalto writes that moral courage involves “facing other persons while upholding some morally motivated cause and enduring resistance or retaliation that may occur in response to one’s actions”.
We often think of courage as involving being brave when taking an action that presents a danger to ourselves. It takes courage to jump into dangerous surf to save someone from drowning. In this sense, courage is an enabling device.
Morris demonstrated this aspect of courage: he was aware of the retaliation that he would experience as a result of blowing the whistle yet did so anyway.
However, moral courage involves something else: a requirement to face others. This requirement, Pianalto writes, involves resisting “the objectification of others, even those [we] oppose in value and action”. Corporate whistleblowers are exercising moral agency by taking actions that uphold or preserve what we think is morally right and just. However, moral courage also involves recognising the moral agency of others. It is easy to other-ise those we consider our moral adversaries. We can justify taking action against them easier if we denounce them as being morally depraved.
By not considering the corporation as being made up of other humans, i.e., other moral agents just like ourselves, we may become more inclined to ignore the conditions of harm minimisation set out above. We might be prioritising the moral values we are trying to uphold at the expense of the moral responsibility we have to those that might be adversely affected by our actions. As Pianalto writes, by offering justifications for our actions, we are “[acknowledging] the capacity of others to give and receive reasons, to modify their views, revise their intentions and to change their minds…”.
Morris seems to have exhibited moral courage. He took every precaution necessary, heeding (whether he was aware of it or not) the guidelines set by ethicists like De George to protect not only his family (who raised concerns about how they might be affected by his actions), but also those other moral agents working for ASIC and the CBA that may not have been involved in the wrongdoing.
Whistleblowing on corporate wrongdoing is a serious act, one that requires us to take mindful steps. If these steps are taken, they can reduce the moral courage required of us to act.
If you’re struggling with navigating a difficult decision in your professional or personal life, our free independent helpline, Ethi-call can provide expert and impartial guidance to examine all aspects of the situation and help you find a path forward. Book a call now.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Eleanor Roosevelt
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Plato
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Who’s your daddy?
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Moral injury is a new test for employers
BY Kristina Novakovic
Dr. Kristina Novakovic is an ethicist and Associate Researcher at RAND Australia. Her current areas of research include the ethics and governance of emerging technologies and issues in military ethics.
A new era of reckoning: Teela Reid on The Voice to Parliament

A new era of reckoning: Teela Reid on The Voice to Parliament
Opinion + AnalysisPolitics + Human RightsRelationships
BY The Ethics Centre 22 MAY 2023
Later this year Australians will be asked to vote in a referendum on a Voice to Parliament. Can this conversation for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander constitutional recognition reconcile the truth of Australia’s past? Or have we embarked on a new era of reckoning with the risk that comes with a referendum?
In April 2022, Proud Wiradjuri and Wailwan woman and lawyer, Teela Reid sat down with Dr Simon Longstaff AO to discuss what reckoning means to her, what we need to make an informed decision on this vote, and what it means for us – collectively and individually.
Dr Simon Longstaff: When I think of reckoning, three things come to mind. Firstly, there’s ‘reckoning’ as in finding your bearings, dead reckoning. There’s another sense in which you reckon up the bill. And then there’s the third sense in which reckoning can be taken as a moment of recognition of one’s responsibilities and making us confront the reality of who and where we are, and what we’ve done. Perhaps we can touch on all three of those…
Teela Reid: My essay, Reckoning, Not Reconciliation, was born out of a frustration with the concept of reconciliation. I had attempted to dismiss it in some ways – whether that was to be provocative or just trying to grapple with my own sense of the world. The past three, almost four decades, has been defined in so-called Australia under this notion of reconciliation. And so, for me, as a Wiradjuri Wailwan woman, the life that I have been fortunate to live, had nothing to do with reconciliation, but it was in fact in spite of it. For me, having grown up in my community with the stories of my ancestors, my paternal and maternal lineages being hounded onto missions, laws passed so we couldn’t speak our native tongue, this notion of reconciliation kind of popped up.
I remember growing up in that community and then walking into school where we were trained that this notion of reconciliation was to make us feel good. There was almost a sense of denial of the truth. I remember, for example, learning about the Anzacs and there were no soldiers that we were told about that were Aboriginal men or women. And then I’d walk home and my grandparents would sit me around the campfire and give me a whole different education.
I remember just feeling really frustrated with the world. I want to unravel that and unpack this notion of reckoning. To me, it’s about everyone on this continent embracing the discomfort of the hard work we need to get done.
Dr Simon Longstaff: How do you look at the obligations you have – in a structure where elders still are the most significant decision makers within a community – and the need to balance that cultural obligation with obligations arising in a structure like the law; where it’s about the quality of reason, the precision of language and the authority of precedent?
Teela Reid: The western law is a discipline, it’s a practice. I vividly recall being at law school wanting to throw my textbooks up against the library when we were learning about Dicey’s rule of law where we’re all equal before the law. I remember thinking “How do I reconcile this with the stories that I know?” Clearly, the law has never treated my people fairly. There’s never been a fair go in this country for First Nations Peoples. So having those stories in my heart and in my spirit, I still took the opportunity that I was given to go to law school and now to practice law. It’s something I don’t take lightly at all, because I think we would be much worse off as a peoples if we were to take those opportunities for granted and not do the hard yards and live out those opportunities to empower our people.
Dr Simon Longstaff: Can these different definitions of ‘reckoning’ exist side by side? Or is that a very significant tension in your life?
Teela Reid: It’s a constant tension, to be very frank. It is a very constant tension to not lose yourself as a First Nations woman in this place that’s now called Australia and you’re constantly walking a fine line. When I think about reckoning, it’s also about power. It’s about who has the authority to make decisions in different contexts while at the community level our governance systems operate in a very specific way. I think that’s what Australia forgets. We have very ancient governance systems here still very much intact. They might not be written in legislation or rule books, but they’re passed down orally through our ways of knowing and being.
We have this higher order in Australia where there’s parliament, there’s states, there’s territories, there’s people making all these different decisions, but at the very heart of that, there is still the omission of the First Nations and there’s still an act of erasure in that. And the symbols are everywhere. It’s in the flag, it’s in the anthem, it’s in these ways that Australians speak their identity that I just don’t relate to.
Dr Simon Longstaff: The concept of ‘payback’ is sometimes misunderstood as if it’s based in the need for revenge. Instead, it’s about those who have done wrong making restoring balance to the community – paying back what has been taken to those who have suffered loss. Is that the kind of reckoning that you have in mind – bringing it to that point where people recognise loss as a give and take?
Teela Reid: It’s about the reconciling of the balance. There does need to be compensation, there does need to be these tough decisions and reparations for what First Nations Peoples have lost there.
The other way in which I see it, there is a level of discomfort that comes down to this truth telling notion that we’re going to need to embrace. Where Australians are at now – each one of you are advocates, you’re campaigners. You have agency in this movement. Reckoning is going to be a really difficult process, unlike reconciliation where we’ve all felt good with our wraps, our cupcakes and our teas. No, this is going to be quite difficult.
For so long, for 250+ years, as a nation we’ve avoided that discomfort that comes with trying to heal these wounds. Because you might not see the physical wounds, but they’re very deep and they’re intergenerational. When we think of reckoning, we’re all going to have to step up to the plate. And often what happens in a truth telling process, it’s that First Nations Peoples get the onus of having to speak our truth, when in fact white Australia needs to speak its truth. What did your ancestors do to my ancestors? Let’s start to have an open dialogue and take responsibility for that pain. Because I don’t think that we can heal until we reckon with the discomfort and the pain that I think as a nation is going to take many years to get through.
Dr Simon Longstaff: Whatever the result, the proposed referendum on a Voice to Parliament is going to be an extraordinary moment. What are your hopes at this point?
Teela Reid: I hope that people are willing to step up and be engaged and make informed choices for themselves in a conversation that should absolutely be based on the facts and not one in which we should be enlivening racism or anything like that. I do believe it’ll pass. I think there is so much goodwill in the Australian community.
If you look at history, the most successful referendum in 1967, shows that Australians actually feel very deeply on this issue. I’ve travelled to lots of different parts of the country, and engaged with fence seaters or people who want to protest to these kinds of conversations. By the end of it, you sit down, you listen, you work through these conversations and people’s hearts really get it.
Dr Simon Longstaff: Is this a beginning of a new set of possibilities in this country?
Teela Reid: I do believe it is. We all know the Uluru Statement has called for a First Nation’s Voice. One of the things I am grappling with both in the legal sense and the moral sense, it’s the enormous compromise our people have to make decade after decade after decade for this nation to just have a breakthrough. It happened with land rights. The Barunga Statement was gifted to Hawke. Hawke promised a treaty, he gave the nation reconciliation. It’s probably why we’re three, four decades behind right now. I don’t think that Prime Ministers like Hawke should be revered for what they’ve done. Even around when Whitlam came in for his short time in power, there were decades of activism and movements that were demanding big things, big changes. And it was only because of that activism that within those three, four years there was able to be this watershed moment of legislation and changes.
One of the things I am grappling with both in the legal sense and the moral sense, it’s the enormous compromise our people have to make decade after decade after decade for this nation to just have a breakthrough.
And so here I am thinking now, there’s another compromise being made. Perhaps this is more my moment of having to grapple with the way in which compromises are made in the political space.
I hope that everyday Australians are able to take this opportunity this year to actually reflect and educate themselves on the bigger picture and part of the story to this. Because we’re only really seeing it through that one little kind of myopic lens now that there’s going to be one ballot box and you’re going to be voting yes or no. But there is so much more to this.
Simon Longstaff: Are you optimistic that people understand this? Can we resolve the question of legitimacy?
Teela Reid: I do believe it’ll pass, yes. I think there’s so much good faith and goodwill in the people. The strategy behind this movement is correct. Going to the people and not the politicians is what changed this nation. At every single turning point the only reason it’s on the national agenda is because of everyday Australians. It won’t be easy. I think that people shouldn’t get complacent about where we are now. Between now and the ballot box, every single one of you is going to have start your own campaign. Take this extremely seriously. For someone like me, it doesn’t stop.
For everything you need to know about the Voice to Parliament visit here.
This is an abridged version of In Conversation with Teela Reid. Watch the full discussion below.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Elf on the Shelf is a fun and festive way to teach your child to submit to the surveillance state
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Dignity
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Science + Technology
Age of the machines: Do algorithms spell doom for humanity?
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Relationships
There is more than one kind of safe space
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
I'm really annoyed right now: 'Beef' and the uses of anger

I’m really annoyed right now: ‘Beef’ and the uses of anger
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY Joseph Earp 15 MAY 2023
Beef, the acclaimed new Netflix show, starts with an incident of one of the most commonplace examples of extreme emotion in our society – road rage.
We’ve all been there. You’re having a bad day. Or, if you’re the two heroes of Beef, a bad life – Danny (Steven Yeun), is a frustrated contractor, has sailed from one disappointment to the next, while Amy (Ali Wong), has big dreams that she can’t quite seem to realise. In another life, these two might have joined forces to combat the stresses that seem ready to swallow them whole. Instead, Danny almost runs into Amy in a brutalist parking lot.
Rather than either of them letting this go, the pair escalate their titular beef. They swear at one another. They make threatening motions with their cars. And then, before they know it, they’re all-out-furious, embroiled in a comically overblown chase sequence on the highway.
And it doesn’t end there, either. After this one act of aggression, Danny and Amy become locked in a series of escalating vengeful manoeuvres, from pissing on each other’s bathroom floors to all-out violence. It’s one incident of rage that ruins both of their lives. And, most troubling of all, Danny and Amy seem to love their fury. They embrace it totally, even as houses burn to the ground around them.

The consequences of anger
Clearly, Beef tells us that anger has the ability to escalate – that it’s an emotional state that can start minor, and then, if we don’t do anything about it, has the power to totally consume us. As Jennifer S. Lerner and Larissa Z. Tiedens note in their paper Portrait of the Angry Decision Maker, anger has “uniquely captivating properties” – if we’re not careful, it’ll make us one-track minded.
It’s partially for this reason that anger is often viewed as a “negative” emotion, one we would do better without. As philosophers Paul Litvak, Jennifer Lerner, and Larissa Z. Tiedens point out in their paper Fuel In The Fire, “anger makes people indiscriminately punitive, indiscriminately optimistic about their own chances of success, careless in their thought, and eager to take action.”
The angry person is not typically viewed as the one in the best place to make judgements. The angry person can act, as Danny and Amy do, irrationally, frequently moving against their own best interests. How many people have we all met whose rage has made them ruin a relationship that they value, or get themselves in trouble at work?

Much therapeutic practice is designed to eradicate negative emotions. Psychological practices like DBT (Dialectical Behaviour Therapy) encourage patients to rid themselves of anger, so that they might think clearly. This follows a version of the model of emotions favoured by the stoics. Marcus Aurelius, a Roman emperor and key proponent of the Stoic model, once wrote, “A real man doesn’t give way to anger and discontent, and such a person has strength, courage, and endurance—unlike the angry and complaining.”
On this model of emotional regulation, the right thing to do is take anger as a kind of emotional data, process it, wait for it to pass, and then act. Not out of anger. Deciding what to do only when calm.
What anger does
We might be quick to assume, like the Stoics, that anger is something to always be avoided. But in doing so, we ignore the way anger gets things done. Consider the anger at the heart of key civil rights movements from across the years. “If you’re not angry, you’re not paying attention,” has been a rallying cry used for everything from the fight for feminist rights, to the struggle against racism. There are clearly injustices that we are right to feel angry about.
In fact, dismissing someone’s concerns because they are angry has sometimes been used to try and deflate moves towards equality. Suffragettes, for instance, were often painted by the press as “hysterical” and out of control, their righteous fury seen as cause to eradicate their movements.
Moreover, anger has uniquely focusing effects. We see this in Beef. Before they almost crash into each other, Danny and Amy are aimless, buffeted around by forces bigger than them. The fury that they feel at one another focuses them. It is something that they control; something within their power. It inspires action from people whose lives have been marked by inaction.
So where is the point of balance between these two perspectives? Can we feel anger, and allow it to focus us, without allowing it to destroy our life, and make us bad decision makers?
The philosopher Martha Nussbaum believes so. Nussbaum is well-known for her rehabilitation of stoic philosophy – much of her philosophical work has been about bringing that ancient movement back into the light.
In her book Anger and Forgiveness, she embraces key features of the stoic opinion on anger. She calls anger a “trap”, and notes that she does not believe that anger “is morally right and justified.” For her, anger has all the negative qualities described above – it often leads to actions designed as “payback”, retaliative gestures that are seen to “assuage the pain or make good the damage.” She does not believe anger does this. She thinks it merely adds more hurt to a pile of hurt, hurting the aggressor as much as the victim they lash out at.
But Nussbaum does not dismiss anger out of hand. This makes her different to many stoics. She thinks anger is to be eradicated, but creates a related category to that feeling called “transition-anger.” This is not simply anger. It is not the desire to punish. It is not defined by wallowing in negative emotions. Instead, she describes the “entire cognitive content” of “transition-anger” as being made up of the thought, “How outrageous. That should not happen again.”
Transition-anger doesn’t make us merely lash out at those who have hurt us. Instead, it directs us towards positive forward action. We use it to focus ourselves. But that focus drives us towards good moral behaviour. It turns unmoved citizens into powerful figures of protest. It creates community, people united in their desire to make the world a better place.
Amy and Danny aren’t bad moral actors merely because they’re angry, then. They’re bad moral actors because they do the wrong things with their anger. It’s not that they should never have felt rage. It’s that they allowed that rage to make them ugly and cruel, when it should have made them kinder.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Free markets must beware creeping breakdown in legitimacy
READ
Society + Culture
10 dangerous reads for FODI24
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
CoronaVirus reveals our sinophobic underbelly
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
Unconscious bias: we’re blind to our own prejudice
BY Joseph Earp
Joseph Earp is a poet, journalist and philosophy student. He is currently undertaking his PhD at the University of Sydney, studying the work of David Hume.
Why we find conformity so despairing

We have a conflicted relationship with conformity. We are disdainful of others’ blind adherence to fads. We scoff at duck lips, rote woke speak, fiddle-leaf figs and picket-fence-and-two-kid aspirations.
But few of us go out on original limbs ourselves. We fear ostracisation as much as we do being labelled “sheeple”.
Conformity is an understandable evolutionary response to loneliness, the ultimate existential threat. We don’t have fangs or sharp claws; we don’t run particularly fast. Homo sapiens’ sole defence is our ability to coalesce into a collective that can then outsmart a predator. We are toast if we are cast out.
So we prioritise our belonging to a tribe or community over almost everything else, particularly in times of threat or uncertainty. At the height of the pandemic, former Obama Surgeon, General Vivek Murthy noted that a lot of nervous Americans were sharing anti-vax information on Facebook, even though they knew it to be false. Why? Because when we share friends’ and colleagues’ hysterical posts we demonstrate our tribal support. We are effectively saying, we sign up to the herd. Truth, when we fear being cast out, is a secondary concern.
Austrian philosopher and psychologist Erich Fromm wrote about this phenomenon in reaction to the rising opulence and conformity of the mid-1950s in his wonderful treatise, The Art of Loving. He pivots his thesis from the observation that humans experience a unique loneliness that stems from our self-conscious awareness that we will die (and therefore don’t matter). No other species, to our knowledge, has this awareness; we are alone in this aloneness. All of which sees us as unable to be present and “at One” with ourselves and the world around us for we are forever grasping into the future, seeking certainties.
Where does all this end up for us? Fromm argues, this disconnection from ourselves and the present, as well as the world around us, condemns us to a life searching for ways to unite and to experience the original Oneness as best we can.
One way to do this, he says, is by experimenting with drugs or by having sex. These work (rapturously!). But, alas, their effectiveness is short-lived.
The most effective and lasting way to connect, however, is to love. Fromm clarifies his definition of love. He’s specifically referring to productive love, which is the proactive giving of love, as opposed to the passive act of being loved. Love, to be clear, is not something we wait for. Or that we have to fear that we will miss out on. Love is what the alive “productive character” gets to experience.
But love is hard. And so the most common way we go about curing our loneliness and reconnecting with the One, is conforming. Doing as the herd does.
We conform by signing up for practices, mores and norms that corral us with the herd. We effectively hand our quest to live in the present, to be connected with nature and our nature, over to third parties – the church, governments, “democracy”, autocrats, cult leaders, and so on. Because, well, it’s easier than loving.
Of course, these institutions and models, whether it be Christianity, or Communism, evolved and took off to the extent to which they were able to make us feel less separate with their edicts and rulebooks.
But here’s the problem: we now delegate our non-separation to capitalism.
Fromm argues, as early as the 1950s, that mostly we conform to capitalism’s edicts and mores. We buy into its messaging. We mould the way we behave and look lured by the seductive promise that when we do we will belong to a big friendly herd of fellow… consumers (not citizens).
Capitalism is the most common way for humans to feel less separate because it’s the easiest way.
The system does all the work for us. We just have to hop on the conveyor belt and the jingles, the McDonald toys-with-purchase, the trickling down, the algorithms and the surveillance technology will take care of the rest.
Of course, same-sameness and herd mentality isn’t a problem in and of itself. Who cares if everyone cuts their hair into mullet for a season. But when it’s driven by capitalism, the abatement of our collective loneliness is not the driver. The vested interests of the market system are. Capitalism necessarily requires the stoking of our most selfish, individualist tendencies. The market system needs us to compete, to lapse into greed, to compare ourselves with others. And so capitalism’s promise comes at a massive price. Indeed, and ironically, the price is – yep! – our separateness.
But there’s also this: If we follow Fromm’s logic, conforming is, in effect, the cheap drug fix for the massive, original ache of our separation.
You see, while ever we revert to conformity as a way to connect, then we are dissuaded from doing it via the far more effective route, namely via the much harder practice – or art – of love. To this extent you could say that conformity stops us from choosing love.
Loving, of course, requires accessing a whole range of virtuous practices, such as courage and vulnerability. The comfy conveyor belt of consuming our way into the herd negates or demotivates us from practicing these virtues, too.
Plus, conformity in a democratic but capitalist culture is particularly powerful (and dangerous) because it sells the idea that the we remain very original and individualised in our behaviour. Our tattoo is radical (even though everyone has one); the world’s most popular SUV denotes adventurous “lone wolf”.
At least in an autocracy the people know they have lost their agency. They remain alive to it all; we slip into a distinct lack of curiosity and numbness, which we don’t fight or rise up against.
So what’s the alternative?
Jung asked in The Development of Personality: “What is it, in the end, that induces a man to go his own way and to rise out of unconscious identity with the mass as out of a swathing mist?” Jung answers his own question with the idea of having a “vocation”, a drive that comes from God. But in this instance we could argue that the way out of our stale, conveyor belt-ish conformity is to just do the more difficult path. Practice love! Now! Do not pass Go!
After all, as Fromm argues, conformity doesn’t satiate. “Union by conformity is not intense….it is calm, dictated by routine, and for this very reason often is insufficient to pacify the anxiety of separateness.” Fromm believes we need intensity for unification to feel real, to stick. Only love, he says, is sufficiently intense.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Beyond cynicism: The deeper ethical message of Ted Lasso
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
The philosophy of Virginia Woolf
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
How to break up with a friend
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Relationships
“Animal rights should trump human interests” – what’s the debate?
BY Sarah Wilson
Sarah Wilson is a multi-New York Times and Amazon best-selling author, podcaster, international keynote speaker, philanthropist and climate change advisor. Sarah is known globally for founding the I Quit Sugar movement – a digital wellness program and 13 award-winning books that sell in 52 countries – which saw millions around the world transform their health. In 2022 Sarah sold the business and gave everything to charity. Sarah is an experienced journalist and broadcaster. She was previously the editor of Cosmopolitan Australia at age 29; host of Masterchef Australia; was a News Corp journalist and columnist; and has hosted ABC’s Compass, Ten’s The Project and more. She is also a regular commentator on news and current affairs programs in Australia, the US and UK.
Meet David Blunt, our new Fellow exploring the role ethics can play in politics

Meet David Blunt, our new Fellow exploring the role ethics can play in politics
Opinion + AnalysisRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY The Ethics Centre 8 MAY 2023
We’re thrilled to announce we’ve appointed Dr Gwilym David Blunt as an Ethics Centre Fellow.
A writer and commentator on global politics and philosophy, David has spent time as a Senior Lecturer in International Politics at City, University of London and as a Leverhulme Early Career Fellow at the University of Cambridge. Now based in Australia, David has published numerous books, appeared on ABC The Drum and Monocle Daily, and has written for The Conversation, ABC and International Affairs.
To welcome him, we sat down with David to discuss the important role ethics can play when it comes to politics, human rights and philanthropy.
What attracts you to the field of philosophy?
We are often told to ‘go with your gut’ when making decisions. This has always struck me as genuinely terrible advice. Our instincts can be conditioned by any number of prejudices or misconceptions. Philosophy is a way of interrogating these instincts and thinking systematically about hard questions.
How does your background in international politics and human rights shape your approach to philosophy and ethics?
International politics fascinates me because it is often treated as a place where ethics don’t apply. It’s seen as a place in which raw power determines the norms that govern politics, something that few would say is acceptable in domestic politics. Yet, this seems ridiculous.
Take the Russian invasion of Ukraine, many people around the world reacted in horror because wars of aggression are wrong. This is more than an intuition. Self-determination is grounded in an ethical judgement that people have a right to determine their collective destiny without interference. We might question the scope of this right, but most people will agree that at the very minimum it prohibits wars of aggression. There is clearly a place for ethics in world politics.
In fact it is more than a place, there is an urgency for ethics in world politics. The Covid-19 pandemic clearly showed how humanity as a whole faces shared challenges. The viruses that cause pandemics and the greenhouse gases that cause climate change don’t respect the arbitrary lines we draw on maps. We cannot hide behind closed borders and hope it all just goes away. These threats raise ethical questions about duties and responsibilities, where burdens lie, and what we owe to the future.
What kind of work will you be engaging with at The Ethics Centre?
The Ethics Centre is hosting me while I work on my next book which is on philanthropy. This is a topic that I’ve been interested in for a long time, but was on the side burner until the pandemic brought it back into focus. My work usually looks at the grimmer aspects of political philosophy, such as war, terrorism, and extreme inequality. So, it is nice to be working on something that gives some reasons to be hopeful about humanity. Although philanthropy raises a lot of interesting questions about justice, reputation laundering, and fairness.
I’ll also be writing some articles and assisting as a media spokesperson.
Which philosopher has most impacted the way you think?
It’s difficult to pick one, but I think it would have to be Philip Pettit, who isn’t a household name, but, along with Quentin Skinner, revived republicanism in political philosophy, which is what grounds my work. Now, don’t confuse republicanism with Donald Trump or right-wing MAGA politics or even with anti-monarchism. Republicanism is at its core a philosophy of freedom; it’s central claim is no person can be free if they are under the arbitrary power of someone else.
You have also done a lot of research on poverty and the distribution of wealth. What role do you think philanthropy and charity has or should have in that space?
I like to compare philanthropy with the façade of a building. It is something that beautifies, but it isn’t necessary to create a stable and functional structure. To continue this analogy, the parts of a building that keep it up, foundations and reinforced concrete, these are the province of justice. My worry with philanthropy is that it is taking up those structural roles, that it is subverting the role of justice. This isn’t a trivial matter because philanthropy is often characterised by the arbitrary power that republicans tend to worry about. Access to healthcare or education should not rest on the whim of a wealthy person, even if they are a good person, these are things that all people are owed as matter of right.
Your recent book Global Poverty, Injustice and Resistance argues our right to politically resist. We’re currently seeing some extreme cases of human right infringements around the world – what’s an example of resistance you’ve noticed that seems to be having a significant effect?
Resistance is such an interesting subject, because it covers such a wide range of activities. Most people tend to think of revolutions or mass civil disobedience as the paradigm examples of resistance, but I find the less visible forms of resistance more compelling.
I think the best example is illegal or irregular immigration for socio-economic reasons. This topic is one that generates a lot of extreme feelings in wealthy states like Australia and the United States, which is why I find it interesting. People who flee extreme poverty are voting with their feet against our current global political system, where many people are denied a reasonably dignified human life simply because they were born in the wrong country.
Many people’s first instinct is to say that illegal immigrants are doing something wrong, because they are breaking the law, but this goes back to what I said that the beginning of this interview: our instincts can be wrong.
We need to seriously start asking questions about why people cross borders illegally. It takes a lot for someone to leave their home to go to a distant land where they might know no one, have to learn new customs and language, and there is a chance they might die in the journey. We need to think about our complicity with the economic systems that produce avoidable poverty and exacerbate climate change, the push factors for this sort of migration. My hope is that this may help to create systemic change.
What are you reading, watching or listening to at the moment?
For work, I’m finishing up reading Paul Vallely’s massive Philanthropy: From Aristotle to Zuckerberg which is a good accessible examination of philanthropy and re-reading Will MacAskill’s What We Owe the Future for a short piece I’m working on. And I’m also revisiting some of the greatest hits of republicanism from Pettit and Skinner for a new YouTube series I’m doing.
For pleasure, I’m reading Donna Tartt’s The Goldfinch, which is really amazingly written. She’s one of those people who makes me actively jealous of their wordcraft. And I’m reading my wife I, Claudius before bed.
Watching, we are doing a nostalgia trip and rewatching the X-Files, which is fun even if the last few seasons are pretty bad. The sad thing about watching it in 2023 is that fringy, conspiracy theory stuff was just fun entertainment 30 years ago and now it has turned extremely sinister, which kind of drains a bit of the joy out of it.
Listening, I’m a big Last Podcast on the Left fan, because sometimes I just need to learn about cults, aliens, cryptids, and true crime. And since moving to Australia I’ve been getting into Australian music and have been bingeing King Gizzard and the Lizard Wizard.
Lastly, the big one – what does ethics mean to you?
Putting it simply, ethics is my ‘bullshit detector’; it helps me recognise my own bullshit, which keeps me from being complacent, and the bullshit of society at large, which seems to be really piling up.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Male suicide is a global health issue in need of understanding
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A burning question about the bushfires
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Ethics
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
I’m really annoyed right now: ‘Beef’ and the uses of anger
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
ESG is not just about ticking boxes, it’s about earning the public’s trust

ESG is not just about ticking boxes, it’s about earning the public’s trust
Opinion + AnalysisBusiness + LeadershipClimate + EnvironmentRelationships
BY Cris Parker The Ethics Alliance 3 MAY 2023
If businesses want to earn the public’s trust, they need to take ESG seriously, and communicate what they’re doing authentically and transparently.
In the eyes of today’s public, businesses must do more than just provide quality products and services, they also have a responsibility to be good corporate citizens and make a positive contribution to society and the environment. This is one reason why so many businesses have made a commitment to Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) standards.
ESG is a framework used to assess a business’s activities and performance on ethical and sustainable issues. This includes an organisation’s ability to safeguard the environment, manage relationships with employees, supply chains and the community, and how company leadership, shareholder rights and internal controls monitor the outcomes. Importantly, the framework serves as a tool to assess how an organisation manages risks and opportunities in our changing world.
The problem is that most members of the public don’t have a good understanding of ESG. According to the SEC Newgate ESG Monitor report, only 12% of Australians had a “good understanding” of ESG. This disconnect between ESG activities and public perception is a problem because it undermines trust in business, especially if ESG activities have been misrepresented.
Members of the Ethics Alliance gathered in April 2023 to discuss the importance of SEC Newgate’s research and consider challenges that organisations face in the way they address ESG and community expectations.
For starters, the ESG Monitor indicated that 38% of Australians feel completely uninformed about companies’ ESG activities. Interestingly, it also suggested 72% of people either “never” or “rarely” look at the ESG reporting, while only a mere 8% of people trust ESG reporting.
Some of this scepticism around ESG may have been cultivated due to it politicisation. In April 2023 the leader of the opposition, Peter Dutton, commented: “To be frank, some business leaders need to stop craving popularity on social media by signing up to every social cause, even though they may not believe in it.” This attitude acts in contrast to the global research from the 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer that shows 82% of people expect CEOs to take a public stand on climate change. And to Dutton’s point, they certainly expect authenticity.
The public holds high expectations for businesses to use their influence for good. SEC Newgate’s study showed that of those surveyed, 80% agree that companies have a responsibility to behave like good citizens and consider their impact on other people and the planet. It also showed that 66% of people are also willing to give a company a second chance if it was transparent about its mistake and stated how it would do better in the future.
If businesses want to live up to community expectations and strengthen their social value, then they need to carefully choose which ESG initiatives to focus on and ensure they have legitimacy in those areas. When evaluating, they should ask the following: Is it genuine? Is it meaningful? Is the organisation committed? And how do I know for sure or where is the proof?
By demonstrating a clear link between sustainability efforts and overall strategy, businesses can better align their initiatives with community expectations.
One starting point is a materiality assessment, which is a process to identify and prioritise the most relevant and significant ESG factors that have a substantial impact on the business’s operations, financial performance and stakeholder interests. This exploration can help identify the most pressing issues that align with the purpose and resonate with the community.
Other principles for organisations to consider when developing their ESG framework that emerged from The Alliance’s discussions were:
- Ethical conduct – including treating employees fairly, avoiding unethical practices, and minimising environmental harm.
- Giving back – which may involve investing in local communities, adopting environmentally friendly practices, or supporting social initiatives.
- Transparency and accountability –stakeholders, including consumers, employees, and shareholders, often have differing perspectives on ESG issues, making it challenging for businesses to balance these conflicting demands and trade-offs.
Communication also needs to be well considered by organisations in order to address the disconnect between the community’s need for transparent ESG information and their desire to learn about it. Connecting with stakeholders transparently about an organisation’s progress and mistakes can help meet these challenges.
ESG is about more than just accounting. It’s demonstrating a business’s responsibility and recognising the importance of sustainable practices in safeguarding our planet. ESG needs to be a whole company effort that is undertaken authentically and communicated transparently to the public that reflects its purpose, values and principles. The more businesses that do this, the more the public will understand what ESG is and the more they will come to trust businesses as being responsible corporate citizens.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership
Has passivity contributed to the rise of corrupt lawyers?
Big thinker
Relationships
Big Thinker: Tyson Yunkaporta
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights
No justice, no peace in healing Trump’s America
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Truth & Honesty
BY Cris Parker
Cris Parker is the former Head of The Ethics Alliance and a Director of the Banking and Finance Oath at The Ethics Centre.
BY The Ethics Alliance
The Ethics Alliance is a community of organisations sharing insights and learning together, to find a better way of doing business. The Alliance is an initiative of The Ethics Centre.
We already know how to cancel. We also need to know how to forgive

We already know how to cancel. We also need to know how to forgive
Opinion + AnalysisRelationships
BY Dr Tim Dean 1 MAY 2023
We have a well-worn script for how to behave when a public figure does something wrong. What we don’t have is a script for what to do if they make amends.
First comes the outrage, then the sharing, then the public condemnation, where the force of thousands of indignant wills declare that the wrongdoer is no longer a member of our moral community. Then we cancel.
This script is powerful. It is predictable. It helps remove a perceived threat. But it doesn’t heal the moral wound. It doesn’t rebalance the scales. It doesn’t include lines for rehabilitation, re-education or rebuilding moral capital. The script only tells us how to push people out.
What we need is another script, one we can use if they make amends. If the wrongdoer owns what they’ve done, if they express genuine contrition and issue a heartfelt apology, if they demonstrate a lasting change to their behaviour for the better, what do we do?
The missing script
The first thing to decide is whether we’re in a position to forgive at all. There are a couple of reasons why we might not be. For a start, we might not even be the right person to judge in the first place.
Many of us are quick to judge these days. The media and internet have opened us up to a world of outrages that call out for condemnation, and the frantic pace of modern discourse makes us feel like we must have an opinion on every issue. We are also often motivated to show solidarity with our in-group by sharing outrage over the same subjects, even if we know little about them. And the logic of second-order punishment – where we punish those who refuse to punish wrongdoers – means we fear retribution from our own team if we don’t jump on the outrage train.
But none of these are good reasons to jump to a hasty conclusion, based on a news headline, a couple of tweets and a few second-hand hot takes. Many of the issues we face are more complex than can be understood, let alone judged, without careful consideration. Many of the details are hidden from our view or veiled by the hasty or biased interpretations of others.
The second reason as individuals we might not be in a position to forgive is that sometimes the only person who can forgive is the individual who was harmed. I can’t unilaterally forgive a thief for stealing from you, or a celebrity for cheating on their partner. I simply lack the standing to speak on behalf of the person who was harmed.
However, there are cases where we, as members of a moral community, can be in a position to judge – and forgive – an act of wrongdoing. Acts of stealing or infidelity don’t just harm the victims, they violate the norms of our community. That’s why we still get outraged at things that don’t impact us directly or offensive acts that have no apparent victim.
This is a different kind of forgiveness. It’s not speaking on behalf of the victim, it’s speaking on behalf of the moral community. If the wrongdoer apologises and makes amends to those they’ve harmed, the community can accept that apology, drop the enmity towards them and welcome them back into the fold.
This kind of “public forgiveness” is an important part of a healthy moral community. Without it, the community pursues a purity culture that only knows how to push people out.
Set the bar
The next thing we should ask ourselves: what would the wrongdoer need to do to justify our forgiveness?
For some wrongdoers, the answer will be “there’s nothing they can do”. There are such things like terrorist attacks, mass shootings, genocide and violent sexual assault that we might not reasonably expect anyone to forgive, especially those directly affected.
However, we need to think carefully about what is considered unforgiveable, and not allow that category to grow too large.
Only the most serious moral transgressions should be considered unforgiveable. For everything else, we need to set the bar high enough that wrongdoers must earn their forgiveness, but not so high that the pariahs will one day outnumber the pure.
Similarly, when it comes to character there may be people whose behaviour is so consistently bad that we can conclude that they are beyond redemption. But we must be very cautious about inferring too much about character from only one example of wrongdoing.
There has been a trend in recent years of leaping from outrage at a particular act – say a poorly worded tweet or an off-colour joke – to condemnation of the individual’s entire moral fibre. It’s a tendency to see the slightest slip as revealing deeper moral corruption, proving they are unworthy of forgiveness or rehabilitation.
While it’s tempting to see others as having an immutable moral fibre and painting them as either virtuous or wicked, we must remember our moral fibre is malleable. Throughout the course of our lives, our own moral views evolve with changes in our circumstances and the influence others have on us. We must believe the same of others too. This means setting a very high bar before judging character.
Open the door
Once we have set an appropriately high bar, we should invite people clear it. We should look for signs that they are aware that what they did was wrong. They should own their actions and show they can articulate how they harmed others. This involves them recognising how their act was received, even if they didn’t intend for it to be received that way.
We should also look for signs of genuine remorse, which suggests that the wrongdoer shares our negative judgement of what they did. It shows their moral standards are aligned with ours.
When assessing a public apology, we can look for “costly” gestures that make that apology more likely to be authentic. A murmured apology in private, or delivered at a curated press conference may be less authentic than an unscripted public statement. Emotion matters too, but we should recognise that not all people feel or express emotion in the same way; just because someone isn’t in tears doesn’t mean they are not sincere.
Ultimately, what is most deserving of forgiveness is not words but actions. If someone changes how they behave in an enduring way, then that’s the most reliable sign that they have realigned their values to accord with those of the community. At that point, we should be inclined to invite them back into the moral community.
The final stage of the new script for public forgiveness mirrors the script for sharing outrage. Public forgiveness needs to be expressed in public. And those witnessing public forgiveness should read that as an opportunity to re-evaluate their own judgements of the wrongdoer and decide if they, too, are ready to forgive.
There are times when condemnation is justified. There are times when people ought to be cancelled. But if it’s a one-way street, we risk living in a culture where the circle of what – or who – is acceptable is forever shrinking. We need to have a pathway to redemption and forgiveness, and that pathway needs to become a script that we can all apply.
For a deeper dive on Cancel Culture, David Baddiel, Roxane Gay, Andy Mills, Megan Phelps-Roper and Tim Dean present Uncancelled Culture as part of Festival of Dangerous Ideas 2024. Tickets on sale now.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Michel Foucault
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships
Three ways philosophy can help you decide what to do
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
Why your new year’s resolution needs military ethics
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships, Society + Culture