Thought experiment: The original position

Thought experiment: The original position
ExplainerSociety + CulturePolitics + Human Rights
BY The Ethics Centre 20 MAR 2025
If you were tasked with remaking society from scratch, how would you decide on the rules that should govern it?
This is the starting point of an influential thought experiment posed by the American 20th century political philosopher, John Rawls, that was intended to help us think about what a just society would look like.
Imagine you are at the very first gathering of people looking to create a society together. Rawls called this hypothetical gathering the “original position”. However, you also sit behind what Rawls called a “veil of ignorance”, so you have no idea who you will be in your society. This means you don’t know whether you will be rich, poor, male, female, able, disabled, religious, atheist, or even what your own idea of a good life looks like.
Rawls argued that these people in the original position, sitting behind a veil of ignorance, would be able to come up with a fair set of rules to run society because they would be truly impartial. And even though it’s impossible for anyone to actually “forget” who they are, the thought experiment has proven to be a highly influential tool for thinking about what a truly fair society might entail.
Social contract
Rawls’ thought experiment harkens back to a long philosophical tradition of thinking about how society – and the rules that govern it – emerged, and how they might be ethically justified. Centuries ago, thinkers like Thomas Hobbes, Jean-Jacques Rousseau and John Lock speculated that in the deep past, there were no societies as we understand them today. Instead, people lived in an anarchic “state of nature,” where each individual was governed only by their self-interest.
However, as people came together to cooperate for mutual benefit, they also got into destructive conflicts as their interests inevitably clashed. Hobbes painted a bleak picture of the state of nature as a “war of all against all” that persisted until people agreed to enter into a kind of “social contract,” where each person gives up some of their freedoms – such as the freedom to harm others – as long as everyone else in the contract does the same.
Hobbes argued that this would involve everyone outsourcing the rules of society to a monarch with absolute power – an idea that many more modern thinkers found to be unacceptably authoritarian. Locke, on the other hand, saw the social contract as a way to decide if a government had legitimacy. He argued that a government only has legitimacy if the people it governs could hypothetically come together to agree on how it’s run. This helped establish the basis of modern liberal democracy.
Rawls wanted to take the idea of a social contract further. He asked what kinds of rules people might come up with if they sat down in the original position with their peers and decided on them together.
Two principles
Rawls argued that two principles would emerge from the original position. The first principle is that each person in the society would have an equal right to the most expansive system of basic freedoms that are compatible with similar freedoms for everyone else. He believed these included things like political freedom, freedom of speech and assembly, freedom of thought, the right to own property and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
The second principle, which he called the “difference principle”, referred to how power and wealth should be distributed in the society. He argued that everyone should have equal opportunity to hold positions of authority and power, and that wealth should be distributed in a way that benefits the least advantaged members of society.
This means there can be inequality, and some people can be vastly more wealthy than others, but only if that inequality benefits those with the least wealth and power. So a world where everyone has $100 is not as just as a world where some people have $10,000, but the poorest have at least $101.
Since Rawls published his idea of the original position in A Theory of Justice in 1972, it has sparked tremendous discussion and debate among philosophers and political theorists, and helped inform how we think about liberal society. To this day, Rawls’ idea of the original position is a useful tool to think about what kinds of rules ought to govern society.

Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Why Anzac Day’s soft power is so important to social cohesion
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Big Thinker: Mary Wollstonecraft
Reports
Politics + Human Rights
The Cloven Giant: Reclaiming Intrinsic Dignity
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Why certain things shouldn’t be “owned”
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Big Thinker: Epicurus
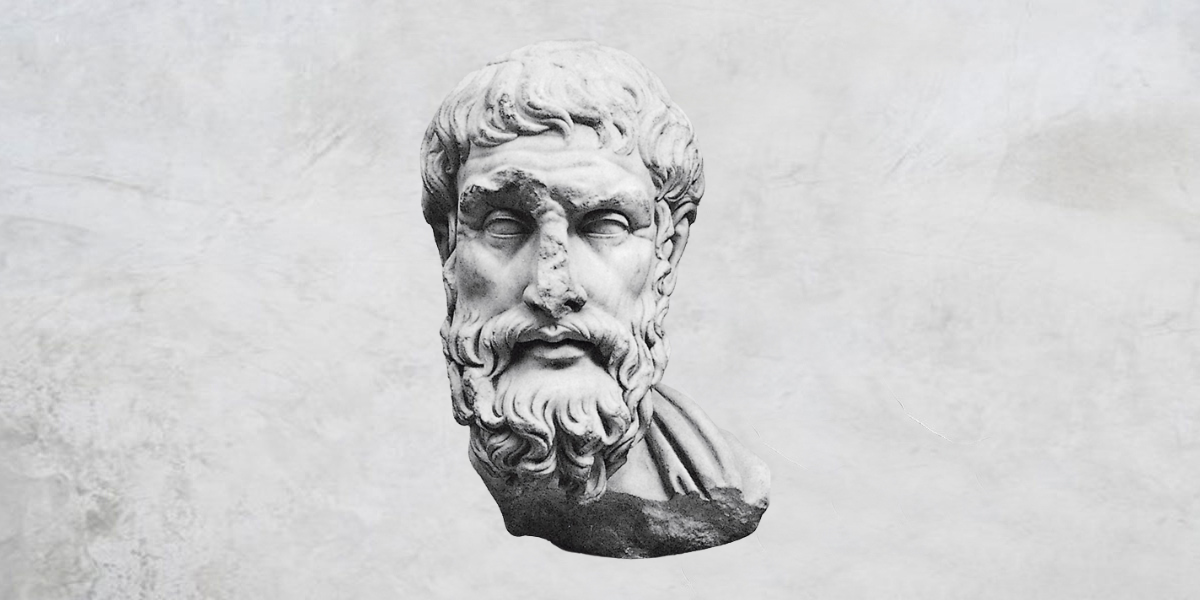

Epicurus (341–270 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and founder of the highly influential school of philosophy, Epicureanism.
In a time dominated by Platonism, Epicurus established a competing school in Athens known as “the Garden”. Many of his teachings were direct contradictions of the teachings of Plato, other schools of thought and generally accepted ideas in areas like theology and politics. He also flouted norms of the time by openly allowing women and slaves to join and participate in the school.
Though he strongly insisted otherwise, dubbing himself “self-taught”, records indicate Epicurus was greatly influenced by many philosophers of and before his time such as Democritus, Pyrrho and Plato.
Theology and Ethics
Two significant departures from the popular ancient Greek thought involved Epicurus’ ideas about theology. In general, he was critical of popular religion, though in a much more restrained way than his later followers.
One departure was his thoughts on the afterlife. Epicurus believed that there was no afterlife, and that any belief in it, especially the idea that the afterlife could involve punishment and suffering, was a harmful superstition that prevented people from living a good life.
“Accustom thyself to believe that death is nothing to us, for good and evil imply sentience, and death is the privation of all sentience; . . . Death, therefore, the most awful of evils, is nothing to us, seeing that, when we are, death is not come, and, when death is come, we are not.”
From Letter to Menoeceus
Another departure was his thoughts on the gods, and specifically their involvement in human affairs, also known as divine providence. Unlike most, Epicurus believed in the gods while simultaneously believing that they were completely removed from the mortal realm and uninvolved in human affairs.
The Epicurean view of the gods was that they were perfect beings, and involvement in anything outside their perfection would tarnish that perfection. The view denies that they exhibit any control over humans or the world, and that they instead function mainly as aspirational figures – beings to admire and emulate.
Both of these departures from popular ancient Greek religion came from his unique hedonistic philosophy. Epicurus believed that the ultimate purpose of philosophy was to achieve, and help others to achieve, certain states of being that characterise the eudaimonic (happy, flourishing) life.
Specifically, he thought that eudaimonia was attained through internal peace (ataraxia), an absence of pain (aponia) and a life of friendship.
This was the basis of his hedonism – unique in that he defined pleasure as an absence of suffering and so had a far greater focus on moderation than what is typically associated with hedonism.
In fact, Epicurus was disapproving of excessiveness generally:
“…the pleasant life is produced not by a string of drinking bouts and revelries, nor by the enjoyment of boys and women, nor by fish and the other items on an expensive menu, but by sober reasoning.”
These ideas informed his theological thoughts. He believed that a belief in the afterlife was superstitious and bad because it was most often a source of fear. Instead of acting morally to avoid the risk of punishment in the afterlife, which causes suffering in the current life, Epicurus taught that we should instead act morally because we will inevitably suffer from guilt or the fear of being discovered if we do not.
Likewise, he taught that while the gods had no interest in the affairs of humans, we should still act morally and kindly because those who do will have no fear, leading to ataraxia.
“…it is not possible to live pleasurably without living sensibly and nobly and justly.”
Pleasure and Desire
As part of his ethical teachings, Epicurus noted different types of pleasures and desires that prevent us from achieving a life free from suffering and trouble.
He was particularly focused on desire because he saw it, like fear, as a ubiquitous source of suffering. He taught that there are three kinds of desires: two natural, and one empty. Natural desires can be necessary (like food or shelter) or unnecessary (like luxury food or recreational sex). Empty desires on the other hand correspond to no genuine, natural need and often can never be satisfied (wealth, fame, immortality), leading to continuous pain of unfulfilled desire.
Unfortunately, like many Hellenistic philosophers, the vast majority of Epicurus’ writings have remained undiscovered, instead pulled together largely through the writings of contemporaries, followers and later historians. Despite this, his ideas have resurfaced throughout the centuries since and influenced the thinking of ancient and modern philosophers alike.

Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Relationships
Do we exaggerate the difference age makes?
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Barbie and what it means to be human
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships, Society + Culture
Extending the education pathway
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Five dangerous ideas to ponder over the break
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
7 thinkers improving our ethical understanding of the environment

7 thinkers improving our ethical understanding of the environment
Big thinkerClimate + Environment
BY Cameryn Cass 5 JUN 2024
Despite centuries of advocacy urging us to consider our actions, the urgent problem of climate change and conservation of our earth is one that often feels the most insurmountable.
In celebration of World Environmental Day, these seven key thinkers and activists from across history have contributed to our ethical understanding of the environment and how we can lessen our impact.
Aldo Leopold (1887-1948)

Aldo Leopold was a conservationist, forester, philosopher, and educator who dedicated his life to coexisting with nature and learning from it, with many considering him to be the father of American wildlife ecology.
His non-fiction book, A Sand County Almanac, calls for the development of a land ethic, as conservation is unachievable so long as resources are controlled by economic interests. He wrote, “a land ethic changes the role of Homo sapiens from conqueror of the land-community to plain member and citizen of it.” By including land in our understanding of community, it no longer is property; instead, it becomes inherently valuable and, in turn, worthy of protection and respect. “We can be ethical only in relation to something we can see, feel, understand, love, or otherwise have faith in,” he wrote.
Leopold additionally stressed the need to evaluate and update the content of our conservation education. He said it’s not enough to join a few organisations, follow the law, and trust the government will do the rest. “In our attempt to make conservation easy, we have made it trivial.”
Seyyed Hossein Nasr (1933-present)

Nasr, an internationally celebrated thinker from Iran, is, at present, a professor of Islamic Studies at George Washington University. He looks at the natural world through a religious lens, thus becoming the founder of environmentalism in the Muslim world. He calls Islam a “green religion,” as it’s easy for followers to sympathise with the natural world, since “the Qur’an addresses not only human beings, but also the cosmos. All creatures participate in Islam.” In Islam, all living things are equally valuable, equally deserving of life, equally valid. Nasr highlights how “we human beings cannot be happy without the happiness of the rest of creation. We have killed enough, massacred enough of God’s other creatures.”
He juxtaposes Islamic values with Christian ones, and how the latter’s “most devout followers don’t show much interest in the environment.” In all the verses of the New Testament, he points out, there’s not one mention of nature. “To be modern is to destroy the world of nature. That’s the great tragedy of it, and we should try to find out why.”
Naomi Klein (1970-present)

As a Canadian journalist, filmmaker, New York Times best-selling author and professor of climate justice, Naomi Klein’s commitment to activism spans many mediums, across borders. She sees our world’s current state as one major, interconnected problem: Climate change isn’t separate from medical crises which aren’t separate from political crises, and so on. In her eyes, it’s all connected and it all rests on the initial sin of stealing lands from Indigenous people.
In her Festival of Dangerous Ideas 2015 talk, Capitalism and the Climate, she emphasised the Pope’s idea of a “throwaway culture.” It’s what’s allowed generations of Australians, Canadians, and Americans alike to take from Native people, and it’s the same concept that’s degrading and destroying our planet. “We extract and do not replenish and wonder where the fish have disappeared. And why the soil requires evermore inputs, like phosphates, to stay fertile.” Klein calls for the creation of a “culture of caretaking in which no one and nowhere is thrown away. In which the inherent value of people and all life is foundational.”
Tyson Yunkaporta (present)

Aboriginal people have lived in Australia for over 65,000 years – far longer than any other humans have anywhere else on the planet. Tyson Yunkaporta, an Aboriginal scholar and author, believes that we stand to resolve a lot of our current environmental problems by turning to their ancient practices, or, at the very least, considering them. Aboriginal “patterns still flow with the movement of the earth.” They remain connected to the planet, he said, living in harmony and coexisting with the natural world in ways non-Indigenous people do not.
Yunkaporta thus encourages readers to question Western thinking and approach problems with an Aboriginal lens instead. As he wrote in his book, Sand Talk, we ought “to live and work in accordance with a natural order, rather than against it.”
Pythagoras (570 BC-495 BC)

Though Pythagoras is typically remembered for his contribution to mathematics (you might remember his famed Pythagorean Theorem from high school math class) he was actually better known for his beliefs on reincarnation and diet in his day. In fact, he was the first modern vegetarian in the West and is regarded as the father of ethical vegetarianism.
While the actual impact of cutting out meat from one’s diet is often disputed, individuals can have impact by lessening their own ecological footprint. By cutting out meat, it can be argued that one stands to dramatically reduce the resources – like land, water, and oil – required to sustain their diet. Pythagoras far predated these ecological footprint considerations; instead, he grounded his vegetarian beliefs in reincarnation. By killing animals and eating their meat, he said, we run the risk of eating our companions. “Meat is for beasts to feed on… what a wicked thing it is for flesh to be the tomb of flesh… for one live creature to continue living through one live creature’s death.”
Vandana Shiva (1952-present)

Vandana Shiva is an ecofeminist, physicist, ecologist, activist, editor, and author known for her steadfast commitment to work in environmental conservation, specifically agriculture. Famously, she opposed Asia’s Green Revolution, which, while ramping up food production in less-developed countries, the heavy use of pesticides harmed native seed diversity and traditional agricultural practices.
To try and do her part to give back, in 1982, Shiva founded the Research Foundation for Science, Technology, and Ecology to develop sustainable agricultural practices. In her Festival of Dangerous Ideas talk in 2013, Growth = Poverty, she condemns GDP and growth, drawing on experiences from life in India. Gross Domestic Product, she says, doesn’t account for things like pollution in the rivers, and if it did, India and China would have negative scores. Instead, it creates a false standard of living and, in doing so, “it has perpetuated a model of generating non-sustainability, inequality, and a deep violence within society and within the self.”
Kongqiu (551 BC-479 BC)

Better known as Confucius, this ancient Chinese philosopher’s teachings are, to this day, the bedrock of East Asian culture.
Confucius believed that all life has qi, which is essentially life force that nurtures humans and nature alike. In essence, qi supports the idea that humans and nature are isogenous, of the same origin and interconnected. In accordance with this perspective, Confucius stressed that humans ought to be kind to the land to achieve harmony and balance.
Present day scholars look to this ancient Chinese wisdom as a piece to solving the puzzle that is climate change. If humans adopted the idea that we are not separate from nature and instead an extension of it, as Confucius said, then perhaps we’d see this destruction to the land as destruction to ourselves and finally change our unsustainable ways.

Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Science + Technology
The kiss of death: energy policies keep killing our PMs
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
A burning question about the bushfires
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment
Why it was wrong to kill Harambe
Explainer
Climate + Environment
Ethics Explainer: Longtermism
BY Cameryn Cass
Cameryn Cass is a curious writer and an editor-in-training who studied at Michigan State University. Her primary focus is environmental storytelling, as she deeply loves the natural world and intends to use her voice to defend it. Outside of work, she loves to hike, rock climb and practice yoga.
Big Thinker: Judith Jarvis Thomson

Big Thinker: Judith Jarvis Thomson
Big thinkerPolitics + Human Rights
BY The Ethics Centre 11 JUL 2023
Judith Jarvis Thomson (1929-2020) is one of the most influential ethicists and metaphysicians of the 20th century. She’s known for changing the conversation around abortion, as well as modernising what we now know as the trolley problem.
Thomson was born in New York City on October 4th, 1929. Her mother was Catholic of Czech heritage and her father was Jewish, who both met at a socialist summer camp. While her parents were religious, they didn’t impose their beliefs on her.
At the age of 14, Thomson converted to Judaism, after her mother died and her father remarried a Jewish woman two years later. As an adult, she wasn’t particularly religious but she did describe herself publicly as “feel[ing] concern for Israel and for the future of the Jewish people.”
In 1950, Thomson graduated from Barnard College with a Bachelor of Arts (BA), majoring in philosophy, and then received a second BA in philosophy from Cambridge University in England in 1952. She then went on to receive her Masters in philosophy from Cambridge in 1956 and her PhD in philosophy from Columbia University in New York in 1959.
Violinists, trolleys and philosophical work
Even though she had received her PhD from Columbia, the philosophy department wouldn’t keep her as a professor as they didn’t hire women. In 1962, she began working as an assistant professor at Barnard college, though she later moved to Boston University and then MIT with her husband, James Thomson, for the majority of her career.
Thomson is most famous for her thought experiments, especially the violinist case and the trolley problem. In 1971, Thomson published her book A Defense of Abortion, which presented a new kind of argument for why abortions are permissible during a time of heightened debate in the US as a result of the second wave feminist movement. Arguments that defended a woman’s right to an abortion circulated feminist publications and eventually led to the Supreme Court ruling in favour of Roe v. Wade (1973).
“Opponents of abortion commonly spend most of their time establishing that the foetus is a person, and hardly any time explaining the step from there to the impermissibility of abortion.” – Judith Jarvis Thomson
The famous violinist case asks us to imagine if it is permissible to “unplug” ourselves from a famous violinist, even if it is only for nine months and being plugged in is the only thing keeping them alive. As Thomas Nagel said, “she expresses very clearly the essentially negative character of the right to life, which is that it’s a right not to be killed unjustly, and not a right to be provided with everything necessary for life.” To this day, the violinist case is taught in classrooms and recognised as one of the most influential thought experiments arguing for the permissibility of abortion.
Thomson is famous for another famous thought experiment, the trolley problem. In her 1976 paper “Killing, Letting Die and the Trolley Problem,” Judith Jarvis Thomson articulates a famous thought experiment, first imagined by Philippa Foot, that encourages us to think about the moral relevance of killing people, as opposed to letting people die by doing nothing to save them.
In the trolley problem thought experiment, a runaway trolley will kill five innocent people unless someone pulls a lever. If the lever is pulled, the trolley will divert onto a different track and only one person will die. As an extension to Foot’s argument, Thomson asks us to think if there is something different about pushing a large man off a bridge, thereby killing him, to prevent five people from dying from the runaway trolley. Why does it feel different to pull a lever rather than push a person? Both have the same potential outcomes and distinguish between killing a person and letting a person die.
In the end, what Thomson finds is that oftentimes, the action as well as the outcome are morally relevant in our decision making process.
Legacy
Thomson’s extensive philosophical career hasn’t gone unnoticed. In 2012, she was awarded the American Philosophical Association’s prestigious Quinn Prize for her “service to philosophy and philosophers.” In 2015, she was awarded an honorary doctorate by the University of Cambridge, and then in 2016 she was awarded another honorary doctorate from Harvard.
Thomson continues to inspire women in philosophy. As one of her colleagues, Sally Haslanger, says: “she entered the field when only a tiny number of women even considered pursuing a career in philosophy and proved beyond doubt that a woman could meet the highest standards of philosophical excellence … She is the atomic ice-breaker for women in philosophy.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Where do ethics and politics meet?
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Critical Race Theory
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
We are the Voice
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights
Australia, it’s time to curb immigration
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Big Thinker: Ralph Waldo Emerson

Big Thinker: Ralph Waldo Emerson
Big thinkerClimate + EnvironmentRelationships
BY The Ethics Centre 28 APR 2023
Committed to individualism and credited as the father of transcendentalism, Ralph Waldo Emerson (1803-1882) was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher and poet.
Initially on a path to follow his father’s footsteps and serve in the Christian ministry, Emerson attended Harvard’s Divinity School to become a pastor. But as time went on and he delved deeper into his religious studies, he realised an unignorable sense of detachment and divergence from the traditional religious values he was immersed in. And so he left the Second Unitarian Church and decided to forge his own path.
“To be yourself in a world that is constantly trying to make you something else is the greatest accomplishment.”
Emerson’s influential career began with public lectures in Boston that would inspire some of his most renowned essays and ideas. His lectures centred on human culture, English literature, biography and philosophy. He was known for popularising the major movement known as transcendentalism.
The Father of Transcendentalism
“Transcendental” was initially coined by philosopher Immanuel Kant in his theory of transcendental idealism. It’s a theory of perception that holds space and time, along with our five senses, are all subjective experiences and don’t exist outside of the human experience.
Even though Kant coined the term, Emerson is regarded as the father of transcendentalism.
Emerson’s transcendentalism, which became one of America’s first literature and philosophical movements, holds that we ought to be doubtful of knowledge we get from our five senses or even logic and reason; the only trustworthy source of knowledge manifests itself in our personal intuition and self-revelations.
In one of his first lectures, “The Uses of Natural History”, Emerson planted the initial seed for the movement when he explained science as something innately human. He emphasised nature to be an extension of one’s self: “the whole of Nature is a metaphor or image of the human mind.”
His book-length 1836 essay “Nature” is what officially and explicitly defined transcendentalism.
In essence, transcendentalists believe nature is paramount: all their ideals are rooted in the natural world. They believe all things are inherently good, humans and nature alike. In much the same way, transcendentalists see the divinity – the “God” – in everything and everyone. As Emerson wrote, “I am part or particle of God.” Transcendentalists also believe in the human potential for achieving greatness and genius.
Emerson is responsible for introducing a number of people to metaphysical concepts for the first time. A group he helped found in the late 1830’s called the Transcendental Club had dangerous conversations that critiqued societal institutions of the time, such as organised religion and slavery. Its members included prominent thinkers of the time, like Henry David Thoreau and Margaret Fuller, and allowed a space for transcendentalist ideas to grow.
Self-Reliance
As the title of one of his most famous essays, “Self-Reliance” describes one of his principal philosophies: relying solely on ourselves. Emerson’s transcendentalism has been equated to romantic individualism because of his emphasis on the self. For understanding and greatness, Emerson believed we ought only to rely on ourselves and trust our intuition. In fact, he believed the only thing separating the common person from “greatness” is that the “greats” have the gall to admit precisely what they’re feeling when they feel it. As humans, much of our experiences and emotions are shared, and Emerson saw beauty in such commonalities.
At the same time, he cited conformity as a major barrier to achieving greatness. He thought we should be comfortable and proud of being distinctly ourselves. He praised individuality and the pursuit of achieving “an original relation to the universe” by tuning inwards.
The key to unlocking genius is listening to what Emerson called our “creative insight”. He felt such insight was decidedly divine, God’s way of individually speaking to us. This insight is necessary for anyone to accomplish anything meaningful, and so Emerson encouraged everyone to trust their own creative insight over societal ones. Listening to our divinity, our creative insight, yields a life lived authentically.
“It is easy in the world to live after the world’s opinion; it is easy in solitude to live after our own; but the great man is he who in the midst of the crowd keeps with perfect sweetness the independence of solitude.”
It’s these transcendentalist ideologies that would eventually inspire philosopher Henry David Thoreau to reject society and go into the woods in order “to live deliberately and front only the essential facts of life”. And that same line of thinking is what inspired Christopher McCandless, an infamous American adventurer, to abandon family and escape to Fairbanks, Alaska in the 1990s. His story of living in the solitude of wilderness was later popularised in the film and novel Into the Wild.
Although some find wisdom and beauty in Emerson’s fierce admiration of solitude and complete rejection of groupthink, others see privilege in his ideals. Not everyone is able to exercise free will; not everyone can afford to stray from the norm and escape their social circumstances. And so to some, his ideas are lofty and unattainable, less you have the power of class and money on your side.
Beyond privilege, others see selfishness in his philosophies. By tuning inwards and considering only our own needs and desires, what is lost? What might we sacrifice when we neglect those around us? When we disregard even our loved ones? And yet, Emerson never said anything definitively:
“But it is the fault of our own rhetoric that we cannot strongly state one fact without seeming to belie some other. I hold our actual knowledge is very cheap.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Virtue Ethics
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Stoicism
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Love and morality
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
The twin foundations of leadership
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Five Australian female thinkers who have impacted our world

Five Australian female thinkers who have impacted our world
Big thinkerRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY The Ethics Centre 8 MAR 2023
In a world where some women still struggle to have their voices heard, there are many female thinkers whose contributions throughout history have impacted our thinking today. This International Women’s Day, we’re celebrating five influential Australian philosophers, activists, academics and thinkers who have shaped our ethical landscape and beyond.
Kate Manne
Kate Manne (1983-present) is an Australian philosopher best known for her feminist, moral and social philosophies, and her work around misogyny and masculine entitlement. Notably, instead of thinking of misogyny as hatred for women, Manne redefines the word and focuses on its systematic nature, specifically in how law enforcement polices women and girls to uphold gender norms.
To illustrate masculine entitlement, Manne coined the term “himpathy”, which explains “the disproportionate … sympathy extended to a male perpetrator over his … less privileged, female targets in cases of sexual assault, harassment, and other misogynistic behaviour.” She took a deep dive into this idea in her 2020 book Entitled: How Male Privilege Hurts Women and critiqued Justice Kavanaugh’s appointment to the US Supreme Court, despite allegations of sexual assault, as “himpathy” in action.
Marcia Langton
Marcia Langton (1951-present) is considered one of Australia’s top academics, anthropologists and geographers. As the great–great–granddaughter of survivors of the frontier massacres and a Yiman person, Langton uses her influential platform to advocate for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people. When her great aunt Celia Smith, an organiser of the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders, convinced her to work with the council in 1967, Langton was launched into her outspoken career of Aboriginal activism.
Since, she’s worked on vital pieces of research and legislation impacting Indigenous people and has held the Foundation Chair of Australian Indigenous Studies at University of Melbourne since 2000. More recently, she’s worked on the Voice to Parliament that would recognise First Peoples in the Constitution, permitting them “to have a say in the legislation that affects their lives.” To her, upholding Indigenous knowledge and rights goes beyond environmental preservation: It’s cultural preservation.
Veena Sahajwalla
Veena Sahajwalla (undisclosed-present) is an Australian scientist, inventor and professor. Named one of Australia’s 100 most influential engineers in 2015 and one of the 100 most innovative in 2016, Sahajwalla is putting New South Wales on a path to a net zero carbon, circular economy. Nicknamed “Queen of Waste”, she’s worked to repurpose everything from old clothes to beer bottles and abandoned mattresses. Growing up in Mumbai, India, she was introduced to the art of recycling through waste-pickers.
Her most famous invention, “Green Steel”, replaces coking coal in steel production with old, shredded tyres. The process is much less carbon-intensive and prevents 2 million tyres from hitting the landfill each year. This, in addition to her numerous other achievements – such as being councillor on the Australian Climate Council and opening the world’s first e-waste microfactory on the University of New South Wales’s campus – led to her being named Australian of the Year in 2022

Germaine Greer
Germaine Greer (1939-present) is a writer and regarded one of the major voices of the radical feminism movement in the latter half of the 20th century. Born in Melbourne, her 1970 book, The Female Eunuch, made her a household name where she argued the expectation for women to be feminine – in the clothes they wear, in marriage, in having a nuclear family – is what represses them. And so she calls for liberation, for revolution, because this repression cultivates political inaction.
Since then, she’s written several other books on feminism, literature and the environment. Of all her ideas and claims, she holds that freedom is the most dangerous, though critics say otherwise. Some of Greer’s views of have created controversy, including her views on gender binaries and expressions, rape and the #MeToo movement. While her audacious language, beliefs and controversy have cultivated furore at times, Greer remains a prominent participant in intellectual discourse and debate.

Val Plumwood
Val Plumwood (1939-2008) was an Australian philosopher, activist and ecofeminist. Her work focused on anthropocentrism and discouraging the idea that humans are superior to and separate from nature. This “standpoint of mastery”, as she called it, legitimised the “othering” of the natural world, which included women, indigenous and non-humans.
She experienced a major paradigm shift that coloured her opposition to anthropocentrism after she was attacked by a crocodile while canoeing alone at Kakadu National Park. She couldn’t believe such a thing was happening to her, a human. She went from being top of the food chain to part of it, having “no more significance than any other edible being.” To Plumwood, the flawed mindset of only human life mattering is the root of our planet’s degradation. She proposed nurturing the natural world for nature’s own good instead of our own, famously questioning, “Is there a need for a new, an environmental, ethic – an ethic of nature?”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Health + Wellbeing, Society + Culture
The five biggest myths of ethical fashion
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
There’s no good reason to keep women off the front lines
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
But how do you know? Hijack and the ethics of risk
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
A parade of vices: Which Succession horror story are you?
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
9 LGBTQIA+ big thinkers you should know about

9 LGBTQIA+ big thinkers you should know about
Big thinkerRelationshipsSociety + Culture
BY The Ethics Centre 15 FEB 2023
In celebration of Sydney World Pride and Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras, we’ve profiled nine notable thinkers who have contributed to our understanding of gender, sexuality and identity in some way. Whether navigating such spaces themselves or contributing to prominent research in the field, these figures have propelled public awareness of LGBTQIA+ issues in a meaningful way.
Michael Foucault (he/him)
Michael Foucault (1926-1984) was a daring, outspoken French philosopher, historian and psychologist. Much of his work was concerned with power and the random, coincidental ways in which big ideas and movements manifest in public consciousness. He explored the idea of sexuality in great extent and the modern fixation to define it and attribute sexual relations to an identity. To him, such definitions and labels effectively “other” parts of the population whose sexual behaviours are seen as deviant from the norm, even though evidence of same sex relations is present throughout human history.
Foucault thoroughly explored these ideas in his study, The History of Sexuality. He did not believe sexuality could be definitively defined – and any attempt to define it, in his eyes, constrained the mobility of human sexuality, which he believed ought to be fluid. Foucault’s provocative ideas and the content of The History of Sexuality laid the foundation for what Teresa de Lauretis would later call “queer theory”.
Judith Butler (they/them)
Judith Butler (1954-present) is an American activist whose writings and philosophies colour their commitment to radical equality. They are best known for writing Gender Trouble: Feminism and the Subversion of Identity, which is widely considered a founding text of queer theory. In the world-renowned book, Butler rejects the stance that gender equals biology, instead viewing gender as a product of behaviours and self-expression. To them, gender is produced by performance and is the root of their idea of “gender performativity”.
To eliminate any confusion on its definition, Butler explains that “We are formed through gender assignment, gender norms and expectations. But we’re not trapped. We can work and play with them [and] open-up spaces that feel better or more real for us.”
Audre Lorde (she/her)
Professionally a poet, professor and philosopher, Audre Lorde (1934-1992) also proudly carried the titles of intersectional feminist, civil rights activist, mother, socialist, “Black, lesbian [and] warrior.” She is also the woman behind the popular manifesto “the master’s tools will never dismantle the master’s house.”
Lorde’s self-expression and personal philosophy has became one of the greatest contributions to the discourse on discrimination and equality today. By offering an authentic depiction of the female, queer and Black experience, she portrayed the good, the bad and the complex. She felt academic discourse on feminism was white and heterosexual centric, lacking consideration of the lived realities so she put the stories of these women at the centre of her literature. An advocate for difference amongst human beings, Lorde’s difference was key to helping eradicate discrimination and moving forward in unity.
Raewyn Connell (she/her)
Raewyn Connell (1944-present) is an Australian sociologist. Born in Sydney, she approaches her research work with what she calls “southern theory”. Essentially, this perspective gives space to the global south’s backgrounds, which are often overshadowed by northern narratives. Connell was initially recognised for her research on class dynamics, exploring how class and power are inextricably linked and thus defined class as a social structure. This social framework propelled Connell into the realm of sexuality, which she also viewed as a social structure. Exploring how class influences and shapes gender, she understood gender as multi-dimensional and subject to change; something far beyond a mere aspect of our social identity.
In Masculinities – one of her most famous works — Connell coined the term “hegemonic masculinity”, which is the most dominant and socially celebrated version of a man. Though best known for her work in male studies, she explained that “my theoretical concern was the gender order as a whole; masculinity was one piece of the jigsaw”. Additionally, she’s written about her experience as a trans woman, gender equality, poverty, AIDS prevention and education.
Dennis Altman (he/him)
Dennis Altman (1943-present) is an Australian queer thinker and professor of politics at La Trobe University. His 1971 book, Homosexual: Oppression and Liberation, kickstarted his outstanding career that eventually led The Bulletin to name him one of the 100 most influential Australians. He primarily pondered the differences between radical gay activists who question heteronormative frameworks versus the tamer gay equality activists who demanded space in such frameworks. As time went on, Altman’s predictions of the normalisation of homosexuality laid out in his 1971 book proved correct. And though such advancements are certainly ones to celebrate, part of Altman mourns the radical roots of gay liberation.
For his complete support of gay rights, his opposition of same sex marriage might come as a surprise, but not if you consider the fact that he opposes marriage of any kind. In rejecting “the assumption that there is only one way of living a life”, Altman never married his partner of twenty years. He vehemently stands by the “equal right not to marry” and refuses to seek permission from the state and religious bodies that don’t want to sanction same sex relationships.

Susan Sontag (she/her)
Susan Sontag (1933-2004) was a relentless and prolific writer, philosopher, playwright, filmmaker and activist. She obsessively pursued the truth and had the courage to express it, no matter how unpalatable. To her, “All understanding begins with our not accepting the world as it appears.” Sontag’s first notable work, Notes on “Camp”, is what propelled her into the public eye, especially after it appeared in Time Magazine. Best known for detailing modern culture and aesthetics, her work expanded definitions of the word “camp” – for instance, using it to define works of art when they fail at being serious.
Her extremely publicised divorce from sociologist and cultural critic Philip Rieff in 1957 forced her into the public eye and involuntarily exposed her sexuality. Rather famously, after that event, she never formally came out as lesbian or bisexual. On this, in an interview with the New Yorker, she said, “That I have had girlfriends as well as boyfriends is what? Is something I never thought I was supposed to say since it seems to me the most natural thing in the world.”

Natalie Wynn (she/her)
Natalie Wynn (1988-present) is an American, Baltimore-based YouTube personality whose work aims to educate via theatrical entertainment and humour. In a play-like fashion, Wynn plays different characters and wears complex costumes to try and voice all sides of an issue, from which the audience can draw their own conclusions. On her channel, ContraPoints (like counterarguments), she tries to make people think; and beyond that, she wants them to question why they think that way in the first place. Wynn questions, “What matters more: The way things are or the way things look?”
As a transgender woman, many of her videos tackle trans experience, sexuality and gender roles. Wynn principally tries to depolarise conversations that typically divide people and humanise those who are questioning their own identity and sexuality. She claims that “in a free society, different people will have lots of different sexual lifestyles,” and she uses her platform to give space to such lifestyles.
Masha Gessen (they/them)
Masha Gessen (1967-present) is an unreserved, influential journalist, activist and author. Born in Russia, they relocated to America to realise greater sexual freedoms. Called “Russia’s leading LGBT rights activist” they have candidly discussed living in Russia as an openly gay person at the time – where homosexual propaganda is illegal and removing children from same sex households is possible.
Gessen has brought international queer issues into academic discourse to better understand the anti-queer movement, like that in Russia. They’ve blatantly critiqued Russia’s president Vladimir Putin since he was first elected and holds that former American president Donald Trump is “worse” than him. Gessen continues to expose injustices and Russia’s rise of LGBTQIA+ hate crimes in the wake of the state’s homophobia.
Alok Vaid-Menon (they/them)
Alok Vaid-Menon (they/them) is an internationally acclaimed writer, comedian, poet, and public speaker whose work explores themes of trauma, belonging, and the human condition. Their 2020 book Beyond the Gender Binary has been described as a “clarion call for a new approach to gender in the 21st century.”
Their approach to fundamental and often violent clashes with peace and compassion can feel radically hopeful. Vaid-Menon says “I’m fighting for trans ordinariness… I want to be able to walk down the street wearing what I want without it having to be an event.”
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
Trying to make sense of senseless acts of violence is a natural response – but not always the best one
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture
Lisa Frank and the ethics of copyright
Opinion + Analysis
Society + Culture, Politics + Human Rights
‘The Zone of Interest’ and the lengths we’ll go to ignore evil
Opinion + Analysis
Relationships, Society + Culture
Inside The Mind Of FODI Festival Director Danielle Harvey
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Big Thinker: Kimberlé Crenshaw

Kimberlé Crenshaw (1959-present) is one of the most influential feminist philosophers of our time. She is known for her advocacy for American civil rights, being a leading scholar of critical race theory, and pioneering what we now know as the third wave of feminism.
Crenshaw was born in Ohio, US in 1959. As a child, she grew up through the US civil rights and second wave feminist movements, both which occured throughout the 1960s and 70s. This time of revolutionary movements towards equality influenced how Crenshaw was raised.
“My mom was a little bit more radical and confrontational and my father was a little bit more Martin Luther King and ‘find common ground’. Which is probably why there are strains of both of those in my work.”
In 1984, Crenshaw graduated from Harvard Law School. At this time, there was only one woman and one Black professor of the 60 who were tenured. She is now a tenured professor at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and splits her time there with the Columbia School of Law in NYC.
Where do race and gender meet?
“I argue that Black women are sometimes excluded from feminist theory and antiracist policy discourse because both are predicated on a discrete set of experiences that often does not accurately reflect the interaction of race and gender.”
Crenshaw is most notable for coining the term “intersectionality,” which refers to the idea that when someone has multiple identities, it causes them to experience different and compounded forms of oppression. Rather than oppression being additive across multiple identities, intersectionality tells us that the experience of oppression will be multiplied. For example, a Black woman will experience discrimination because she is Black, because she is a woman, and also because she is a Black woman – which is a different kind of discrimination altogether.
“Because the intersectional experience is greater than the sum of racism and sexism, any analysis that does not take intersectionality into account cannot sufficiently address the particular manner in which Black women are subordinated.”
In the academic world, the term intersectionality debuted in Crenshaw’s 1989 paper Demarginalizing the Intersection of Race and Sex: A Black Feminist Critique of Antidiscrimination Doctrine, Feminist Theory and Antiracist Politics. Many scholars would say that the publishing of this paper catalysed the third wave of feminism, which is characterised by advocates demanding a more wholistic type of equality for people of all genders, races, socioeconomic backgrounds, abilities, ages, and in all countries.
Two years after the paper was published, Crenshaw assisted Professor Anita Hill’s legal team during Judge Clarence Thomas’s confirmation hearing to the US Supreme Court in October of 1991. In an interview with the Guardian, she reflects that the experience cemented the need for an intersectional theory of social justice. It was clear that “race was playing a role in making some women vulnerable to heightened patterns of sexual abuse [a]nd … anti-racism wasn’t very good at dealing with that issue.”
Intersectionality finally appeared in the Oxford English Dictionary in 2015, where it is defined as “the interconnected nature of social categorizations such as race, class, and gender, regarded as creating overlapping and interdependent systems of discrimination or disadvantage.”
A founder of critical race theory
“You can’t fix a problem you can’t name.”
Crenshaw has also spent a large part of her academic career developing and writing about what is now known as critical race theory. In its purest form, critical race theory is a 40-year-old academic framework that concerns itself with defining and understanding the plethora of ways that race impacts American institutions and systems, and how American institutions and culture uphold racist ideals. Crenshaw’s own definition, however, is more of a verb than a noun. For her, critical race theory is “a way of seeing, attending to, accounting for, tracing and analysing the ways that race is produced.”
One of the big cultural issues in the 21st century in America has been whether to teach critical race theory in public schools across the country. Parents and politicians across America have fought to remove what they think critical race theory is out of children’s education. They have argued that CRT is racist and teaches kids to “hate their own country.” Crenshaw now says she sees her work “as talking back against those who would normalise and neutralise intolerable conditions in our lives.”
Where to now?
Crenshaw continues to educate and inspire the next generation by teaching classes in Advanced Critical Race Theory, Civil Rights, Intersectional Perspectives on Race, Gender and the Criminalization of Women & Girls, and Race, Law and Representation at UCLA. At Columbia, she continues to work on the AAPF and through the forum, co-authored a paper in 2015 with Andrea Richie entitled Say Her Name: Resisting Police Brutality Against Black Women.
She regularly writes for a number of publications and provides commentary for the new outlets MSNBC and NPR. Crenshaw also hosts her own podcast Intersectionality Matters.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Nurses and naked photos
Big thinker
Politics + Human Rights
Big Thinker: John Locke
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights
Learning risk management from Harambe
Opinion + Analysis
Politics + Human Rights, Society + Culture
Respect for persons lost in proposed legislation
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Big Thinker: Steven Pinker

Steven Pinker (1954-present) is an experimental psychologist who is “interested in all aspects of language, mind, and human nature.” In 2021, Academic Influence calculated that he was the second-most influential psychologist in the world in the decade 2010-2020.
Steven Pinker is a Canadian-American cognitive psychologist, psycholinguist, popular science author and public intellectual. He grew up in Montreal, earning his Bachelor’s degree in experimental psychology from McGill University and his PhD from Harvard University. He is currently the Johnstone Family Professor in the Department of Psychology at Harvard.
At the start of his graduate studies, Pinker found himself interested in language, and in particular, language development in children. In 1994, he went on to publish the first of his nine books written for a general audience, entitled The Language Instinct. In the book, Pinker introduces the reader to some of the fundamental parts of language, and argues that language itself is an instinct that makes humans unique.
Language, society and the mind
Try and have a thought without any language. It might be an idea or a memory that appears in your mind with no words or internal monologue. It’s quite difficult to switch off the voice in our heads for more than a few seconds. Pinker researches this connection between language and how our minds work.
To date, Pinker is the author of nine books written for a general audience. He covers a wide range of topics and questions that get at the heart of how we learn languages and what this does to our minds. His book The Stuff of Thought (2007) looks at how language shapes the way we think. He begins by suggesting that when we use language, we are doing two things:
- Conveying a message to someone
- Negotiating the social relationship between ourselves and whoever we are speaking to
For example, when a professor stands at the front of a lecture hall and tells her students “may I have your attention, class is about to begin” the professor is doing two things. First, she is alerting her students that class is starting (the message), and second, she is operating within the professor-student hierarchy (the social relationship) in which students should give their attention.
Taking this framework for language, Pinker works to untangle some of the complicated questions around language, such as “Why do so many swear words involve topics like sex, bodily functions or the divine?” and “Why do some children’s names thrive while others fall out of favour?”
Trends of today: is violence declining?
Pinker’s academic interests and research extends beyond language. In 2011, he published The Better Angels of Our Nature, which makes the claim that violence in human societies has generally decreased steadily over time.
“Historical data from past centuries are far less complete, but the existing estimates of death tolls, when calculated as a proportion of the world’s population at the time, show at least nine atrocities before the 20th century (that we know of) which may have been worse than World War II.”
Violence in this case does not just mean war. Pinker also looks at collapsing empires, the slave trade, the murder of native peoples, treatment of children and religious persecution as acts of violence in the world. While it feels like we see and hear about a lot of violence today, he notes that it’s often because these are ‘newsworthy’ events.
“In the case of violence, you never see a reporter with a microphone and a sound truck in front of a high school announcing that the school has not been shot up today, or in an African capital noting that a civil war has not erupted.”
After establishing the trend of declining violence, he looks at historical factors that work to explain why we live in a less violent world. Some of these trends include increasing respect for women, the rise in technological progress, and more application of knowledge and rationality to human affairs.
Current work
Steven Pinker’s work has received a number of prizes for his books, including the William James Book Prize three times, the Los Angeles Times Science Book Prize, the Eleanor Maccoby Book Prize, the Cundill Recognition of Excellence in History Award, and the Plain English International Award. He has also served as an editor and advisor for a variety of scientific, scholarly, media and humanist organisations.
Steven Pinker still spends his time researching a diverse array of topics in psychology, language, historical and recent trends in violence, and neurobiology. One specific area he is currently researching is the role of common knowledge (i.e., things that we know other people know without having to say what we know) in language and other social phenomena.
Steven Pinker presents Enlightenment or Dark Age? as part of Festival of Dangerous Ideas 2022. Tickets on sale now.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics explainer: Cultural Pluralism
Explainer
Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Trust
Opinion + Analysis
Climate + Environment, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
This is what comes after climate grief
Opinion + Analysis
Business + Leadership, Relationships
So your boss installed CCTV cameras
BY The Ethics Centre
The Ethics Centre is a not-for-profit organisation developing innovative programs, services and experiences, designed to bring ethics to the centre of professional and personal life.
Big Thinker: Joanna Bourke

Joanna Bourke (1963 – present) is an historian, academic and philosopher who specialises in understanding the history of social and cultural phenomena. Her work has profoundly shaped our understanding of many fundamental aspects of human experience.
Joanna Bourke was born in New Zealand, and lived in Zambia, Solomon Island, and Haiti as a young child. She graduated from Auckland University with a Bachelor of Arts and a Master of Arts in history, and went on to complete her PhD at the Australian National University (ANU) in Canberra.
The dark parts of human experience
After writing her dissertation, titled Husbandry to Housewifery: Rural Women and Development in Ireland, 1890-1914 (1989), Bourke became interested in the experiences of men and women during wartime. Her work as a social and cultural historian has led her down a path of dealing with some of the less pleasant parts of being human, including topics such as pain, killing, war, violence, fear and rape. Bourke has been drawn to these elements of human experience because she feels that “these are the disciplines that have the most to offer us in terms of intellectual responses to current crises.”
Bourke’s book An Intimate History of Killing (1999) asks the question: what are the factors within society and in a war that turn a regular person into a good killer, or more politely, a good soldier? To answer her question, she uses excerpts from diaries, letters, memoirs and reports of Australian, British and American veterans of WWI, WWII and the Vietnam war. Bourke concludes that ordinary, gentle human beings can (and often do) become enthusiastic killers during a war because the structure of war encourages soldiers to feel pleasure from killing.
Some of her writing is also born out of personal experience. After a massive operation and a broken morphine drip, Bourke started thinking about pain and how difficult it is to describe in the English language. In her book The Story of Pain: From Prayer to Painkillers (2014), she concludes that “it is useful to think about pain in adverbial terms” because “it describes the way we experience something, not what is experienced.” As well as tracing the history of pain from the 1800s to present, she also details how factors such as race, class, gender and age have influenced the medical treatment of pain and often resulted in cruel abuse and neglect.
“Life’s too short for second editions.”
Joanna Bourke’s academic interests are vast. She has written 13 books and published over 100 articles, often tackling controversial and taboo topics.
In her recent book Loving Animals: On Beastiality, Zoophilia and Post Human Love (2020), Bourke argues that we should take a more nuanced approach to how we understand loving relationships between humans and non-human animals. When we take this more nuanced approach, Bourke finds that we are able to gain a clearer understanding of the nature of relationships, love and what we owe each other.
“I will be suggesting that animals are actors in society. This serves to challenge the anthropocentrism of history, human exceptionalism, and the idea that ‘culture’ is an entirely human preserve.”
Bourke begins by pointing out that “studies suggesting a link between bestiality and psychosis should be treated with caution due to sampling bias, because they were conducted on people already within the penal system, rather than a cross-section of the population.” She calls us to think about how we can so freely say that we love our pets, but turn a blind eye to slaughterhouses and factory farming. Bourke wants us to ask: what does it mean to love a non-human animal, and more broadly, what does it mean to love?
When we remove human exceptionalism from our understanding of human-animal relationships (which Bourke urges that we must), we can begin to think more about what we owe animals and how moral attitudes such as care, compassion, affection and pleasure are not unique to human beings.
Current work
Bourke is currently a professor of history at Birkbeck, University of London in England. She is also the Principal Investigator for a project called SHaME, or Sexual Harms and Medical Encounters. The project explores the medical and psychiatric aspects of sexual violence, with the aim of moving beyond the shame of sexual assault and address it as a global health crisis.
Her newest book Disgrace: Global Reflections on Sexual Violence, which has been partially motivated by her work with SHaME, will be available for purchase in Australia on August 15.
Joanna Bourke presents The Last Taboo as part of Festival of Dangerous Ideas 2022. Tickets on sale now.
Ethics in your inbox.
Get the latest inspiration, intelligence, events & more.
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy
You might be interested in…
Explainer
Business + Leadership, Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Power
Explainer
Politics + Human Rights, Relationships
Ethics Explainer: Social philosophy
Opinion + Analysis
Health + Wellbeing, Relationships
The truths COVID revealed about consumerism
Explainer
Relationships